Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energetics MCQ
Energetics MCQ
Uploaded by
Ng Swee Loong StevenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : VSEPR TheoryDocument17 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : VSEPR TheoryRavindar Purohit100% (1)
- Practical Organic Chemistry III ExamDocument3 pagesPractical Organic Chemistry III ExamTesfahun100% (1)
- Acids Bases Salts MCQsDocument18 pagesAcids Bases Salts MCQsSoniaAlexNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 20 - Coordination Compounds Nomenclature WorksheetDocument2 pagesWorksheet 20 - Coordination Compounds Nomenclature WorksheetKarmendra100% (1)
- Mechanism Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesMechanism Multiple Choice QuestionsAnonymous pgjIAZoNo ratings yet
- Mole Supplemental WorksheetDocument2 pagesMole Supplemental WorksheetNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Diesel Injection Pump COVEC-FDocument36 pagesDiesel Injection Pump COVEC-FPorras Edwin71% (7)
- Coal Mill SafetyDocument17 pagesCoal Mill SafetyJoko Dewoto100% (4)
- Topic 9 19 MC PracticeDocument18 pagesTopic 9 19 MC PracticeDharmesh Ramnarayan Yadav100% (1)
- Atomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersMalak AlqaidoomNo ratings yet
- Chem MCQ FinalDocument258 pagesChem MCQ FinalDare DevilNo ratings yet
- Redox MCQsDocument7 pagesRedox MCQsHarsh Walavalkar100% (1)
- Unit 11 MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 11 MCQJay VermaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemistry MCQDocument69 pagesIndustrial Chemistry MCQSatvik BeheraNo ratings yet
- G 11&12 Chemistry (2000-2011)Document50 pagesG 11&12 Chemistry (2000-2011)Samuel Legissa100% (4)
- Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure QuestionsDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding & Molecular Structure QuestionssingamroopaNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeyDocument3 pagesAlkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeySameer HussainNo ratings yet
- Test - D18 Dec 2022Document9 pagesTest - D18 Dec 2022PrinceNo ratings yet
- Class-XII (Chemistry) Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Objective Type QuestionsDocument9 pagesClass-XII (Chemistry) Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Objective Type QuestionsPranav DhimanNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument17 pagesElectrochemistryzohaibsalamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 10 Multiple-Choice Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Alkanes MCQDocument2 pagesAlkanes MCQJeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- MCQs pdf-1 PDFDocument5 pagesMCQs pdf-1 PDFEmman Ann100% (3)
- MCQ Structure of AtomDocument15 pagesMCQ Structure of AtomSasuke Itachi100% (1)
- Periodic Classification Revision QuestionsDocument6 pagesPeriodic Classification Revision QuestionsSumiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQs HandoutsDocument26 pagesChemistry MCQs HandoutsOsama Hasan91% (11)
- Chemistry Ch-1 Part IDocument5 pagesChemistry Ch-1 Part IDr. Abdul Haq BalochNo ratings yet
- Chemistry McqsDocument51 pagesChemistry McqsEngr Muhammad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1Document195 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1aditya kumar Agarwal100% (1)
- Mcqs Chapter No1 Basic Concepts McqsDocument6 pagesMcqs Chapter No1 Basic Concepts McqsHaider JalalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium MCQDocument13 pagesChemical Equilibrium MCQNidhi SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument29 pagesAldehydes and KetonesJiya singhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocument57 pagesChemistry Hydrogen and Its CompoundsYogesh Dongre100% (2)
- 10 Chapter Electrochemistry Short Question With Answers PDFDocument11 pages10 Chapter Electrochemistry Short Question With Answers PDFMARITIM GEOFFREY KIPLANGATNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds (Exercise+Answers)Document32 pagesCoordination Compounds (Exercise+Answers)Hanukkah100% (1)
- CM - TNJN HGVDocument4 pagesCM - TNJN HGV何小霞No ratings yet
- 8 CHAPTER CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQs PDFDocument6 pages8 CHAPTER CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQs PDFAmina Khan100% (3)
- Experimental Chemistry MCQs QuizDocument5 pagesExperimental Chemistry MCQs QuizIram TahiraNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases 8.1 and 8.2 MCQDocument4 pagesAcids and Bases 8.1 and 8.2 MCQAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Stoichiometry Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesCH 3 Stoichiometry Multiple ChoiceSusie Zhang100% (1)
- 0optical Isomerism - QuizDocument3 pages0optical Isomerism - QuizSanjay Mani Tripathi50% (2)
- CH 14Document28 pagesCH 14ffffffff dfdfdfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseAri Adiantari100% (1)
- Extraction of Metals (Multiple Choice) QPDocument9 pagesExtraction of Metals (Multiple Choice) QPAnsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis MCQDocument11 pagesElectrolysis MCQSavarinathan Maria Rayappan100% (1)
- Sicmyb - DPP Mole ConceptDocument6 pagesSicmyb - DPP Mole ConceptBorn to fightNo ratings yet
- IIT-JAM 2006 With Solution PDFDocument24 pagesIIT-JAM 2006 With Solution PDFgaurav100% (1)
- Exercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsDocument7 pagesExercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsNavita RajgariaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Transition Metals QuestionsDocument6 pagesChemistry Transition Metals Questionspersonpeople100% (1)
- Unit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument25 pagesUnit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsSAMBASIVA RAO YEMINENINo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Mcqs QuestionsDocument9 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Mcqs QuestionsGyanendra Vikram Maurya100% (1)
- Chapter 10. Sulphuric Acid: Short QuestionsDocument14 pagesChapter 10. Sulphuric Acid: Short QuestionsAbhay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes - MCQDocument9 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes - MCQMinuteBrain LearningNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKMahrishiShukla100% (1)
- Amines MCQDocument3 pagesAmines MCQaleena'No ratings yet
- MCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Document7 pagesMCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Sanjeev Chaudhary100% (1)
- 9.coordination Compounds KCET PYQsDocument2 pages9.coordination Compounds KCET PYQsPunith kumar100% (1)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry MCQs PDFDocument33 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry MCQs PDFSanjana Sanjay100% (1)
- Kinetics McqsDocument31 pagesKinetics McqsTayyaba SadaqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions CH 18 Samplepractice Exam Questions and AnswersDocument20 pagesChemistry Chemical Reactions CH 18 Samplepractice Exam Questions and Answersdao hoangNo ratings yet
- 2 Quizizz 2019 ptVIIIe DocDocument10 pages2 Quizizz 2019 ptVIIIe DocKM Tsang Ka ManNo ratings yet
- General Chemsitry 1 Course Test 2 2013Document6 pagesGeneral Chemsitry 1 Course Test 2 2013John BrownNo ratings yet
- Mole JokesDocument1 pageMole JokesNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Chemical ChangesDocument5 pagesChemical ChangesNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table SQ AnsDocument20 pagesPeriodic Table SQ AnsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Kinetics MCQDocument57 pagesKinetics MCQNg Swee Loong Steven100% (2)
- Periodic Table SQDocument17 pagesPeriodic Table SQNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Balanced EquationsDocument29 pagesBalanced EquationsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Mole GamesDocument3 pagesMole GamesNg Swee Loong Steven100% (1)
- Mole Project ChecklistDocument1 pageMole Project ChecklistNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Mole Internet ActivityDocument1 pageMole Internet ActivityNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice AnswersDocument16 pagesMultiple Choice AnswersholdonpainendsNo ratings yet
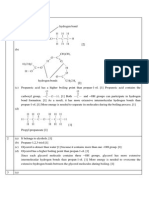
- Industrial Chemistry MCQDocument69 pagesIndustrial Chemistry MCQNg Swee Loong Steven93% (15)
- Structured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part X Chemical EquilibriumDocument26 pagesStructured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part X Chemical EquilibriumNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds SQ AnsDocument51 pagesCarbon Compounds SQ AnsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Structured Question AnswersDocument33 pagesStructured Question AnswersNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Structured Questions AnswersDocument23 pagesStructured Questions AnswersNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- MCQ CeDocument64 pagesMCQ CePankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Structured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part VIII Chemical Reactions and EnergyDocument21 pagesStructured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part VIII Chemical Reactions and EnergyNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds MCQ AnsDocument30 pagesCarbon Compounds MCQ AnsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry MCQ AnsDocument7 pagesAnalytical Chemistry MCQ AnsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry AnswerDocument41 pagesAnalytical Chemistry AnswerNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- ChemistryQB Topic8a MC eDocument57 pagesChemistryQB Topic8a MC eNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- ChemistryQB Topic8a MC eDocument57 pagesChemistryQB Topic8a MC eNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- ChemistryQB Topic8c SQ eDocument27 pagesChemistryQB Topic8c SQ eNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Discharge Ignition of Energetic MaterialsDocument9 pagesElectrostatic Discharge Ignition of Energetic Materialspamos1111No ratings yet
- Form I: Mylan Laboratories Limited, Unit 3Document75 pagesForm I: Mylan Laboratories Limited, Unit 3jyothiNo ratings yet
- Ramadan Youssef Sakr Moustafa - Lecture 2-Chemical ReactionDocument49 pagesRamadan Youssef Sakr Moustafa - Lecture 2-Chemical ReactionAhmed GadNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet No.1Document1 pageProblem Sheet No.1Imran TahirNo ratings yet
- 2.5. Industrial Pollutants - 1102: Dilution PollutionDocument5 pages2.5. Industrial Pollutants - 1102: Dilution PollutionHina AftabNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation & ControlDocument56 pagesBoiler Operation & ControlMohammad Rawoof100% (2)
- Bcu370 Burner Control - Brochure PDFDocument6 pagesBcu370 Burner Control - Brochure PDFFernando QueirozNo ratings yet
