Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Central Bicol State University of Agriculture San Jose, Pili, Camarines Sur College of Development Education
Central Bicol State University of Agriculture San Jose, Pili, Camarines Sur College of Development Education
Uploaded by
JOSE ESGUERRAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Central Bicol State University of Agriculture San Jose, Pili, Camarines Sur College of Development Education
Central Bicol State University of Agriculture San Jose, Pili, Camarines Sur College of Development Education
Uploaded by
JOSE ESGUERRACopyright:
Available Formats
CENTRAL BICOL STATE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE
SAN JOSE, PILI, CAMARINES SUR
COLLEGE OF DEVELOPMENT EDUCATION
LABORATORY EXERCISE NO. 1
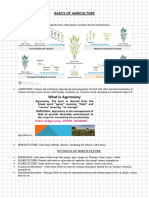
DIFFERENT TERMINOLOGIES
AGRICULTURE - the science, art, or occupation concerned with
cultivating land, raising crops, and feeding, breeding, and raising
livestock; farming.
AGRONOMY - the science of soil management and the production
of field crops.
ANNUAL PLANT - is a plant that completes its life cycle, from
germination to the production of seed, within one year, and then
dies.
BIENNIAL - is a flowering plant that takes two years to complete its
biological lifecycle.
BOTANY - the science of plants; the branch of biology that deals
with plant life.
BROADCAST SEEDING - is a method of seeding that involves
scattering seed, by hand or mechanically, over a relatively large
area.
CLIMATE The Weather conditions prevailing in an area in general
or over a long period.
COTYLEDON - is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of
a plant.
COVER CROPS - is a type of plant grown to suppress weeds, help
build and improve soil, and control diseases and pests.
CROSS FERTILIZATION - fertilization in which the gametes are
produced by separate individuals or sometimes by individuals of
different kinds
CROWN - refers to the totality of the plant's aboveground parts,
including stems, leaves, and reproductive structures.
CUTTING - a stem, leaf, or root that is cut from a plant and used to
grow a new plant.
FERTILITY - the quality of being able to produce young or fruit.
FORAGES - grasses and other plants that are eaten by animals.
GREEN MANURE - a growing crop, such as clover or grass, that is
plowed under the soil to improve fertility.
HARROW - A farm implement consisting of a heavy frame with
sharp teeth or upright disks, used to break up and even off plowed
ground.
HORTICULTURE - The science or art of cultivating fruits,
vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants.
HUMID CLIMATE - a climate with an excess of moisture, in which
the solar heat received is insufficient to evaporate all moisture
occurring in the form of precipitation.
HYBRID - the offspring of two animals or plants of different breeds,
varieties, species, or genera, especially as produced through
human manipulation for specific genetic characteristics.
INSECTISIDE - a substance or preparation used for killing insects.
LEGUME - A pod of such a plant, which splits into two valves with
the seeds attached to one edge of the valves.
MELLOW SOIL A soil easily work and penetrated.
NODE - is the area of a plant's stem from which the leaves grow.
NUTRIENTS - any of the mineral substances that are absorbed by
the roots of plants for nourishment.
PASTURE - land covered with grass or herbage and grazed by or
suitable for grazing by livestock.
POLLINATION - the transfer of pollen from the anther to the
stigma.
PREEMERGENCE - occurring or applied before the emergence of a
plant from the soil.
POSTEMERGENCE - occurring or applied after emergence of a plant
from the soil and before full growth.
RILL EROSION - Removal of soil by running water with formation of
shallow channels that can be smoothed out completely by normal
tillage.
SEEDING - any propagative part of a plant, including tubers, bulbs,
etc., especially as preserved for growing a new crop.
SILAGE - fodder converted into succulent feed for livestock
through processes of anaerobic acid fermentation
SOIL EROSION - Removal of topsoil faster than the soil forming
processes can replace it, due to natural, animal, and human
activity (over grazing, over cultivation, forest clearing, mechanized
farming, etc.). Soil erosion results in land infertility and leads to
desertification and devastating flooding.
SOWING - to scatter seed over (land, earth, etc.) for the purpose of
growth.
