Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air and Water: Measuring The Percentage of Oxygen in Air
Air and Water: Measuring The Percentage of Oxygen in Air
Uploaded by
Joseph LimCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Folio Chemistry F4 (Manufactured Substances in Industry)Document31 pagesFolio Chemistry F4 (Manufactured Substances in Industry)JackOss93No ratings yet
- Manufacture of Oxygen by Linde Frankl's ProcessDocument60 pagesManufacture of Oxygen by Linde Frankl's ProcessAhmed Ali100% (1)
- Water Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsFrom EverandWater Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Foglerp10 3 SolDocument5 pagesFoglerp10 3 SolWahyu Riansyah100% (1)
- Comparacion Entre ASTM D7169 y TBPDocument28 pagesComparacion Entre ASTM D7169 y TBPDesiree Molina100% (1)
- Air and WaterDocument9 pagesAir and WaterFrancis EssilfieNo ratings yet
- Air and Water IGCSE NotesDocument26 pagesAir and Water IGCSE NotesMisbah Kamran100% (1)
- Chapter 5-The Air Around UsDocument50 pagesChapter 5-The Air Around UsGenevieve Yong100% (1)
- Topic.10 Chemistry of Our EnviromentDocument12 pagesTopic.10 Chemistry of Our EnviromentJoyce AmirNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Air and WaterDocument6 pagesCH 11 Air and Waterlayan alharbiNo ratings yet
- Air and The Atmosphere - AKHS Edition 2020Document27 pagesAir and The Atmosphere - AKHS Edition 2020Kim SewoonNo ratings yet
- MYP 4 Chemistry I-BookDocument121 pagesMYP 4 Chemistry I-Bookchaitanya.kalambkarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, L-7, Air and AtmosphereDocument5 pagesChemistry, L-7, Air and AtmospheremilliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project (1) (Mohamed Part)Document6 pagesChemistry Project (1) (Mohamed Part)mohamed amirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The EnviromentDocument32 pagesChemistry of The Enviromentsalman ahsanNo ratings yet
- Air NotesDocument11 pagesAir NotesFatima AliNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument32 pagesChemistryEthan PhilipNo ratings yet
- Air and Water ChemistryDocument24 pagesAir and Water ChemistryShaman Samuel GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Lee Hock TiangDocument27 pagesPrepared By: Lee Hock TiangNick LeeNo ratings yet
- N, Co, O and Inert/ Noble Gases. Air Also Contains Very Small Traces of Methane Gas, S, So, CO and Oxides of Nitrogen E.G. NO, N O, NoDocument16 pagesN, Co, O and Inert/ Noble Gases. Air Also Contains Very Small Traces of Methane Gas, S, So, CO and Oxides of Nitrogen E.G. NO, N O, NotavongaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Air WaterDocument13 pagesChapter 11 Air WaterAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Air Combustion, Rusting and Fire Fighting.Document18 pagesTopic 6 Air Combustion, Rusting and Fire Fighting.Trump DonaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document7 pagesChapter 7rajana ramliNo ratings yet
- AIR NotesDocument5 pagesAIR NotesjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Products and Effects of CombustionDocument5 pagesProducts and Effects of CombustionLaura IonescuNo ratings yet
- Athmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsDocument12 pagesAthmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Module - 2Document3 pagesChapter 19 Module - 2piyushdbhatiNo ratings yet
- Survey of Industrial Chemestry - Philip J. ChenierDocument13 pagesSurvey of Industrial Chemestry - Philip J. ChenierBiain A SecasNo ratings yet
- Volume Composition of Gases Present in Dry Air.: Nitrogen: Oxygen: Noble Gases: (Mainly) Carbon DioxideDocument28 pagesVolume Composition of Gases Present in Dry Air.: Nitrogen: Oxygen: Noble Gases: (Mainly) Carbon DioxideLee Jia YingNo ratings yet
- CLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionDocument12 pagesCLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionHirakjyoti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Chemistry of Our EnvironmentDocument6 pagesChapter 17 - Chemistry of Our Environmenthagridpotter658No ratings yet