- Normas Astm para Carbones Y Coques: Standard Terminology ofDocument14 pagesNormas Astm para Carbones Y Coques: Standard Terminology ofJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- Dr.M.P.Bhatti Sehar Afzal 1009-BH-CHEM-16: Government College University LahoreDocument7 pagesDr.M.P.Bhatti Sehar Afzal 1009-BH-CHEM-16: Government College University LahoreAayat MughalNo ratings yet
- Kinglake 90 116Document14 pagesKinglake 90 116robertaNo ratings yet
- Pns-Paes 246-2010 PDFDocument13 pagesPns-Paes 246-2010 PDFJoselito TucitNo ratings yet
- Lower (LEL) & Upper (UEL) Explosive Limits PDFDocument1 pageLower (LEL) & Upper (UEL) Explosive Limits PDFSale RadosavljevicNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Narayana Group of SchoolsDocument13 pagesInstructions:: Narayana Group of SchoolsAryaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0263876222004075 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0263876222004075 MainNUR IRYANIE BINTI AMIRUDDIN -No ratings yet
- Praesentation TBU - Fluidised Bed Combustion - EN PDFDocument32 pagesPraesentation TBU - Fluidised Bed Combustion - EN PDFjamjam1062No ratings yet
- Msds HNO3Document6 pagesMsds HNO3Ariesa Nurruhiyatna Al-adzaniNo ratings yet
- Service and Repair Manual: Coolant Heaters DBW 2010 DBW 2020 DBW 300Document84 pagesService and Repair Manual: Coolant Heaters DBW 2010 DBW 2020 DBW 300MiguelNo ratings yet
- MCQ IcgtDocument28 pagesMCQ IcgtSunny BhatiaNo ratings yet
- FIRE TECHNOLOGY AND ARSON INVESTIGATION QUESTIONS For CBRC NAGADocument10 pagesFIRE TECHNOLOGY AND ARSON INVESTIGATION QUESTIONS For CBRC NAGAJason CaballaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0360319922016998 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S0360319922016998 MainCarlos Herrique MatioloNo ratings yet
- Inert Gas SystemDocument69 pagesInert Gas SystemKishore Gopal89% (9)
- 4 in 1 Portable SmokehouseDocument5 pages4 in 1 Portable SmokehouseLeilani Delgado MoselinaNo ratings yet
- Answer 08 - Ithink - Soalan-B7Document3 pagesAnswer 08 - Ithink - Soalan-B7SUDARCHELVI A/P ALAGANDRAN Moe0% (1)
- Me 303 CH12Document47 pagesMe 303 CH12Osman KutluNo ratings yet
- Fire Emergency Preparedness SeminarDocument65 pagesFire Emergency Preparedness SeminarTAURUS EMS100% (1)
- Automobile Lesson Plan 2016 2017Document26 pagesAutomobile Lesson Plan 2016 2017Kiran ChristopherNo ratings yet
- CPV St. Charles Revised PSD - 082411Document363 pagesCPV St. Charles Revised PSD - 082411hermieNo ratings yet
- Combustion Modeling of Dual-Fuel Engines - 2Document2 pagesCombustion Modeling of Dual-Fuel Engines - 2helenNo ratings yet
Energetics MCQ
Energetics MCQ
Uploaded by
Ng Swee Loong StevenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energetics MCQ
Energetics MCQ
Uploaded by
Ng Swee Loong StevenCopyright:
Available Formats
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
Multiple Choice Questions
Section 35.1
1. Which of the following statements concerning energy is correct?
A. According to the Law of Conservation of Energy, energy can either be created or
destroyed.
B. The enthalpy of a substance can be measured directly using appropriate
apparatus.
C. If a chemical reaction is carried out at constant pressure, the heat change
measured is called the change in internal energy of the reaction.
D. The total amount of energy remains constant.
2.
A reaction between magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid is carried out in a
stoppered flask. The heat change is found to be 433.8 kJ. If the same reaction is
carried out again without the stopper, what would be the enthalpy change?
A. Below 433.8 kJ, as there is energy lost to the surroundings.
B. Same as 433.8 kJ, as the difference in work done between two cases is
negligible.
C. Above 433.8 kJ, as the latter case does not have work done against the wall of
flask.
D. Same as 433.8 kJ, as the enthalpy change is independent of volume or pressure
of flask.
3.
The change in internal energy and enthalpy change of a reaction involving gases in an
open system are 156.0 kJ and 130.0 kJ respectively. Why is there a difference
between the two values?
A. The products of the reaction absorb energy to form the bonds.
B. The reactants of the reaction absorb energy to break the bonds.
C. There is work done on the surroundings by the reaction.
D. The calculation must be wrong as the total energy should remain the same
before and after the reaction, as stated by the Law of Conservation of Energy.
4.
The reaction between zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid is carried out in two different
conditions respectively. One reaction is carried out in a stoppered flask, which is
regarded as a closed system. The other is carried out in a flask without a stopper,
which is regarded as an open system. Which of the following statements concerning
the two reactions are correct?
(1) The pressure increases in the closed system.
(2) The change in internal energy of the reaction in the open system is smaller than
1
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
that in the closed system.
(3) The heat change of the reaction in the open system is smaller than that in the
closed system.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
5.
All chemical reactions involve
A. catalysts.
B. changes of physical state.
C. energy changes.
D. formation of radioactive substances.
6.
Which of the following statements about the Law of Conservation of Energy are
correct?
(1) The total amount of energy of the system and its surroundings remains constant.
(2) Energy can be changed from one form to another, e.g. chemical energy is
converted to heat energy.
(3) Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
7.
Which of the following is the most common form of energy transfer during a
chemical reaction?
A. Heat
B. Light
C. Electrical
D. Mechanical
8.
Which of the following concerning enthalpy are correct?
(1) It refers to the heat content of a substance.
(2) It cannot be measured directly.
(3) It is denoted by the symbol H.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
2
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
C.
D.
9.
(2) and (3) only
(1), (2) and (3)
Which of the following concerning enthalpy change of a reaction are correct?
(1) It is the heat change of a reaction measured under constant volume.
(2) It is equal to enthalpy of products minus enthalpy of reactants.
(3) It is denoted by the symbol of H.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
10. Which of the following is the correct unit for enthalpy and enthalpy change?
A.
B.
C
dm3
C.
D.
kJ
No unit
11. Which of the following correctly represents the enthalpy change of a chemical
reaction?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Total enthalpy of reactants Total enthalpy of products
Total enthalpy of products Total enthalpy of reactants
Total enthalpy of reactants + Total enthalpy of products
Total enthalpy of products
12. Which of the following statements concerning enthalpy change is correct?
A. Enthalpy change is equal to change in internal energy of the system at constant
pressure.
B. Enthalpy change indicates the reaction is heat releasing.
C. Enthalpy change is an absolute value.
D. Enthalpy change is equal to the sum of change in internal energy of the system
and the work done on the surroundings at constant pressure.
13. The change in internal energy and enthalpy change of a reaction are 367.0 kJ and
291.0 kJ respectively. What is the total amount of energy change of the system and its
surroundings?
A. 291.0 kJ
B. 0 kJ
3
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
C.
D.
367.0 kJ
76.0 kJ
14. The enthalpy change and the work done on the surroundings of a reaction are 65.0 J
and 38.0 J respectively. What is the change in internal energy of the reaction?
A. 103.0 J
B. 65.0 J
C. 38.0 J
D. 27.0 J
Section 35.2
15. Which of the following is an endothermic reaction?
A. Cracking
B. Neutralization
C. Combustion
D. Precipitation
16. Which of the following reaction(s) is/are exothermic?
(1) 2NaOH(aq) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) Na 2 SO 4 (aq) + 2H 2 O(l)
(2)
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
CaCO 3 (s) CaO(s) + CO 2 (g)
ZnSO 4 (aq) + 2NaOH(aq) Zn(OH) 2 (s) + Na 2 SO 4 (aq)
(1) only
(2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
17. Which of the following statement(s) about dissolving NH 4 NO 3 in water is/are
correct?
(1) The process involves heat release.
(2) The temperature of water decreases.
(3) The process involves a positive enthalpy change.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
18. For the following reaction:
C 10 H 22 (l) C 4 H 8 (g) + C 6 H 14 (l)
Which of the following statements are correct?
(1)
(2)
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
CC bond is broken during the reaction.
CC bond is formed during the reaction.
The reaction is exothermic.
(1) and (2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
(1), (2) and (3)
19. Which of the following descriptions about mixing hydrated barium hydroxide with
ammonium chloride are correct?
(1) Water drops under the beaker containing the reaction mixture are frozen.
(2) The enthalpy change of the reaction is positive.
(3) A fume is released from the reaction mixture.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
20. Which of the following processes are endothermic?
(1) Condensation of steam
(2) Melting of ice
(3) Evaporation of water
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
21. Which of the following reactions involve absorption of energy?
(1) Breaking a covalent bond in a chlorine molecule.
(2) Adding zinc granule to dilute hydrochloric acid.
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
Heating limestone strongly at about 900C.
(1) and (2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
(1), (2) and (3)
5
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
22. Which of the following statements concerning exothermic reaction are correct?
(1) In an exothermic reaction, the enthalpies of products are relatively lower than
that of reactants.
(2) It involves releasing energy to the surroundings.
(3) It involves negative enthalpy change.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
23. Which of the following showing the form of energy change when burning wood is
correct?
A. Potential energy changes to kinetic energy
B. Chemical energy changes to light and heat energy
C. Internal energy changes to potential energy
D. Light energy changes to heat energy
24. Coal can be used as an energy source because
(1) it is non-renewable.
(2) burning of coal is an exothermic reaction.
(3) it is readily available.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
25. Which of the following processes are exothermic?
(1) Burning a candle
(2) Melting an ice-cream
(3) Forming snowflakes
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
26. Which of the following is NOT an endothermic process?
A.