You might also like
- Bgcse Agric NotesDocument282 pagesBgcse Agric NotesBame Makilinda100% (3)
- The Resilient Farm and Homestead: Perennial Plants and ResiliencyDocument9 pagesThe Resilient Farm and Homestead: Perennial Plants and ResiliencyChelsea Green Publishing100% (3)
- Green RMDocument46 pagesGreen RManil1695No ratings yet
- Organic VegetablesDocument123 pagesOrganic VegetablesMarcus Camby75% (4)
- Raj Rewal Asia Games HousingDocument8 pagesRaj Rewal Asia Games HousingShubh Cheema60% (5)
- Agriculture Notes NeoDocument130 pagesAgriculture Notes NeoGodzila BwNo ratings yet
- Agronomy and HorticulturalDocument9 pagesAgronomy and HorticulturalKathirasan VadiveluNo ratings yet
- II-6 Agronomy 1-23Document24 pagesII-6 Agronomy 1-23SannyBombeoJomocNo ratings yet
- Classification of Agricultural Crops: MysoreDocument9 pagesClassification of Agricultural Crops: MysoreRahmat ZakariyyahNo ratings yet
- Agric NotesDocument126 pagesAgric Noteskhumoetsile sadiNo ratings yet
- EPP Reviewer2ndDocument2 pagesEPP Reviewer2ndMariejo DumalagNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 CULTURAL PRACTICES IN CROP OPERATION AT101Document6 pagesLesson 4 CULTURAL PRACTICES IN CROP OPERATION AT101Gerardo AgunatNo ratings yet
- Agronomic CropsDocument11 pagesAgronomic CropsIan James AnonasNo ratings yet
- AFADocument23 pagesAFArebecca tanaidNo ratings yet
- Classification of Crop DetailedDocument11 pagesClassification of Crop DetailedRahulNo ratings yet
- Agriculture NotesDocument127 pagesAgriculture Notestonikay219No ratings yet
- CH 1 - Crop Production (Notes)Document2 pagesCH 1 - Crop Production (Notes)binu_praveen100% (1)
- Crop Production Clsass 8Document7 pagesCrop Production Clsass 8Vikash SharmaNo ratings yet
- EstherDocument17 pagesEsthersharonkathleen28No ratings yet
- Final Presentation Basic Weed Science IIDocument68 pagesFinal Presentation Basic Weed Science IIPhoebe O. TumammanNo ratings yet
- Isabella Persad Agricultural Science - Section A - Introduction To AgricultureDocument37 pagesIsabella Persad Agricultural Science - Section A - Introduction To AgricultureIsabella persadNo ratings yet
- Nat Ag Winter Wheat in N Europe by Marc BonfilsDocument5 pagesNat Ag Winter Wheat in N Europe by Marc BonfilsOrto di CartaNo ratings yet
- Crop and Production MLPDocument3 pagesCrop and Production MLPDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Establishing Horticultural ProjectDocument8 pagesEstablishing Horticultural ProjectWILMOR A. DIONESNo ratings yet
- Cropping Systems: What Is A Cropping System?Document4 pagesCropping Systems: What Is A Cropping System?Daniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Special Purpose CropDocument17 pagesSpecial Purpose CropAndruuu eeeNo ratings yet
- Core Competency 1: Perform Nursery OperationDocument5 pagesCore Competency 1: Perform Nursery OperationAnneNo ratings yet
- Classification of Crop Plants (Modified)Document28 pagesClassification of Crop Plants (Modified)lemma4aNo ratings yet
- Agriculture RevisionDocument18 pagesAgriculture RevisionJaedon Pabarue-LimaNo ratings yet
- Livestock Production or Animal Husbandry: APIS - Bee COLERE - CultureDocument17 pagesLivestock Production or Animal Husbandry: APIS - Bee COLERE - CulturePrincess Jhoy Pascua TuringanNo ratings yet
- Vege Production 07052021Document117 pagesVege Production 07052021Kesh YahNo ratings yet
- AGR 201 - Week 8 E-NotesDocument16 pagesAGR 201 - Week 8 E-Notesdaisyokoth6No ratings yet
- CpSci 101 - Module 5 - Lesson 3 and 4 Descriptive Classification & Agricultural ClasiificationDocument8 pagesCpSci 101 - Module 5 - Lesson 3 and 4 Descriptive Classification & Agricultural ClasiificationRegan Roldan RolaNo ratings yet