- Q1. Write Briefly On Composition of Atmosphere Ans.: It Is Caused by Burning Fossil Fuels, Like Coal and PetroleumDocument6 pagesQ1. Write Briefly On Composition of Atmosphere Ans.: It Is Caused by Burning Fossil Fuels, Like Coal and PetroleumRonnith NandyNo ratings yet
- Athmosphere and Environment - 1 - 2Document2 pagesAthmosphere and Environment - 1 - 2Asim HussainNo ratings yet
- ICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 8 Exercise QuestionsDocument16 pagesICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 8 Exercise QuestionsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Air Part IDocument23 pagesAir Part IGuru Bhat100% (1)
- 2324 Level M Chemistry Topic Air NotesDocument5 pages2324 Level M Chemistry Topic Air Notesmaryamzerarka26No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Manufactured Substances in Industry: Stage 1Document12 pagesChapter 9: Manufactured Substances in Industry: Stage 1malcovishesNo ratings yet
- Air and BurningDocument11 pagesAir and Burningsanat kr pratihar100% (1)
- Class 7 Air and AtmosphereDocument4 pagesClass 7 Air and AtmosphereBranded HackerNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry (Air)Document32 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry (Air)Hussain HashmiNo ratings yet
- BCHE 111L - ULO3aDocument5 pagesBCHE 111L - ULO3aKaris DemetriaNo ratings yet
- ATMOSPHEHEREDocument3 pagesATMOSPHEHEREMyshaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry New NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry New NotesDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Worksheet AirDocument4 pagesYear 11 Worksheet AirMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Manufacture Nitric AcidDocument9 pagesManufacture Nitric AcidDjayustinus Heri HermawanNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text 1Document5 pagesExplanation Text 1haderaspatiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideDocument15 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideS M AkashNo ratings yet
- Nitrgen Fertlisers-1Document8 pagesNitrgen Fertlisers-1Imen KsibiNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 11 Air and Water - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument77 pagesFlashcards - Topic 11 Air and Water - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEKendrickNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank 2017 NewDocument22 pagesChemistry Question Bank 2017 Newஅன்புடன் அஸ்வின்No ratings yet
- Folio KimiaDocument12 pagesFolio KimiaAishiteru RamenNo ratings yet
- II. Cycles of MatterDocument19 pagesII. Cycles of Matterapi-239353579No ratings yet
- Chapter 15, 16 - Air and Water & Sulfur & Inorganic Carbon PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 15, 16 - Air and Water & Sulfur & Inorganic Carbon PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument38 pagesChemistry NotesTedNo ratings yet
- Water and AirDocument45 pagesWater and Air青木ケイNo ratings yet
- Gaseous FuelsDocument8 pagesGaseous FuelsvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Air NotesDocument6 pagesAir NotesSadaf ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Air and CombustionDocument38 pagesAir and Combustionhassanpeter617No ratings yet
- Hydrogen ProductionDocument14 pagesHydrogen ProductionAbid YusufNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts about Nitrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Nitrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Noxerior Brochure Special Plants 2014Document7 pagesNoxerior Brochure Special Plants 2014Arjav DesaiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Engineering and AutomationDocument2 pagesDynamic Engineering and Automationusaid saifullahNo ratings yet
- Chromatography 1686504920Document21 pagesChromatography 1686504920Annisa JuliayantiNo ratings yet
- Polimerisasi PolietilenaDocument16 pagesPolimerisasi PolietilenaKidung Wulan UtamiNo ratings yet
