Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermo Practice Problems
Thermo Practice Problems
Uploaded by
Keyang SunOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermo Practice Problems
Thermo Practice Problems
Uploaded by
Keyang SunCopyright:
Available Formats
CBE 141: Chem. Eng.
Thermodynamics
Exam 2 Practice Problems
These problems are meant to give you extra practice on concepts that are fair game for the
exam. Solutions will not be posted, but we might work through some of these during office
hours on request.
1. Show that the maximum coefficient of performance for any heat pump cycle
operating between two regions at temperatures TC and TH is:
!
=
! !
Next, show that the maximum coefficient of performance for a heat pump used for
cooling is:
!
=
! !
2. CO2 needs to be compressed from P1=1 bar, T1 = 300 K to P2=40 bar to transport
it to remote sites for sequestration. What is the minimum energy requirement per kg
of CO2 for the compressor? Should the compressor operate adiabatically or
isothermally for the best energy efficiency? The environment is at Tenv= 300 K.
Ans: 310 kJ/kg for adiabatic operation, 197 kJ/kg for isothermal
3. Derive an expression for the efficiency of the Diesel cycle in terms of r (compression
ratio) and the re (expansion ratio). You might find this page helpful:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diesel_cycle
4. The internal energy of a gas is expressed as
= !/!
N moles of this substance, initially at T0 and P0, are expanded reversibly and
adiabatically until the pressure is halved. What is the final temperature?
5. Show that, for the van der Waals equation,
=
!
the residual enthalpy HR is equal to:
2
! =
You should start with a total derivative. In order to make isolating the derivatives
mathematically tractable, you will need to do a change of variables from P to V. This
will change your bounds of integration as well, and you should substitute
!"
= !" .
Similarly, show that
! = ln 1
CBE 141: Chem. Eng. Thermodynamics
Exam 2 Practice Problems
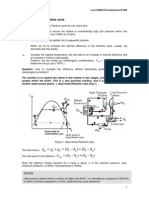
6. Refrigerant HFC-134a (1,1,1,2 tetrafluoroethane) has been used since the early
1990s in automobile air conditioning applications, replacing earlier ozone-depleting
refrigerants. In a typical cycle, the warm coil operates at a maximum temperature of
130 F and the cooling coil is at 40 F. Calculate the process conditions, amount of
work and heat and efficiency of the cycle of the figure below. (Unfortunately, HFC134a has very large global warming potential (1300 times as large as CO2) and is in
the process of being phased out.)
(The data for this refrigerant can be found in the NIST webbook.)
Ans: COP = 4.66, QH=-158 kJ/kg, QC=130 kJ/kg
7. (Modified from HW 5, the ungraded Problem 6): Using thermodynamic derivatives,
derive ! ! for the general case as a function of P, T, and V only.
Show that this simplifies to R using the ideal gas EOS. What is it for the truncated
virial equation Z=1+BP/RT, if B is assumed to be constant?
Finally, show that ! > ! must always hold.
8. Starting with the fundamental equation for enthalpy,
a. Show that the isobars in the vapor region of a Mollier (H-S) diagram (see
Figure 6.4 in SVNA) must have both positive slope and positive curvature.
b. What is the slope of the isobar in the vapor-liquid coexistence line?
c. How does the isotherm compare to the isobar in the V-L coexistence line?
