Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laws/Definition: 1. Introduction To Physics
Laws/Definition: 1. Introduction To Physics
Uploaded by
Siti Salmah ErangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laws/Definition: 1. Introduction To Physics
Laws/Definition: 1. Introduction To Physics
Uploaded by
Siti Salmah ErangCopyright:
Available Formats
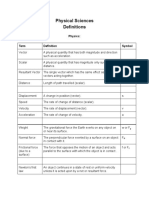
LAWS/DEFINITION
1. INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS
Sensitivity
Accuracy
Consistency
Parallax error
Zero error
Ability of instrument to detect
small change of quantity
measured.
Ability of instrument to give
reading closer to actual value.
Ability of instrument to give
constant reading every time
the measurement is made
When eyes is not
perpendicular to the scale
when take the reading
When the instrument give
reading when it is suppose to
be zero
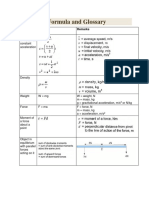
2. FORCES AND MOTION
Weight (N)
Gravitational force (N)
Gravitational
Acceleration due to
acceleration, g (10 gravitational force.
ms-2)
Elasticity
Property of matter that enables
an object to turn to its original
size and shape when the forces
acting on it are removed.
Inertia
Tendency of object to remain
at rest or moving with
constant velocity
Impulsive force
Rate of change of momentum
Impulse
Change of momentum
Focal point
Focal length of
lens
Focal length of
concave mirror
Snell law.
Refractive index
Point that all parallel light with
principal axis are converge to.
Distance between focal point
and the optical center
Distance between pole and the
principal focal point
Sin i
------- = constant
Sin r
Sin i
------Sin r
Refraction of light. Light change its speed and
direction when travel through
different medium
6. WAVES
Monochromatic
light
Constructive
interference
Destructive
interference
Frequency
Wavelength
Light that has one wavelength
only
When trough meet
trough//when crest meet crest
When trough meet crest
Number of oscillation in 1s
Distance between 2
consecutive trough/crest/wave
front
Diffraction
Wave phenomenon when wave
travel through obstacle of
gap/slit
Coherent sources Two sources that have same
frequency and same phase.
7. ELECTRICITY
3. FORCES AND PRESSURE
Ohms Law
Pressure
Force acting normally to the
unit of surface area.
Archimedes
A body that is wholly or
Principles
partially immerse in liquid, the
buoyant force = weight of
liquid displaced
Bernoulli principle Pressure of the fluid is lower
when speed of the fluid is
higher
4. HEAT
Thermal
equilibrium
Heat
Temperature
Specific heat
capacity
Heat capacity
Thermal
equilibrium
When net rate heat transfer
between two bodies is zero
Type of energy
Degree of hotness
Energy required to increase the
temperature of 1 kg substance
by 1oC.
Energy required to change
temperature of object by 1oC
Net heat transfer between two
bodies is zero.//temperature of
two body touching each other
is equal.
5. LIGHT
Critical angle
Angle of incidence when angle
of refraction=90o
Current is directly proportional
to the voltage when physical
condition and temperature is
constant,
9V battery
The battery supply 9J of
electrical energy to transfer 1C
of charge
9W, 12V bulb
The bulb use 9J of electrical
energy in 1s when connected to
12V power supply
8A
8C of charges has been transfer
in 1s
Emf
The work done by a source in
driving a unit of charge around
a complete circuit.
Potential
Work done to transfer 1C of
difference//voltage charge from one point to
another
Power
Amount of energy use in 1C
8. ELECTROMAGNETISM
Electromagnetic
induction
Catapult field
Electromagnet
Production of induced current
in solenoid when the solenoid
cut the magnetic field
Non-uniform magnetic field.
Soft iron winding with solenoid,
has magnetic field when
current flow through the
magnet and lost it when no
current flow.
Lenz Law
Determine the
direction of force
produced by
current carrying
conductor in
magnetic field
Determine pole of
solenoid
Determine the
direction of
current produced
by generator
Induced current produced in
the solenoid always oppose the
effect causing it
Use Fleming Left Hand Rule
Use right hand grip rule.
Use Flemings Right Hand Rule.
9. ELECTRONICS
Thermionic
emission
Logic gates
Electron release by a hot metal
surface
Electronic switch that have one
or more inputs but have only
one output
10. RADIOACTIVITY
Radioisotope
Nuclear fission
Nuclear fusion
Half life
Beta particle
Alpha particle
Gamma ray
The isotope with unstable
nuclei that emit radioactive
radiations.
A process of breaking up heavy
nucleus into lighter nucleus
A process of merging lighter
nuclei into heavy nucleus.
Time taken for un-decay nuclei
become half from its original
amount.
Fast moving electron.
Helium nucleus
An electromagnetic wave
==============================
Precautionary steps during experiment
Eye must be perpendicular to the scale of
ammeter/voltmeter/meter rule when take the
reading.