- Separation of Hydrocarbons by Packed Column GC: Bulletin 743LDocument12 pagesSeparation of Hydrocarbons by Packed Column GC: Bulletin 743LANU CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Platts History of Oil Infographic NoDocument1 pagePlatts History of Oil Infographic Nojohndo3No ratings yet
- Crude Tower Simulation (Aspen Plus V8.6)Document53 pagesCrude Tower Simulation (Aspen Plus V8.6)Nabeel SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Costs of Storing and Transporting HydrogenDocument216 pagesCosts of Storing and Transporting Hydrogenknoxd77No ratings yet
- CHM271 - Chapter 5 Chemical Kinetics (Part 1-3)Document40 pagesCHM271 - Chapter 5 Chemical Kinetics (Part 1-3)happyflowerNo ratings yet
- Black Liquor Incineration - Process, Chemistry and Ash Fusion Characteristics-By AjDocument41 pagesBlack Liquor Incineration - Process, Chemistry and Ash Fusion Characteristics-By AjAnkit Jain100% (2)
- A Review of Current Practices For The Completion in North Sea AreaDocument24 pagesA Review of Current Practices For The Completion in North Sea AreaGrant HosieNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil PricesDocument6 pagesCrude Oil Pricesshubhanjali kesharwaniNo ratings yet
- 300 MW Anthracite Coal Fired Power Station Boiler & AuxiliariesDocument277 pages300 MW Anthracite Coal Fired Power Station Boiler & AuxiliariesSendhilKumarNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy: Felipe Centeno, Khamid Mahkamov, Electo E. Silva Lora, Rubenildo V. AndradeDocument12 pagesRenewable Energy: Felipe Centeno, Khamid Mahkamov, Electo E. Silva Lora, Rubenildo V. AndradeAndres Mauricio Rojas MantillaNo ratings yet
- Downloadable Contractor DirectoryDocument4 pagesDownloadable Contractor DirectoryJAGUAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Presentation Slides About India LNGDocument3 pagesPresentation Slides About India LNGSatish Kumar100% (1)
- Unit+9 Chemical+Kinetics PDFDocument7 pagesUnit+9 Chemical+Kinetics PDFSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- Achieve Success in Gasoline HydrotreatingDocument6 pagesAchieve Success in Gasoline Hydrotreatingdonald55555No ratings yet
- CHM 096 Tutorial 2: (Chemical Equilibrium)Document3 pagesCHM 096 Tutorial 2: (Chemical Equilibrium)Sheh Muhammad AfnanNo ratings yet
- The Reaction Quotient (Q) : Name - Chem Worksheet 18-4Document1 pageThe Reaction Quotient (Q) : Name - Chem Worksheet 18-4Temwani Malema0% (1)
- Cylinder Pressure-Relief Devices: Safetygram 15Document4 pagesCylinder Pressure-Relief Devices: Safetygram 15johnNo ratings yet
- Exothermic & Endothermic Reactions 1 QPDocument23 pagesExothermic & Endothermic Reactions 1 QPGoogle map with MING HIN LINo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 - MCQ Separation of SubstancesDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 6 - MCQ Separation of Substancesvinod1577100% (3)
- Introduction To City Gas DistributionDocument19 pagesIntroduction To City Gas DistributionKarmendraNo ratings yet
- Casale Technologies For New Grass-Roots PlantsDocument10 pagesCasale Technologies For New Grass-Roots PlantsNguyen Thanh SangNo ratings yet
- Report On WTPDocument3 pagesReport On WTPshakilNo ratings yet
- 04 Solid Bed DehydrationDocument23 pages04 Solid Bed DehydrationMohamed SahnounNo ratings yet
- Dehydration of Natural Gas by Solid DesiccantDocument20 pagesDehydration of Natural Gas by Solid DesiccantMadhankumar LakshmipathyNo ratings yet
Air and Water: Measuring The Percentage of Oxygen in Air
Air and Water: Measuring The Percentage of Oxygen in Air
Uploaded by
Joseph LimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air and Water: Measuring The Percentage of Oxygen in Air
Air and Water: Measuring The Percentage of Oxygen in Air
Uploaded by
Joseph LimCopyright:
Available Formats
Air and Water
1. The air consist of 78% of nitrogen; 21% of oxygen and the remaining 1% are
others gases ( CO2; water vapour and noble gases)
2. Oxygen is important to us as we need it for the process called respiration.
3. Glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy
4. The energy from respiration keeps us warm and allow us to move as well as
contributing to different reaction in our bodies.