B.
C.
D.
CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(l)
C 3 H 8 (g) C 2 H 4 (g) + CH 4 (g)
NH 4 NO 3 (s) + aq NH 4 NO 3 (aq)
CaCO 3 (s) CaO(s) + CO 2 (g)
27. Which of the following combinations is correct?
Bond-breaking processes
Bond-forming processes
A.
require energy
release energy
B.
release energy
require energy
C.
use and release energy
do not involve any energy
intake or release
D.
do not involve any energy
intake or release
use and release energy
28. For an exothermic reaction, the enthalpies of products are
A. always higher than that of reactants.
B. always the same as that of reactants.
C. always lower than that of reactants.
D. independent of enthalpies of reactants.
29. Which of the following definitions about an endothermic reaction is correct?
A. A reaction in which heat energy is converted into electrical energy.
B. A reaction in which electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
C. A reaction in which chemical energy is converted into heat energy.
D. A reaction in which heat energy is converted into chemical energy.
30. Which of the following statements concerning the reaction:
CH 3 CH 2 OH(l) + 3O 2 (g) 2CO 2 (g) + 3H 2 O(l) is/are correct?
(1) Two C=O bonds are broken during the reaction.
(2)
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
One CC bond is broken during the reaction.
Two OH bonds are broken during the reaction.
(1) only
(2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
31. For the following reactions:
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 (g) +
(CH 3 ) 2 CHCH 3 (g) +
13
O 2 (g) 4CO 2 (g) +
2
13
O 2 (g) 4CO 2 (g) +
2
H 1 = 2878 kJ mol1
H 2 = 2869 kJ mol1
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(1) The energy stored in butane is less than that in 2-methylpropane.
(2)
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
Both reactions involve breaking of CH bonds.
Converting 2-methylpropane to butane is an endothermic reaction.
(1) only
(2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
32. Which of the following statement(s) concerning an exothermic reaction is/are
INCORRECT?
(1) It involves a negative enthalpy change.
(2) The total enthalpy of the products is greater than that of the reactants.
(3) The reaction system is hotter than the surroundings.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
33. Which of the following statement(s) concerning an endothermic reaction is/are
INCORRECT?
(1) It involves a positive enthalpy change.
(2) The total enthalpy of the products is less than that of the reactants.
(3) The reaction system is colder than the surroundings.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
34. Which of the following are the daily applications of exothermic reactions?
(1) Burning hydrogen in a gas burner.
(2) The heat pad in hand-warmer.
(3) Breaking down larger alkenes into smaller alkanes and alkenes.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
35. Which of the following statements concerning bond-breaking and bond-forming
processes are correct?
(1) Both processes involve enthalpy change.
(2) The energy difference between these two processes is the enthalpy change of a
chemical reaction.
(3) Both processes involve temperature change.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
36. Which of the following statements concerning an endothermic reaction are correct?
(1) Heat is given out to the surroundings.
(2) It involves a positive enthalpy change.
(3) The bond-forming processes give out less energy than that is required in the
bond-breaking processes.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
37. Which of the following reactions gives the products with relatively higher enthalpies
than the reactants?
A. Burning methane in excess air
B. Adding zinc sulphate solution into sodium hydroxide solution
C. Mixing hydrated barium hydroxide and ammonium chloride
D. Mixing sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
38. Which of the following statements concerning both exothermic and endothermic
reactions is/are correct?
(1) Both reactions have energy transfer in the system.
(2) Both reactions give products with relatively lower heat content than the
reactants.
(3) Both reactions are spontaneous.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
39. Which of the following statements concerning an endothermic reaction are correct?
(1) The reaction involves absorption of heat energy.
(2) The enthalpy change of the reaction is positive.
(3) The bond-forming process gives out more energy than that is needed in the
bond-breaking process.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
40. Which of the following reactions is exothermic?
A.
B.
C.
D.
C 8 H 18 (l) C 4 H 8 (g) + C 4 H 10 (l)
H 2 O(s) H 2 O(l)
O 2 (g) 2O(g)
Cl(g) + e Cl(g)
A. Both statements are true and the 2nd statement is a correct explanation
of the 1st statement.
B. Both statements are true and the 2nd statement is NOT a correct
explanation of the 1st statement.
C. The 1st statement is false but the 2nd statement is true.
D. Both statements are false.
10
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
Sections 35.135.2
41. An endothermic reaction involves
absorption of heat.
In an endothermic reaction, the total
enthalpy of products is greater than that
of the reactants.
42.The heat change at constant pressure
is equal to the enthalpy change of the
reaction.
The change in internal energy is equal to
the difference between enthalpy change
of the reaction and the work done on the
surroundings.
43.The dissolving of ammonium nitrate
in water is an endothermic reaction
which gives a cooling effect.
A commercial instant cold pack is used
to treat athletes injuries.
44.No energy is absorbed or released in
a physical change.
Physical changes do not involve
breaking of covalent bonds.
45.A chemical reaction with positive
enthalpy change involves
bond-breaking processes only.
During the bond-breaking processes,
energy has to be supplied to break the
chemical bonds. Thus, the
bond-breaking processes are
endothermic.
46.Some endothermic reactions are
spontaneous.
The reaction between hydrated barium
hydroxide and ammonium chloride
when mixing is a spontaneous
endothermic reaction.
Section 36.1
47. The value of H f for CH 2 O is assumed to be x kJ mol1. Which of the following
thermochemical equations represents the H f of CH 2 O?
A.
C(g) + H 2 (g) +
1
O 2 (g) CH 2 O(l)
2
H f = x kJ mol1
B.
C(s) + H 2 (g) +
1
O 2 (g) CH 2 O(l)
2
H f = x kJ mol1
C.
D.
C(g) + 2H 2 (g) + O(g) CH 2 O(l)
CO(g) + H 2 (g) CH 2 O(l)
H f = x kJ mol1
H f = x kJ mol1
11
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
48. Which of the following represents the equation for the standard enthalpy change of
formation of nitrogen dioxide?
A.
N(g) + 2O(g) NO 2 (g)
B.
1
N 2 (g) + O 2 (g) NO 2 (g)
2
C.
1
N 2 O 4 (g) NO 2 (g)
2
D.
NO(g) +
1
O 2 NO 2 (g)
2
49. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(1) Dissolving NH 4 Cl(s) into H 2 O(l) is an endothermic process.
(2) Adding 10.0 cm3 of 12.0 M H 2 SO 4 (aq) into 40.0 cm3 of water is an exothermic
process.
(3) Mixing 20.0 cm3 of 1.0 M NaOH(aq) with 20.0 cm3 of 1.0 M HCl(aq) is an
exothermic process.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
50. The table below shows the energy released when burning 1.0 g of each of four
organic compounds methane, ethanol, propanol and octane.
Name
Energy released/kJ g1
Methane
55.7
Ethanol
29.8
Propanol
33.6
Octane
48.4
The standard enthalpy change of combustion of one of the above organic compounds
is 2016 kJ mol1. What is the organic compound?
A. Methane
B. Ethanol
C. Propanol
D. Octane
12
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
51. Which of the following is/are the standard condition(s) adopted for measuring the
enthalpy changes?
(1) 273 K
(2)
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
101 325 Nm2
Iodine in gaseous state
(1) only
(2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
52. H 2 (g) + Cl 2 (g) 2HCl(g)
H = 184.6 kJ mol1
Which of the following statements concerning the above reaction is correct?
A. One hydrogen molecule reacts with one chlorine molecule, releasing 184.6 kJ
energy.
B. 1 mole of hydrogen reacts completely to produce 2 moles of hydrogen chloride
gas, releasing 184.6 kJ energy.
C.
Under 1 atm and 25C, 1 mole of hydrogen reacts completely with 1 mole of
chlorine to produce 2 moles of hydrogen chloride, releasing 184.6 kJ energy.
D.
Under 1 atm and 25C, 1 mole of hydrogen reacts completely with 1 mole of
chlorine to produce 2 moles of hydrogen chloride, absorbing 184.6 kJ energy.
53. B 2 H 6 (g) + 3O 2 (g) B 2 O 3 (s) + 3H 2 O(g)
Which of the following represents the enthalpy change of the above reaction?
A. H f [B 2 O 3 (s)]
B. 3 H f [H 2 O(g)]
C. 3 H c [O 2 (g)]
D. H c [B 2 H 6 (g)]
54. Which of the following represents an equation for the standard enthalpy change of
formation of Fe 3 O 4 (s)?
A.
B.
C.
D.
3Fe(s) + 2O 2 (g) Fe 3 O 4 (s)
3Fe(s) + 4O(g) Fe 3 O 4 (s)
3FeO(s) + H 2 O(g) Fe 3 O 4 (s) + H 2 (g)
FeO(s) + Fe 2 O 3 (s) Fe 3 O 4 (s)
13
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
55. Consider the following reactions:
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H 2 O(l)
H 1
HCN(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCN(aq) + H 2 O(l)
H 2
Which of the following statement(s) concerning the above reactions is/are
INCORRECT?
(1) Both reactions have positive enthalpy changes.
(2) Both reactions can be represented by an ionic equation:
H+(aq) + OH(aq) H 2 O(l)
(3) H 1 is less negative than H 2 .
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
56. Which of the following equations correctly represents the standard enthalpy change
of combustion?
A.
B.
C.
D.
2C(s) + O 2 (g) 2CO(g)
2CH 4 (g) + 3O 2 (g) 2CO(g) + 4H 2 O(g)
2H 2 S(g) + O 2 (g) 2S(s) + 2H 2 O(g)
2H 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2H 2 O(l)
57. Which of the following equations represents the standard enthalpy change of
formation of hydrogen bromide?
A.
B.
H 2 (g) + Br 2 (g) 2HBr(g)
H 2 (g) + Br 2 (l) 2HBr(g)
C.