All connection must be tight enough.
Take several reading and find the average.
For each value of manipulated variable, take
several reading of responding variable and find
the average
Do not on the switch for longer time.
Turn off the switch when not take the reading.
You might also like
- PDF New Perspectives On The Internet Comprehensive Loose Leaf Version 10Th Edition Jessica Evans Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF New Perspectives On The Internet Comprehensive Loose Leaf Version 10Th Edition Jessica Evans Ebook Full Chapterlorna.rayfield998100% (3)
- The Dark ManDocument2 pagesThe Dark ManHyemi Mimi100% (1)
- Physics GlossaryDocument21 pagesPhysics GlossaryKing VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DefinitionsDocument8 pagesPhysical Science DefinitionsJason KampsNo ratings yet
- IB HL Physics DefinitionsDocument7 pagesIB HL Physics DefinitionsshinyrayquazaNo ratings yet
- Generalized Problematic Internet Use Scale 2 (Gpius 2) Scale Items & InstructionsDocument2 pagesGeneralized Problematic Internet Use Scale 2 (Gpius 2) Scale Items & InstructionsShariqa100% (1)
- Definitions & LawsDocument4 pagesDefinitions & LawsNabyh AhmedNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics List of DefinitionDocument12 pagesSPM Physics List of DefinitionCrazyElfNo ratings yet
- Physics SPMDocument2 pagesPhysics SPMIman0% (1)
- General Notes and Definitions For InstanDocument12 pagesGeneral Notes and Definitions For Instandazai osamuNo ratings yet
- Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesExam QuestionsJohnNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Presentation FinalDocument24 pagesLab 1 Presentation Finalvenkat_09No ratings yet
- Light From Any Ordinary Source (Such As A Flame) Is Usually: Unpolarized The Wavelength of Red Light Is 700 Nm. Its Frequency IsDocument7 pagesLight From Any Ordinary Source (Such As A Flame) Is Usually: Unpolarized The Wavelength of Red Light Is 700 Nm. Its Frequency IsAbrish AliNo ratings yet
- Definition Menaning PhysicsDocument14 pagesDefinition Menaning PhysicsIEyra ShaHeraNo ratings yet
- List of Definitions Spm-PhysicsDocument14 pagesList of Definitions Spm-PhysicsNiceman NatiqiNo ratings yet
- h2 A Level Physics Definition ListDocument4 pagesh2 A Level Physics Definition ListJanel NgNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics NotesDocument16 pagesIGCSE Physics NotesMhdAboualy84% (32)
- h2 Physics DefinitionsDocument7 pagesh2 Physics DefinitionsJerald LimNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics CheatsheetDocument11 pagesO Level Physics Cheatsheetkoh_tian_2No ratings yet
- Physics Definition List Form 5Document6 pagesPhysics Definition List Form 5Yinxin OngNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyDocument12 pagesUnit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyShivani MajithiaNo ratings yet
- GCSC Physics GlossaryDocument8 pagesGCSC Physics GlossarysmeenaNo ratings yet
- Definitions AS PhysicsDocument4 pagesDefinitions AS PhysicsFazelah YakubNo ratings yet
- Definitions A2 PhysicsDocument8 pagesDefinitions A2 PhysicsBallonNo ratings yet
- Physics A Level DefinitionsDocument12 pagesPhysics A Level DefinitionsNaillah Saba100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument213 pagesPhysicsBilal Hussain Shah100% (1)
- Physics 2Document187 pagesPhysics 2Bilal Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC CCC CC CDocument15 pagesCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC CCC CC CArmoha RushdanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - WAVESDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - WAVESSiraf IldaNo ratings yet
- Handout 1Document64 pagesHandout 1Sonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Physics: PressureDocument7 pagesPhysics: PressureJason TehNo ratings yet
- UPCAT Physics Review Part 2Document37 pagesUPCAT Physics Review Part 2Clarise VicenteNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Definition ListDocument25 pagesSPM Physics Definition ListIvan TehNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument40 pagesObjectivesEunielyn SecretoNo ratings yet
- 物理定义Document4 pages物理定义Ming ZengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To PhysicsDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Physicsbrenwong@ymail.comNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument10 pagesPhysicswww.shubhasreetabbu2001No ratings yet
- Presentation - Basic Aircraft Familiarization Course - AvionicsDocument39 pagesPresentation - Basic Aircraft Familiarization Course - AvionicsFlorencioPautangNo ratings yet
- All 9702 DefinitionsDocument4 pagesAll 9702 DefinitionsGame ZoneNo ratings yet
- Physics All DefinitionsDocument3 pagesPhysics All DefinitionssamNo ratings yet
