Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Herniated Disc: Spine Conditions 1
Herniated Disc: Spine Conditions 1
Uploaded by
andrzej36Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Herniated Disc: Spine Conditions 1
Herniated Disc: Spine Conditions 1
Uploaded by
andrzej36Copyright:
Available Formats
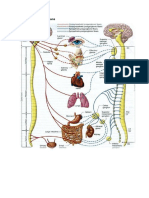
Spine Conditions
Herniated disc
A herniated disc occurs when one of the small, spongy discs that cushion the vertebrae bulges or breaks open. This
condition, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, can affect any part of the spine, but is most common in the lower
back.
Treatments for a herniated disc include:
Medication
Physical therapy
Artificial disc replacement
Spinal fusion
Laminaplasty
Microendoscopic discectomy
Epidural steroid blocks
Selective nerve root blocks/transforaminal epidural steroid blocks
Compression fracture
A compression fracture is a broken vertebra in the spine. It usually occurs due to severe trauma, but is also the result of
cancer or osteoporosis. Compression fractures are most common in the vertebrae of the lower back.
The treatment for a compression fracture is kyphoplasty.
Degenerative disc disease
Degenerative disc disease refers to the normal breakdown of spinal discs as we age. A sudden injury leading to a
herniated disc may also begin the degeneration process. The condition causes back or neck pain, and can lead to
osteoarthritis or spinal stenosis.
Treatments for degenerative disc disease include:
Medication
Physical Therapy
Artificial disc replacement
Spinal fusion
Epidural injections
Epidural steroid blocks
Selective nerve root blocks/transforaminal epidural steroid blocks
Myelopathy
Myelopathy is the gradual loss of nerve function caused by disorders of the spine. The condition commonly results from
spinal injury or spinal stenosis, a progressive narrowing of the spinal canal.
Myelopathy treatments include:
Medication
Physical therapy
Laminectomy
Spinal fusion
Kyphosis
Kyphosis is a progressive disorder that causes curvature of the thoracic spine in children and adults. It is most often the
result of developmental problems, trauma, degenerative diseases (such as arthritis) or osteoporosis with compression
fractures.
Spine Conditions
Treatments for kyphosis include:
Physical therapy
Spinal fusion
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine. Instead of the gentle inward and outward curves of a normal spine, scoliosis
produces an S or C shape. The condition is primarily congenital, but also results from traumatic injury or
osteoporosis.
Scoliosis treatments include:
Physical therapy
Spinal fusion
Facet blocks
Sciatica
Sciatica is pain, tingling or numbness caused by irritation of the sciatic nerve in the lower back. It can result from a
herniated disc pressing against the nerve roots, spinal stenosis, arthritis or an injury-induced pinched nerve.
Treatments for sciatica include:
Medication
Physical therapy
Laminectomy
Spinal fusion
Epidural steroid blocks
Selective nerve root blocks/transforaminal epidural steroid blocks
Sympathetic blocks
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal, which places pressure on the spinal cord. While the condition can affect
any part of the spine, it is most common in the lumbar and cervical regions. Some people are born with stenosis; others
develop it as they age.
Treatments for spinal stenosis include:
Medication
Physical therapy
Laminaplasty
Laminectomy
Spinal fusion
Interspinous/interlaminar implant
Epidural steroid blocks
Selective nerve root blocks/transforaminal epidural steroid blocks
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is a forward slip of one vertebra in the spinal column and usually occurs in the lumbar region. Some
people are born with a defective vertebra; in others, trauma, a stress fracture, infection or disease may cause the problem.
The condition is on the rise among children and adolescents who are active in athletics.
