Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Training Report (Thermal Power Plant) : Functional Discription
A Training Report (Thermal Power Plant) : Functional Discription
Uploaded by
TrRihaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Training Report (Thermal Power Plant) : Functional Discription
A Training Report (Thermal Power Plant) : Functional Discription
Uploaded by
TrRihaCopyright:
Available Formats
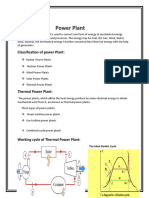
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
FUNCTIONAL DISCRIPTION
The thermal power plant burns fuels & uses the resultant to make the steam, which drives the
turbo generator. The fuel i.e COAL is burnt in pulverized form. The pressure energy of the
steam produced is converted into mechanical energy is fed to the generator where the
magnets rotates inside a set of stator winding & thus power is produced. In India 65% of the
total power is generated by thermal power stations .To understand the working of the thermal
power station plant, we can divide the whole process into following parts:
1. COAL FLOW:In coal fired plants, raw materials are air & water in PTPS, coal is
transported through railway wagon from M\s. COAL INDIA & is kept reserved on a buffer
stocks. The brought out to the station is unloaded with the help of wagon tippler. After
unloading, the coal is sent to crusher house with the help of conveyer belts. The coal which is
now reduced to very small pieces is sent to the coal bunkers with the help conveyer belt. The
raw coal is fed to coal mills through raw coal feeders. Raw coal feeders basically regulate
raw coal to pulverize mill. The raw pulverized coal is fed to the furnace with the help of
primary fan through pulverized coal pipes. A portion of the primary air is heated utilizing the
heat of the flue gases & then mixed with the cold air as per requirement by the pulverized
coal. Normally the temperature of is maintained at 60 to 70 degree. The coal is now burnt in
the furnace using oil in the beginning, showered through the nozzles at different elevation in
the furnace. To provide air for combustion, the heat of the flue gases also heat it. The heat
produced due to combustion is utilized for the conversion of water into steam. This water is
stored in the boiler drum. There are two sets of pipes attached to the drum, one called RISER
& other is DOWN CORNER through which the water comes to the RING HEADER & steam
moves up due to the density difference of water &steam. This steam is super-heated using
super heaters & meanwhile the flue gases are thrown out in the atmosphere through chimney.
2
. STEAM FLOW:The super-heated steam is sent to the turbine through pipe lines.
There are three turbines in the units, using the steam at different temperature & pressures.
After passing through high pressure turbine the steam is sent to the reheater for rising the
steam is sent to the intermediate pressure turbine through reheated line .Here it losses most of
its temp. & pressure & finally sent to low pressure turbines helps in increasing the efficiency
1 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
of the plant. The turbine in turn connecting with a generator produces electricity then this
electricity is stepped up to 220kv with the help of step up transformer & supplied to various
substations. Meanwhile, the steam through low pressure turbine is condenser and the
condensed water is stored in hot well.
3. WATER FLOW:The condenser water is extracted from the hot well through
condenser extraction pumps & sent to the boiler drum with the help of boiler feed pump
before passing through low pressure heater & deaerater . While loss in water is made up from
C.S. TANK. The C.S. tank is directly connected to hot well. The water in condenser is sent to
cooling tower for cooling. After cooling this water is again sent to condenser with the help of
circulating water pump. The loss is made up from raw water pump house through calorifier
pump hous
BOILER FEED PUMP:-
2 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
BRIEF EXPLANATION:1. WAGON TIPPLER:It is the machine which is used to tip the coal from the
wagon. The coal tipped is directly fed to conveyer belt. Its capacity is 12 wagon per hour.
2. CRUSHER:It crushes the coal into small pieces.
3. COAL MILLS:In it small pieces of coal are converted into pulverized form. They
are 6 in number.
4. FURNACE:It is the chamber in which fuel burns & fire blows.
5. BOILER DRUM:It contains water for boiling.
6. ELECTROSTATIC PRECIPITATOR:In this we have electrodes which
attracts fly ash & extract it from flue gases so that it cannot enter atmosphere.
7. CHIMNEY:It is used to release flue gases into the atmosphere.
8. TURBINE:Turbine is the part which revolves due to steam pressure. It is of three
types:
a) HIGH PRESSURE TURBINE
b) INTERMEDIATE PRESSURE TURBINE
c) LOW PRESSURE TURBINE
9. TURBO GENERATOR:It is the main machine which produces 210 MW
electricity. It is water & hydrogen gas cooled therefore it is contained in cylindrical chamber.
10. CONDENSER:It condenses steam coming from low pressure turbine to hot water.
3 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
11. COOLING WATER PUMP:This pump send water from cooling tower to
condenser.
12. COOLING TOWER:It is used to cool the water its height is near about 143.5 mtr.
13. RAW WATER PUMP HOUSE:It supplies raw water to the boiler.
14. CLEARIFIER PUMP HOUSE:The water from raw is cleared at clearifier by putting
ALUM in it & filtering it & then supplied to the condenser.
15. CONDENSATE EXTRACTION PUMP:-
C.E.P pump is used to extract the condense
water from the hot well & supply to deaerater after passing through L.P. heater &
economisier , so that high pressure steam in the cylinder can be created.
16. LOW PRESSURE HEATER:It is used to increase the temp. of water, in this
way efficiency of system increases.
17. DEAREATER:It is used to remove air from water, which is entrapped in the
water molecules. It is very important part because the entrapped air drum badly.