You might also like
- Bach Violin Sonata Partita Barenreiter PDFDocument60 pagesBach Violin Sonata Partita Barenreiter PDFhilaryleung100% (4)
- CSTR ExampleDocument8 pagesCSTR Examplenatalia_campelo100% (2)
- Introduction To Modern Statistical Mechanics (David Chandler) PDFDocument286 pagesIntroduction To Modern Statistical Mechanics (David Chandler) PDFKeyang Sun50% (4)
- Gas TurbineDocument7 pagesGas TurbineVishal ReddyNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument263 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningAjeet Verma92% (12)
- HW3 SolutionsDocument19 pagesHW3 SolutionsmhishamnaeemNo ratings yet
- VL Solo Lark AscendingDocument6 pagesVL Solo Lark Ascendingvkaro100% (3)
- Romance in F Major, Op.50 - BeethovenDocument13 pagesRomance in F Major, Op.50 - BeethovenKeyang Sun100% (1)
- 125452033-Thermodynamics D.J.Dunn PDFDocument185 pages125452033-Thermodynamics D.J.Dunn PDFkalite123No ratings yet
- FINAL EXAMINATION ME 213 (2nd COVID EDITION)Document2 pagesFINAL EXAMINATION ME 213 (2nd COVID EDITION)Joshua S. LanzaderasNo ratings yet
- ENGRD 221 - Thermodynamics (Prof. N. Zabaras) Prelim IDocument9 pagesENGRD 221 - Thermodynamics (Prof. N. Zabaras) Prelim IMurat TülekNo ratings yet
- GL Manuscript 1276 TobalyDocument8 pagesGL Manuscript 1276 Tobalyxkeiii92xNo ratings yet
- IChO 2015 Problems and SolutionsDocument71 pagesIChO 2015 Problems and SolutionsScience Olympiad Blog100% (2)
- 47th IChO-Theoretical Problems With Solutions and Grading Schemes Final 26 07Document41 pages47th IChO-Theoretical Problems With Solutions and Grading Schemes Final 26 07George UmbrarescuNo ratings yet
- EML3100 Quiz 12 & 13 2013Document8 pagesEML3100 Quiz 12 & 13 2013Mhen1970No ratings yet
- WK 4 TR2019 - ICE TheoryDocument72 pagesWK 4 TR2019 - ICE TheoryHoàng LongNo ratings yet
- Model Answer - Heat Engine Jan 2012 - 3rd Year MechDocument7 pagesModel Answer - Heat Engine Jan 2012 - 3rd Year Mechkdm895101No ratings yet
- HW 13Document5 pagesHW 13muru0105No ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Tutorial 1 Revisi-33337566Document185 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Tutorial 1 Revisi-33337566Jim Lee LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Omestic Refrigerator: StatementDocument4 pagesOmestic Refrigerator: StatementHoracio RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pac Ihx Sur RefoidirDocument24 pagesPac Ihx Sur RefoidirfredNo ratings yet
- HW1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHW1 SolutionsRunner ScottNo ratings yet
- Thermo QualsDocument26 pagesThermo QualsLuc LeNo ratings yet
- Eth AssignmentsDocument4 pagesEth AssignmentsAyush2273No ratings yet
- Rankine ReheatDocument2 pagesRankine ReheatHany Elsawy AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- City and Guilds 9210 Level 6 Module - Unit 128 Applied ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesCity and Guilds 9210 Level 6 Module - Unit 128 Applied ThermodynamicsAlaa ShammaaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cycle BraytonDocument15 pagesBasic Cycle BraytonMarin Andreea100% (2)
- Thermodynamics PoeDocument8 pagesThermodynamics Poeg0227518cNo ratings yet
- GT ThermodynamicsDocument22 pagesGT Thermodynamicsforzama100% (1)
- Assign - Engg. ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesAssign - Engg. ThermodynamicsSagarZopeNo ratings yet
- البحث الثانيDocument15 pagesالبحث الثانيBahaa SalehNo ratings yet
- 6159b9a3-a853-4554-bf38-b5a65964ffceDocument39 pages6159b9a3-a853-4554-bf38-b5a65964ffceUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4c - First Law - Refrigerators (Updated 3 - 13 - 2013)Document6 pagesChapter 4c - First Law - Refrigerators (Updated 3 - 13 - 2013)suranjanacNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 ThermoDocument27 pagesTutorial 3 ThermoHaiqal AzizNo ratings yet