1
1
H 2 (g) + Br 2 (g) HBr(g)
2
2
D.
1
1
H 2 (g) + Br 2 (l) HBr(g)
2
2
58. Which of the following standard enthalpy changes is/are always negative?
(1) Standard enthalpy change of formation
(2) Standard enthalpy change of neutralization
(3) Standard enthalpy change of solution
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
14
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
59. Which of the following graphs correctly illustrates the temperature change when
ammonium nitrate crystals are dissolved in a beaker of water at room temperature?
A.
Temperature
Time
B.
Temperature
Time
C.
Temperature
Time
D.
Temperature
Time
15
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
60. Which of the following combinations when mixing will have the greatest standard
enthalpy change of neutralization?
Acid
Alkali
A.
CH 3 COOH
NaOH
B.
HNO 3
NaOH
C.
HCN
NH 3
D.
HCl
NH 3
Enthalpy
61. The enthalpy level diagram shown below represents the standard enthalpy change for
complete combustion of C(graphite).
C(graphite) + O 2 (g)
H c = 393.5 kJ mol1
CO 2 (g)
Reaction coordinate
Which of the following diagrams represents the standard enthalpy change for the complete
combustion of C(graphite) if 2 moles of oxygen are used?
B.
C(graphite) + O 2 (g)
H
C(graphite) +
Enthalpy
Enthalpy
A.
= 393.5 kJ
CO 2 (g)
H c = 196.8 kJ mol1
CO 2 (g) + O 2 (g)
Reaction coordinate
2C(graphite) + 2O 2 (g)
Enthalpy
Enthalpy
D.
C(graphite) + 2O 2 (g)
CO 2 (g) +
Reaction coordinate
Reaction coordinate
C.
H c = 787.0 kJ mol1
H c = 787.0 kJ mol1
2CO 2 (g)
Reaction coordinate
16
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
62. The thermochemical equation shown below refers to the combustion of ammonia.
4NH 3 (g) + 3O 2 (g) 2N 2 (g) + 6H 2 O(g)
H c = x kJ
Which of the following statements concerning the above reaction are correct?
(1) x is negative in value.
(2) The standard enthalpy change of combustion of ammonia is
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
1
x kJ mol1.
4
The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is 4 H c [NH 3 (g)].
(1) and (2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
(1), (2) and (3)
63. Which of the following is/are standard condition(s) adopted for measuring the
enthalpy changes?
(1) A temperature of 273 K
(2) A pressure of one atmosphere
(3) Carbon in the form of diamond
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
64. Which of the following concerning the standard state of an element are correct?
(1)
(2)
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
It is the most stable form of the element at 25C and 1 atm.
It is one of the standard conditions adopted for measuring the enthalpy changes.
It is the normal physical state of the element.
(1) and (2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
(1), (2) and (3)
17
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
65. Which of the following about standard enthalpy change of reaction are correct?
(1)
(2)
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
It is often expressed as H .
The unit used for standard enthalpy change of reaction is kJ mol1.
It is a general name for the enthalpy change of any reaction.
(1) and (2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
(1), (2) and (3)
66. Consider the following thermochemical equation.
2CO(g) + O 2 (g) 2CO 2 (g)
H = 566.0 kJ
What is the standard enthalpy change of combustion of CO(g)?
A.
B.
C.
D.
+283.0 kJ mol1
283.0 kJ mol1
+566.0 kJ mol1
566.0 kJ mol1
67. Consider the following equation.
2CO(g) + O 2 (g) 2CO 2 (g)
H = 566.0 kJ
Which of the following definitions concerning the standard enthalpy change of above
reaction is correct?
A. Standard enthalpy change of reaction
B. Standard enthalpy change of formation of CO 2 (g)
C. Standard enthalpy change of combustion of CO(g)
D. Standard enthalpy change of formation of 2CO 2 (g)
68. Consider the following chemical equation.
2C(s) + 2O 2 (g) 2CO 2 (g)
H = 790.0 kJ
Which of the following statements concerning the above reaction are correct?
(1) The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is 790.0 kJ.
(2) The reaction can be either regarded as a combustion reaction or a formation
reaction.
(3) The enthalpy change of reaction is measured under standard conditions.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
18
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
69. Which of the following value(s) may be either positive or negative?
(1) The standard enthalpy change of formation
(2) The standard enthalpy change of neutralization
(3) The standard enthalpy change of solution
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
70. Which of the following definitions for the standard enthalpy change of solution is
correct?
A. Standard enthalpy change of solution of a substance is the enthalpy change
under standard conditions when 1 g of it is dissolved in a sufficiently large
volume of solvent.
B. Standard enthalpy change of solution of a substance is the enthalpy change
under standard conditions when 1 mole of the substance is dissolved in 1 mole
of water.
C. Standard enthalpy change of solution of a substance is the enthalpy change
under standard conditions when 1 mole of it is dissolved in a sufficiently large
volume of solvent.
D. Standard enthalpy change of solution of a substance is the enthalpy change at
273 K and 1 atm when 1 mole of the substance is dissolved in a sufficiently
large volume of solvent.
71. Which of the following substance(s) has/have zero H f ?
(1) Diamond
(2) Hydrogen gas
(3) Sodium
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
19
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
Section 36.2
72. The mass and the specific heat capacity of a substance are m g and c J g1 K1
respectively. It was heated until the temperature rose by t C. What is the enthalpy
change of the heating process?
A. mct
B. mc(t + 273)
C.
mct
1000
D.
mc(t 273)
73. A 50.0 cm3 sample of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid was mixed with 50.0 cm3 of 1.0 M
sodium hydroxide solution in a simple calorimeter. The temperature of the reaction
mixture rose from 21.0C to 27.5C. What is the enthalpy change of the reaction:
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) H 2 O(l) + NaCl(aq)?
(Assume that the specific heat capacity and density of the reaction mixture are 4.2 J
g1 K1 and 1.0 g cm3 respectively.)
A. 2.7 kJ mol1
B. 10.8 kJ mol1
C. 27.0 kJ mol1
D. 54.6 kJ mol1
74. A 1.0 g sample of hexane (C 6 H 14 ) was burnt with excess oxygen in a bomb
calorimeter which has a calorimeter constant of 10.3 kJ C1. The temperature of the
calorimeter rose from 22.64C to 29.30C. Which of the following is the enthalpy
change of combustion of hexane?
A.
B.
C.
D.
68.6 kJ mol1
8.92 102 kJ mol1
5.91 103 kJ mol1
6.73 103 kJ mol1
75. A 0.1375 g sample of solid magnesium was burnt in a constant-volume bomb
calorimeter which contained 1000 g of water. The temperature rose by 0.59C. The
heat capacities of water and bomb calorimeter are 4.2 J g1 C1 and 1769 J C1
respectively. What would be the enthalpy change of combustion of magnesium?
A.
B.
C.
D.
3.5 kJ mol1
25.5 kJ mol1
289.0 kJ mol1
622.4 kJ mol1
20
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
76. Magnesium oxide can be prepared by burning magnesium in excess oxygen. The
standard enthalpy change of formation of MgO is 1203 kJ mol1. What is the heat
released for forming 1.0 g of MgO?
A. 0.025 kJ
B. 29.8 kJ
C. 40.0 kJ
D. 1203 kJ
77. A student used a simple calorimeter to determine the enthalpy change of combustion
of ethanol. The following data was recorded.
Initial mass of spirit burner = 133.20 g
Initial temperature of water = 25.0C
Final mass of spirit burner = 132.05 g
Final temperature of water = 45.5C
Mass of water in the can = 300.0 g
Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J
g1 K1
Determine the enthalpy change of combustion of ethanol using the above data.
A.
B.
C.
D.
22.4 kJ mol1
25.7 kJ mol1
1033.2 kJ mol1
1180.1 kJ mol1
78. When 30.0 cm3 of 0.10 M Ba(OH) 2 (aq) is added to 30.0 cm3 of 0.10 M H 2 SO 4 (aq) in
an expanded polystyrene cup, there was a rise in temperature of T 1 . The experiment
was repeated by using 60.0 cm3 of each solution and the rise in temperature was T 2 .
What is the relationship between T 1 and T 2 ?
A. T 2 is equal to T 1
B. T 2 is the double of T 1
C. T 2 is the triple of T 1
D. T 2 is the half of T 1
79. Which of the following enthalpy changes is measured by the bomb calorimeter?
A. The enthalpy changes of neutralization
B. The enthalpy changes of combustion
C. The enthalpy changes of solution
D. The enthalpy changes of formation
21
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
80. A student carried out an experiment to determine the standard enthalpy change of
combustion of liquid propan-1-ol using the apparatus shown in the diagram.
beaker
water
propan-1-ol
The following data was recorded
Mass of propan-1-ol burnt = 0.60 g
Mass of water in the beaker = 200.0 g
Initial temperature of water = 21.0C
The student wanted to predict the final temperature of water before the experiment.
What would be the predicted final temperature of the water?
(Given that the theoretical standard enthalpy change of combustion of propan-1-ol is
2021 kJ mol1 and the specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 J g1 K1.)
A. 24.2C
B 29.1C
C. 45.1C
D. 48.4C
81. A spirit burner containing liquid methanol is used to heat up a beaker of water (200.0
g) from 15.5C to 100.0C.
(Given: the specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g1 K1, H c [methanol(l)] =
715.0 kJ mol1)
Which of the following is the mass of methanol needed for the heating process?
A. 1.59 g
B. 2.23 g
C. 3.18 g
D. 6.35 g
22
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
82. Which of the following assumptions are made when using a simple calorimeter to
determine the enthalpy change of a reaction?
(1) The density of the reaction mixture is the same as that of water.
(2) The specific heat capacities of the calorimeter and the thermometer
arenegligible.