18. BOILER FEED PUMP(B.F.P.):It is the heaviest drive in the plant & supply
water to boiler drum from reaerater.
19. HIGH PRESSURE HEATER(H.P.):In this temp of water increases, thus
efficiency further increases.
20. ECONOMISER:-
4 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
In this flue gases exchange heat to the water to increase system
efficiency.
GENRAL WORKING DIAGRAM:-
6.6 KV CIRCUIT BREAKER:A circuit breaker is a device which:a) Makes or Break a circuit either manually or by remote control under normal conditions.
b) Breaks a circuit automatically under fault condition.
Thus a circuit breaker is just a switch which can be operated under normal & abnormal
conditions both automatic or manually. To perform this operation, a circuit breaker is
essential consist of fixed & moving contacts called electrodes. When a fault occurs on power
5 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
system, the trip coil of circuit breakers is energized which pulls apart moving contacts, thus
open the circuit dc supply is used for the operation of circuit breaker. On the basis of medium
used the circuit breaker are classified as:
a) OIL CIRCUIT BREAKER
b) AIR BLAST CIRCUIT BREKER
c) SULPHER HEXAFLUORIDE CIRCUIT BREAKER
a) OIL CIRCUIT BREAKER:It is well known that a circuit carrying a large current is
broken, an arc occurs at that point when the contacts are separate, the arching is specially
severe when high voltages are involved & if a short circuit occurs on a high voltage cable
which is supplied from large power station. The arc would be powerful to bridge the contacts
of the switch & destroy it by burning. The device is employed as an oil breaker. An oil
breaker posses the property of always break an alternative current at its zero value.
These switches are suitable for high voltage of 6.6 kv. The contacts of these switches, which
break high tension circuits are immersed in oil to ensure rapid & effective rapture of the
circuit. When the arc occurs, the oil in its path is vaporized & the gas thereby generated
extracts a pressure is utilized in arc controlled oil across the path of the arc, thereby efficiency
assisting its interruption.
SPECIFICATION:LOW OIL CIRCUIT BRRAKER:TYPE-E7532/10
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Voltage- 6.6/11kv
Current- 3150 A.
Frequency- 50 Hz
Short Time Current- 50/35 KA for 1/3 S
Breaking Current- 44/39.4 KA
Weight- 350 KGS
TYPE-E7512/10
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Voltage- 6.6/11 KV
Current- 1250 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Short Time Current- 50/40 KA for 1/3 S
Breaking Current- 44/39.4 KA
6 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
6. Weight- 210 KGS
TYPE-7525/10
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Voltage- 6.6/11 KV
Current- 2500 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Short Time Current- 50/35 KA for 1/3 S
