Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science HW
Science HW
Uploaded by
Carlota TuqueroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science HW
Science HW
Uploaded by
Carlota TuqueroCopyright:
Available Formats
Science HW
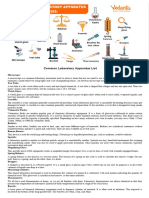
A Beaker is a simple container for stirring, mixing and heating liquids commonly
used in many laboratories. Beakers are generally cylindrical in shape, with a flat
bottom. Most also have a small spout (or "beak") to aid pouring as shown in the
picture.
An Erlenmeyer flask or conical flask[ is a type of laboratory flask which
features a flat bottom, a conical body, and a cylindrical neck.
A Pestle and mortar is a device used since ancient times to prepare
ingredients or substances by crushing and grinding them into a fine paste or
powder. The substance to be ground is placed in the mortar and ground, crushed
or mixed using the pestle.
A test tube, also known as a culture tube or sample tube, is a common piece
of laboratory glassware consisting of a finger-like length of glass or clear plastic
tubing, open at the top, usually with a rounded U-shaped bottom.
A microscope (from the Ancient Greek: , mikrs, "small" and ,
skopen, "to look" or "see") is an instrument used to see objects that are too
small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an
instrument is called microscopy. Microscopic means invisible to the eye unless
aided by a microscope.
A tripod is a portable three-legged frame, used as a platform for supporting the weight and
maintaining the stability of some other object. A tripod provides stability against downward
forces and horizontal forces and movements about horizontal axes. The positioning of the
three legs away from the vertical centre allows the tripod better leverage for resisting lateral
forces.
A graduated cylinder, measuring cylinder or mixing cylinder is a common
piece of laboratory equipment used to measure the volume of a liquid. It has a
narrow cylindrical shape. Each marked line on the graduated cylinder represents
the amount of liquid that has been measured.
The triple beam balance is used to measure masses very precisely; the reading error is 0.05
gram. With the pan empty, move the three sliders on the three beams to their leftmost
positions, so that the balance reads zero. If the indicator on the far right is not aligned with
the fixed mark, then calibrate the balance by turning the set screw on the left under the pan.
A Glass rod, stirring rod or stir rod is a piece of laboratory equipment used to
mix chemicals and liquids for laboratory purposes. They are usually made of solid
glass, about the thickness and slightly longer than a drinking straw, with rounded
ends. Like most laboratory glass, stir rods are made of borosilicate (commonly
known as pyrex).
A funnel is a pipe with a wide, often conical mouth and a narrow stem. It is used
to channel liquid or fine-grained substances into containers with a small opening.
Without a funnel, spillage would occur.
A magnifying glass (called a hand lens in laboratory contexts) is a convex
lens that is used to produce a magnified image of an object. The lens is usually
mounted in a frame with a handle (see image).
A Petri dish (sometimes spelled "Petrie dish" and alternatively known as a
Petri plate or cell-culture dish), named after the German bacteriologist Julius
Richard Petri,[1] is a shallow cylindrical glass or plastic lidded dish that biologists
use to culture cells[2] such as bacteria or small mosses.[3]
Tongs are a tool used to grip and lift objects, of which there are many forms
adapted to their specific use.
The definition of wire gauze is a type of very fine, woven wire that looks like netting.
An example of wire gauze is what may be used to support a beaker during heating in a
science experiment.
A spatula is "a small implement with a broad, flat, flexible blade used to mix,
spread and lift material"[1] including foods, drugs, plaster and paints. It derives
from the Latin word for a flat piece of wood or splint (a diminutive form of the
Latin spatha, meaning broadsword), and hence can also refer to a tongue
depressor. The words spade (digging tool) and spathe are similarly derived. The
word spatula is known to have been used in English since 1525.
a short glass tube fitted with a rubber bulb and used to measure liquids by drops
called also eyedropper, medicine dropper
A Bunsen burner, named after Robert Bunsen, is a common piece of
laboratory equipment that produces a single open gas flame, which is used for
heating, sterilization, and combustion. The gas can be natural gas (which is
mainly methane) or a liquefied petroleum gas.
