Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inflammatory Diseases
Inflammatory Diseases
Uploaded by
Rosmary0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
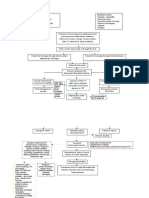
121 views2 pages1. The document describes several inflammatory diseases of the brain and meninges including bacterial meningitis, viral meningitis, brain abscesses, viral encephalitis, botulism, tetanus, diphtheria, and neurosyphilis.
2. It provides information on the causative agents, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for each disease.
3. The diseases are caused by a variety of bacteria, viruses and other pathogens which cause inflammation in the brain or meninges through different mechanisms and result in distinct clinical presentations.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document describes several inflammatory diseases of the brain and meninges including bacterial meningitis, viral meningitis, brain abscesses, viral encephalitis, botulism, tetanus, diphtheria, and neurosyphilis.
2. It provides information on the causative agents, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for each disease.
3. The diseases are caused by a variety of bacteria, viruses and other pathogens which cause inflammation in the brain or meninges through different mechanisms and result in distinct clinical presentations.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
121 views2 pagesInflammatory Diseases
Inflammatory Diseases
Uploaded by
Rosmary1. The document describes several inflammatory diseases of the brain and meninges including bacterial meningitis, viral meningitis, brain abscesses, viral encephalitis, botulism, tetanus, diphtheria, and neurosyphilis.
2. It provides information on the causative agents, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for each disease.
3. The diseases are caused by a variety of bacteria, viruses and other pathogens which cause inflammation in the brain or meninges through different mechanisms and result in distinct clinical presentations.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
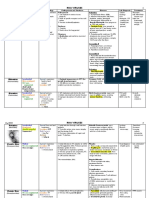
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES
BACTERIAL MENINGITIS BRAIN ABSCESS VIRAL MENINGITIS VIRAL ENCEPHALITIS
Causative agent neisseria meningitides, streptococcus streptococcus aureus, H. zoster arbovirus herpes simplex
pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae staphylococcus aureus, H. simplex
toxoplasmosis Cytomegalovirus
pathophysio 1. Inflammatory Response of 1. Microorganism causes 1. case of mumps arthropods such as mosquito and tick organism causes local
meningeal vessels to causative agent Abscess formation 2. organism spreads to infect humans and cause widespread necrotizing hemorrhage of the
2. Exudate formed by WBC 2. Which can either: brain nerve degeneration brain
3. Impaired CSF flow a. Spread 3. causes meningeal
4. increased ICP b. cause tissue necrosis irritation
5. vessels engorge and rupture and edema
S/sx Meningeal lethargy intense h/a same with meningitis same with meningitis
Irritation S/sx** drowsiness Meningeal
decreased LOC n/v Irritation S/sx**
fever increased icp -h/a
expressive aphasia(for frontal
lobe abscess)
Dx Lumbar Tap*** Lumbar Tap*** Lumbar Tap*** Lumbar Tap*** Lumbar Tap***
Gram Staining of CSF CT scan Polymerase Chain PCRT
Reaction Test(PCRT)
Ix Cephalosorins: Anticonvulsants- symptomatic tx such as Acyclovir
a. rifampin phenytoin anticonvulsants Vidarabine
b. cefotaxime Analgesics
c. vancomycin Antiemetics
Anticonvulsants: Phenytoin Antibiotics- pen G,
Corticosteroids: Dexamethasone vancomycin,
Diuretics: Mannitol metronidazole
Others:
a. acetaminophen for fever
b. codeine for h/a
others repiratory iso until (–)CSF culture is craniotomy and drainage bed rest seasonal and geographic in nature complications include
obtained (surg ix) dementia and aphasia
**S/sx of meningeal irritation: ***Normal Lumbar Tap Results Diabetes Amphotericin B
1. nuchal rigidity(stiff neck) 1. glucose-6-50 mg/dl Organ Transplant Fluconazole
2. + brudzinski’s sign- passive flexion of 2. normal CHON-15-45 mg/dl b. Types Flucytosine
neck causes flexion of legs Cryptococcus Mucormycosis
3. + kernig’s sign- leg is fully bent in the FUNGAL INFXNS Caused by Cryptococcus caused by a neurotoxin
hip and knee, and subsequent extension of a. Risk Factors: neoformans good prognosis if treated earlier
the knee is painful Leukemia fatal begins in the nasal mucosal
4. Photophobia Immunosuppresion Meds: lining
5. H/a
BOTULISM TETANUS DIPTHERIA NEUROSYPHILIS