Breaking Current- 44/39.4 KA
Weight- 220 KGS
INDEX
INCOMER
TIE
LOAD
1250 A Circuit Breaker
2500 A Circuit Breaker
3150 A Circuit Breaker
III-A
1. Dummy For Tie To 5A
2. Tie To 5A
3. Dummy For Tie To C-11-A
4. Tie To CC-II A
5. R.W.T. III
6. F.O.T III A
7. Bus P.T
8. S.S.T. III A
9. S.B.T II A
10. TO C.H.S. III A
11. C.M. 8A,340KW,325A
12. I.D.F.M. 5B, 130KW,147.5A
13. Ash Water Recovery T/F
14. H.P.W.P.M. III B, 260KW,29A
15. H.P.W.P.M. IIIA,260KW, 29A
7 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
16. C.W.P.M. 3C, 1265KW, 140A
17. A.H.T. III A
18. C.L.M.T. III A
19. B.C.W.P.M. III B, 135KW,38A
20. B.C.W.P.M. III A, 335KW,38A
21. Incomer
22. Dummy For Incomer
23. Tie For Unit 6 A
III-B
1. Tie To Unit 6B
2. Dummy For Incomer
3. Incomer
4. B.C.W.P.M. IIIC, 335 KW, 38 A
5. B.C.W.P.M. IIID, 335 KW, 38 A
6. C.L.W.T. IIIB
7. A.H.T. IIIB
8. H.P.W.P.M. IIIC, 260 KW, 26 A
9. H.P.W.P.M. IIID, 260 KW, 26 A
10. H.P.W.P.M. IIIE, 260 KW, 26 A
11. SPARE MOTOR
12. E.P.T.
13. C.M. 8B, 340 KW, 325A
14. C.H.S.
15. S.B.T. IIIB
16. S.S.T. IIIB
17. Bus P.T
18. F.O.T. IIIB
19. B.F.P.M. IIIB, 3500KW, 360 A
20. Tie To C-II-B
21. Dummy For Tie To C-II-B
22. Tie To 5B
23. Dummy For Tie To 5B
INDEX
5(A)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
U.S.T-5
E.P.T-5
Bus P.T
B.F.P.M-5 A, 3500 KW, 360 A
P.A.F.M-5 A, 1250 KW, 132 A
F.D.F.M-5 A, 750 KW, 80.2 A
P.M-5A, 340KW, 40.7 A
P.M-5B, 340 KW, 40.7 A
8 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
9. P.M-5C, 340 KW, 40.7 A
10. I.D.F.M-5A,1300 KW, 147.5 A
11. RECT. T/F
12. C.W.M.-5A,500 KW,525 A
13. C.W.P.M.-5A,265 KW,140 A
14. Incomer
15. Dummy For Incomer
16. Tie To SSIII-A
17. Dummy For Tie To SSIII-A
5(B)
1. Dummy For Tie To SSIII-B
2. Tie To SSIII-B
3. Dummy For Incomer
4. Incomer
5. C.W.P.M-5B, 265 KW, 140 A
6. C.P.M-5B, 500 KW, 525 A
7. 11 KW, Temporary Supply
8. I.D.F.M-5C,1300 KW, 147.5 A
9. P.M-5D, 340 KW, 40.7 A
10. P.M-5E, 340 KW, 40.7 A
11. P.M-5F, 340 KW, 40.7 A
12. F.D.F.M-5B, 750 KW, 80.2 A
13. P.A.F.M-5B, 1250 KW, 132 A
14. B.F.P.M-5C, 3500 KW, 360 A
15. Bus P.T
16. E.P.T-5B
17. Spare Motor
MOTOR:A) HIGH TENSION MOTOR
High tension motors operated at high voltages. In TAU DEVI LAL THERMAL POWER
STATION, these motors are operated at 6.6 kv. Some of these motors are as follow:1. CIRCULATING WATER(C.W) PUMP MOTORS:-
a) SPPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Maker B.H.E.L.
Capacity(K.W.)-1265 KW
Rated Voltage(VOLTS)-6600 V
Rated R.P.M-493
Rated Current-140 A
9 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
6. Connections-Star
7. Duty-Continuous
8. Insulation Class-F
9. Installation Position-Vertical
10. Quantity-3
b) FUNCTION:C.W. pump is used to circulate cooling water to the condenser so that low pressure steam in
the cylinder can be converted into water.
2. C.E.P. PUMP MOTOR:-
a) SPECFICATION:1. Maker B.H.E.L
2. Capacity(K.W.)-500 KW
3. Rated Voltage(VOLTS)-6600 V
4. Rated R.P.M-1482
5. Rated Current-52.8 A
6. Connections-Star
7. Duty-Continuous
8. Insulation Class-F
9. Installation Position-Vertical
10. Quantity-3
b) FUNCTION:C.E.P Pump is used to extract the condense water from the hot well & supply to deareater
after passing through L.P. heater & economizer, so that the high pressure steam in the
cylinder can be created.
3. BOILER FEED PUMP(B.F.P.) MOTOR:a) SPECIFICATION:1. Maker B.H.E.L
2. Capacity(K.W.)-500 KW
3. Rated Voltage(VOLTS)-6600 V
4. Rated R.P.M-1482
5. Rated Current-52.8 A
6. Connections-Star
7. Duty-Continuous
8. Insulation Class-F
9. Installation Position-Vertical
10. Quantity-3
10 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
b) FUNCTION:Its function is to supply the water to the boiler drum. It takes water from the deareator by
creating strong suction. It is the biggest motor in the plant.
4. COAL MILL MOTOR:a) SPPECIFICATION:1. Maker B.H.E.L
2. Capacity (K.W.)-340 KW
3. Rated Voltage(VOLTS)-6600 V
4. Rated R.P.M-992
5. Rated Current-40.7 A
6. Connections-Star
7. Duty-Continuous
8. Insulation Class-F
9. Installation Position-Horizontal
10. Quantity-6
b) FUNCTION:Its function is to grid the coal pieces to fine powder (pulverized) form i.e up to size of 25
micron.
5. COAL CRUSHER:a) SPPECIFICATION:1. Maker N.G.F.E.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Capacity (K.W.)-600 KW
Rated Voltage(VOLTS)-6600 V
Rated R.P.M-747
Rated Current-72 A
Connections-Star
Quantity-2
b) FUNCTION:Its function is to crush the big size coal pieces to a size of 25 mili meter square, which are
than carried to bunker through conveyor belt.
6. PRIMARY AIR FAN MOTOR:11 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
a) SPPECIFICATION:1. Maker B.H.E.L.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Capacity (K.W.)-1250 KW
Rated Voltage(VOLTS)-6600 V
Rated R.P.M-1487
Rated Current-132 A
Connections-Star
Duty-Continuous
Insulation Class-F
Quantity-3
b) FUNCTION:Its function is to carry pulverized coal from the coal mill to the furnace for its ignition. It
creates strong draft of air that carries pulverized coal.
7. FORCE DRAUGHT(F.D.) FAN MOTOR:a) SPECIFICATION:1. Maker B.H.E.L.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Capacity (K.W.)-750 KW
Rated Voltage(VOLTS)-6600 V
Rated R.P.M-1490
Rated Current-80.2 A
Connections-Star
Duty-Continuous
Insulation Class-F
Quantity-2
b) FUNCTION:F.D. fan is used to supply fresh air to furnace for the proper ignition of coal into the furnace.
8. INDUCED DRAFT(I.D.) FAN:a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Maker B.H.E.L
Capacity (K.W.)-1300 KW
Rated Voltage(VOLTS)-6600 V
Rated R.P.M-750
Rated Current-147.5 A
Connections-Star
Duty-Continuous
12 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
8. Insulation Class-F
9. Quantity-3
b) FUNCTION:Its function is to discharge flue gases to the atmosphere through the chimney after passing
through the precipitator.
10. BEARING COOLING WATER PUMP MOTOR:a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Maker B.H.E.L
Capacity (K.W.)-1300 KW
Rated Voltage(VOLTS)-6600 V
Rated R.P.M-750
Rated Current-147.5 A
Connections-Star
Duty-Continuous
Insulation Class-F
b) FUNCTION:It supply cooling water to the motor & other auxiliary for cooling purpose.