(3) There is no heat loss to the surroundings.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
83. Which of the following pieces of information are required to determine the heat
released in the combustion of ethanol by using a simple calorimeter?
(1) The mass of water
(2) The specific heat capacity of water
(3) The rise in the temperature of water
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
84. Which of the following can be determined directly by the simple calorimetric
methods?
(1) Enthalpy change of combustion
(2) Enthalpy change of solution
(3) Enthalpy change of formation
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
23
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
85. Which of the following concerning the standard enthalpy change of combustion are
correct?
(1) It is always negative.
(2) It can be determined by the simple calorimetric methods.
(3) It determines whether a fuel is suitable for use or not.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
86. Which of the following concerning the reaction between nitric acid and sodium
hydroxide are correct?
(1) The standard enthalpy change of the reaction is negative.
(2) Nitrate ions and sodium ions are spectator ions.
(3) The standard enthalpy change of the reaction can be determined by the simple
calorimetric methods.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
87. Given that:
HCN(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCN(aq) + H 2 O(l)
H neut = x kJ mol1
HNO 3 (aq) + NaOH(aq) NaNO 3 (aq) + H 2 O(l)
H neut = y kJ mol1
Which of the following statements concerning the above two reactions are correct?
(1) Both x and y can be determined by the simple calorimetric methods.
(2) x is less negative than y.
(3) Both reactions involve the reactions between hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions
only.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
24
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
88. A 25.0 cm3 sample of 3.0 M hydrochloric acid at 25.0C was mixed with 25.0 cm3 of
3.0 M sodium hydroxide at 25.0C in a simple calorimeter. The highest temperature
recorded after mixing was 45.0C. Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction
between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.
(Assume that the specific heat capacity and the density of the reaction mixture are 4.2
J g1 K1 and 1.0 g cm3 respectively.)
A. 28.0 kJ mol1
B. 42.0 kJ mol1
C. 56.0 kJ mol1
D. 112.0 kJ mol1
89. When 1.0 g of anhydrous lithium chloride (LiCl) is added to 20.0 g of water, the
temperature rise is 9.8C. Assume that the specific heat capacity and the density of
the solution are 4.2 J g1 K1 and 1.0 g cm3 respectively. Which of the following
statements concerning the above experiment is/are correct?
(1) The above experiment can be carried out in a simple calorimeter.
(2) The thermochemical equation is:
LiCl(s) + H 2 O(l) LiCl H 2 O(aq)
H soln = 34.9 kJ mol1
(3) The enthalpy change of solution per one mole of LiCl is 34.9 kJ mol1.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
90. Consider the following reaction.
2Na 2 O(s) + O 2 (g) 2Na 2 O 2 (s)
H = 176.0 kJ
Which of the following statement(s) concerning the above reaction is/are correct?
(1) The standard enthalpy change of formation of Na 2 O 2 (s) is 88.0 kJ mol1.
(2) The standard enthalpy change of reaction is 176.0 kJ.
(3) The standard enthalpy change of reaction can be determined by simple
calorimetric methods.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
25
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
91. Which of the following are necessary for accurate determination of standard enthalpy
change of combustion?
(1) The combustion experiment is carried out in a simple calorimeter.
(2) The combustion experiment is carried out under standard conditions.
(3) The combustion experiment is carried out in a condition with excess supply of
oxygen.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
92. An experiment was carried to determine the enthalpy change of neutralization
between HCl(aq) and NaOH(aq). The experimental set-up was shown below.
a thermometer
a beaker
a mixture of HCl(aq)
and NaOH(aq)
Which of the following statements concerning the above experiment are correct?
(1) The experiment should be carried out in a vacuum flask in order to reduce
errors.
(2) The experimental value is less negative than the theoretical value of the enthalpy
change of neutralization between HCl(aq) and NaOH(aq).
(3) The major error of the experiment is heat loss to the surroundings due to
convection, conduction and evaporation.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
26
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
93. Which of the following devices is the most accurate to determine the standard
enthalpy change of combustion?
A. A simple calorimeter
B. A vacuum flask
C. A bomb calorimeter
D. An expanded polystyrene cup
94. Given that:
CH 3 COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) CH 3 COONa(aq) + H 2 O(l)
H neut = x kJ mol1
Which of the following concerning the enthaply change of the above reaction is/are
INCORRECT?
(1) x may be either positive or negative in value.
(2) The above reaction involves complete ionization of CH 3 COOH.
(3) x can be determined by the simple calorimetric methods.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
95. Which of the following is NOT the major source of error when using the simple
calorimetric methods to determine the standard enthalpy change of neutralization?
A. The density of the reaction mixture deviates from that of water.
B. The specific heat capacities of the expanded polystyrene cup and the
thermometer are not considered in calculation.
C. The reaction condition is not standard.
D. Taking reading from the thermometer by naked eyes.
Section 36.1
96.The standard enthalpy change of
neutralization between strong acids and
strong alkalis are more negative than
that between weak acids and strong
alkalis.
The neutralization reactions between
weak acids and strong alkalis release
less energy because some energy has to
be supplied for complete ionization of
the weak acids.
97.The standard state for the element
of phosphorus is yellow phosphorus.
The most stable form of an element at
298 K and 1 atm is chosen as the
standard state.
27
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
98.The standard enthalpy changes for
the neutralization reactions between
strong acids and strong alkalis are
about 57.0 kJ mol1.
99.The standard enthalpy change of
solution of a salt determines whether it
is suitable to be employed in instant
hot packs or instant cold packs.
The neutralization reactions between
strong acids and strong alkalis are the
reactions of hydrogen ions and
hydroxide ions.
The standard enthalpy change of
solution of a salt may be either positive
or negative.
Section 36.2
100.Expanded polystyrene cups are
often used as the apparatus to construct
a simple calorimeter.
Expanded polystyrene cups are good
insulators of heat.
Section 37.1
101. Which of the following about enthalpy change of a reaction are correct?
(1) It depends on the difference in enthalpy between the reactants and products.
(2) It does not depend on the route taken to get from the reactants to the products.
(3) It can be determined by applying Hesss Law.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
102. Which of the following about enthalpy level diagram are correct?
(1) It can be used to represent the enthalpy changes of chemical reactions.
(2) It can be drawn if the relative energy levels of reactants and products involved
are known.
(3) Each horizontal line in the diagram represents the relative energy level of
reactants and products for a chemical reaction respectively.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
28
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
Enthalpy
103. Which of the following statements concerning the enthalpy level diagram shown
below is/are INCORRECT?
H = +100.0 kJ mol1
Reaction coordinate
(1) The horizontal lines represent the relative energy levels of reactants and
products in chemical reactions.
(2)
(3)
A.
B.
C.
D.
The energy released from the reaction to the surroundings is 100.0 kJ mol1.
The reaction is endothermic.
(1) only
(2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
104. Which of the following statements concerning Hesss Law are correct?
(1) It states that the overall enthalpy change of a chemical reaction is the same,
regardless of the route by which the reaction takes place.
(2) It is applied to determine the standard enthalpy change of formation of a
substance indirectly.
(3) It is a direct consequence of the Law of Conservation of Energy.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
29
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
Enthalpy
105.
2NO(g) + O 2 (g)
H 1
N 2 (g) + 2O 2 (g)
H 2
2NO 2 (g)
H A
Reaction coordinate
Which of the following statements concerning the above enthalpy level diagram for
the formation of NO 2 (g) are correct?
(1) H A = H 1 + H 2
(2) Each horizontal line represents the relative energy level of reactants and
products for the chemical reaction respectively.
(3) The reaction is endothermic, as the line for the products is above that for the
reactants.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
106. Which of the following statements concerning Hesss Law are correct?
(1) It states that the overall enthalpy change of a chemical reaction is independent of
the reaction route taken.
(2) It states that the overall enthalpy change of a chemical reaction is dependent of
the difference in enthalpy between the reactants and products.
(3) It is the concept used by chemists to determine enthalpy changes of reactions
that cannot be found by experiment directly.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
30
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
107. By using Hesss Law,
(1) the enthalpies of products in a reaction can be determined.
(2) the enthalpy changes of reactions that cannot be performed easily can be found.
(3) enthalpy change cycles and enthalpy level diagrams can be constructed.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
108. Which of the following statements concerning enthalpy change cycle are correct?
(1) It can represent the enthalpy changes of the reactions.
(2) It relates the different pathways of a reaction in a closed loop.
(3) The number of atoms of species involved in any enthalpy change cycle has to be
balanced.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
109. Which of the following information is required for drawing enthalpy level diagram?
A. The masses of species involved in a chemical reaction.
B. The relative energy levels of species involved in a chemical reaction.
C. The number of moles of species involved in a chemical reaction.
D. The specific heat capacities of species involved in a chemical reaction.
Section 37.2
110. Given that:
H f [CO 2 (g)] = 395.0 kJ mol1
H f [H 2 O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1
H f [C 2 H 5 OH(l)] = 273.0 kJ mol1
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of combustion of ethanol,
H c [C 2 H 5 OH(l)]?
A.
B.
C.
D.
408.0 kJ mol1
954.0 kJ mol1
1375 kJ mol1
1921 kJ mol1
31
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
111. Given that:
H f [CO 2 (g)] = 395.0 kJ mol1
H f [H 2 O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1
H c [C 4 H 10 (g)] = 2880 kJ mol1
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of formation of butane,
H f [C 4 H 10 (g)]?
A.
B.
C.
D.
112.
130.0 kJ mol1
234.0 kJ mol1
5890 kJ mol1
+130.0 kJ mol1
Given that:
H f [NO 2 (g)] = +34.0 kJ mol1
H f [NO(g)] = +90.0 kJ mol1
What is the standard enthalpy change of the following reaction:
2NO(g) + O 2 (g) 2NO 2 (g)?
