Professional Documents
Culture Documents
H Bridge
H Bridge
Uploaded by
Tun TunCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CTS-7700 Service ManualDocument109 pagesCTS-7700 Service Manualvasquezbencomo100% (1)
- Final Thesis ElevatorDocument112 pagesFinal Thesis ElevatorTun Tun67% (3)
- MOSFET TransistorDocument17 pagesMOSFET TransistorOmer BallakNo ratings yet
- MOSFET - TutorialspointDocument3 pagesMOSFET - Tutorialspointgunasekaran k100% (1)
- MOSFET D-Type (Amplifier) (FInal)Document15 pagesMOSFET D-Type (Amplifier) (FInal)Muhammad HaqimNo ratings yet
- Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentDocument20 pagesMetal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentSokoine Hamad DenisNo ratings yet
- Final MosfetDocument33 pagesFinal MosfetabdallaNo ratings yet
- Power Mosfets: Introduction To Fet'SDocument21 pagesPower Mosfets: Introduction To Fet'SSharth KumarNo ratings yet
- Technical Examination Level - 7Document37 pagesTechnical Examination Level - 7Madhunath YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture11!11!12284 MosfetDocument28 pagesLecture11!11!12284 Mosfetshivali.vannarathNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3Document8 pagesUnit - 3AgnathavasiNo ratings yet
- ELC 107 Post-Lab 5 (Enhancement and Depletion Type MOSFET)Document4 pagesELC 107 Post-Lab 5 (Enhancement and Depletion Type MOSFET)Dean Karlo BardelozaNo ratings yet
- D AND E MOSFETsDocument13 pagesD AND E MOSFETsSRMEA SAN RAFAEL BULACANNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QuestionsDocument52 pagesCMOS Interview QuestionsKAMARUDHEEN KP100% (1)
- Unit 5 NotesDocument9 pagesUnit 5 NotesShashikant PandeyNo ratings yet
- MOSFET As A SwitchDocument11 pagesMOSFET As A Switchrahul samanta100% (1)
- The Basic Structure: Field Effect TransistorDocument10 pagesThe Basic Structure: Field Effect TransistormokhaladNo ratings yet
- EEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesEEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsFaria SharifNo ratings yet
- Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Document6 pagesMetal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Yasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Metal Oxide Semi-Conductor Field Effect TransistorDocument21 pagesMosfet: Metal Oxide Semi-Conductor Field Effect TransistorSai RohithNo ratings yet
- 510.22E - Lecture - 7Document12 pages510.22E - Lecture - 7SantosNo ratings yet
- The MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: "NO Current Flows Into The Gate"Document11 pagesThe MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: "NO Current Flows Into The Gate"Aan BeckhsNo ratings yet
- E MosfetDocument5 pagesE MosfetSRMEA SAN RAFAEL BULACANNo ratings yet
- Lab - 12 Transistor MOSFETDocument11 pagesLab - 12 Transistor MOSFETNecotNo ratings yet
- 04 Transistor MOSFETDocument18 pages04 Transistor MOSFETNatalie mirelesNo ratings yet
- The Metal Oxide FETDocument7 pagesThe Metal Oxide FETSitty GuNo ratings yet
- Basic Sturcture of MosfetDocument2 pagesBasic Sturcture of MosfetbofshafiqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture.7electronic Circuits 2Document17 pagesLecture.7electronic Circuits 2eafc2444No ratings yet
- Mofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTDocument17 pagesMofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTTejas krishnakanthNo ratings yet
- Principle of MOSFET Device TechnologyDocument3 pagesPrinciple of MOSFET Device TechnologyCHING HUI YEENo ratings yet
- The Mosfet: Home TransistorsDocument10 pagesThe Mosfet: Home TransistorsPrabashaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Document37 pagesCourse Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Dr Sunipa RoyNo ratings yet
- MosfetDocument8 pagesMosfetHarshit OjhaNo ratings yet
- SECA1503Document149 pagesSECA1503Thabasum Aara SNo ratings yet
- Sedra SmithDocument52 pagesSedra SmithJiveshNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument22 pagesElectronicsVARSHITH REDDY JNo ratings yet