B) LOW TENSION MOTOR
Low tension motors are those which are of 415V. They are mainly used in H.T. motor
auxiliary.
1. B.C.W. DRAIN MOTOR:a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Capacity- 136 KW
Rated r.p.m- 987
Rated Current- 43 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Make- Krilosker
Insulation Class- B
b) FUNCTION:13 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
It pump the B.C. water to sump.
2. SEAL WATER PUMP MOTOR:a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Capacity- 25 KW
Rated r.p.m- 1479
Rated Current- 43 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Make- NGEF
Insulation Class- B
b) FUNCTION:It provides a layer of water to the lower position of boiler in order to seal it from the entry of
atmospheric air.
3. SEAL WATER VAPOUR EXHAUST FAN:a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Capacity- 1.5 KW
Rated r.p.m- 6205
Rated Current- 3.1 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Make- NGEF
Insulation Class- B
b) FUNCTION:It prevents the entry of air bubbles in the turbine cylinder by providing the opposite push.
4. CENTRIFUGE PUMP MOTOR:a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Capacity- 7.5 KW
Rated r.p.m- 1440
Rated Current- 14 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Make- NGEF
Insulation Class- B
14 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
b) FUNCTION:To centrifuge the vapor that enter by change in turbine an remove them.
5. ASH SLURRY PUMP MOTOR:a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Capacity-100KW
Rated r.p.m- 1485
Rated Current- 176 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Make- NGEF
Insulation Class- B
b) FUNCTION:To pump ash slurry to the ash disposal area.
7. EMERGENCY OIL PUMP:a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Capacity-15KW
Rated r.p.m- 1425
Rated Current- 125 A
Frequency- D.C.
Make- NGEF
Insulation Class- B
b) FUNCTION:To provide oil to the shaft & bearing of the turbine if seal oil pump & taking oil pump fails.
7. RAW WATER MOTOR PUMP:a) SPECIFICATION:-
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Capacity-15KW
Rated r.p.m- 1425
Rated Current- 125 A
Frequency- D.C.
Make- NGEF
15 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
6. Insulation Class- B
b) FUNCTION:It is use to pump raw water from the lake to the plant.
8.
INSTRUMENT AIR COMPRESSOR:-
a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Capacity- 105 KW
Rated R.P.M- 1485
Rated Current- 184 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Phase- 3
Make- Kirlosker
Insulation class- B
b) FUNCTION:It is used to compress the air used to control pneumatic controlled instrument at a pressure at
a pressure 6 to 7 kg/cm cube.
9.
SERVICE AIR COMPRESSOR:-
a) SPECIFICTION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Capacity- 30 KW
Rated R.P.M- 1485
Rated Current- 184 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Phase- 3
Make- NGEF
Insulation class- B
b) FUNCTION:Its function is similar to instrument air compressor.
16 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
10.
CLEARIFIER WATER PUMP MOTOR:-
a) SPECIFICATION:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Capacity- 30 KW
Rated R.P.M- 1470
Rated Current- 53 A
Frequency- 50 Hz
Phase- 3
Make- Crompton
7. Insulation class- B
b) FUNCTION:It pump the filtered water from clear to D.M. water treatment plant.
TRANSFORMERS
Transformer is the most convenient & economical device for transfer of power from one
voltage to another voltage at the same frequency. It works on the principle of electromagnetic
induction. There is hardly any installation without a transformer due to this equipment, it has
been possible to transmit bulk power to load centers from far off power house to various
machineries & switchgears of the power plant. Transformers are of two types:-
1. STEP UP TRANSFORMER:Which step up the voltage at secondary side called step up transformer.
2. STEP DOWN TRANSFORMER:Which step down the voltage at secondary side are called step down transformer.
MAIN PARTS OF POWER TRANSFORMERS
17 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
1. PRIMARY WINDING
2. SECONDARY WINDING
3. OIL TANK
4. DRAIN COKE
5. CONSERVATOR
6. BREATHER
7. TUBES FOR COOLING
8. TRANSFORMER OIL
9. EARTH POINT
10. EXPLOSION VENT
11. TEMPRATURE GAUGE
12. BUKHOLZ RELAY
13. PRIMARY TERMINALS
14. SECONDARY TERMINALS
ACCESSORIES OF TRANSFORMERS
1. OIL CONSERVATOR:Oil conservator is a short of dum mounted on the top of
transformer. A level indicator is fixed to it, which gives alarm at low level. Conservator is
connected through a pipe to the transformer tank containing oil. This oil expand & contract
depending upon the heat produced & so the oil level in conservator is left open to the
atmosphere through a breather so that the extra air may go out or come in.
2. BREATHER:The breather is a box containing calcium chloride or silica gel to absorb
moisture of our entering the conservator as it is well known fact that the insulating property
of the transformer oils lost if a small amount of moisture enter in it. So dry air is allows to
pass through the breather.
When oil level in oil conservator changes, air moes in & out of the
conservator. This action is known as breathing. Dry silica gel is of the blue color. It turns pale
pink as it absorbs moisture. The wet silica gel can be regenerated by drying.
3. BUCKHOLZ RELAY:This relay is a gas actuated relay which is meant for the
protecting of oil immersed transformer from insulation failure. Core heating or any type of
internal fault which may cause the heating of oil beyond the specified temp.. Due to any
18 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
internal fault, oil is heated up & oil vapor so formed causes either the alarm circuit or trip the
circuit.