A. 112.0 kJ mol1
B. +112.0 kJ mol1
C. +124.0 kJ mol1
D. +248.0 kJ mol1
113. Given that:
S(s) + O 2 (g) SO 2 (g)
H 1 = 296.8 kJ mol1
2SO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2SO 3 (g)
H 2 = 196.0 kJ mol1
What is the standard enthalpy change of the following reaction?
2S(s) + 3O 2 (g) 2SO 3 (g)
A. 100.8 kJ mol1
B. 397.6 kJ mol1
C. 492.8 kJ mol1
D. 789.6 kJ mol1
114. Given that:
H c [C 2 H 2 (g)] = x kJ mol1
H c [H 2 (g)] = y kJ mol1
H c [C 2 H 6 (g)] = z kJ mol1
Calculate the standard enthalpy change of the following reaction:
C 2 H 2 (g) + 2H 2 (g) C 2 H 6 (g)
A. x + 2y z
32
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
B.
C.
D.
x+yz
2xy z
z x 2y
115. The standard enthalpy change of the following reaction is 1852 kJ mol1.
3Mg(s) + KClO 3 (s) 3MgO(s) + KCl(s)
Given that the standard enthalpy change of formation of KClO 3 and KCl are 391.0 kJ
mol1 and 437.0 kJ mol1 respectively, calculate the standard enthalpy change of
formation of MgO.
A.
B.
C.
D.
1806 kJ mol1
633.0 kJ mol1
602.0 kJ mol1
341.0 kJ mol1
Enthalpy
116. Consider the following enthalpy level diagram.
2NO(g) + O 2 (g)
H 1 =
H 2 = 112.0 kJ mol1
+180.0 kJ mol1
2NO 2 (g)
N 2 (g) + 2O 2 (g)
Reaction coordinate
What is the standard enthalpy change of the following reaction?
N 2 (g) + 2O 2 (g) 2NO 2 (g)
A. 292.0 kJ mol1
B. 68.0 kJ mol1
C. +68.0 kJ mol1
D. +292.0 kJ mol1
117. Consider the following reaction.
C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) + 6O 2 (g) 6CO 2 (g) + 6H 2 O(l)
Which of the following information is/are required to determine the standard
enthalpy change of the above reaction, H r ?
(1) H f [CO 2 (g)]
(2) H f [H 2 O(l)]
(3) H f [C 6 H 12 O 6 (s)]
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
33
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
C.
D.
(2) and (3) only
(1), (2) and (3)
118. Given that:
2H 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2H 2 O(l)
H 1
H 2 O(l) H 2 O(g)
H 2
What is the standard enthalpy change of the following reaction?
2H 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2H 2 O(g)
A. H 1 2H 2
B. H 1 + 2H 2
C. H 1 H 2
D. H 1 + H 2
119.Given that:
H f [CO 2 (g)] = H 1
H f [H 2 O(l)] = H 2
H f [C 8 H 18 (l)] = H 3
Which of the following statements concerning the combustion of C 8 H 18 (l) are correct?
(1) The chemical equation for the combustion of C 8 H 18 (l) is
C 8 H 18 (l) +
25
O 2 (g) 8CO 2 (g) + 9H 2 O(l).
2
(2) The standard enthalpy change of combustion of C 8 H 18 (l) is
8H 1 + 9H 2 H 3 .
(3) The standard enthalpy change of combustion of C 8 H 18 (l) can be determined by the
simple calorimetric methods.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
120. 1.0 g of each of the following substances was burned in a bomb calorimeter. In each
case, the quantity of energy released was determined and tabulated as follows:
Substance
Energy released/kJ g1
C(graphite)
32.8
H 2 (g)
143.0
C 4 H 10 (g)
49.6
What is the standard enthalpy change of formation of butane, C 4 H 10 (g)?
34
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
A.
B.
C.
D.
+2197 kJ mol1
127.4 kJ mol1
2197 kJ mol1
5881 kJ mol1
121. H f [CO 2 (g)] = 395.0 kJ mol1
H f [SO 2 (g)] = 297.0 kJ mol1
H c [CS 2 (l)] = 1075 kJ mol1
What is the enthalpy change involved in the formation of 1.0 g of CS 2 (l)?
A. 1.13 kJ
B. 1.95 kJ
C. 5.04 kJ
D. 86.0 kJ
122. Given that:
H 2 O(g) H 2 O(l)
H 1
C 2 H 5 OH(g) C 2 H 5 OH(l)
H 2
C 2 H 5 OH(g) + 3O 2 (g) 2CO 2 (g) + 3H 2 O(g)
H 3
What is the standard enthalpy change of the following reaction:
C 2 H 5 OH(l) + 3O 2 (g) 2CO 2 (g) + 3H 2 O(l)
A. H 1 + H 2 + H 3
B. 2H 1 + 2H 2 + 2H 3
C. 3H 1 + H 2 + H 3
D. 3H 1 H 2 + H 3
35
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
123. Given that:
P 4 (white) + 5O 2 (g) P 4 O 10 (s)
P(red) +
5
1
O 2 (g) P 4 O 10 (s)
4
4
H 1 = 2983.2 kJ mol1
H 2 = 738.5 kJ mol1
Which of the following statements concerning the conversion of white phosphorus to
red phosphorus is/are correct?
(1) The reaction is exothermic.
(2) The enthalpy of red phosphorus is relatively higher than that of white
phosphorus.
(3) Red phosphorus is more stable than white phosphorus.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
124. Given that:
Na 2 CO 3 10H 2 O(s) Na 2 CO 3 (s) + 10H 2 O(g)
H 1 = +532.36 kJ mol1
Na 2 CO 3 10H 2 O(s) Na 2 CO 3 H 2 O(s) +
9H 2 O(g)
H 2 = +473.63 kJ mol1
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of dehydration of Na 2 CO 3
H 2 O(s)?
A.
B.
C.
D.
+58.73 kJ mol1
58.73 kJ mol1
+1005.99 kJ mol1
1005.99 kJ mol1
125. Given that:
P(s) +
3
Cl 2 (g) PCl 3 (g)
2
PCl 5 (g) PCl 3 (g) + Cl 2 (g)
H 1 = 306.0 kJ mol1
H 2 = +93.0 kJ mol1
What is the standard enthalpy change of formation of PCl 5 (g)?
A.
B.
C.
D.
399.0 kJ mol1
+399.0 kJ mol1
213.0 kJ mol1
+213.0 kJ mol1
36
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
126. Given that:
BaSO 4 (s) + 4C(s) 4CO(g) + BaS(s)
H 1 = +571.2 kJ mol1
BaSO 4 (s) + 2C(s) 2CO 2 (g) + BaS(s)
H 2 = +226.2 kJ mol1
What is the standard enthalpy change of the following reaction?
C(s) + CO 2 (g) 2CO(g)
A. 172.5 kJ mol1
B. +172.5 kJ mol1
C. 345 kJ mol1
D. +345 kJ mol1
127. Given that:
H f [CO 2 (g)] = 395.0 kJ mol1
H f [H 2 O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1
H f [C 4 H 6 (g)] = +108.0 kJ mol1
What is the standard enthalpy change of the following reaction?
C 4 H 6 (g) +
A.
B.
C.
D.
11
O 2 (g) 4CO 2 (g) + 3H 2 O(l)
2
2330 kJ mol1
+2330 kJ mol1
2546 kJ mol1
+2546 kJ mol1
128. Consider the following enthalpy change cycle.
A + 2B
H 1
H 2
AB 2
H 3
AB + B
What is H 1 ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
H 2
H 3
H 2
H 2
H 3
H 2
+ H 3
H 3
37
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
129. Consider the following enthalpy change cycle.
A + BC
H 1
AB + C
H 2
H 3
AC + B
What is H 1 ?
A. H 2 + H 3
B.
C.
D.
H 2 H 3
H 3 H 2
H 2 H 3
130. The standard enthalpy change of combustion of graphite and diamond are 393.5 kJ
mol1 and 395.4 kJ mol1 respectively. Which of the following is the standard
enthalpy change of formation of diamond from graphite?
A.
B.
C.
D.
1.9 kJ mol1
+1.9 kJ mol1
788.9 kJ mol1
+788.9 kJ mol1
131. Given that:
H f [CO 2 (g)] = 393.5 kJ mol1
H f [H 2 O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1
H f [CH 4 (g)] = 74.0 kJ mol1
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of combustion of methane, H c
[CH 4 (g)]?
A.
B.
C.
D.
+252.5 kJ mol1
605.5 kJ mol1
891.5 kJ mol1
1039.5 kJ mol1
38
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
132. Given that:
H f [CO 2 (g)] = 393.5 kJ mol1
H f [H 2 O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1
H f [C 6 H 6 (l)] = +226.0 kJ mol1
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of combustion of benzene,
H c [C 6 H 6 (l)]?
A.
B.
C.
D.
+2993 kJ mol1
905.5 kJ mol1
2993 kJ mol1
3445 kJ mol1
133. Given that:
H f [CO 2 (g)] = 393.5 kJ mol1
H f [H 2 O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1
H f [NaHCO 3 (s)] = 951.0 kJ mol1
H f [Na 2 CO 3 (s)] = 1131 kJ mol1
WhichofthefollowingisthestandardenthalpychangeofdecompositionforNaHCO 3 (s)
i.e. 2NaHCO 3 (s)Na 2 CO 3 (s)+H 2 O(l)+CO 2 (g)?
A.
B.
C.
D.
859.5 kJ mol1
3713 kJ mol1
+91.5 kJ mol1
+1403 kJ mol1
134. Given that:
N 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2NO(g)
H 1 = +180.0 kJ mol1
2NO 2 (g) 2NO(g) + O 2 (g)
H 2 = +112.0 kJ mol1
What is the standard enthalpy change of the following reaction?
