Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk Factors: Stroke Prevention
Risk Factors: Stroke Prevention
Uploaded by
PanduRespatiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk Factors: Stroke Prevention
Risk Factors: Stroke Prevention
Uploaded by
PanduRespatiCopyright:
Available Formats
Stroke Prevention
The good news is that 80 percent of all strokes are preventable. It starts with managing key risk factors,
including high blood pressure, cigarette smoking, atrial fibrillation and physical inactivity. More than half
of all strokes are caused by uncontrolled hypertension or high blood pressure, making it the most
important risk factor to control.
Medical treatments may be used to control high blood pressure and/or manage atrial fibrillation among
high-risk patients. Those medicines include:
Anticoagulants/Antiplatelets
Antiplatelet agents such as aspirin and anticoagulants, such as warfarin, interfere with the
blood's ability to clot and can play an important role in preventing stroke. Read more about
anticoagulants.
Antihypertensives
Antihypertensives are medications that treat high blood pressure. Depending on the type of
medication, they can lower blood pressure by opening the blood vessels, decreasing blood
volume or decreasing the rate and/or force of heart contraction. Learn about the types of
antihypertensives.
Additionally, when arteries show plaque buildup or blockage, medical procedures may be needed. Such
as:
Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy, also called carotid artery surgery, is a procedure in which blood vessel
blockage (fatty plaque) is surgically removed from the carotid artery.
View a detailed
illustration of carotid
endarterectomy (opens
in new window).
Angioplasty/Stents
Doctors sometimes use
balloon angioplasty
and implantable steel
screens called stents to
treat cardiovascular
disease and help open
up the blocked blood
vessel.
When a Stroke Occurs: Quick
Stroke Treatment Can Save
Lives
If youre having a stroke, its critical that you get medical attention right away. Immediate treatment may
minimize the long-term effects of a stroke and prevent death.
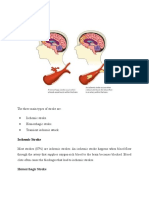
There are two types of strokes: hemorrhagic or ischemic. An ischemic stroke occurs as a result of an
obstruction within a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain. It accounts for 87 percent of all stroke
cases. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures and spills blood into brain
tissue. The most common cause for the rupture is uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure).
There are two other types of weakened blood vessels that also cause hemorrhagic stroke: aneurysms
and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). Treatment differs depending on the type of stroke.
Ischemic Stroke Treatment
tPA, the Gold Standard
The only FDA approved treatment for ischemic strokes is tissue plasminogen activator (tPA, also known
as IV rtPA, given through an IV in the arm). tPA works by dissolving the clot and improving blood flow to
the part of the brain being deprived of blood flow. If administered within 3 hours(and up to 4.5 hours in
certain eligible patients), tPA may improve the chances of recovering from a stroke. A significant number
of stroke victims dont get to the hospital in time for tPA treatment; this is why its so important to identify
a stroke immediately.
You might also like
- Medication Template PrednisoneDocument5 pagesMedication Template PrednisoneJudith MeranvilNo ratings yet
- Lefort 1 OsteotomyDocument36 pagesLefort 1 OsteotomyNidhi Jayan100% (2)
- Ischemic Stroke: Let's Talk AboutDocument2 pagesIschemic Stroke: Let's Talk AboutMarhaban WienNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Disease (Emphasis On CVA)Document29 pagesCerebrovascular Disease (Emphasis On CVA)OlynsieMorrisNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument38 pagesStrokekiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- Ucm 309725Document2 pagesUcm 309725haryatikennitaNo ratings yet
- Causes Symptoms Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument10 pagesCauses Symptoms Diagnosis and TreatmentcellinectnNo ratings yet
- DR NzooloDocument21 pagesDR NzooloJohn chrisant Mwansa the future presdoNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack Risk Factors: Non-Coronary Artery Disease Causes of Heart Attack May Also Occur, These IncludeDocument12 pagesHeart Attack Risk Factors: Non-Coronary Artery Disease Causes of Heart Attack May Also Occur, These IncludeHazwan AkmalNo ratings yet
- The Diabetes and The BrainDocument26 pagesThe Diabetes and The BrainPrecious SantayanaNo ratings yet
- Types of StrokeDocument12 pagesTypes of Strokefakher adnanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway of Acute Stroke: Renz Darwin C. CastañadayDocument32 pagesClinical Pathway of Acute Stroke: Renz Darwin C. CastañadayRenz CastañadayNo ratings yet
- Mi DrugsDocument5 pagesMi DrugsKing Nehpets AlczNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Chapter-IDocument34 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Chapter-IKausal VermaNo ratings yet
- Stroke PreventionDocument7 pagesStroke Preventionellla 38No ratings yet