Measuring the percentage of oxygen in air
1. Heat the tube containing copper using Bunsen burner. Then push in plunge A
and force the air to plunge B and from B to A. Repeat few times. Oxygen will
react with copper, turning it black.
2. Stop heating after about 3 minutes, and allow it to cool. Then push the air
into one syringe and measure its volume.
3. Repeat step 1 and 2 until the volume of the gas remain steady.
Separation of air
1. Air can be separated using fractional distillation but first air is cooled to liquid
before proceeding.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Air is pumped into the plant, and filtered to remove the particles.
Next, water vapour, carbon dioxide and pollutant are removed.
Then the air is compressed and is cooled down again by recycling cold air.
The cold, compressed air is passed through a jet, into a larger space allowing
the air to expand rapidly which makes it very cold.
Note: Step 3 & 4 are repeated several times and each time the air get cooler.
5. The liquid air is pumped into the fractionating column. It is slowly warmed up
and the gases boil off one by one.
The main air pollutant
Pollutant
Carbon monoxide
Sources
When carbon compound
in fossil fuels burnt in
absent/too little of air.
Sulphur dioxide
When Sulphur compound
in fossil fuels burnt.
Power station are the
main source.
Nitrogen oxides
When nitrogen and
oxygen react together.
Combustion of tetra-etyl
lead will produce particles
of other lead compound
Lead compounds
Harm
Poisonous as it combined
with haemoglobin in
blood and prevents it
from carrying oxygen
around the body.
Irritates the eyes and
throat and causes
respiration problem.
Causes acid rain that
corrodes building walls,
sculpture.
Cause respiratory
problem and acid rain
Damage childrens brains
and it also damage
kidneys and nervous
system in adults
Ways to reduce air pollution
1. Through flue gas desulfurization
2. Banning of lead in petrol
3. Using catalytic converters in exhaust.
Catalytic converter
1. Harmful gases are produced when petrol is burned.
2. Catalytic converter absorbed these harmful gases and form other gases that
are not harmful.
3. The catalyst are usually made of transition element such as platimum,
palladium, and rhodiums which are coated onto a ceramic honeycomb
(increase surface area).
4. The converter usually have two compartment A and B:
A: harmful component are reduced. Nitrogen and oxygen is flowed to B.
2NO(g) N2(g) + O2(g)
B: harmful compounds are oxidized, using the oxygen from A.
2CO(g) + O2(g) 2CO2(g)
The harmless products then flow out the exhaust pipe.
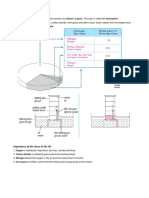
Rusting
1. Rusting is the corrosion of iron and steel.
2. Testing of rusting:
a. Test tube with dry air (calcium carbonate to dry the air)
b. Test tube with boiled water
c. Test tube with air and water
d. As a result, the nail in C has rust on it. Rusting required water and air.
e. 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) + 4H2O(l) 2Fe2O3.2H2O(s)
3. Way to prevent rusting:
a. Cover the iron:
- Paint
- Grease
- Galvanising
b. Sacrificial protection
Water
1. Uses of water:
Places
Uses
Home
Drinking, cooking, washing
Farms
Drinking and water crops
Industry
Solvent, Washing, Cooling
Power station
Make steam which drive the turbine
2. Underground water are known as groundwater and the rocks that trap or
hold the underground water is known as aquifer.
3. Water treatment:
i.
The water is pumped in and a screen is used to trap big particles.
ii.
A coagulant is added to make the suspended small particles stick
together. (iron(III) sulfate)
iii.