N 2 (g) + 2O 2 (g) 2NO 2 (g)
A. +68.0 kJ mol1
B. +292.0 kJ mol1
C. 68.0 kJ mol1
D. 292.0 kJ mol1
39
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
135. Given that:
H 2 (g) +
1
O 2 (g) H 2 O(l)
2
H 1 = 286.0 kJ mol1
N 2 O 5 (g) + H 2 O(l) 2HNO 3 (l)
H 2 = 77.0 kJ mol1
1
3
1
N 2 (g) + O 2 (g) + H 2 (g) HNO 3 (l)
2
2
2
H 3 = 174.0 kJ mol1
What is the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction?
2N 2 (g) + 5O 2 (g) 2N 2 O 5 (g)
A. 1422 kJ mol1
B. 619.0 kJ mol1
C. +189.0 kJ mol1
D. +30.0 kJ mol1
136. Consider the enthalpy change cycle shown below:
7C(s) + 4H 2 (g)
+7O 2 (g)
H 1
C 7 H 8 (l)
+2O 2 (g)
H 2
+9O 2 (g)
H 3
7CO 2 (g) + 4H 2 O(l)
Which of the following representations is correct?
A. H = H 1 + H 2 + H 3
B. H = H 1 + H 2 H 3
C. H = H 1 H 2 + H 3
D. H = H 1 H 2 H 3
137. Which of the following concerning the enthalpy change cycle shown below are
correct?
C 2 H 2 (g) +
5
+ O 2 (g)
2
H 1
H
+O 2 (g)
H 2
C 2 H 6 (g)
7
+ O 2 (g)
2
H 3
2CO 2 (g) + 3H 2 O(l)
40
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
(1) H = H 1 + H 2 H 3
(2) H 1 = H c [C 2 H 2 (g)]
(3) H
A.
B.
C.
D.
= H c [C 2 H 2 (g)] + 2 H c [H 2 (g)] H c [C 2 H 6 (g)]
(1) and (2) only
(1) and (3) only
(2) and (3) only
(1), (2) and (3)
138. Consider the enthalpy change cycle shown below:
NH 3 (g) + HCl(g)
NH 4 Cl(s)
H 2
H 1
1
1
N 2 (g) + 2H 2 (g) + Cl 2 (g)
2
2
Which of the following represents H 1 ?
A. H c [NH 3 (g)] + H f [HCl(g)]
B. H f [NH 3 (g)] + H c [HCl(g)]
C. H f [NH 3 (g)] + H f [HCl(g)]
D. H c [NH 3 (g)] + H c [HCl(g)]
[HCl(g)]
139. Given that:
H f [NO 2 (g)] = 32.0 kJ mol1
H f [NO(g)] = 90.0 kJ mol1
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of the reaction:
2NO 2 (g) 2NO(g) + O 2 (g)?
A. +58.0 kJ mol1
B. +116.0 kJ mol1
C. 58.0 kJ mol1
D. 116.0 kJ mol1
140. Given that:
O 2 (g) + O(g) O 3 (g)
H 1 = 105.0 kJ mol1
1
O 2 (g) + O 2 (g) O 3 (g)
2
H 2 = +143.0 kJ mol1
41
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of reaction:
A.
B.
C.
D.
1
O 2 (g) O(g)?
2
+248.0 kJ mol1
+38.0 kJ mol1
0 kJ mol1
248.0 kJ mol1
141. Given that:
H 1 = 393.5 kJ mol1
C(graphite) + O 2 (g) CO 2 (g)
H 2 (g) +
1
O 2 (g) H 2 O(l)
2
H 2 = 285.8 kJ mol1
H 3 = 3120 kJ mol1
2C 2 H 6 (g) + 7O 2 (g) 4CO 2 (g) + 6H 2 O(l)
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of formation of C 2 H 6 (g)?
A.
B.
C.
D.
+2440.7 kJ mol1
+1475.6 kJ mol1
3204.2 kJ mol1
84.4 kJ mol1
142. Given that:
CH 4 (g) + O 2 (g) CH 2 O(g) + H 2 O(g)
H 1 = 890.4 kJ mol1
CH 2 O(g) + O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + H 2 O(g)
H 2 = 563.5 kJ mol1
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of the reaction:
CH 4 (g) + 2O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(g)?
A. 1453.9 kJ mol1
B. 326.9 kJ mol1
C. 236.6 kJ mol1
D. +118.3 kJ mol1
143. Given that:
2C 2 H 5 OH(l) + 6O 2 (l) 4CO 2 (g) + 6H 2 O(l)
H = 2734 kJ mol1
H f [CO 2 (g)] = 395.0 kJ mol1
H f [H 2 O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1
What of the following is the standard enthalpy change of formation of C 2 H 5 OH(l)?
A.
B.
C.
281.0 kJ mol1
562.0 kJ mol1
+1026.5 kJ mol1
42
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
D.
+2053 kJ mol1
144. Given that:
H f [CO 2 (g)] = 395.0 kJ mol1
H f [CH 3 OH(l)] = 239.0 kJ
mol1
H f [H 2 O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1
Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of combustion of methanol,
CH 3 OH(l)?
A.
B.
C.
D.
442.0 kJ mol1
728.0 kJ mol1
1206 kJ mol1
+920.0 kJ mol1
145. Some standard enthalpy changes of formation are given in the table below.
Substance
H f /kJ mol1
CH 4 (g)
C 2 H 2 (g)
C 2 H 4 (g)
C 2 H 6 (g)
CO 2 (g)
H 2 O(l)
74.8
226.9
52.6
84.5
395.0
286.0
Which of the following hydrocarbons will release the greatest amount of heat when
burning 1.0 g of it in excess oxygen?
A. CH 4
B. C 2 H 2
C. C 2 H 4
D. C 2 H 6
146. Given that:
H f [CO(g)] = 110.5 kJ mol1
H f [CO 2 (g)] = 393.5 kJ mol1
What is the enthalpy change of the following reaction:
2CO(g) + 2CO 2 (g) 4C(s) + 3O 2 (g)?
A. 1008 kJ mol1
B. 566.0 kJ mol1
C. 504.0 kJ mol1
D. +1008 kJ mol1
147. Given that:
H c [C 2 H 2 (g)] = 1300 kJ mol1
H c [H 2 (g)] = 286.0 kJ mol1
43
HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View
Part VIII Chemical Reactions and Energy
H c [C 2 H 6 (g)] = 1560 kJ mol1
What is the enthalpy change of the following reaction:
C 2 H 2 (g) + 2H 2 (g) C 2 H 6 (g)?
A. 26 kJ mol1
B. +26 kJ mol1
C. 312 kJ mol1
D. +312 kJ mol1
Section 37.1
148.The enthalpy changes of some
reactions have to be determined
indirectly by applying Hesss Law.
Some reactions cannot be easily or
safely carried out in a calorimeter or
may lead to the formation of side
products.
149.Enthalpy level diagrams can
represent the enthalpy changes of the
reactions.
Enthalpy level diagrams can show
clearly the relative energy levels of
species involved in the reactions.