- DynaMed Plus - Stroke (Acute Management)Document126 pagesDynaMed Plus - Stroke (Acute Management)Sarah Shafa MarwadhaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical System of The HeartDocument4 pagesElectrical System of The HeartEldhaNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument11 pagesStrokemakioedesemiNo ratings yet
- Stroke Syndrome - BenyDocument22 pagesStroke Syndrome - BenyyericosabathinoNo ratings yet
- Management of StrokeDocument24 pagesManagement of StrokeEngel TuranganNo ratings yet
- Reference Summary: X-Plain™ ArrhythmiaDocument4 pagesReference Summary: X-Plain™ ArrhythmiazipzipzipNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument7 pagesStrokeD/Badr Saleh Al jabryNo ratings yet
- About StrokeDocument1 pageAbout StrokeZarida ArabainNo ratings yet
- Pubmed Health: Ventricular TachycardiaDocument8 pagesPubmed Health: Ventricular Tachycardiaphysio_shaheenNo ratings yet
- Treatment: Stroke UnitDocument6 pagesTreatment: Stroke Unitgraze_hinataNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrilationDocument6 pagesAtrial FibrilationMarieNo ratings yet
- Carotid Artery Disease FlyerDocument2 pagesCarotid Artery Disease Flyerdinh son myNo ratings yet
- Stroke CVA Cerebrovascular Accident MedlinePlusDocument10 pagesStroke CVA Cerebrovascular Accident MedlinePlussiska dwiNo ratings yet
- What Is StrokeDocument6 pagesWhat Is StrokeY. Beatrice AbigailNo ratings yet
- Stroke - FAST, Symptoms, Causes, Types, Treatment, PreventionDocument20 pagesStroke - FAST, Symptoms, Causes, Types, Treatment, PreventionMustafa AL ShlashNo ratings yet
- Clinical Exposure Vi Assignment: Faculty of Medicine Universitas Pelita HarapanDocument16 pagesClinical Exposure Vi Assignment: Faculty of Medicine Universitas Pelita HarapanSteven MatualiNo ratings yet
- A Stroke RecoveryDocument2 pagesA Stroke Recoverymanjukumard2007No ratings yet
- Arterial ThrombosisDocument4 pagesArterial ThrombosisFaraida Jilzani ArsadNo ratings yet
- Transient Ischemic AttackDocument7 pagesTransient Ischemic AttackJennifer DimapilisNo ratings yet
- Symptoms: Heart Failure Blood Clots AneurysmDocument7 pagesSymptoms: Heart Failure Blood Clots Aneurysmjohn mendozaNo ratings yet
- Intracerebral HemorrhageDocument5 pagesIntracerebral HemorrhageyulitawijayaNo ratings yet
- Treatment For AisDocument3 pagesTreatment For AisXentur XenNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Stroke GuideDocument12 pagesIschaemic Stroke Guidefatii.seedNo ratings yet
- Stroke 15.1Document27 pagesStroke 15.1Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- What Is A StrokeDocument10 pagesWhat Is A StrokeRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Lacunar Stroke Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesLacunar Stroke Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsRismanto TorsioNo ratings yet
- What Is A Heart AttackDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Heart AttackAlia MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Merck Manual Consumer VersionDocument3 pagesIntracerebral Hemorrhage: Merck Manual Consumer VersionAlamul HudaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Jumarang, Kim Enrico M. BSN401 STI - Global CityDocument6 pagesHypertension: Jumarang, Kim Enrico M. BSN401 STI - Global CityKim Enrico JumarangNo ratings yet
- Hypertension & Stroke: Prepared By: Sharinah Ainee S. Pasandalan BSN-III, Group 4Document56 pagesHypertension & Stroke: Prepared By: Sharinah Ainee S. Pasandalan BSN-III, Group 4Sharinah Ainee Sabalburo PasandalanNo ratings yet
- TiaDocument2 pagesTiaapi-114739487100% (1)
- Pharmacologic Treatment For Cardiac Failure: ACE InhibitorsDocument36 pagesPharmacologic Treatment For Cardiac Failure: ACE InhibitorsGleden UmayamNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Disorders: PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular Disorders: PathophysiologyMhae De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar StrokeDocument17 pagesCerebellar StrokeAna CotomanNo ratings yet
- STROKEDocument3 pagesSTROKEAddy IletoNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of Ischemic Strokes Is Widely Known. Ischemic Strokes Are TheDocument7 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Ischemic Strokes Is Widely Known. Ischemic Strokes Are Theprnczb13No ratings yet
- Dent Clin N Am 50 (2006) 625-633Document9 pagesDent Clin N Am 50 (2006) 625-633lalajanNo ratings yet
- DepressionDocument9 pagesDepressionelrasymorsyNo ratings yet
- 3 StrokeDocument2 pages3 Strokebendot29No ratings yet
- Arrhythmia (Irregular Heartbeats) Symptoms, Types, and TreatmentDocument5 pagesArrhythmia (Irregular Heartbeats) Symptoms, Types, and TreatmentCyberMeow100% (1)
- Arrhythmias - : Normal HeartbeatDocument4 pagesArrhythmias - : Normal HeartbeatToni Baskoro KristantoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrhythmiaDocument1 pageCardiac DysrhythmiainfectionmanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY PROJECT (Class 12)Document21 pagesBIOLOGY PROJECT (Class 12)Manoghna MaheshNo ratings yet