- ETI 2203 Lesson 7Document10 pagesETI 2203 Lesson 7amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- High-Side and Low-Side SwitchesDocument3 pagesHigh-Side and Low-Side SwitcheskheralahNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 - MOSFET Working Principle - NSESP 2021Document15 pagesGROUP 3 - MOSFET Working Principle - NSESP 2021Sisilia Anabina TariganNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Mosfet 8-4-2021Document11 pagesVlsi Mosfet 8-4-2021GaneshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Mosfet Transistor)Document22 pagesChapter 4 (Mosfet Transistor)Muriel MeyouNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document12 pagesLec 1Lovish Kumar VatwaniNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Circuits: Khurram Bughio Lecturer Electrical Engineering, MUETDocument29 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits: Khurram Bughio Lecturer Electrical Engineering, MUETNoor SabaNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument4 pagesMOSFETelen19111036 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- FET/MOSFET Characteristics: ObjectiveDocument13 pagesFET/MOSFET Characteristics: ObjectiveZeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- BJT and MosfetDocument10 pagesBJT and MosfetankitabcNo ratings yet
- EEN11L - 3 Experiment No 2 MOSFET - LDocument20 pagesEEN11L - 3 Experiment No 2 MOSFET - LRichie LatNo ratings yet
- Controlled Devices FET, BJT, IGBTDocument51 pagesControlled Devices FET, BJT, IGBTHolloGramNo ratings yet
- Power MOSFET: Basic StructureDocument10 pagesPower MOSFET: Basic StructureDomagoj ProphectusNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesExperiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsManikandan P Engineering EEE100% (1)
- Unit1 Mosfet RevDocument36 pagesUnit1 Mosfet RevMohak KumarNo ratings yet
- Mosfet CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesMosfet CharacteristicsAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- EEE 202S Exp4Document9 pagesEEE 202S Exp4Sudipto PramanikNo ratings yet
- Electronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorDocument21 pagesElectronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorGawrav BaishyaNo ratings yet
- FETs 11Document55 pagesFETs 11بلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorDocument11 pagesField Effect TransistorAriel OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Sesi II 2021 Topicd Lect3Document29 pagesSesi II 2021 Topicd Lect3mbagavan 0712No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Tunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationFrom EverandTunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument1 pageReferenceTun TunNo ratings yet
- Project ElevatorDocument45 pagesProject ElevatorTun TunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ElevatorDocument32 pagesChapter 2 ElevatorTun Tun100% (1)
- Application of Image Processing Technology in Evaluating Weldline Quality On Injection Molding ProductsDocument1 pageApplication of Image Processing Technology in Evaluating Weldline Quality On Injection Molding ProductsTun TunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ElevatorDocument32 pagesChapter 2 ElevatorTun Tun100% (1)
- Project ElevatorDocument45 pagesProject ElevatorTun TunNo ratings yet
- OSN 3500 2500 1500 Hardware Description ManualDocument379 pagesOSN 3500 2500 1500 Hardware Description Manualngtinh100% (19)
- DP CardReader 14061 DriversDocument578 pagesDP CardReader 14061 Driversberto_716No ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document27 pagesChapter 01khang-nguyen-7620No ratings yet
- Electronic Switching Harshita Uptu NotesDocument2 pagesElectronic Switching Harshita Uptu NotesHarsh Vardhan100% (1)
- Understanding Lead-Off Detection in ECGDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Lead-Off Detection in ECGGabriel GarcíaNo ratings yet
- An 1281Document11 pagesAn 1281Ioan TudosaNo ratings yet
- LTspice ShortcutsDocument1 pageLTspice ShortcutsMelina RussoNo ratings yet
- Tronsmart Element t6 Max Bluetooth Speaker Manual OptimizedDocument10 pagesTronsmart Element t6 Max Bluetooth Speaker Manual OptimizedMircea CatalinNo ratings yet
- McsDocument16 pagesMcsAmmar IkramNo ratings yet