4. EXPLOSION VENT:It is also a safety device of the transformer which protects the
transformer tank from gases induced by & any type of short circuit in the transformer. This
consists of a vertical pipe closed by a dia frame made of thin Bakelite sheet. This dia pharm
burst or slides out in case of abnormal pressure inside the tank. A diverter plate is used at the
bottom of the explosion vent to ensure that gases produced inside the transformer are directed
toward the buckholz relay & dont get collected inside the ventilation & equal the pressure
on each side of the diverter plate.
5. TEMPRAURE INDICATOR:It is also a protective device fitted to the transformer
to indicate temp. of transformer oil. For measuring temp. of the oil, bulb of the vapor
pressure type thermometer is placed in the hot oil & dial of the thermometer is mounted
outside the tank. Two indicating pointer black & red are provided. Alarm contacts are also
provided which come into action when predetermined higher temp. is reached under
abnormal operating conditions.
6. BUSHING:The bushing serves as supports & insulation of the bus bars & transformer
terminal. The bushing consist of porcelain shell body, upper & lower locating washer used for
fixing with the hole drilled for fixing bolt & it is supplied with an earth bolt.
7. MAGNETIC OIL GAUGE:The magnetic oil level gauge supervises the level of oil
in the conservator tank. The oil level gauge is provided on the transformer are of dial type
with minimum & maximum level marking & a pointer which indicate the level of oil in the
conservator. Something the scale is also graduated for oil temperature on the basis of its
level.
8. TAP CHANGER:The voltage control of transmission & distribution systems is
obtained by tap changer. Tap changer are either on load or off load tap changer. Tap changer
is fitted with the transformer for adjusting secondary voltage.
IMPORTANT TRANSFORMERS IN THE PLANT
19 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
1. GENRATOR TRANSFORMER(240 MVA, 15.75 KV/220KV):It converts 15.75 kv which is supplied from generator 220 kv & supplied it to the bus
bar/grid.
2. STATION SERVICE TRANSFORMER(40 MVA, 220 KV/7 KV):It converts 220 kv which is coming to station from BBMB to 7 kv & fed to station auxiliary.
3. UNIT AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER(15MVA, 15.75KV/7KV):It converts 15.75 kv which is supplied which is supplied from generator to 7 kv to fed unit
auxiliary.
SWITCHYARD COMPONENTS
20 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
1. SWITCH-GEAR:Switch gear is a control switch that controls the operations of a
i)
ii)
power circuit. The two function of a switch in a power system are:To permit the transmission lines to be convenient put into & taken out from service.
To disable the some plant & lines when these become faulty, to be rapidly & safety isolated
by automatic means.
The first of these can be served by relatively simple switches the second
however require circuit breakers, which are more robust & capable of breaking the large
value of fault power that results in faults on major power system. Since all plants & lines are
liable to develop fault as a result of mechanical damage, electrical breakdown, error in
operation etc. The simple isolators switch in favour of automatic circuit breaker even for
switching function. The whole switchgear assembly consists of two parts:-
a) PANEL:Panel consists of protective relays, mounted of potential transformer, current
transformer, ammeter, voltmeters & energy meter. The potential transformer is mounted on
the panel. The primary is connected to 11 kv & the reduce voltage from the secondary is
given to energy meter as line voltages & for protective purposes.
b) TROLLY:The trolly consists of current carrying contacts called electrodes. These are
normally engaged but in predetermined conditions, separate to interrupt the circuit, when the
contacts are made.
2. BUS BAR ARRANGEMENT:Conductors to which a number of circuits of
circuits are connected called bus bars. In power plants, shut down results disconnection of
supply to a large area. Hence to avoid shut down the major plants should have elaborate bus
bar arrangement with duplicate buses, alternative supply arrangement section etc. The extra
high voltage equipments such as isolators, circuit breaker are generally costly hence
unnecessary equipment should not be provided.
1. SINGLE BUS BAR ARRANGEMENT:The single arrangement consists of a
single bus bar to which various feeders are connected. In case of fault or maintenance of bus.
21 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
The entire bus bar has to be de-energised & the total shut down results. This scheme is most
economical & simple.
2.
DOUBLE BUS BAR ARRANGEMENT:The double bus system provides
additional flexibility, continuity of supply & permit periodic maintenance. In the event of
fault on the bus bar the other can be used. The figure shows to the bus bar arrangement. There
are two buses called main bus & reserve bus. The coupler can be closed so as to connect two
buses while transferring the power to the reserve bus.
Closed bus coupler, the two buses are now the same potential.
Closed isolator on reserve bus.
Open isolator on main bus.
i)
ii)
iii)
3.
LIGHTING ARRESTER:A lighting arrester is device, which proves low
impedance path for the flow of current between the line & earth when the system voltage
increase more than the desire value & regain its original properties of the desire value &
regain is original properties of an insulator at normal voltage. It is connected between line &
earth at the switch yard near the transformer. The lighting arresters are extensively used for
protection of transformers, switch gears and electrical equipment of over head lines, power
houses & sub station. These are also use to protect the line & equipments from sky lighting
following are the main type of lighting arrester:1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Horn Gap Lighting Arrester
Explosion Type Lighting Arrester
Oxide Film Lighting Arrester
Pellet Lighting Arrester
Thyrite Lighting
Auto Value Lighting Arrester
EXPULSION TYPE LIGHTING ARRESTER:IT CONSIST OF1. A tube made of fiber which is very effective gas evolving materials.