Air is blown through the water in floatation tanks to make the
coagulated particles to float and are skimmed off.
iv.
The water is then passed through a bed of fine sand to filter it.
v.
The water may go through further filter such as more sand or charcoal
to remove bad taste and odour.
vi.
Chlorine is added to kill bacteria and microbes
vii.
Fluoride is added to prevent tooth decay.
viii.
Lastly, water is pumped to the storage reservoir ready to pump to
homes.
You might also like
- Folio Chemistry F4 (Manufactured Substances in Industry)Document31 pagesFolio Chemistry F4 (Manufactured Substances in Industry)JackOss93No ratings yet
- Manufacture of Oxygen by Linde Frankl's ProcessDocument60 pagesManufacture of Oxygen by Linde Frankl's ProcessAhmed Ali100% (1)
- Water Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsFrom EverandWater Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Foglerp10 3 SolDocument5 pagesFoglerp10 3 SolWahyu Riansyah100% (1)
- Comparacion Entre ASTM D7169 y TBPDocument28 pagesComparacion Entre ASTM D7169 y TBPDesiree Molina100% (1)
- Air and WaterDocument9 pagesAir and WaterFrancis EssilfieNo ratings yet
- Air and Water IGCSE NotesDocument26 pagesAir and Water IGCSE NotesMisbah Kamran100% (1)
- Chapter 5-The Air Around UsDocument50 pagesChapter 5-The Air Around UsGenevieve Yong100% (1)
- Topic.10 Chemistry of Our EnviromentDocument12 pagesTopic.10 Chemistry of Our EnviromentJoyce AmirNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Air and WaterDocument6 pagesCH 11 Air and Waterlayan alharbiNo ratings yet
- Air and The Atmosphere - AKHS Edition 2020Document27 pagesAir and The Atmosphere - AKHS Edition 2020Kim SewoonNo ratings yet
- MYP 4 Chemistry I-BookDocument121 pagesMYP 4 Chemistry I-Bookchaitanya.kalambkarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, L-7, Air and AtmosphereDocument5 pagesChemistry, L-7, Air and AtmospheremilliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project (1) (Mohamed Part)Document6 pagesChemistry Project (1) (Mohamed Part)mohamed amirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The EnviromentDocument32 pagesChemistry of The Enviromentsalman ahsanNo ratings yet
- Air NotesDocument11 pagesAir NotesFatima AliNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument32 pagesChemistryEthan PhilipNo ratings yet
- Air and Water ChemistryDocument24 pagesAir and Water ChemistryShaman Samuel GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Lee Hock TiangDocument27 pagesPrepared By: Lee Hock TiangNick LeeNo ratings yet
- N, Co, O and Inert/ Noble Gases. Air Also Contains Very Small Traces of Methane Gas, S, So, CO and Oxides of Nitrogen E.G. NO, N O, NoDocument16 pagesN, Co, O and Inert/ Noble Gases. Air Also Contains Very Small Traces of Methane Gas, S, So, CO and Oxides of Nitrogen E.G. NO, N O, NotavongaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Air WaterDocument13 pagesChapter 11 Air WaterAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Air Combustion, Rusting and Fire Fighting.Document18 pagesTopic 6 Air Combustion, Rusting and Fire Fighting.Trump DonaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document7 pagesChapter 7rajana ramliNo ratings yet
- AIR NotesDocument5 pagesAIR NotesjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Products and Effects of CombustionDocument5 pagesProducts and Effects of CombustionLaura IonescuNo ratings yet
- Athmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsDocument12 pagesAthmosphere and Environment Research For O LevelsAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Module - 2Document3 pagesChapter 19 Module - 2piyushdbhatiNo ratings yet
- Survey of Industrial Chemestry - Philip J. ChenierDocument13 pagesSurvey of Industrial Chemestry - Philip J. ChenierBiain A SecasNo ratings yet