- QUESTION: Why Are Seed Plants Successful On LandDocument8 pagesQUESTION: Why Are Seed Plants Successful On LandtanatswaNo ratings yet
- Combined Science Notes Vegetative Propagation-Wps OfficeDocument3 pagesCombined Science Notes Vegetative Propagation-Wps OfficendomolancubeNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Science Work.Document15 pagesAgricultural Science Work.Isabella persad100% (1)
- Agri Fishery ReviewerDocument7 pagesAgri Fishery ReviewerYr Rah Wleynse IINo ratings yet
- c1-2 AN2 Forages1-1Document5 pagesc1-2 AN2 Forages1-1Alexandra AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Cucumber ProductionDocument4 pagesCucumber ProductionJosh Saleng0% (1)
- Cultural and Production Practices For Crop Agriculture: Land PreparationDocument3 pagesCultural and Production Practices For Crop Agriculture: Land PreparationJacob MunozNo ratings yet
- Crop ProductionDocument8 pagesCrop ProductionkuevoradzogloriaNo ratings yet
- Kitubo SHS. TVL. ACP2. Agricultural Crops Production Handouts PDFDocument21 pagesKitubo SHS. TVL. ACP2. Agricultural Crops Production Handouts PDFCarl SeanNo ratings yet
- Ard nOTESDocument9 pagesArd nOTESrodagab903No ratings yet
- Crop Science 1.bonbonDocument2 pagesCrop Science 1.bonbonjapethNo ratings yet
- Las Kuatras Marias - Integrated Diversified Organic Farming SystemDocument4 pagesLas Kuatras Marias - Integrated Diversified Organic Farming SystemDenz MercadoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ForagesDocument36 pagesIntroduction To ForagesAiman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Crop Production 8thDocument20 pagesCrop Production 8thVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Tress That Is Used To Construct Houses For Man and Animals. Made From Fiber and Harvested From Wood PulpDocument13 pagesTress That Is Used To Construct Houses For Man and Animals. Made From Fiber and Harvested From Wood PulpLesli Daryl Antolin SanMateoNo ratings yet
- Classificationofagriculturalcrops2 PDFDocument10 pagesClassificationofagriculturalcrops2 PDFBema Dejeran LabastidaNo ratings yet
- Propagation and Dissemination of Weed Seeds PropagationDocument7 pagesPropagation and Dissemination of Weed Seeds PropagationAMIR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Epp Agriculture-1Document17 pagesEpp Agriculture-1Ryan Jeffrey FabilaneNo ratings yet
- Weeds (Afp)Document94 pagesWeeds (Afp)Chrisz Etrata BibayNo ratings yet
- Commercial Pumpkin Production For New Mexico: College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental SciencesDocument4 pagesCommercial Pumpkin Production For New Mexico: College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciencesmember1000No ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 Economic vs. Biological Yields of Crops and The Factors Affecting Their ProductionDocument62 pagesLesson 1.2 Economic vs. Biological Yields of Crops and The Factors Affecting Their ProductionLyrie CutaraNo ratings yet
- French BeansDocument3 pagesFrench BeanssekarkkNo ratings yet
- SunnhempDocument3 pagesSunnhempapi-402657252No ratings yet
- Larry Santoyo Constructing The Food Forest OrchardDocument3 pagesLarry Santoyo Constructing The Food Forest OrchardabcdescuNo ratings yet
- General AgricultureDocument16 pagesGeneral AgricultureKarimNo ratings yet