2. An isolating spark gap.
3. An spark gap inside the fiber tube.
22 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
During operation, arc due to impulse spark or inside the fiber tube causes some fiber material
of the tube voltage in form of gas, which is expelled through a vent from the bottom of the
tube, thus extinguishing the arc just like in circuit breaker. Since the gases generated is
hollow & diverter is open at its lower end.
THYRITE LIGHTING ARRESTER:This type of lighting arrester consists of number of discs of inorganic ceramic compound.
These discs are placed in a series having some gaps in between them & are sealed in a
porcelain tube. This tube has metallic cap & electrodes at its end. The compound used for
discs serve as an insulator but changes to a good conductor when voltage across it rises to a
certain predetermined value. It is used up to 220
FIG:- HC PS2202
23 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
210 MW TURBO GENERATOR
GENERAL:Modern feature of direct cooling by water & hydrogen are incorporated in
the 210 mw turbo generator, thus evolve an economical & reliable design. The machine is
provided with a fast acting excitation system & dependable auxiliary service to give
prolonged trouble free operation over the year. All the material that goes into the
manufacturer of this machine subjected to the various test as per national & international
standards. Each components under goes series of stage wise tests. Description of various
parts is given below:-
1. STATOR WINDING & INSULATION:The stator has a three phase, double
layer, short chorded, bar type winding, having two parallel parts. Each coil side consists of
glass insulated solid & hollow conductors with cooling water passing through the patter. The
elementary conductors are transposed in the slot portion of winding to minimize eddy current
losses.
Adequate protection is provided to avoid corona & other discharges. In the slots, the sides are
firmly held in the position by fiber slot wages, which are mechanically strong & have high
dielectric properties. The overhang portion of the coil is securely lashed with glass chord to
bondage rings & special brackets of non magnetic steel, which are in turns fixed to the core
press rings. On short circuits the force between the conductors tends to open the cone formed
by overhang portion of the coils, but the movement is effectively presented by supports &
lashing.
2.
DISTILLATE HEADER OR STATOR WATER HEADER:Ring type water
header, made of copper are provided separately for distillate inlet & outlet in the stator on
turbine side. The headers are supported on insulators & isolated from stator body. The
24 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
winding ends are solidly soldered into the coil lugs which are than ultrasonically tested.
Individual bars are provides with water inlet/outlet connection made of P.T.F.E. houses. The
bar head are insulated by fiber mould corners. The complete water path assembly is subjected
to the rigid hydroalic pneumatic tests at various stages to ensure water tightness & to detect
blocking of the flows paths.
3. TERMINAL BUSHING:Water cooled terminal bushing are housed in the lower part
of the stator on the slip ring side. Porcelain insulators are provided to insulate the terminal
bars from the stator body. Effective sealing is provided between the terminals bushing the
stator body to avoid any possibility of leakage of hydrogen. Terminals bushing are housed
inside a chamber made of non magnetic steels plates. Three phase terminals are brought out
to the facilitate externals connections. The terminal plate of the end terminals, where bus bar
connections are made is silver plated.
The terminal bushing can be replaced without removing the stator from foundation. Provision
is made for fixing the external bus ducts with the terminal plate.
4. ROTOR:The rotor is of cylindrical type shaft & body being forged in one piece from
chromium, nickel, molybdenum & vanadium steel. Prior to matching, a series of
comprehensive ultrasonic examination & other tests are carried out on rotor body & shaft
portion to ensure of any internal defects. The rotor with all the details assembled,
dynamically balanced to a high degree of accuracy & subjected to 20% over speeding for 2
minutes ensuring mechanical strength.
5. FIELD WINDING:The field winding is made from hard drawn silver bearing copper.
Rotor winding is held in position against centrifugal forces & by non magnetic steel retaining
rings in the over hang portion. Gap pick up system is employed for direct hydrogen cooling
of rotor winding. Several groups of ventilation ducts are mounted on the sides of the rotor
coil for gas passage. The rotor slot wedge are of special profiles with elliptical holes rolled
into match the ventilation ducts on the winding stacks, the end winding are insulated from
rings with the help of glass epoxy mould segments. Copper segments type damper winding is
provided in the end zone of rotor to prevent over heating of returning ring during
asymmetrical & asynchronous operation.
6. SHAFT MOUNTED FANS:25 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
A TRAINING REPORT (THERMAL POWER PLANT)
For circulating the cooling gas inside the generator, two
propeller type fans are shaft mounted on this & of rotor body. Fan hubs are made from alloy
steel forging & are hot fitted on the rotor shaft with sufficient interference. The steel cast fan
blades are machined in the tail portion to suit the fan hub & held in position with the help of
conical pins. The blades can be easily removed from or assembled in the fan hub. Fan shields
fixed to the end shields, guide the flow of gas through the fan sections.
7. SLIP RINGS:The slip ring consists of helically grooved alloy steel rings shrunk on the
rotor shaft & insulated from it. For convenience in assembly both the rings are mounted on a
single, common steel bush, which has an insulated jacket pre mould on it. The complete bush
with slip ring is shrunk on the rotor shaft. The slip rings are provides with inclined holes for
self ventilation. The helical grooves cut on the outer surface of the slip rings improve brush
performance.