- Volume Composition of Gases Present in Dry Air.: Nitrogen: Oxygen: Noble Gases: (Mainly) Carbon DioxideDocument28 pagesVolume Composition of Gases Present in Dry Air.: Nitrogen: Oxygen: Noble Gases: (Mainly) Carbon DioxideLee Jia YingNo ratings yet
- CLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionDocument12 pagesCLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionHirakjyoti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Chemistry of Our EnvironmentDocument6 pagesChapter 17 - Chemistry of Our Environmenthagridpotter658No ratings yet
- Q1. Write Briefly On Composition of Atmosphere Ans.: It Is Caused by Burning Fossil Fuels, Like Coal and PetroleumDocument6 pagesQ1. Write Briefly On Composition of Atmosphere Ans.: It Is Caused by Burning Fossil Fuels, Like Coal and PetroleumRonnith NandyNo ratings yet
- Athmosphere and Environment - 1 - 2Document2 pagesAthmosphere and Environment - 1 - 2Asim HussainNo ratings yet
- ICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 8 Exercise QuestionsDocument16 pagesICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 8 Exercise QuestionsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Air Part IDocument23 pagesAir Part IGuru Bhat100% (1)
- 2324 Level M Chemistry Topic Air NotesDocument5 pages2324 Level M Chemistry Topic Air Notesmaryamzerarka26No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Manufactured Substances in Industry: Stage 1Document12 pagesChapter 9: Manufactured Substances in Industry: Stage 1malcovishesNo ratings yet
- Air and BurningDocument11 pagesAir and Burningsanat kr pratihar100% (1)
- Class 7 Air and AtmosphereDocument4 pagesClass 7 Air and AtmosphereBranded HackerNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry (Air)Document32 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry (Air)Hussain HashmiNo ratings yet
- BCHE 111L - ULO3aDocument5 pagesBCHE 111L - ULO3aKaris DemetriaNo ratings yet
- ATMOSPHEHEREDocument3 pagesATMOSPHEHEREMyshaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry New NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry New NotesDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Worksheet AirDocument4 pagesYear 11 Worksheet AirMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Manufacture Nitric AcidDocument9 pagesManufacture Nitric AcidDjayustinus Heri HermawanNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text 1Document5 pagesExplanation Text 1haderaspatiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideDocument15 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideS M AkashNo ratings yet
- Nitrgen Fertlisers-1Document8 pagesNitrgen Fertlisers-1Imen KsibiNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 11 Air and Water - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument77 pagesFlashcards - Topic 11 Air and Water - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEKendrickNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank 2017 NewDocument22 pagesChemistry Question Bank 2017 Newஅன்புடன் அஸ்வின்No ratings yet
- Folio KimiaDocument12 pagesFolio KimiaAishiteru RamenNo ratings yet
- II. Cycles of MatterDocument19 pagesII. Cycles of Matterapi-239353579No ratings yet
- Chapter 15, 16 - Air and Water & Sulfur & Inorganic Carbon PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 15, 16 - Air and Water & Sulfur & Inorganic Carbon PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument38 pagesChemistry NotesTedNo ratings yet
- Water and AirDocument45 pagesWater and Air青木ケイNo ratings yet
- Gaseous FuelsDocument8 pagesGaseous FuelsvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Air NotesDocument6 pagesAir NotesSadaf ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Air and CombustionDocument38 pagesAir and Combustionhassanpeter617No ratings yet