- Practical Work 6 - CMOS + Rubrics PDFDocument10 pagesPractical Work 6 - CMOS + Rubrics PDFRiki SmithNo ratings yet
- Modbus and Modbus TCPDocument45 pagesModbus and Modbus TCPmohammedansin1No ratings yet
- Rohini 41414986331Document12 pagesRohini 41414986331Sridarshini VikkramNo ratings yet
- AN17821A Power Amplifier DatasheetDocument6 pagesAN17821A Power Amplifier DatasheetAbderrazek YACOUBI100% (1)
- LTE Alarms TroubleshootingDocument22 pagesLTE Alarms Troubleshootingnirmal_elex7863No ratings yet
- Slides On Drawing Lecture-2: Demonstration On Complete Drawing of An Architectural StructureDocument11 pagesSlides On Drawing Lecture-2: Demonstration On Complete Drawing of An Architectural StructureReal NazihNo ratings yet
- BIX Mount and ConnectorDocument6 pagesBIX Mount and ConnectorHassan FawazNo ratings yet
- SK3 SK4 SK2 PL1 SK1 SK5 SK6 SK7: Signal Strength (Rssi)Document1 pageSK3 SK4 SK2 PL1 SK1 SK5 SK6 SK7: Signal Strength (Rssi)Steven MckelvieNo ratings yet
- High-Current Voltage Output Circuit Using A Precision DACDocument5 pagesHigh-Current Voltage Output Circuit Using A Precision DACdasdracheNo ratings yet
- KATALOG PRODUK ELEKTRONIKwewewDocument3 pagesKATALOG PRODUK ELEKTRONIKwewewBims CompanyNo ratings yet
- Altium Designer FeatureDocument1 pageAltium Designer Featuredrew.unitedNo ratings yet
- Dimetra Applications CatalogueDocument58 pagesDimetra Applications CatalogueJuan FernandezNo ratings yet
- 3 - 00651-Lza7016011uen.b-Emerson Values PDFDocument30 pages3 - 00651-Lza7016011uen.b-Emerson Values PDFMamadou SoumahoroNo ratings yet
- An0002 Efm32 Hardware Design ConsiderationsDocument16 pagesAn0002 Efm32 Hardware Design ConsiderationsRam SakthiNo ratings yet
- Fuse and Relay: General InfromationDocument9 pagesFuse and Relay: General InfromationZakaria KalomarNo ratings yet
- 1850 TSS-5C DatasheetDocument2 pages1850 TSS-5C DatasheetNguyen TrungNo ratings yet
- IQAN Accessories Brochure HY33-8319 UKDocument12 pagesIQAN Accessories Brochure HY33-8319 UKabdelhadi houssinNo ratings yet
- S280-70-1 Below SN 20000Document44 pagesS280-70-1 Below SN 20000Neldy Dorantes MatuNo ratings yet
- AV Receiver: Owner'S ManualDocument78 pagesAV Receiver: Owner'S ManualPedro AbrilesNo ratings yet
H Bridge
H Bridge
Uploaded by
Tun TunOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
H Bridge
H Bridge
Uploaded by
Tun TunCopyright:
Available Formats
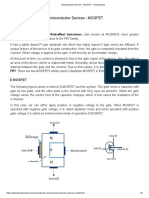
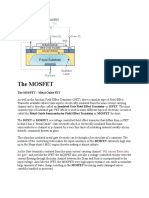
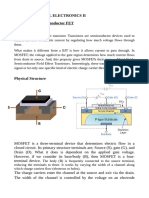
MOSFET stands for Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
means effective Transistor have metal and oxide semiconductor. Figure 11 shows
the structure of n-channel MOSFET and the symbol of type n-channel and pchannel MOSFET
MOSFET has 3 pins called Gate (G), Drain (D) and Source (S). Basically, in
N-channel MOSFET, if the voltage in G is greater than S from 3V then it is
saturated conduct MOSFET. Then the resistance between two pins D and S are
very small (called the conduct resistance DS) MOSFET is equivalent to a lock. In
contrast, in the P-channel MOSFET, the voltage in G feet less than S about 3V, the
MOSFET S conduct, the lead resistance is also very small. Because the
conductivity of the MOSFET voltage depends on G, MOSFET is known as voltage
control, ideal for digital circuits where the voltage is used as logic level (level 0 is
0V, 5V is level 1).
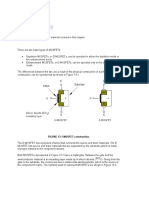
MOSFET is used instead of the BJT in the H-bridge circuit because the
current it can conduct is very high, suitable for high power circuit. Because of how
it works, we can imagine a similar N-channel MOSFET as BJT NPN type and Pchannel MOSFET as PNP BJT. Conventional MOSFET manufacturers typically
create a pair of MOSFET includes an N-channel component and a P-channel
components, 2 MOSFET has parameters similar to each other and are often used
together. Like the BJT, in the H-bridge circuit, each MOSFET only appropriate for
a given position, N-channel MOSFET is used for locking the lower and P-channel
MOSFET for locking the top. To explain, take for example a N-channel MOSFET
is used to control a DC motor as shown in Figure 12.