You might also like
- Chemistry ApparatusDocument8 pagesChemistry ApparatusLian Tuliao67% (15)
- Science Dictionary for Kids: The Essential Guide to Science Terms, Concepts, and StrategiesFrom EverandScience Dictionary for Kids: The Essential Guide to Science Terms, Concepts, and StrategiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lab MicroscopeDocument6 pagesLab MicroscopeJenny Lyn GesmundoNo ratings yet
- InstrumentDocument2 pagesInstrumentKidrock TupasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory EquipmentsDocument11 pagesChemistry Laboratory EquipmentsEliutario IgnacioNo ratings yet
- ChemicalDocument4 pagesChemicalericmahusay11No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Week 1 Lesson 2Document3 pagesGrade 8 Week 1 Lesson 2alleynekenisha5No ratings yet
- Laboratory Equipment Flame Brass Glass Stainless Steel AluminiumDocument9 pagesLaboratory Equipment Flame Brass Glass Stainless Steel AluminiumKenneth P PablicoNo ratings yet
- 1.analytical Balance Description:: MG Dust Vented Balance Safety EnclosureDocument10 pages1.analytical Balance Description:: MG Dust Vented Balance Safety EnclosureJeck AbañoNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Accuracy and PrecisionDocument6 pagesMaintaining Accuracy and PrecisionAkshit ParmarNo ratings yet
- Know Your Lab Equipments: Test TubeDocument9 pagesKnow Your Lab Equipments: Test TubeWelly Boss HwiNo ratings yet
- Ingles Laboratory Apagas LaboratorioDocument11 pagesIngles Laboratory Apagas LaboratorioGraciela CastilloNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word 97 - 2003 DocumentDocument8 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word 97 - 2003 Documentgraceymeg_reyesNo ratings yet
- Lab ChuchuDocument2 pagesLab Chuchubwcmccn9rqNo ratings yet
- Lab AppDocument6 pagesLab AppErika Perez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsesDocument20 pagesList of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their Usesdexter timbanganNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsesDocument5 pagesLaboratory Apparatus and Their UsesKevin Tan80% (5)
- Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument2 pagesCommon Laboratory ApparatusAngelica Joy FloresNo ratings yet
- Acn Laboratory ApparatusDocument40 pagesAcn Laboratory ApparatusAlma Cecilia QuiaoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Apparatus: Submitted By: Ma. Francesca Louise C. BaldemorDocument5 pagesLaboratory Apparatus: Submitted By: Ma. Francesca Louise C. BaldemorDaniel HaleNo ratings yet
- W1 L5 - Laboratory ApparatusDocument23 pagesW1 L5 - Laboratory ApparatusSaba OsamahNo ratings yet
- KumiDocument29 pagesKumimonike07No ratings yet
- Lab EquipmentsDocument10 pagesLab Equipmentschouroukbelkacemi236No ratings yet
- BS MTDocument3 pagesBS MTGenrev LisondraNo ratings yet
- 50 Laboratory Apparatuses Biochemistry: OCTOBER 31, 2020Document14 pages50 Laboratory Apparatuses Biochemistry: OCTOBER 31, 2020Allen TandocNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument37 pagesLaboratory Apparatusalancstnd67% (3)
- Laboratory Apparatus and Its FunctionDocument4 pagesLaboratory Apparatus and Its FunctionTrese ShanelleNo ratings yet
- BEAKERS Are Made Up of TemperedDocument12 pagesBEAKERS Are Made Up of TemperedmnmrznNo ratings yet
- Laboratory EquipmentsDocument16 pagesLaboratory EquipmentsedomanpcNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ActDocument4 pagesChemistry ActDarren ArguellesNo ratings yet
- Identification of Laboratory 1Document15 pagesIdentification of Laboratory 1kimberlymapagalNo ratings yet
- CHEM2212 - ESTANOCO - SAMUEL.M. - Activity 1 LABORATORY EQUIPMENTDocument6 pagesCHEM2212 - ESTANOCO - SAMUEL.M. - Activity 1 LABORATORY EQUIPMENTSam EstanocoNo ratings yet