You might also like
- Theraputic Guidelines Version 3 - 2019 My TrialDocument163 pagesTheraputic Guidelines Version 3 - 2019 My TrialJANARDHAN H P100% (2)
- Sciatica Exercises & Home Treatment: Simple, Effective Care For Sciatica And Piriformis SyndromeFrom EverandSciatica Exercises & Home Treatment: Simple, Effective Care For Sciatica And Piriformis SyndromeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Merritts Neurology Handbook PDFDocument4 pagesMerritts Neurology Handbook PDFKhaled GharaibehNo ratings yet
- Concept Report AYUSH HospitalDocument34 pagesConcept Report AYUSH HospitalVinay Raj100% (1)
- Final - Bme 298 Final Project SkeletonDocument22 pagesFinal - Bme 298 Final Project Skeletonapi-522861974No ratings yet
- SpondylolisthesisDocument9 pagesSpondylolisthesisIris Balino100% (1)
- Nicholas Breeze Wood - Sacred Drums of SiberiaDocument63 pagesNicholas Breeze Wood - Sacred Drums of SiberiaSoror Babalon100% (2)
- Spinal Nerve PicDocument6 pagesSpinal Nerve PicJacklynlim LkcNo ratings yet
- What Structures Make Up The Back?: CongenitalDocument5 pagesWhat Structures Make Up The Back?: Congenitalselvi lestariNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument7 pagesSpinal Cord CompressionDashNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain 20-ns-5161 March 2020 508cDocument24 pagesLow Back Pain 20-ns-5161 March 2020 508cRajib ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DisorderDocument7 pagesMusculoskeletal DisorderAshutz AmorNo ratings yet
- Intervertebral Disc Prolapse: AnnulusDocument2 pagesIntervertebral Disc Prolapse: AnnulusIndra KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Lec3 DiscDocument50 pagesLec3 Discsana mumtazNo ratings yet
- Spinal Degenerative DiseaseDocument1 pageSpinal Degenerative DiseasejabolbolNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Cervical Disk DegenerationDocument5 pagesAnatomy: Cervical Disk DegenerationSUALI RAVEENDRA NAIKNo ratings yet
- What Does Thoracic Spondylosis Mean? Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument4 pagesWhat Does Thoracic Spondylosis Mean? Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmenttiarmayantiNo ratings yet
- Sciatica Nerve (Causes and Treatment)Document4 pagesSciatica Nerve (Causes and Treatment)esmollahanNo ratings yet
- Sciatica: Pseudosciatica or Non-Discogenic Sciatica, Which Causes Symptoms Similar To Spinal NerveDocument5 pagesSciatica: Pseudosciatica or Non-Discogenic Sciatica, Which Causes Symptoms Similar To Spinal NerveLeah BakerNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain and SciaticaDocument24 pagesLow Back Pain and SciaticaOVVCMOULINo ratings yet
- SPINAL Deformity: TypesDocument5 pagesSPINAL Deformity: TypesMd Sherajul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument22 pagesSpinal Cord CompressionVikas SinghNo ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus - Herniated DiscDocument4 pagesHerniated Nucleus Pulposus - Herniated DiscArvieDelfinNo ratings yet
- Cedera Medulla SpinalisDocument49 pagesCedera Medulla SpinalisDimas Nugroho NugrohoNo ratings yet
- The Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainFrom EverandThe Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainNo ratings yet
- Cedera Medulla SpinalisDocument49 pagesCedera Medulla SpinalisAtika NajlaNo ratings yet
- Osteochondrosis of The SpineDocument94 pagesOsteochondrosis of The SpineMoroccan Girl In UkraineNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Spondylosis: DefinitionDocument6 pagesCase Study On Spondylosis: Definitionsai vasavi bandaruNo ratings yet
- What Structures Make Up The Back?Document11 pagesWhat Structures Make Up The Back?MariaTheresiaNo ratings yet
- SciaticaDocument25 pagesSciaticaBenita Putri MD100% (1)
- Cervical Laminectomy: AnatomyDocument9 pagesCervical Laminectomy: AnatomyAgung Choro de ObesNo ratings yet
- Eli PPT BMDocument4 pagesEli PPT BMali mughalNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Spinal DisordersDocument2 pagesDegenerative Spinal DisordersjabolbolNo ratings yet