causative agent Clostridium botulinum Clostridium tetani Corynebacterium diptheriae Treponema pallidum
pathophysio blocks AcH resulting to impaired autonomic agent inhibits transmission of reflex after direct contact or indirect contact with after onset of syphilis, disease may be
and voluntary neuromuscular arc and at the presynaptic site fomites, organism is transmitted and affects the exacerbated, spread to the meninges and
treansmission/also called food poisoning causing the diff. s/sx throat and skin, causing the diff. s/sx the rest of the CNS
and cause the diff. s/sx
s/sx ptosis, diplopia, dysarthria Trismus thick, patchy, greenish mucus membrane Argyll-robertson pupil-pin prick pupils
Incontinence fever severe h/a
Risus Sardonicus sore throat Nuchal Rigidity
Dypsnea and Dysphagia Mental confusion
Rigidity of Muscles abnormal reflexes
Opisthotonus-high arch back abnormal gait
rigidity
Pain
dx culture and sensi blood and csf culture schick test, skin test, nose and throat culture Venereal Disease Research Laboratory
Test
Lumbar Tap
CT, MRI
FTA-ABS
med ix Botulinum antitoxin Tetanus immunoglobulin Penicillin Penicillin
Tetanus Antitoxin Erythromycin
Valium
Penicillin
Vecuronium
other info or ix avoid damaged ends of canned goods quiet and dim env’t strict iso TYPES
discard suspected foods wound dressing elevate head a. asymptomatic-abnormal CSF
tracheo and mech vent oral hygiene b. meningovascular- cranial nerve
immunization-DPT palsies, damage to blood vessels
liquid and soft diet c. tabes dorsalis-loss of position sense in
tracheo set at bedside feet and legs
General Paresis
Personality changes
Affect irritability
Reflexes are hyper
Eye changes-argyll
Sensorium-delusions
Intellect
Speech
You might also like
- Patient Confidentiality Part BDocument6 pagesPatient Confidentiality Part BSojiNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology - Semifinals - Neisseria and MoraxellaDocument10 pagesBacteriology - Semifinals - Neisseria and MoraxellaUshuaia Ira Marie L. GallaronNo ratings yet
- Perception and Coordination Module ADocument3 pagesPerception and Coordination Module ARosmary100% (1)
- The 1991 CIA World Factbook by United States. Central Intelligence AgencyDocument1,324 pagesThe 1991 CIA World Factbook by United States. Central Intelligence AgencyGutenberg.org100% (1)
- Lack of Immunity To Specific Pathogens Associated With Young AgeDocument8 pagesLack of Immunity To Specific Pathogens Associated With Young AgeywykmdNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument2 pagesMeningitismyat252No ratings yet
- SepsisDocument3 pagesSepsisMaisarah RepinNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Cereus Bacteremia and Meningoen PDFDocument4 pagesBacillus Cereus Bacteremia and Meningoen PDFdr israrNo ratings yet
- Sweat Chloride Test: 1. Splenic Rupture 2. Avoid Sports and Physical Activity 3. Atypical LymphocytesDocument7 pagesSweat Chloride Test: 1. Splenic Rupture 2. Avoid Sports and Physical Activity 3. Atypical LymphocytesAnonymous GfqHQ5SNwNo ratings yet
- Enumerate The Aetiological Agents of Meningeal Involvement in ChildrenDocument21 pagesEnumerate The Aetiological Agents of Meningeal Involvement in ChildrenAbhirup BoseNo ratings yet
- Neurologic InfectionsDocument6 pagesNeurologic InfectionsHazel ZullaNo ratings yet
- Sore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaDocument19 pagesSore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaainaNo ratings yet
- Infections of The Central Nervous System Audio (Autosaved)Document72 pagesInfections of The Central Nervous System Audio (Autosaved)hnm mnhNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Nervous SystemAnaNo ratings yet
- Pathology BrainDocument4 pagesPathology BrainAshuNo ratings yet
- What Is Meningitis?Document7 pagesWhat Is Meningitis?laujeroNo ratings yet
- 5 Bacterial Infection and PathogenesisDocument31 pages5 Bacterial Infection and PathogenesisjakeyNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument40 pagesBacterial MeningitisDinesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Diseases Affecting The Central Nervous SyetemDocument32 pagesDiseases Affecting The Central Nervous SyetemJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- MICP (Autosaved) DONEDocument7 pagesMICP (Autosaved) DONEEdna ChanNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis in ChildrenDocument18 pagesTuberculosis in ChildrenEliza Mendoza MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Black Death: Our Lady of Fatima UniversityDocument7 pagesCase Study of Black Death: Our Lady of Fatima UniversityJanna PimentelNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument2 pagesMeningitisedrian02No ratings yet