- T 9109Document9 pagesT 9109Ayush Singh BeruvarNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Steam Turbine Performance-MergedDocument26 pagesFactors Affecting Steam Turbine Performance-MergedrahulNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycles - Mech Engineering: Thermodynamics Carnot CycleDocument22 pagesGas Power Cycles - Mech Engineering: Thermodynamics Carnot CycleShihab RahmanNo ratings yet
- Thermo Prject 2-1Document20 pagesThermo Prject 2-1Syed AhmerNo ratings yet
- Group10 Cpe 1 3Document16 pagesGroup10 Cpe 1 3Joshua MistalNo ratings yet
- Aplied Thermodynamics Tutorial 1, Revision of Isentropic Efeciency Advanced Steam Cycles.Document80 pagesAplied Thermodynamics Tutorial 1, Revision of Isentropic Efeciency Advanced Steam Cycles.Moch Bagus BahtiarNo ratings yet
- System. What Will Be The First Law Equation For The Below System?Document3 pagesSystem. What Will Be The First Law Equation For The Below System?dpurnimaNo ratings yet
- EG-261 Jan 2023Document20 pagesEG-261 Jan 2023guliyeva.nilgunNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITDocument47 pagesGas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITmohan govindasamyNo ratings yet
- 3102 HT & Thermo 2014 PrimaryDocument8 pages3102 HT & Thermo 2014 PrimaryAkmal BhattiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Solutions To ExercisesDocument123 pagesDetailed Solutions To Exerciseslutfi awn100% (5)
- The GasDocument3 pagesThe GasCarl Bryan Tadle ReñosNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument13 pagesExercisesRajpriya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas and Application of Second LawDocument49 pagesIdeal Gas and Application of Second LawAbdulRehman VirkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8B - Gas Power Plant Brayton CycleDocument17 pagesChapter 8B - Gas Power Plant Brayton CycleBF3nobel100% (1)
- Mech-Engg., Thermal EngineeringDocument8 pagesMech-Engg., Thermal Engineeringnims1964No ratings yet
- ASU - Double Column ProcessDocument5 pagesASU - Double Column ProcessMH CNo ratings yet
- Zakho University Mechanical Eng. Dept. 2 Year 2018-2019 Mechanical Lab/ Refrigeration and ACDocument7 pagesZakho University Mechanical Eng. Dept. 2 Year 2018-2019 Mechanical Lab/ Refrigeration and ACNorvinyeLorlortorYekoNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument27 pagesHeat ExchangerKashish Mehta75% (4)
- IV B. TECH (Chemical Engineering) I SemesterDocument14 pagesIV B. TECH (Chemical Engineering) I SemesterPiyush AmbulgekarNo ratings yet
- All Papers of Thermodyanmics and Heat TransferDocument19 pagesAll Papers of Thermodyanmics and Heat TransfervismayluhadiyaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarFrom EverandCarbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- SBV Project ProposalDocument2 pagesSBV Project ProposalKeyang SunNo ratings yet
- Semibullvalene SynthesisDocument5 pagesSemibullvalene SynthesisKeyang SunNo ratings yet
- Jftot PDFDocument5 pagesJftot PDFKeyang SunNo ratings yet
- Antoine's ConstantsDocument109 pagesAntoine's ConstantsKeyang Sun100% (1)
- Practical Organic ChemistryDocument598 pagesPractical Organic ChemistryGerardo Estrada99% (127)
- Violin Concerto No.1 (Mozart)Document8 pagesViolin Concerto No.1 (Mozart)Keyang SunNo ratings yet
- IMSLP57480 PMLP03603 Tchaikovsky Bial Romeo and Juliet Overture FantasieDocument21 pagesIMSLP57480 PMLP03603 Tchaikovsky Bial Romeo and Juliet Overture FantasiemutiseusNo ratings yet
- Field Guide Alien Species in European Forests PDFDocument132 pagesField Guide Alien Species in European Forests PDFIonut MarianNo ratings yet