- Spinal Stenosis 3Document8 pagesSpinal Stenosis 3hunter_axl01No ratings yet
- Dr. K.B.Sudhikumar Prof. & HOD Dept. of Salyatantra, GAC, TripunithuraDocument69 pagesDr. K.B.Sudhikumar Prof. & HOD Dept. of Salyatantra, GAC, Tripunithuraapi-73271717No ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument4 pagesGeneric NameupinandipinNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain LeafDocument4 pagesLow Back Pain LeafJohn BrittoNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Herniated DiscDocument5 pagesLumbar Herniated DiscRinda AndreanditaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Lumbar Disc HerniationDocument24 pages6 - Lumbar Disc HerniationHADI BADWANNo ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument13 pagesHerniated Nucleus PulposusLorebell100% (4)
- Case StudyDocument30 pagesCase StudyNur Solehah0% (1)
- Degenerative Disc DiseaseDocument13 pagesDegenerative Disc Diseasehouki shanaNo ratings yet
- SpondylosisDocument1 pageSpondylosisshailesh284No ratings yet
- Lumbar Disk HerniationDocument6 pagesLumbar Disk HerniationShivaji DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Low Back PainDocument8 pagesLow Back PainLev KalikaNo ratings yet
- 21 - Spondylolisthesis - D3Document31 pages21 - Spondylolisthesis - D3Mohamed Magdy El MeligieNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Disc Herniation: Prof - Dr.Hidayet Sarı Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation DepartmentDocument19 pagesLumbar Disc Herniation: Prof - Dr.Hidayet Sarı Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation DepartmentAnonymous pJfAvlNo ratings yet
- Spondylosis: Vertebral ColumnDocument12 pagesSpondylosis: Vertebral ColumnVdct MglNo ratings yet
- Common Causes of Back PainDocument6 pagesCommon Causes of Back Painshailja kalolaNo ratings yet
- Total Rehabilitation: The Benefits of Aquatic TherapyDocument6 pagesTotal Rehabilitation: The Benefits of Aquatic TherapyAleCsss123No ratings yet
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Definitive GuideDocument4 pagesLumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Definitive GuideGuyNo ratings yet
- Word To PDFDocument119 pagesWord To PDFshravaniNo ratings yet
- Cervical Herniated Disc or Ruptured DiscDocument4 pagesCervical Herniated Disc or Ruptured DiscUwais AlNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain Numbness: Strain SciaticaDocument5 pagesLow Back Pain Numbness: Strain SciaticaCarol KayasNo ratings yet
- Head INJURIES SruthyDocument27 pagesHead INJURIES SruthySreenath SukumaranNo ratings yet
- SpondylolisthesisDocument31 pagesSpondylolisthesisMD ABDUR RAHANNo ratings yet
- Cervical PainDocument15 pagesCervical Painsteffiecruz06No ratings yet
- Sciatica: By: Allison BrooksDocument12 pagesSciatica: By: Allison BrooksBeta WattimenaNo ratings yet
- Back Pain BackupDocument9 pagesBack Pain BackupArun Kumar PTNo ratings yet
- S Pondy Lols Ys ThesisDocument35 pagesS Pondy Lols Ys ThesisSal LieNo ratings yet
- Rachialgia - Written ReportDocument4 pagesRachialgia - Written ReportNathaly MoraNo ratings yet
- HNP 1Document4 pagesHNP 1Kirsten CajayonNo ratings yet
- Medical History - ExerciseDocument1 pageMedical History - Exerciseandrzej36No ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument1 pagePassive Voiceandrzej36No ratings yet
- Anatomy Terms and Related AdjectivesDocument1 pageAnatomy Terms and Related Adjectivesandrzej36No ratings yet
- Diseases and Illnesses of The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesDiseases and Illnesses of The Respiratory Systemandrzej36No ratings yet
- Begin Here: Neck Pain Diagnosis Symptoms Diagnosis Self-CareDocument1 pageBegin Here: Neck Pain Diagnosis Symptoms Diagnosis Self-Careandrzej36No ratings yet
- Function of Digestive TractDocument1 pageFunction of Digestive Tractandrzej36No ratings yet
- Antibiotics GeneralGuidelinesDocument1 pageAntibiotics GeneralGuidelinesandrzej36No ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument1 pageVaccinesandrzej36No ratings yet