- Meningite Bacteriene MPSHDocument5 pagesMeningite Bacteriene MPSHRoxana PoraicuNo ratings yet
- Supratentorial: Common Neuro Surgeries Common Drugs Administered PreopDocument4 pagesSupratentorial: Common Neuro Surgeries Common Drugs Administered PreopMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Bordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andDocument38 pagesBordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andkrstnkyslNo ratings yet
- PyomeningitisDocument54 pagesPyomeningitisRiya BagdiNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Central Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesDiseases of The Central Nervous SystemWTF192No ratings yet
- CNS Infections Aug 2022 Harsha - 2nd DraftDocument106 pagesCNS Infections Aug 2022 Harsha - 2nd Draftharsha sinhaNo ratings yet
- Meningitis: EtiologyDocument4 pagesMeningitis: EtiologyAbdalrahman AhmedNo ratings yet
- تَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٢?Document14 pagesتَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٢?سلطان محمد فوزي سلمانNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: InflammatoryDocument6 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: InflammatoryAlyssa BatasNo ratings yet
- CNS Sepsis: PathologyDocument2 pagesCNS Sepsis: Pathologyyoyo06chillinNo ratings yet
- DR Bambang EnsefalitisDocument46 pagesDR Bambang EnsefalitisSemestaNo ratings yet
- Rna Viruses: EnterovirusDocument4 pagesRna Viruses: EnterovirusYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Bacterial Infections Cheat Sheet: by ViaJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- X0xheather - Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections PDFDocument5 pagesX0xheather - Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections PDFAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Meningitis 2Document10 pagesCase Presentation Meningitis 2Nizar IJNo ratings yet
- TuberkulosisanakDocument106 pagesTuberkulosisanakUdin NicotinicNo ratings yet
- Corynebacterium DiphtheriaDocument5 pagesCorynebacterium Diphtheriacccarrot.carrot3No ratings yet
- Management of Client With Infectious DiseasesDocument12 pagesManagement of Client With Infectious DiseasesHazel ZullaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases Pharmacotherapy: Lesson 5 Central Nervous System InfectionDocument63 pagesInfectious Diseases Pharmacotherapy: Lesson 5 Central Nervous System Infectionbest batiNo ratings yet
- LP After Correct.Document32 pagesLP After Correct.Academic Nurse. M.M AbbasNo ratings yet
- Problem 3.01 Nervous System Study Guide 3Document2 pagesProblem 3.01 Nervous System Study Guide 3Monish NaiduNo ratings yet
- I. Definition: Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument6 pagesI. Definition: Pulmonary Tuberculosisjulie-pearl-6329No ratings yet
- (Neuro) 016 Cns-InfectionDocument18 pages(Neuro) 016 Cns-Infection3BBEGILJUDY ANNBNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument34 pagesChapter IINycoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: or Generalized Patchy InfiltrateDocument3 pagesPneumonia: or Generalized Patchy InfiltrateizyanzatiNo ratings yet
- Po TTDocument3 pagesPo TTmecz26No ratings yet
- NBDE Part 1 Diseases / Clinical Correlates: Study Online atDocument19 pagesNBDE Part 1 Diseases / Clinical Correlates: Study Online atSchat ZiNo ratings yet
- PATHO Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesPATHO Infectious DiseasesamheartsssNo ratings yet
- Herpes Zoster-Predicting and Minimizing The Impact of Post-Herpetic NeuralgiaDocument8 pagesHerpes Zoster-Predicting and Minimizing The Impact of Post-Herpetic NeuralgiaDevi DamayantiNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY ShortDocument4 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY ShortBSN 2 - Sasis, Rusmaryte C.No ratings yet
- MRCPCH q15Document30 pagesMRCPCH q15Galaleldin AliNo ratings yet
- 13.bacterial MeningitisDocument23 pages13.bacterial Meningitisrayyanalmaskri20No ratings yet
- ENT Summery TABLEDocument19 pagesENT Summery TABLEtaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- 2018 COMPARATIVE MICRO MeningoencephalitisDocument6 pages2018 COMPARATIVE MICRO MeningoencephalitisMarianneTee-ruhNo ratings yet
- Clinpharm Notes 4 TopicsDocument8 pagesClinpharm Notes 4 TopicsALESANDRA DAWN PAYOTNo ratings yet
- Diphteria, Pertussis and Staphylococcal Infections-1Document15 pagesDiphteria, Pertussis and Staphylococcal Infections-1Nwosu Ogbonna GabrielNo ratings yet