- Work Plan For School Based EqDocument2 pagesWork Plan For School Based EqFabro F. MhiseyNo ratings yet
- Etechwin BESS Datasheet en V1.0Document13 pagesEtechwin BESS Datasheet en V1.0kukos setosariNo ratings yet
- Locking Plates - Advantages & Indications 1-11Document27 pagesLocking Plates - Advantages & Indications 1-11nishantsinghbmeNo ratings yet
- G Ed Suc: Uide To The I OllegesDocument56 pagesG Ed Suc: Uide To The I OllegesZacNo ratings yet
- Extended Care Facility Emergency Response GuidelinesDocument13 pagesExtended Care Facility Emergency Response GuidelinesdavidNo ratings yet
- FERMENTATIONDocument17 pagesFERMENTATIONKrizel Ashley GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Edwards Hemodynamic Monitoring For COVID Critically Ill PatientsDocument3 pagesEdwards Hemodynamic Monitoring For COVID Critically Ill PatientsblanquishemNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin Retention in Agricultural SoilDocument10 pagesCiprofloxacin Retention in Agricultural SoilNellyNo ratings yet
- Activity Proposal Tree PlantingDocument1 pageActivity Proposal Tree PlantingJanet Floreno VillasanaNo ratings yet
- Engl5 Problem Solution EssayDocument7 pagesEngl5 Problem Solution Essayapi-511280084No ratings yet
- Ethics ChecklistDocument3 pagesEthics ChecklistRaj Karthik RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7B Cargo InsuranceDocument11 pagesLecture 7B Cargo InsurancesNo ratings yet
- Translated Into Plain English: Iso 9001 2008 Quality Management RequirementsDocument12 pagesTranslated Into Plain English: Iso 9001 2008 Quality Management RequirementsAnonymous WEOT84lNo ratings yet
- Prodotti Manuali Documento 43Document16 pagesProdotti Manuali Documento 43whorne24No ratings yet
- Introduction To Labor Economics: Chapter 2 - The Labor MarketDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Labor Economics: Chapter 2 - The Labor Marketqulb abbasNo ratings yet
- 4 Day Male FinalDocument5 pages4 Day Male FinalRedliviusNo ratings yet
- Muslim Women Protection of Rights On Divorce Act, 1986Document20 pagesMuslim Women Protection of Rights On Divorce Act, 1986Saurabh MishraNo ratings yet
- CV Manat Ryan Hard NababanDocument1 pageCV Manat Ryan Hard NababanmanatNo ratings yet
- C882 Bond Strength of Epoxy-Resin Systems Used With ConcreteDocument3 pagesC882 Bond Strength of Epoxy-Resin Systems Used With ConcreteHassan MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Donald T. Reilly 75Document16 pagesDonald T. Reilly 75Salman SolehuddinNo ratings yet
- How To Reverse Hearing Loss and TinnitusDocument24 pagesHow To Reverse Hearing Loss and TinnitusMark Sloan100% (4)
- A. Steps For Initiation of Criminal Machinery: 1. Cases in Which PCR Call Was MadeDocument4 pagesA. Steps For Initiation of Criminal Machinery: 1. Cases in Which PCR Call Was MadeAnchit Jassal100% (1)
- PDFDocument7 pagesPDFNupur SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Tape Mobil JVC.Document16 pagesTape Mobil JVC.EdisonNainggolanNo ratings yet
- Academic Answers For Practice Test 2 Listening Section 1: Answer KeysDocument7 pagesAcademic Answers For Practice Test 2 Listening Section 1: Answer KeysVinda EkabudiningsihNo ratings yet
- Nestle: Nestlé's Mission Statement (R1)Document11 pagesNestle: Nestlé's Mission Statement (R1)Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisBedecir, Schrister Hynes D.No ratings yet
- Uhde Brochures PDF en 10000032.00Document12 pagesUhde Brochures PDF en 10000032.00goodsnowman0% (1)
- Costs-Benefit Analysis For Natural Disaster Management: Methodological BackgroundDocument18 pagesCosts-Benefit Analysis For Natural Disaster Management: Methodological BackgroundLuvsansharav NaranbaatarNo ratings yet