- Presentations: A. PreparationDocument2 pagesPresentations: A. Preparationandrzej36No ratings yet
- Common Types of Drugs: CapsuleDocument1 pageCommon Types of Drugs: Capsuleandrzej36No ratings yet
- Bypass SurgeryDocument1 pageBypass Surgeryandrzej36No ratings yet
- 1 Present Simple v. Present ContinuousDocument1 page1 Present Simple v. Present Continuousandrzej36No ratings yet
- AffixesDocument2 pagesAffixesandrzej36No ratings yet
- EczemaDocument1 pageEczemaandrzej36No ratings yet
- Sense of SmellDocument1 pageSense of Smellandrzej36No ratings yet
- Cochlea Eustachian (Auditory) Tube External Auditory Canal (Meatus) Incus Malleus Ossicles Pharynx Pinna Semicircular Canals Stapes Temporal Bone Tympanic Membrane Vestibule Vestibulocochlear NerveDocument1 pageCochlea Eustachian (Auditory) Tube External Auditory Canal (Meatus) Incus Malleus Ossicles Pharynx Pinna Semicircular Canals Stapes Temporal Bone Tympanic Membrane Vestibule Vestibulocochlear Nerveandrzej36No ratings yet
- The Practice of First Aid 1 Initial AssessmentDocument1 pageThe Practice of First Aid 1 Initial Assessmentandrzej36No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageCirculatory Systemandrzej36No ratings yet
- 1 Passive: 1.1 Modal Verbs in The PassiveDocument1 page1 Passive: 1.1 Modal Verbs in The Passiveandrzej36No ratings yet
- Kecamatan Laung Tuhup Dalam Angka 2022Document174 pagesKecamatan Laung Tuhup Dalam Angka 2022BAGREN RESMURANo ratings yet
- Yoruba MedicineDocument4 pagesYoruba MedicinefoknemodruNo ratings yet
- Human Light System Congress 2017Document13 pagesHuman Light System Congress 2017kirill_korotkov_1100% (1)
- Exam 9Document16 pagesExam 9NeWo YanTotNo ratings yet
- IDJ Vol 7 1Document6 pagesIDJ Vol 7 1Saatvik AtriNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Type 2: Cat CalhounDocument2 pagesDiabetes Type 2: Cat Calhounalbar ismuNo ratings yet
- AntaraDocument13 pagesAntaraDeepti KukretiNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of HIVDocument11 pagesPathogenesis of HIVPeter JustinNo ratings yet
- (Oleaceae) Aedes AegyptiDocument23 pages(Oleaceae) Aedes AegyptiEmil Sasil VloggsNo ratings yet
- CHN FNCPDocument1 pageCHN FNCPKathrynne MendozaNo ratings yet
- 11.3 MGR UniversityDocument15 pages11.3 MGR UniversityValarmathiNo ratings yet
- CVR PharmacologyDocument6 pagesCVR PharmacologyRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular: Original DescriptionDocument52 pagesCardiovascular: Original DescriptionMA ComputerNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biochemistry SeriesDocument373 pagesAdvanced Biochemistry SeriesProf Rakesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eureka Fair ProposalDocument6 pagesEureka Fair Proposalammad shahidNo ratings yet
- Sureshot EQDocument4 pagesSureshot EQRamanathan BalachandranNo ratings yet
- Sample Cover Letter Nursing Graduate-3Document1 pageSample Cover Letter Nursing Graduate-3api-401066432No ratings yet
- Application of Principles of Sociology in Health CareDocument85 pagesApplication of Principles of Sociology in Health Caresagar matada vidyaNo ratings yet
- Etizolam Infosheet SDF DrugWatch1 1Document7 pagesEtizolam Infosheet SDF DrugWatch1 1Sinan YolageldiliNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument3 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFPutu Ika WNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0099239906810058Document5 pagesPi Is 0099239906810058Antonis ChaniotisNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Propos 2Document3 pagesPharmacy Propos 2Momo RhieNo ratings yet
- Checklist - Hyperbaric Treatment For Children With Autism A MulticenterDocument3 pagesChecklist - Hyperbaric Treatment For Children With Autism A MulticenterJim GoetzNo ratings yet
- Clerking CaseDocument10 pagesClerking Casebaby shazanaNo ratings yet
- Alternatives Jan 29Document40 pagesAlternatives Jan 29alternativesononly100% (3)
- AU Routine Cleaning SolutionsDocument1 pageAU Routine Cleaning SolutionsTrần Văn BìnhNo ratings yet