- Most Often in Children Younger Than 24 Months of Age: Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesMost Often in Children Younger Than 24 Months of Age: Bacterial MeningitisLalisaM ActivityNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of The Central Nervous System InfectionDocument44 pagesPathogenesis of The Central Nervous System InfectionMira ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesFrom EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesNo ratings yet
- JURIS2Document1 pageJURIS2RosmaryNo ratings yet
- Normal Laboratory ValuesDocument2 pagesNormal Laboratory ValuesRosmary0% (1)
- English (Sequence)Document1 pageEnglish (Sequence)RosmaryNo ratings yet
- Vascular Disturbances (Module C) Cerebrovascular Accident (Cva)Document3 pagesVascular Disturbances (Module C) Cerebrovascular Accident (Cva)RosmaryNo ratings yet
- Discharge Care and RehabilitationDocument1 pageDischarge Care and RehabilitationRosmaryNo ratings yet
- Demyelinating DiseasesDocument2 pagesDemyelinating DiseasesRosmaryNo ratings yet
- Pol Sci/word 1997 DocumentDocument13 pagesPol Sci/word 1997 DocumentRosmaryNo ratings yet
- SALES TRHD 2.odsDocument6 pagesSALES TRHD 2.odsHanddawinartoNo ratings yet
- Lista Precios y Bonifaciones 16-2-2024Document2 pagesLista Precios y Bonifaciones 16-2-2024bfarma002No ratings yet
- Pharmacy Operations: Licensure, Registration and CertifiacationsDocument5 pagesPharmacy Operations: Licensure, Registration and CertifiacationsHitomi Shiroshita100% (1)
- Monograph MetronidazoleDocument4 pagesMonograph MetronidazoleAli MehdiNo ratings yet
- GavisconDocument8 pagesGavisconletisha mamaNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument8 pagesDrugAlyzza DagoyNo ratings yet
- Ivivc JurnalDocument7 pagesIvivc Jurnal4Salma Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- Trial Title: Protocol NumberDocument22 pagesTrial Title: Protocol NumberMilan StojanovićNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocument5 pagesIncreased Intracranial PressureLorelyn Santos CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Pain Management: Section I: Assessing Your UnderstandingDocument14 pagesPain Management: Section I: Assessing Your UnderstandingkeyonaNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Giants Iwal 1 2020Document58 pagesGeriatric Giants Iwal 1 2020selymariaNo ratings yet
- Dysmenorrhea Study FitokiDocument168 pagesDysmenorrhea Study FitokiCarlos FndNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonists and BlockersDocument1 pageAdrenergic Agonists and BlockersMichelle Morgan LongstrethNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan (Larith)Document65 pagesMarketing Plan (Larith)aamirNo ratings yet
- SatadhoutaghritamDocument5 pagesSatadhoutaghritamPrabha VetrichelvanNo ratings yet
- MRCP (UK) and MRCP (I) Part II 200 Cases Case Histories, Data Interpretation, & Photographic MaterialsDocument15 pagesMRCP (UK) and MRCP (I) Part II 200 Cases Case Histories, Data Interpretation, & Photographic MaterialsOsama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCPNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy With EpilepsyDocument40 pagesPregnancy With EpilepsyNaman MishraNo ratings yet
- BQ Gas MedisDocument2 pagesBQ Gas MedisSugino Osaka100% (1)
- Medicine 018 Final PDFDocument22 pagesMedicine 018 Final PDFdrkefyalewtayeNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet: BiologicsDocument4 pagesFact Sheet: BiologicsAldiarsoNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Bromage Score in Post-Spinal Anesthesia PatientsDocument5 pagesFactors Influencing Bromage Score in Post-Spinal Anesthesia PatientsbisyriNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument1 pagePharmacologyAcademic ServicesNo ratings yet
- A Clinician's Guide To Topical Retinoids: Melika Motamedi, Ahmad Chehade, Ravina Sanghera, and Parbeer GrewalDocument8 pagesA Clinician's Guide To Topical Retinoids: Melika Motamedi, Ahmad Chehade, Ravina Sanghera, and Parbeer Grewalzendah123No ratings yet
- Mit Erfolg Zu Telc Deutsch B2 Übungsbuch PDF - DRDocument11 pagesMit Erfolg Zu Telc Deutsch B2 Übungsbuch PDF - DRIvan MNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfractionDocument16 pagesMyocardial InfractionYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Ans (TUSOM Pharmwiki)Document1 pageIntroduction To The Ans (TUSOM Pharmwiki)Dorina98No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - ParacetamolDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY - ParacetamolKristine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Kegel Exercise Dan Root MasturbationDocument6 pagesKegel Exercise Dan Root MasturbationAnita LufiantiNo ratings yet