- Hydrogen ProductionDocument14 pagesHydrogen ProductionAbid YusufNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts about Nitrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Nitrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Noxerior Brochure Special Plants 2014Document7 pagesNoxerior Brochure Special Plants 2014Arjav DesaiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Engineering and AutomationDocument2 pagesDynamic Engineering and Automationusaid saifullahNo ratings yet
- Chromatography 1686504920Document21 pagesChromatography 1686504920Annisa JuliayantiNo ratings yet
- Polimerisasi PolietilenaDocument16 pagesPolimerisasi PolietilenaKidung Wulan UtamiNo ratings yet
- Separation of Hydrocarbons by Packed Column GC: Bulletin 743LDocument12 pagesSeparation of Hydrocarbons by Packed Column GC: Bulletin 743LANU CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Platts History of Oil Infographic NoDocument1 pagePlatts History of Oil Infographic Nojohndo3No ratings yet
- Crude Tower Simulation (Aspen Plus V8.6)Document53 pagesCrude Tower Simulation (Aspen Plus V8.6)Nabeel SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Costs of Storing and Transporting HydrogenDocument216 pagesCosts of Storing and Transporting Hydrogenknoxd77No ratings yet
- CHM271 - Chapter 5 Chemical Kinetics (Part 1-3)Document40 pagesCHM271 - Chapter 5 Chemical Kinetics (Part 1-3)happyflowerNo ratings yet
- Black Liquor Incineration - Process, Chemistry and Ash Fusion Characteristics-By AjDocument41 pagesBlack Liquor Incineration - Process, Chemistry and Ash Fusion Characteristics-By AjAnkit Jain100% (2)
- A Review of Current Practices For The Completion in North Sea AreaDocument24 pagesA Review of Current Practices For The Completion in North Sea AreaGrant HosieNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil PricesDocument6 pagesCrude Oil Pricesshubhanjali kesharwaniNo ratings yet
- 300 MW Anthracite Coal Fired Power Station Boiler & AuxiliariesDocument277 pages300 MW Anthracite Coal Fired Power Station Boiler & AuxiliariesSendhilKumarNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy: Felipe Centeno, Khamid Mahkamov, Electo E. Silva Lora, Rubenildo V. AndradeDocument12 pagesRenewable Energy: Felipe Centeno, Khamid Mahkamov, Electo E. Silva Lora, Rubenildo V. AndradeAndres Mauricio Rojas MantillaNo ratings yet
- Downloadable Contractor DirectoryDocument4 pagesDownloadable Contractor DirectoryJAGUAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Presentation Slides About India LNGDocument3 pagesPresentation Slides About India LNGSatish Kumar100% (1)
- Unit+9 Chemical+Kinetics PDFDocument7 pagesUnit+9 Chemical+Kinetics PDFSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- Achieve Success in Gasoline HydrotreatingDocument6 pagesAchieve Success in Gasoline Hydrotreatingdonald55555No ratings yet
- CHM 096 Tutorial 2: (Chemical Equilibrium)Document3 pagesCHM 096 Tutorial 2: (Chemical Equilibrium)Sheh Muhammad AfnanNo ratings yet
- The Reaction Quotient (Q) : Name - Chem Worksheet 18-4Document1 pageThe Reaction Quotient (Q) : Name - Chem Worksheet 18-4Temwani Malema0% (1)
- Cylinder Pressure-Relief Devices: Safetygram 15Document4 pagesCylinder Pressure-Relief Devices: Safetygram 15johnNo ratings yet
- Exothermic & Endothermic Reactions 1 QPDocument23 pagesExothermic & Endothermic Reactions 1 QPGoogle map with MING HIN LINo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 - MCQ Separation of SubstancesDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 6 - MCQ Separation of Substancesvinod1577100% (3)
- Introduction To City Gas DistributionDocument19 pagesIntroduction To City Gas DistributionKarmendraNo ratings yet
- Casale Technologies For New Grass-Roots PlantsDocument10 pagesCasale Technologies For New Grass-Roots PlantsNguyen Thanh SangNo ratings yet
- Report On WTPDocument3 pagesReport On WTPshakilNo ratings yet
- 04 Solid Bed DehydrationDocument23 pages04 Solid Bed DehydrationMohamed SahnounNo ratings yet
- Dehydration of Natural Gas by Solid DesiccantDocument20 pagesDehydration of Natural Gas by Solid DesiccantMadhankumar LakshmipathyNo ratings yet