- Carotid Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Tests, and TreatmentDocument6 pagesCarotid Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Tests, and TreatmentVijay Baskar SNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument4 pagesStrokeKabirNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: Aphasia Hemiparesis Paresthesia Consciousness Paralysis TongueDocument14 pagesSigns and Symptoms: Aphasia Hemiparesis Paresthesia Consciousness Paralysis TonguenangkilNo ratings yet
- The High Blood Pressure Diet Natural Foods that will Lower your Blood Pressure within Weeks!From EverandThe High Blood Pressure Diet Natural Foods that will Lower your Blood Pressure within Weeks!No ratings yet
- Jadwal Jaga Oktober 2016 REV 3Document1 pageJadwal Jaga Oktober 2016 REV 3PanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- Sol IntracranialDocument76 pagesSol IntracranialPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- FDC TBDocument24 pagesFDC TBPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- DMD PosterDocument2 pagesDMD PosterPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- Text Book Reading: Hipoxic Ischaemic EncephalopatyDocument23 pagesText Book Reading: Hipoxic Ischaemic EncephalopatyPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- Ilmiah Cme-Pir 2015 XviiDocument22 pagesIlmiah Cme-Pir 2015 XviiPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- ADHD Screening in AdultsDocument3 pagesADHD Screening in AdultsPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- Neurological Channelopathies: ReviewDocument14 pagesNeurological Channelopathies: ReviewPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Research ArticleDocument2 pagesPediatric Research Articleapi-653708698No ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Sultan Chaudhry Benny Dua Eric WongDocument7 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Sultan Chaudhry Benny Dua Eric Wongjamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- WHO 2009 Dengue ClassificationDocument31 pagesWHO 2009 Dengue ClassificationGarata DwiNo ratings yet
- Sle in PregnancyDocument19 pagesSle in PregnancyShravyaNo ratings yet
- Treating Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring: Assessment of An Anterior Mandibular Positioning DeviceDocument7 pagesTreating Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring: Assessment of An Anterior Mandibular Positioning Device陈延珑No ratings yet
- Pre-Icar-Self Assessment Test - 2021: by DR Hanuman Mvsc-Scholar-Vsr - GadvasuDocument121 pagesPre-Icar-Self Assessment Test - 2021: by DR Hanuman Mvsc-Scholar-Vsr - Gadvasusuresh nepaliNo ratings yet
- MCQ ParasitologyDocument11 pagesMCQ ParasitologyNida Ridzuan100% (1)
- Paper:Musculoskeletal Physical Therapy Batch 8 Semester 7: C. SubscapularisDocument6 pagesPaper:Musculoskeletal Physical Therapy Batch 8 Semester 7: C. SubscapularisAHMAD AliNo ratings yet
- Heat Tolerance Test PDFDocument7 pagesHeat Tolerance Test PDFMonica LapusNo ratings yet
- By Pajanustan, Ben David B.Document27 pagesBy Pajanustan, Ben David B.Ben DavidNo ratings yet
- Etiologies and Medical AspectsDocument2 pagesEtiologies and Medical AspectsAnastasia Lincoln GreyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and COPD - Dietary Considerations For Better BreathingDocument3 pagesNutrition and COPD - Dietary Considerations For Better BreathingReina NoviaNo ratings yet
- Aspectos Importantes de La Nutrición en Niños Con CáncerDocument11 pagesAspectos Importantes de La Nutrición en Niños Con CáncerNadia DonosoNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 2023 AIAPGETDocument20 pagesQuestion Paper 2023 AIAPGETrohinibrajole123No ratings yet
- Types of Food ContaminationDocument13 pagesTypes of Food ContaminationHelena MbangoNo ratings yet
- Script For PPT PresentationDocument4 pagesScript For PPT PresentationJanine Airah MorgadoNo ratings yet
- Satellite Images Baidu COVID19 Manuscript PreprintDocument10 pagesSatellite Images Baidu COVID19 Manuscript PreprintEconomy 365No ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Alterations of Cardiovascular Function in Children - Nursing Test BanksDocument19 pagesChapter 24 - Alterations of Cardiovascular Function in Children - Nursing Test BanksNeLNo ratings yet
- Physiology of DiabetesDocument52 pagesPhysiology of DiabetesPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- Rainbow pattern-EADV2016 Poster PDFDocument1 pageRainbow pattern-EADV2016 Poster PDFlpozohNo ratings yet
- Learners' Activity Sheets: Health 8Document10 pagesLearners' Activity Sheets: Health 8Leode Joy TulangNo ratings yet
- Uterine FibroidDocument3 pagesUterine FibroiddebasishroutNo ratings yet
- What Is Hypovolemic ShockDocument4 pagesWhat Is Hypovolemic ShockDukittyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Model MCQDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Model MCQPrince Xavier100% (1)
- Drug Study - Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study - Calcium GluconatemikErlhNo ratings yet
- C Section Consent Cesarean-Section-EngDocument2 pagesC Section Consent Cesarean-Section-Engisamail khanNo ratings yet
- Index Disability NeckDocument9 pagesIndex Disability NeckCarolina Bejarano GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic PathologyDocument9 pagesHemodynamic PathologyjoeNo ratings yet