TURBO GENERATOR RATING:CAPACITY IN KW- 210000
POWER FACTOR- 0.85
CAPACITY IN KVA- 247000
STATOR:-1) 15750 V
2) 90.60 A
ROTOR- 310 V, 2600 A
ROTOR R.P.M- 3000
FREQUENCY- 50Hz
PHASE- 3
CONNECTION- STAR
COLLENT- H2+H20
NO, OF POLES- 2
TURBO GENERATOR:-
26 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION & RESEARCH INTEGRATED INSTITUTIONS,
KURUKSHETRA
You might also like
- SNG and LPG Systems Overview PDFDocument57 pagesSNG and LPG Systems Overview PDFMohanad100% (2)
- Summer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarDocument9 pagesSummer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarAliraza7660% (5)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument8 pagesThermal Power PlantShailesh Sankdasariya100% (4)
- Electrical Engg.: Panipat Thermal Power Station (A Unit of H.P.G.C.L., Haryana)Document43 pagesElectrical Engg.: Panipat Thermal Power Station (A Unit of H.P.G.C.L., Haryana)dinesh66jattNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Report ON C & I Maintenance Division Unit-8 AT Panipat Thermal Power StationDocument27 pagesIndustrial Training Report ON C & I Maintenance Division Unit-8 AT Panipat Thermal Power StationAbhishek AroraNo ratings yet
- Generation of Electric PowerDocument108 pagesGeneration of Electric Powermausam sharma100% (1)
- Power Plant FamiliarisationDocument110 pagesPower Plant FamiliarisationmrdipakwaghNo ratings yet
- Harduaganj Thermal Power Plant by Geetesh SharmaDocument66 pagesHarduaganj Thermal Power Plant by Geetesh Sharmageeteshaccurate100% (1)
- Chandrapur CTPS 15 Days Training ReportDocument21 pagesChandrapur CTPS 15 Days Training ReportUday Wankar0% (1)
- Mechanical Engg.: Report On Industrial TrainingDocument44 pagesMechanical Engg.: Report On Industrial TrainingSakshi SanghiNo ratings yet
- CSEB (Chhattisgarh State Electricity Board) Korba East Vocational Training Presentation I IDocument44 pagesCSEB (Chhattisgarh State Electricity Board) Korba East Vocational Training Presentation I Ihaxxo24No ratings yet
- Thermal Plant Ropar 1260MWDocument89 pagesThermal Plant Ropar 1260MWRahul Pandey71% (7)
- Introduction To CFPPDocument34 pagesIntroduction To CFPPVenkat CherukuriNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On NTPC Tanda Ambedkar NagarDocument9 pagesSummer Training Report On NTPC Tanda Ambedkar NagarNaman ShahNo ratings yet
- NTPCDocument32 pagesNTPC12 EC ATUL KUMAR SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Thermal PlantDocument4 pagesThermal PlantHanan Tariq QasuriaNo ratings yet
- Brief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical LocationDocument22 pagesBrief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical Locationcoolvipin1988No ratings yet
- NTPC ReportDocument47 pagesNTPC ReportUpendra Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- JJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemDocument9 pagesJJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemAh Tiang86% (7)
- محطة شبرا الخيمةDocument15 pagesمحطة شبرا الخيمةعبدالله عبدالمنعم100% (1)
- Project Report by Manish YadavDocument53 pagesProject Report by Manish Yadavmanish yaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Full Mechanical Degree Updated On 2 7 2010Document54 pagesFull Mechanical Degree Updated On 2 7 2010Balwan Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- A Practical Training Seminar ON: Suratgarh Super Thermal Power StationDocument30 pagesA Practical Training Seminar ON: Suratgarh Super Thermal Power Stationvipul sharmaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringDocument34 pagesThermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringMos MohNo ratings yet
- Kota Super Thermal Power Station Industrial Training ReportDocument70 pagesKota Super Thermal Power Station Industrial Training ReportShailendra Gautam100% (1)
- JPL-JIPT Manual General DescriptionDocument3 pagesJPL-JIPT Manual General Descriptionmayukh_mitra_2No ratings yet
- Gajendra KumarDocument23 pagesGajendra KumarGAJENDRA KUMARNo ratings yet
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDocument41 pagesReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant - EeDocument20 pagesThermal Power Plant - EePrabhat Chandra100% (1)
- DVC Mejia Thermal Power StationReportDocument35 pagesDVC Mejia Thermal Power StationReportRahul RoyNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument10 pagesThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842No ratings yet
- Pulkit Nag REPORT, Result, Conclusion, RefferenceDocument70 pagesPulkit Nag REPORT, Result, Conclusion, RefferencePulkit NagNo ratings yet
- 1.1.power Plant LayoutDocument5 pages1.1.power Plant LayoutBALAMBAL R100% (1)
- PTPS Training ReportDocument24 pagesPTPS Training ReportShubh JohriNo ratings yet
- Training Report at PtpsDocument38 pagesTraining Report at Ptpsrahul93anNo ratings yet
- Summer Training in Badarpur NTPCDocument54 pagesSummer Training in Badarpur NTPCRohit VermaNo ratings yet
- SWITCHYARD, NTPC SIPAT Training ReportDocument35 pagesSWITCHYARD, NTPC SIPAT Training ReportSuresh Sunny83% (6)