- 50 Common Laboratory Apparatus and Their Uses With PicturesDocument4 pages50 Common Laboratory Apparatus and Their Uses With PicturesDESMOND EZIEKENo ratings yet
- Stress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8From EverandStress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8No ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument17 pagesLaboratory Apparatuszena100% (1)
- Name Description PictureDocument4 pagesName Description PictureHazel AjeroNo ratings yet
- 4Document4 pages4julie anne ricaforteNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab 1 Itlog AssignmentDocument2 pagesChem Lab 1 Itlog Assignmentfamigo451No ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument3 pagesLaboratory ApparatusRacky Carag67% (3)
- Lab EquipmentDocument8 pagesLab EquipmentMathew YoyakkyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory EquipmentsDocument4 pagesLaboratory EquipmentsNichole Ann GinezNo ratings yet
- 02 Unit 1. Common Laboratory GlasswaresDocument59 pages02 Unit 1. Common Laboratory GlasswaresKevin Mark IlaganNo ratings yet
- Equipment in Chemistry LaboratoryDocument5 pagesEquipment in Chemistry LaboratoryIstiva AmeiliaNo ratings yet
- A List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsesDocument15 pagesA List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their Usesjohn erick camotaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument6 pagesSciencenwekemunachimso.nNo ratings yet
- ACOY (September 9)Document4 pagesACOY (September 9)Razul AcoyNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Solution Stopcock: 4. Pipettes and AspiratorDocument2 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Solution Stopcock: 4. Pipettes and AspiratorCheska BustosNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory Apparatus Names and UsesDocument4 pagesCommon Laboratory Apparatus Names and UsesjammyNo ratings yet
- Glass Scientific Experiments Science Chemistry Biology LaboratoriesDocument2 pagesGlass Scientific Experiments Science Chemistry Biology LaboratoriesMiguelAlonsoBenitoNo ratings yet
- Word BankDocument1 pageWord BankRustica AwaNo ratings yet
- List of Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsesDocument7 pagesList of Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsesNhorain A. Ariman-MayoNo ratings yet
- Glossary PHARMACY AND LABORATORYDocument3 pagesGlossary PHARMACY AND LABORATORYNataly Balbin TarmeñoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Educational 6Document7 pagesLaboratory Educational 6Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Funnel - WikipediaDocument12 pagesFunnel - WikipediaZeroseveen SeveenNo ratings yet
- CrucibleDocument10 pagesCrucibleAlegna PalenzuelaNo ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument27 pagesApparatusLearn EverythingNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 Introduction To BiochemistryDocument5 pagesWEEK 1 Introduction To BiochemistryCosmic PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Apparatus and Equipment: Elisha Roselle C. Labanero BSCHE 1-2Document10 pagesLaboratory Apparatus and Equipment: Elisha Roselle C. Labanero BSCHE 1-2Rhodora Carias LabaneroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument48 pagesLaboratory ApparatusGaming FootageNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Mysteries, Fun Laboratory Tools! Chemistry for Kids - Children's Analytic Chemistry BooksFrom EverandChemistry Lab Mysteries, Fun Laboratory Tools! Chemistry for Kids - Children's Analytic Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Retail Management Final ExamDocument17 pagesRetail Management Final ExamAkhilesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Nw4install DHCPDocument10 pagesNw4install DHCPnitrorubyNo ratings yet