- Physics Module AnswerDocument87 pagesPhysics Module AnswerJarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- h2 Physics DefinitionsDocument7 pagesh2 Physics DefinitionsSyed Osama HussainNo ratings yet
- Phy Form 5 DefDocument4 pagesPhy Form 5 DefvitthiyamuruNo ratings yet
- A2 DefinitionsDocument9 pagesA2 DefinitionsraniaNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Definition ListDocument11 pagesSPM Physics Definition ListLawrence ChinNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Terms and DefinitionDocument3 pagesForm 4 Physics Terms and DefinitionJedidah JongNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric Measurements Galvanic or Voltaic Cell: ElectrolyticDocument21 pagesPotentiometric Measurements Galvanic or Voltaic Cell: ElectrolyticAmr GamalNo ratings yet
- All Definitions For Physics 0625 &0972Document8 pagesAll Definitions For Physics 0625 &0972Ahmed SherifNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 ReviewerDocument1 pageSCIENCE 8 Reviewerronnajane.manuelNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 43761Document13 pagesUntitled Document 43761Daiquan StantonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document9 pagesUnit 2abdulnasim123No ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Terms and Definition Chapter 1: Introduction To Physics Physical Quantities Base QuantitiesDocument8 pagesPhysics Form 4 Terms and Definition Chapter 1: Introduction To Physics Physical Quantities Base QuantitiesAmir FaisalNo ratings yet
- Physics O Level Definition and Law and Principles ListDocument9 pagesPhysics O Level Definition and Law and Principles ListTien Wai NgNo ratings yet
- A2-Physics Definitions PDFDocument6 pagesA2-Physics Definitions PDFAbdullah IjazNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureFrom EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureNo ratings yet
- Part UhxDocument51 pagesPart UhxSaif Eddine MJNo ratings yet
- Kohlberg's Stages of Moral DevelopmentDocument14 pagesKohlberg's Stages of Moral DevelopmentMarvelyn De StoTomas IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Understanding Sars-Cov-2-Induced Systemic Amyloidosis: BiorxivDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Sars-Cov-2-Induced Systemic Amyloidosis: BiorxivAntonisNo ratings yet
- Shattered Reflections A Journey Beyond The MirrorDocument13 pagesShattered Reflections A Journey Beyond The MirrorSweetheart PrinceNo ratings yet
- Naamlp 2002 ProceedDocument578 pagesNaamlp 2002 ProceedRussell HartillNo ratings yet
- GDPR ReportDocument84 pagesGDPR ReportKingPlaysNo ratings yet
- Peptides and Proteins: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocument30 pagesPeptides and Proteins: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- How To Download A Windows 10 ISO File - PCWorldDocument3 pagesHow To Download A Windows 10 ISO File - PCWorldRajeev BatraNo ratings yet
- Informe Sobre El Manejo de CostasDocument88 pagesInforme Sobre El Manejo de CostasMetro Puerto RicoNo ratings yet
- Form 137Document2 pagesForm 137Raymund BondeNo ratings yet
- GEO01 - CO1.2 - Introduction To Earth Science (Geology)Document14 pagesGEO01 - CO1.2 - Introduction To Earth Science (Geology)Ghia PalarcaNo ratings yet
- Elrc 4507 Unit PlanDocument4 pagesElrc 4507 Unit Planapi-284973023No ratings yet
- Muac MunichaccDocument24 pagesMuac MunichaccDelavillièreNo ratings yet
- Arlegui Seminar RoomDocument1 pageArlegui Seminar RoomGEMMA PEPITONo ratings yet
- TakeawayDocument6 pagesTakeawayWilman VasquezNo ratings yet
- Teleprotection Equipment ManualDocument71 pagesTeleprotection Equipment ManualThạch TháiNo ratings yet
- LG 49uf680tDocument40 pagesLG 49uf680tnghanoiNo ratings yet
- BlueStack Platform Marketing PlanDocument10 pagesBlueStack Platform Marketing PlanFıratcan KütükNo ratings yet
- Ai-Ai ResumeDocument3 pagesAi-Ai ResumeNeon True BeldiaNo ratings yet
- Essay Wise ChildrenDocument2 pagesEssay Wise ChildrenCarolina MariangelesNo ratings yet
- HMT (U4)Document23 pagesHMT (U4)maniNo ratings yet
- 1.2 FMCC221 - Introduction To International Businesss - Part 1Document19 pages1.2 FMCC221 - Introduction To International Businesss - Part 1Bernie D. TeguenosNo ratings yet
- HSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Document5 pagesHSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Snehal PanchalNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummaryRosida IdaNo ratings yet
- EEET423L Final ProjectDocument7 pagesEEET423L Final ProjectAlan ReyesNo ratings yet
- AQU4518R4 DatasheetDocument2 pagesAQU4518R4 Datasheetcostin.bantoiuNo ratings yet
- STEWART Briony Kumiko and The Dragon FINAL2010Document8 pagesSTEWART Briony Kumiko and The Dragon FINAL2010Tahnee HallNo ratings yet