- SIREreport 118ee0297Document13 pagesSIREreport 118ee0297Bhabani sankar KishanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantsDocument24 pagesThermal Power Plantslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- NTPC KantiDocument33 pagesNTPC Kantivivek mahobiya100% (1)
- Power Plant Training ReportDocument26 pagesPower Plant Training ReportAnil YadavNo ratings yet
- TRNG Proj Rep.Document39 pagesTRNG Proj Rep.sahapinkNo ratings yet
- TPS Internship ReportDocument34 pagesTPS Internship Reportmkhalil1148No ratings yet
- Introduction and Thermal Power PlantDocument27 pagesIntroduction and Thermal Power PlantKshitij AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngDocument93 pagesPower Plant Engsenthilkumarece100% (3)
- Jaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyDocument29 pagesJaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyAashish SangwanNo ratings yet
- D Eng 23 0057 Me 16 04 2024Document20 pagesD Eng 23 0057 Me 16 04 2024Nadith JayNo ratings yet
- Project Report: (1 JUNE, 19 To 30 JUNE, 19)Document34 pagesProject Report: (1 JUNE, 19 To 30 JUNE, 19)AnkurNo ratings yet
- NTPCDocument33 pagesNTPCSubodh DuhanNo ratings yet
- Distributed Digital Control and Monitoring and Information System" by Designing andDocument29 pagesDistributed Digital Control and Monitoring and Information System" by Designing andjhonnyjungleNo ratings yet
- (General) 1-43Document43 pages(General) 1-43Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Kota Thermal Power Plant Report in Standered FormDocument45 pagesKota Thermal Power Plant Report in Standered FormAbhishek Meena100% (2)
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- How it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useFrom EverandHow it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useNo ratings yet
- VEIT Ironing Technology For TextileCare 06 1219Document24 pagesVEIT Ironing Technology For TextileCare 06 1219Ƥαѵαи Καlψαƞ ΚNo ratings yet
- One Pipe Steam DesignDocument44 pagesOne Pipe Steam Designreyes hernandezNo ratings yet
- Unit Operation Laboratory IIDocument26 pagesUnit Operation Laboratory IImurtadaNo ratings yet
- KKS Designation System KKS Designation SystemDocument19 pagesKKS Designation System KKS Designation Systemdexter schmithNo ratings yet
- B&W HRSG OverviewDocument8 pagesB&W HRSG OverviewAnonymous xaayU9b9GNo ratings yet
- List of As-Built Drawings (Mech.) : S/N Doc. / Dwg. No. Doc. / Dwg. TitleDocument4 pagesList of As-Built Drawings (Mech.) : S/N Doc. / Dwg. No. Doc. / Dwg. Titleأبو أنس البرعصيNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance CalculationDocument2 pagesEnergy Balance CalculationSzelee KuekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2SelNo ratings yet
- The Isolation of Eugenol From ClovesDocument3 pagesThe Isolation of Eugenol From ClovesShoomyla RashidNo ratings yet
- Nus Corporati NDocument35 pagesNus Corporati NFadi BoustanyNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Ibrahim Darwish 15101468 12th ReportDocument45 pagesMohamed Ibrahim Darwish 15101468 12th ReportMohamed DarwishNo ratings yet
- Q CalculationDocument2 pagesQ CalculationsubashNo ratings yet
- Heater Tube InspectionDocument129 pagesHeater Tube Inspectionuniquepp100% (2)
- Astm d381 Jtvo9242Document5 pagesAstm d381 Jtvo9242Nayth Andres GalazNo ratings yet
- Primus Overview Catalogue ANGDocument8 pagesPrimus Overview Catalogue ANGpesumasinad0% (1)
- Coal Combustion Theory - Electrical4uDocument11 pagesCoal Combustion Theory - Electrical4uAarthi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument182 pagesPower Plant Engineeringmuhammad azeez100% (3)
- Achieving Zero Discharge in Industrial Waste Water Treatment PlantsDocument13 pagesAchieving Zero Discharge in Industrial Waste Water Treatment PlantsEswaramoorthi Sellappa GounderNo ratings yet
- Boiler Structure and Principle (English)Document28 pagesBoiler Structure and Principle (English)Engr ImranNo ratings yet
- WWW Spiraxsarco Com Resources Steam Engineering Tutorials ST 3Document12 pagesWWW Spiraxsarco Com Resources Steam Engineering Tutorials ST 3Mashudi FikriNo ratings yet
- 6648 0400 5 PS Pi 0001 - F PDFDocument97 pages6648 0400 5 PS Pi 0001 - F PDFMohamed OuichaouiNo ratings yet
- Sulfur P&IDDocument25 pagesSulfur P&IDKrismawan Saptya Yudha0% (1)
- Teacher Thermodynamics II LabDocument47 pagesTeacher Thermodynamics II LabAli Raza100% (1)
- 3D Model of Steam Engine Using Opengl: Indian Institute of Information Technology, AllahabadDocument18 pages3D Model of Steam Engine Using Opengl: Indian Institute of Information Technology, AllahabadRAJ JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Power Plant Volume I PDFDocument850 pagesPart 3 Power Plant Volume I PDFyuchakr100% (5)
- MR - Samaksh Jhalani Machinery-FinalDocument45 pagesMR - Samaksh Jhalani Machinery-FinalSamaksh JhalaniNo ratings yet
- Xsmall: Service ManualDocument42 pagesXsmall: Service ManualCatalin CosminNo ratings yet
- SRU Start-Up Considerations - Shrikant Koli - Black & Veatch PDFDocument26 pagesSRU Start-Up Considerations - Shrikant Koli - Black & Veatch PDFRiyesh KpNo ratings yet
- Tut-Sheet 01Document1 pageTut-Sheet 01Aditi GoyalNo ratings yet