44
You might also like
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : VSEPR TheoryDocument17 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : VSEPR TheoryRavindar Purohit100% (1)
- Practical Organic Chemistry III ExamDocument3 pagesPractical Organic Chemistry III ExamTesfahun100% (1)
- Acids Bases Salts MCQsDocument18 pagesAcids Bases Salts MCQsSoniaAlexNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 20 - Coordination Compounds Nomenclature WorksheetDocument2 pagesWorksheet 20 - Coordination Compounds Nomenclature WorksheetKarmendra100% (1)
- Mechanism Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesMechanism Multiple Choice QuestionsAnonymous pgjIAZoNo ratings yet
- Mole Supplemental WorksheetDocument2 pagesMole Supplemental WorksheetNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Diesel Injection Pump COVEC-FDocument36 pagesDiesel Injection Pump COVEC-FPorras Edwin71% (7)
- Coal Mill SafetyDocument17 pagesCoal Mill SafetyJoko Dewoto100% (4)
- Topic 9 19 MC PracticeDocument18 pagesTopic 9 19 MC PracticeDharmesh Ramnarayan Yadav100% (1)
- Atomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersMalak AlqaidoomNo ratings yet
- Chem MCQ FinalDocument258 pagesChem MCQ FinalDare DevilNo ratings yet
- Redox MCQsDocument7 pagesRedox MCQsHarsh Walavalkar100% (1)
- Unit 11 MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 11 MCQJay VermaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemistry MCQDocument69 pagesIndustrial Chemistry MCQSatvik BeheraNo ratings yet
- G 11&12 Chemistry (2000-2011)Document50 pagesG 11&12 Chemistry (2000-2011)Samuel Legissa100% (4)
- Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure QuestionsDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding & Molecular Structure QuestionssingamroopaNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeyDocument3 pagesAlkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeySameer HussainNo ratings yet
- Test - D18 Dec 2022Document9 pagesTest - D18 Dec 2022PrinceNo ratings yet
- Class-XII (Chemistry) Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Objective Type QuestionsDocument9 pagesClass-XII (Chemistry) Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Objective Type QuestionsPranav DhimanNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument17 pagesElectrochemistryzohaibsalamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 10 Multiple-Choice Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Alkanes MCQDocument2 pagesAlkanes MCQJeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- MCQs pdf-1 PDFDocument5 pagesMCQs pdf-1 PDFEmman Ann100% (3)
- MCQ Structure of AtomDocument15 pagesMCQ Structure of AtomSasuke Itachi100% (1)
- Periodic Classification Revision QuestionsDocument6 pagesPeriodic Classification Revision QuestionsSumiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQs HandoutsDocument26 pagesChemistry MCQs HandoutsOsama Hasan91% (11)
- Chemistry Ch-1 Part IDocument5 pagesChemistry Ch-1 Part IDr. Abdul Haq BalochNo ratings yet
- Chemistry McqsDocument51 pagesChemistry McqsEngr Muhammad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1Document195 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1aditya kumar Agarwal100% (1)
- Mcqs Chapter No1 Basic Concepts McqsDocument6 pagesMcqs Chapter No1 Basic Concepts McqsHaider JalalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium MCQDocument13 pagesChemical Equilibrium MCQNidhi SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument29 pagesAldehydes and KetonesJiya singhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocument57 pagesChemistry Hydrogen and Its CompoundsYogesh Dongre100% (2)
- 10 Chapter Electrochemistry Short Question With Answers PDFDocument11 pages10 Chapter Electrochemistry Short Question With Answers PDFMARITIM GEOFFREY KIPLANGATNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds (Exercise+Answers)Document32 pagesCoordination Compounds (Exercise+Answers)Hanukkah100% (1)
- CM - TNJN HGVDocument4 pagesCM - TNJN HGV何小霞No ratings yet
- 8 CHAPTER CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQs PDFDocument6 pages8 CHAPTER CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQs PDFAmina Khan100% (3)
- Experimental Chemistry MCQs QuizDocument5 pagesExperimental Chemistry MCQs QuizIram TahiraNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases 8.1 and 8.2 MCQDocument4 pagesAcids and Bases 8.1 and 8.2 MCQAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Stoichiometry Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesCH 3 Stoichiometry Multiple ChoiceSusie Zhang100% (1)
- 0optical Isomerism - QuizDocument3 pages0optical Isomerism - QuizSanjay Mani Tripathi50% (2)
- CH 14Document28 pagesCH 14ffffffff dfdfdfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseAri Adiantari100% (1)
- Extraction of Metals (Multiple Choice) QPDocument9 pagesExtraction of Metals (Multiple Choice) QPAnsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis MCQDocument11 pagesElectrolysis MCQSavarinathan Maria Rayappan100% (1)
- Sicmyb - DPP Mole ConceptDocument6 pagesSicmyb - DPP Mole ConceptBorn to fightNo ratings yet
- IIT-JAM 2006 With Solution PDFDocument24 pagesIIT-JAM 2006 With Solution PDFgaurav100% (1)
- Exercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsDocument7 pagesExercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsNavita RajgariaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Transition Metals QuestionsDocument6 pagesChemistry Transition Metals Questionspersonpeople100% (1)
- Unit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument25 pagesUnit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsSAMBASIVA RAO YEMINENINo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Mcqs QuestionsDocument9 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Mcqs QuestionsGyanendra Vikram Maurya100% (1)
- Chapter 10. Sulphuric Acid: Short QuestionsDocument14 pagesChapter 10. Sulphuric Acid: Short QuestionsAbhay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes - MCQDocument9 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes - MCQMinuteBrain LearningNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKMahrishiShukla100% (1)
- Amines MCQDocument3 pagesAmines MCQaleena'No ratings yet
- MCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Document7 pagesMCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Sanjeev Chaudhary100% (1)
- 9.coordination Compounds KCET PYQsDocument2 pages9.coordination Compounds KCET PYQsPunith kumar100% (1)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry MCQs PDFDocument33 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry MCQs PDFSanjana Sanjay100% (1)
- Kinetics McqsDocument31 pagesKinetics McqsTayyaba SadaqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions CH 18 Samplepractice Exam Questions and AnswersDocument20 pagesChemistry Chemical Reactions CH 18 Samplepractice Exam Questions and Answersdao hoangNo ratings yet
- 2 Quizizz 2019 ptVIIIe DocDocument10 pages2 Quizizz 2019 ptVIIIe DocKM Tsang Ka ManNo ratings yet
- General Chemsitry 1 Course Test 2 2013Document6 pagesGeneral Chemsitry 1 Course Test 2 2013John BrownNo ratings yet
- Mole JokesDocument1 pageMole JokesNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Chemical ChangesDocument5 pagesChemical ChangesNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table SQ AnsDocument20 pagesPeriodic Table SQ AnsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Kinetics MCQDocument57 pagesKinetics MCQNg Swee Loong Steven100% (2)
- Periodic Table SQDocument17 pagesPeriodic Table SQNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Balanced EquationsDocument29 pagesBalanced EquationsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Mole GamesDocument3 pagesMole GamesNg Swee Loong Steven100% (1)
- Mole Project ChecklistDocument1 pageMole Project ChecklistNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Mole Internet ActivityDocument1 pageMole Internet ActivityNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice AnswersDocument16 pagesMultiple Choice AnswersholdonpainendsNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemistry MCQDocument69 pagesIndustrial Chemistry MCQNg Swee Loong Steven93% (15)
- Structured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part X Chemical EquilibriumDocument26 pagesStructured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part X Chemical EquilibriumNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds SQ AnsDocument51 pagesCarbon Compounds SQ AnsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Structured Question AnswersDocument33 pagesStructured Question AnswersNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Structured Questions AnswersDocument23 pagesStructured Questions AnswersNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- MCQ CeDocument64 pagesMCQ CePankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Structured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part VIII Chemical Reactions and EnergyDocument21 pagesStructured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part VIII Chemical Reactions and EnergyNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds MCQ AnsDocument30 pagesCarbon Compounds MCQ AnsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry MCQ AnsDocument7 pagesAnalytical Chemistry MCQ AnsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry AnswerDocument41 pagesAnalytical Chemistry AnswerNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- ChemistryQB Topic8a MC eDocument57 pagesChemistryQB Topic8a MC eNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- ChemistryQB Topic8a MC eDocument57 pagesChemistryQB Topic8a MC eNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- ChemistryQB Topic8c SQ eDocument27 pagesChemistryQB Topic8c SQ eNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Discharge Ignition of Energetic MaterialsDocument9 pagesElectrostatic Discharge Ignition of Energetic Materialspamos1111No ratings yet
- Form I: Mylan Laboratories Limited, Unit 3Document75 pagesForm I: Mylan Laboratories Limited, Unit 3jyothiNo ratings yet
- Ramadan Youssef Sakr Moustafa - Lecture 2-Chemical ReactionDocument49 pagesRamadan Youssef Sakr Moustafa - Lecture 2-Chemical ReactionAhmed GadNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet No.1Document1 pageProblem Sheet No.1Imran TahirNo ratings yet
- 2.5. Industrial Pollutants - 1102: Dilution PollutionDocument5 pages2.5. Industrial Pollutants - 1102: Dilution PollutionHina AftabNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation & ControlDocument56 pagesBoiler Operation & ControlMohammad Rawoof100% (2)
- Bcu370 Burner Control - Brochure PDFDocument6 pagesBcu370 Burner Control - Brochure PDFFernando QueirozNo ratings yet
- Normas Astm para Carbones Y Coques: Standard Terminology ofDocument14 pagesNormas Astm para Carbones Y Coques: Standard Terminology ofJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- Dr.M.P.Bhatti Sehar Afzal 1009-BH-CHEM-16: Government College University LahoreDocument7 pagesDr.M.P.Bhatti Sehar Afzal 1009-BH-CHEM-16: Government College University LahoreAayat MughalNo ratings yet
- Kinglake 90 116Document14 pagesKinglake 90 116robertaNo ratings yet
- Pns-Paes 246-2010 PDFDocument13 pagesPns-Paes 246-2010 PDFJoselito TucitNo ratings yet
- Lower (LEL) & Upper (UEL) Explosive Limits PDFDocument1 pageLower (LEL) & Upper (UEL) Explosive Limits PDFSale RadosavljevicNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Narayana Group of SchoolsDocument13 pagesInstructions:: Narayana Group of SchoolsAryaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0263876222004075 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0263876222004075 MainNUR IRYANIE BINTI AMIRUDDIN -No ratings yet
- Praesentation TBU - Fluidised Bed Combustion - EN PDFDocument32 pagesPraesentation TBU - Fluidised Bed Combustion - EN PDFjamjam1062No ratings yet
- Msds HNO3Document6 pagesMsds HNO3Ariesa Nurruhiyatna Al-adzaniNo ratings yet
- Service and Repair Manual: Coolant Heaters DBW 2010 DBW 2020 DBW 300Document84 pagesService and Repair Manual: Coolant Heaters DBW 2010 DBW 2020 DBW 300MiguelNo ratings yet
- MCQ IcgtDocument28 pagesMCQ IcgtSunny BhatiaNo ratings yet
- FIRE TECHNOLOGY AND ARSON INVESTIGATION QUESTIONS For CBRC NAGADocument10 pagesFIRE TECHNOLOGY AND ARSON INVESTIGATION QUESTIONS For CBRC NAGAJason CaballaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0360319922016998 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S0360319922016998 MainCarlos Herrique MatioloNo ratings yet
- Inert Gas SystemDocument69 pagesInert Gas SystemKishore Gopal89% (9)
- 4 in 1 Portable SmokehouseDocument5 pages4 in 1 Portable SmokehouseLeilani Delgado MoselinaNo ratings yet
- Answer 08 - Ithink - Soalan-B7Document3 pagesAnswer 08 - Ithink - Soalan-B7SUDARCHELVI A/P ALAGANDRAN Moe0% (1)
- Me 303 CH12Document47 pagesMe 303 CH12Osman KutluNo ratings yet
- Fire Emergency Preparedness SeminarDocument65 pagesFire Emergency Preparedness SeminarTAURUS EMS100% (1)
- Automobile Lesson Plan 2016 2017Document26 pagesAutomobile Lesson Plan 2016 2017Kiran ChristopherNo ratings yet
- CPV St. Charles Revised PSD - 082411Document363 pagesCPV St. Charles Revised PSD - 082411hermieNo ratings yet
- Combustion Modeling of Dual-Fuel Engines - 2Document2 pagesCombustion Modeling of Dual-Fuel Engines - 2helenNo ratings yet