- Place LandscapeDocument26 pagesPlace LandscapeJefferson MalagueñoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Crops: Professor A. B. Mashingaidze Crop Science and Post Harvest DepartmentDocument40 pagesClassification of Crops: Professor A. B. Mashingaidze Crop Science and Post Harvest DepartmentAlfred MagwedeNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Common Terms in Nursery and Plantation TechniquesDocument10 pagesGlossary of Common Terms in Nursery and Plantation TechniquesJelibeth OnsayagNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HorticultureDocument26 pagesIntroduction To HorticultureGino R. MonteloyolaNo ratings yet
- Water Logging (2) FIDocument32 pagesWater Logging (2) FIVaish NaoNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of Sub-Grade Clayey Soil Using Fly Ash and Coir GeotextileDocument50 pagesStabilization of Sub-Grade Clayey Soil Using Fly Ash and Coir GeotextileJebin SebastianNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Green Building Certification System For Developing G-SEEDDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Green Building Certification System For Developing G-SEEDPEng. Tech. Alvince KoreroNo ratings yet
- Day 02 Vitor KibaltchichDocument9 pagesDay 02 Vitor KibaltchichVitor CoelhoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical Test TLE 7 Hort-CropDocument3 pages2nd Periodical Test TLE 7 Hort-CroplesterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Water Sensitive Urban Design 2016 Full Slides PDFDocument24 pagesLecture 2 - Water Sensitive Urban Design 2016 Full Slides PDFAndyNo ratings yet
- Mulch Options For Erosion Control On Construction SitesDocument5 pagesMulch Options For Erosion Control On Construction SitesStephanyNo ratings yet
- Japanese Gardens PPT 2.Document27 pagesJapanese Gardens PPT 2.Sana Mahreen50% (2)
- (Prelim) Soil ConservationDocument16 pages(Prelim) Soil ConservationMarkNo ratings yet
- Cracks in Residential Basement WallDocument2 pagesCracks in Residential Basement WallaaNo ratings yet
- 326 PDFDocument148 pages326 PDFGiang ThanhNo ratings yet
- Brochure 3c-Lotus-Zing-BrochureDocument26 pagesBrochure 3c-Lotus-Zing-BrochurepiyushNo ratings yet
- Demonstration Lesson in EPP 6Document19 pagesDemonstration Lesson in EPP 6Jessie L. Gimoto100% (2)
- Aquaponics SIP Body-SulitAndTheGangDocument29 pagesAquaponics SIP Body-SulitAndTheGangKristine Javier SulitNo ratings yet
- Paving Materials: 1. Accommodate Intense Use 2. Provide Direction 3. Suggest Rate and Rhythm of MovementDocument46 pagesPaving Materials: 1. Accommodate Intense Use 2. Provide Direction 3. Suggest Rate and Rhythm of MovementatillaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter ExamDocument2 pages1st Quarter ExamSha Ti Mae Tats100% (1)
- Daily Report 05-08-2022 (KK-API)Document2 pagesDaily Report 05-08-2022 (KK-API)Muhammad Aris HabibiNo ratings yet
- Akshay Urja Bhawan, HAREDA, PanchkulaDocument1 pageAkshay Urja Bhawan, HAREDA, PanchkulaSumanNo ratings yet
- Full Borehole Analysis and Soil ReplacementDocument1 pageFull Borehole Analysis and Soil ReplacementAfuye Oluyemi IbiyinkaNo ratings yet
- BioswaleDocument8 pagesBioswaleRIYA SHAHNo ratings yet
- Landscape Ecology: m:/Q&ES/Water Resources/ecol - Land.p65 (Rev.1)Document17 pagesLandscape Ecology: m:/Q&ES/Water Resources/ecol - Land.p65 (Rev.1)timshel144No ratings yet
- Goodell Gardens TourDocument2 pagesGoodell Gardens TourSarahStemenNo ratings yet
- Amc Awd-124 2023.05.14Document1 pageAmc Awd-124 2023.05.14SHEPHERD CONSULTANTNo ratings yet
- ISA - Study Guide Table of ContentsDocument3 pagesISA - Study Guide Table of Contentsasdf123asdfasdfNo ratings yet
- Chrysal CVBN - Chrysal: O OrriiggiinnaallDocument3 pagesChrysal CVBN - Chrysal: O OrriiggiinnaallDurielNo ratings yet
- What Is Modern ArchitectureDocument2 pagesWhat Is Modern ArchitectureJacksonNo ratings yet
- AR Technical ChecklistDocument7 pagesAR Technical Checklistamr saadeddinNo ratings yet