- MAON Google SlidesDocument74 pagesMAON Google SlidesavinteumfilmsNo ratings yet
- Lección 7 - Who - Why-Because (WH Questions)Document3 pagesLección 7 - Who - Why-Because (WH Questions)V QuintNo ratings yet
- When Waves Enter Shallow Water, They Slow Down and Their Amplitude (Height) IncreasesDocument2 pagesWhen Waves Enter Shallow Water, They Slow Down and Their Amplitude (Height) IncreasesPei LingNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformsDocument22 pagesLaplace TransformsAustin JamesNo ratings yet
- 1117 33Document8 pages1117 33tm5u2rNo ratings yet
- Avlon Silent PilerDocument1 pageAvlon Silent PilerDushyantha JayawardenaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Environmental Studies EST 22447 Unit Test 1Document12 pagesMechanical Environmental Studies EST 22447 Unit Test 1Arvind YadavNo ratings yet
- CGC1D Assignment 2.1 Fire and Ice ArticlesDocument3 pagesCGC1D Assignment 2.1 Fire and Ice ArticlesMayaNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Guadalupe Minor Seminary Junior High School: Curriculum Map in Information and Communication TechnologyDocument7 pagesOur Lady of Guadalupe Minor Seminary Junior High School: Curriculum Map in Information and Communication Technologyreycelyn corsinoNo ratings yet
- Grade: 10E ROOM: 212 Homeroom Adviser: John Paolo FernandezDocument1 pageGrade: 10E ROOM: 212 Homeroom Adviser: John Paolo FernandezRangga NarindraNo ratings yet
- Zilog Z8000 Reference ManualDocument299 pagesZilog Z8000 Reference ManualNathalie VillemaireNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction of Aluminium in The Presence of Cobalt, Nickel and Magnesium From Sulphate Solutions by Cyanex 272Document8 pagesSolvent Extraction of Aluminium in The Presence of Cobalt, Nickel and Magnesium From Sulphate Solutions by Cyanex 272Leda HidalgoNo ratings yet
- As I Follow Christ by Dwain N. EsmondDocument138 pagesAs I Follow Christ by Dwain N. EsmondGabor KovacsNo ratings yet
- EskimoDocument2 pagesEskimoabdul sorathiyaNo ratings yet
- Abap Webdynpro Tips For Beginners: Windows and ViewsDocument14 pagesAbap Webdynpro Tips For Beginners: Windows and ViewsEr.Tousif MollickNo ratings yet
- Datron PRC-BC4 Multiple Battery Charger - Operator and Technical ManualDocument28 pagesDatron PRC-BC4 Multiple Battery Charger - Operator and Technical ManualAlexander J RokowetzNo ratings yet
- Innovative Offerings For Membrane and Thermal Desalination PlantsDocument24 pagesInnovative Offerings For Membrane and Thermal Desalination Plantscvolkan1No ratings yet
- Transponder Landing SystemDocument4 pagesTransponder Landing SystemWin MinNo ratings yet
- Pembumian 110705103913 Phpapp02Document33 pagesPembumian 110705103913 Phpapp02Noor Syazwani Md SharifNo ratings yet
- FALLACIESDocument5 pagesFALLACIESJan Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument274 pagesMCQgganyan67% (3)
- Seminar PresentationDocument16 pagesSeminar PresentationVinay KurkuriNo ratings yet
- The Family That Plays TogetherDocument19 pagesThe Family That Plays TogetherAna0% (1)
- RSAL KEMENKES Sby1Document150 pagesRSAL KEMENKES Sby1WAY MINCANGNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Engineering InformationDocument5 pagesPresentation of Engineering InformationDinesh SilvaNo ratings yet
- Saying Hello PDFDocument5 pagesSaying Hello PDFCAMILO ANDRES ACERO SUAREZNo ratings yet
- Grounding and Bonding Testing - Mike LewisDocument117 pagesGrounding and Bonding Testing - Mike LewisAba Emmanuel OcheNo ratings yet