Initially MOSFET is not enabled, no circuit currents, voltage at pin S= 0.
When the MOSFET is enabled and conduct, the conduct resistance DS is
negligible compared to impedance voltage of the motor so the voltage at S is 12V.
To enable the MOSFET the voltage at G must be greater than S at least 3V, means
15V at least while we use the microcontroller to trigger MOSFET, it is difficult to
create voltage 15V. So N-channel MOSFET is not so suitable for the top locking in
the H-bridge circuit. P type MOSFET is used in this case. However, a drawback of
P-channel MOSFET is the conduct resistance DS is greater than that of N type. So,
even well-designed, P-channel MOSFET in the H-bridge circuit using two types of
MOSFET is often hotter and easy to be broken than the N type MOSFET, and the
power of circuit is reduced also. Figure 13 shows an H-bridge circuit using two
types of MOSFET
We use 2 IRF540 N-channel MOSFET and 2 P-channel IRF9540. This type
of MOSFET can endure high current (possibly up to 30A, nominal) and high
voltage, but its disadvantage is the conduct resistance is relatively large (you find
our datasheet for more). To trigger the N-channel MOSFET below it is not too
difficult, just use the microcontroller triggers directly on the line L2 or R2. For top
lock (IRF9540, P-channel) we have to use BJT 2N3904 to trigger. When BJT
2N3904 is not triggered yet, pin G of the MOSFET is connected to VS with 1K
resistors, voltage at G nearly equal to the voltage VS and is also at S of MOSFET
IRF9540, so it would not conduct. When you trigger the line L1 or R1, the BJT
2N3904 conduct and leads the voltage at G fall close to 0V .Then, the voltage at
pin G is much smaller than the voltage at pin S, MOSFET will conduct.
Microcontroller can be used to activate the lines L1, L2, R1 and R2.
You might also like
- CTS-7700 Service ManualDocument109 pagesCTS-7700 Service Manualvasquezbencomo100% (1)
- Final Thesis ElevatorDocument112 pagesFinal Thesis ElevatorTun Tun67% (3)
- MOSFET TransistorDocument17 pagesMOSFET TransistorOmer BallakNo ratings yet
- MOSFET - TutorialspointDocument3 pagesMOSFET - Tutorialspointgunasekaran k100% (1)
- MOSFET D-Type (Amplifier) (FInal)Document15 pagesMOSFET D-Type (Amplifier) (FInal)Muhammad HaqimNo ratings yet
- Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentDocument20 pagesMetal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentSokoine Hamad DenisNo ratings yet
- Final MosfetDocument33 pagesFinal MosfetabdallaNo ratings yet
- Power Mosfets: Introduction To Fet'SDocument21 pagesPower Mosfets: Introduction To Fet'SSharth KumarNo ratings yet
- Technical Examination Level - 7Document37 pagesTechnical Examination Level - 7Madhunath YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture11!11!12284 MosfetDocument28 pagesLecture11!11!12284 Mosfetshivali.vannarathNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3Document8 pagesUnit - 3AgnathavasiNo ratings yet
- ELC 107 Post-Lab 5 (Enhancement and Depletion Type MOSFET)Document4 pagesELC 107 Post-Lab 5 (Enhancement and Depletion Type MOSFET)Dean Karlo BardelozaNo ratings yet
- D AND E MOSFETsDocument13 pagesD AND E MOSFETsSRMEA SAN RAFAEL BULACANNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QuestionsDocument52 pagesCMOS Interview QuestionsKAMARUDHEEN KP100% (1)
- Unit 5 NotesDocument9 pagesUnit 5 NotesShashikant PandeyNo ratings yet
- MOSFET As A SwitchDocument11 pagesMOSFET As A Switchrahul samanta100% (1)
- The Basic Structure: Field Effect TransistorDocument10 pagesThe Basic Structure: Field Effect TransistormokhaladNo ratings yet
- EEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesEEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsFaria SharifNo ratings yet
- Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Document6 pagesMetal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Yasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Metal Oxide Semi-Conductor Field Effect TransistorDocument21 pagesMosfet: Metal Oxide Semi-Conductor Field Effect TransistorSai RohithNo ratings yet
- 510.22E - Lecture - 7Document12 pages510.22E - Lecture - 7SantosNo ratings yet
- The MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: "NO Current Flows Into The Gate"Document11 pagesThe MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: "NO Current Flows Into The Gate"Aan BeckhsNo ratings yet
- E MosfetDocument5 pagesE MosfetSRMEA SAN RAFAEL BULACANNo ratings yet
- Lab - 12 Transistor MOSFETDocument11 pagesLab - 12 Transistor MOSFETNecotNo ratings yet
- 04 Transistor MOSFETDocument18 pages04 Transistor MOSFETNatalie mirelesNo ratings yet
- The Metal Oxide FETDocument7 pagesThe Metal Oxide FETSitty GuNo ratings yet
- Basic Sturcture of MosfetDocument2 pagesBasic Sturcture of MosfetbofshafiqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture.7electronic Circuits 2Document17 pagesLecture.7electronic Circuits 2eafc2444No ratings yet
- Mofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTDocument17 pagesMofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTTejas krishnakanthNo ratings yet
- Principle of MOSFET Device TechnologyDocument3 pagesPrinciple of MOSFET Device TechnologyCHING HUI YEENo ratings yet
- The Mosfet: Home TransistorsDocument10 pagesThe Mosfet: Home TransistorsPrabashaNo ratings yet
- Course Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Document37 pagesCourse Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Dr Sunipa RoyNo ratings yet
- MosfetDocument8 pagesMosfetHarshit OjhaNo ratings yet
- SECA1503Document149 pagesSECA1503Thabasum Aara SNo ratings yet
- Sedra SmithDocument52 pagesSedra SmithJiveshNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument22 pagesElectronicsVARSHITH REDDY JNo ratings yet
- ETI 2203 Lesson 7Document10 pagesETI 2203 Lesson 7amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- High-Side and Low-Side SwitchesDocument3 pagesHigh-Side and Low-Side SwitcheskheralahNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 - MOSFET Working Principle - NSESP 2021Document15 pagesGROUP 3 - MOSFET Working Principle - NSESP 2021Sisilia Anabina TariganNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Mosfet 8-4-2021Document11 pagesVlsi Mosfet 8-4-2021GaneshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Mosfet Transistor)Document22 pagesChapter 4 (Mosfet Transistor)Muriel MeyouNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document12 pagesLec 1Lovish Kumar VatwaniNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Circuits: Khurram Bughio Lecturer Electrical Engineering, MUETDocument29 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits: Khurram Bughio Lecturer Electrical Engineering, MUETNoor SabaNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument4 pagesMOSFETelen19111036 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- FET/MOSFET Characteristics: ObjectiveDocument13 pagesFET/MOSFET Characteristics: ObjectiveZeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- BJT and MosfetDocument10 pagesBJT and MosfetankitabcNo ratings yet
- EEN11L - 3 Experiment No 2 MOSFET - LDocument20 pagesEEN11L - 3 Experiment No 2 MOSFET - LRichie LatNo ratings yet
- Controlled Devices FET, BJT, IGBTDocument51 pagesControlled Devices FET, BJT, IGBTHolloGramNo ratings yet
- Power MOSFET: Basic StructureDocument10 pagesPower MOSFET: Basic StructureDomagoj ProphectusNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesExperiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsManikandan P Engineering EEE100% (1)
- Unit1 Mosfet RevDocument36 pagesUnit1 Mosfet RevMohak KumarNo ratings yet
- Mosfet CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesMosfet CharacteristicsAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- EEE 202S Exp4Document9 pagesEEE 202S Exp4Sudipto PramanikNo ratings yet
- Electronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorDocument21 pagesElectronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorGawrav BaishyaNo ratings yet
- FETs 11Document55 pagesFETs 11بلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorDocument11 pagesField Effect TransistorAriel OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Sesi II 2021 Topicd Lect3Document29 pagesSesi II 2021 Topicd Lect3mbagavan 0712No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Tunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationFrom EverandTunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument1 pageReferenceTun TunNo ratings yet
- Project ElevatorDocument45 pagesProject ElevatorTun TunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ElevatorDocument32 pagesChapter 2 ElevatorTun Tun100% (1)
- Application of Image Processing Technology in Evaluating Weldline Quality On Injection Molding ProductsDocument1 pageApplication of Image Processing Technology in Evaluating Weldline Quality On Injection Molding ProductsTun TunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ElevatorDocument32 pagesChapter 2 ElevatorTun Tun100% (1)
- Project ElevatorDocument45 pagesProject ElevatorTun TunNo ratings yet
- OSN 3500 2500 1500 Hardware Description ManualDocument379 pagesOSN 3500 2500 1500 Hardware Description Manualngtinh100% (19)
- DP CardReader 14061 DriversDocument578 pagesDP CardReader 14061 Driversberto_716No ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document27 pagesChapter 01khang-nguyen-7620No ratings yet
- Electronic Switching Harshita Uptu NotesDocument2 pagesElectronic Switching Harshita Uptu NotesHarsh Vardhan100% (1)
- Understanding Lead-Off Detection in ECGDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Lead-Off Detection in ECGGabriel GarcíaNo ratings yet
- An 1281Document11 pagesAn 1281Ioan TudosaNo ratings yet
- LTspice ShortcutsDocument1 pageLTspice ShortcutsMelina RussoNo ratings yet
- Tronsmart Element t6 Max Bluetooth Speaker Manual OptimizedDocument10 pagesTronsmart Element t6 Max Bluetooth Speaker Manual OptimizedMircea CatalinNo ratings yet
- McsDocument16 pagesMcsAmmar IkramNo ratings yet
- Practical Work 6 - CMOS + Rubrics PDFDocument10 pagesPractical Work 6 - CMOS + Rubrics PDFRiki SmithNo ratings yet
- Modbus and Modbus TCPDocument45 pagesModbus and Modbus TCPmohammedansin1No ratings yet
- Rohini 41414986331Document12 pagesRohini 41414986331Sridarshini VikkramNo ratings yet
- AN17821A Power Amplifier DatasheetDocument6 pagesAN17821A Power Amplifier DatasheetAbderrazek YACOUBI100% (1)
- LTE Alarms TroubleshootingDocument22 pagesLTE Alarms Troubleshootingnirmal_elex7863No ratings yet
- Slides On Drawing Lecture-2: Demonstration On Complete Drawing of An Architectural StructureDocument11 pagesSlides On Drawing Lecture-2: Demonstration On Complete Drawing of An Architectural StructureReal NazihNo ratings yet
- BIX Mount and ConnectorDocument6 pagesBIX Mount and ConnectorHassan FawazNo ratings yet
- SK3 SK4 SK2 PL1 SK1 SK5 SK6 SK7: Signal Strength (Rssi)Document1 pageSK3 SK4 SK2 PL1 SK1 SK5 SK6 SK7: Signal Strength (Rssi)Steven MckelvieNo ratings yet
- High-Current Voltage Output Circuit Using A Precision DACDocument5 pagesHigh-Current Voltage Output Circuit Using A Precision DACdasdracheNo ratings yet
- KATALOG PRODUK ELEKTRONIKwewewDocument3 pagesKATALOG PRODUK ELEKTRONIKwewewBims CompanyNo ratings yet
- Altium Designer FeatureDocument1 pageAltium Designer Featuredrew.unitedNo ratings yet
- Dimetra Applications CatalogueDocument58 pagesDimetra Applications CatalogueJuan FernandezNo ratings yet
- 3 - 00651-Lza7016011uen.b-Emerson Values PDFDocument30 pages3 - 00651-Lza7016011uen.b-Emerson Values PDFMamadou SoumahoroNo ratings yet
- An0002 Efm32 Hardware Design ConsiderationsDocument16 pagesAn0002 Efm32 Hardware Design ConsiderationsRam SakthiNo ratings yet
- Fuse and Relay: General InfromationDocument9 pagesFuse and Relay: General InfromationZakaria KalomarNo ratings yet
- 1850 TSS-5C DatasheetDocument2 pages1850 TSS-5C DatasheetNguyen TrungNo ratings yet
- IQAN Accessories Brochure HY33-8319 UKDocument12 pagesIQAN Accessories Brochure HY33-8319 UKabdelhadi houssinNo ratings yet
- S280-70-1 Below SN 20000Document44 pagesS280-70-1 Below SN 20000Neldy Dorantes MatuNo ratings yet
- AV Receiver: Owner'S ManualDocument78 pagesAV Receiver: Owner'S ManualPedro AbrilesNo ratings yet