Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Molecular Modelling Project 2
Molecular Modelling Project 2
Uploaded by
raneshkumar1992Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Molecular Modelling Project 2
Molecular Modelling Project 2
Uploaded by
raneshkumar1992Copyright:
Available Formats
Department of Chemical Engineering
Elective CE433: Molecular Modelling of Fluids
Modelling the phase equilibria of a carbon
dioxide + methane + ethane mixture with the
PR EOS using Aspen properties
Use the Peng-Robinson equation of state in Aspen-properties to study the phase behaviour of a
three-component mixture containing carbon dioxide, methane and ethane at fixed temperature
T=220K and pressure P=20 bar. We will first investigate in some detail each of the binary
mixtures in order to confirm that the equation of state chosen and the Aspen calculations are
adequate, will correlate binary parameters for one of the mixtures, and finally obtain the phase
diagram of the three-component mixture.
1. Deliverables (hand-in by 09:00 Wednesday 3 December):
1. Pxy plot for CO2+ethane at T=210K and T=230K comparing the experimental data and
the calculated data.
2. Pxy plot for methane+ethane at T=210K and T=230K comparing the experimental data
and the calculated data.
3. Pxy plot for CO2+methane at T=220K and T=240K comparing the experimental data and
the two sets of calculated data. One set of calculated data is obtained using the kij
binary parameter given by Aspen and the other set of calculated data is obtained with
your own correlated value of kij. Provide the two values of kij used.
4. Triangle phase diagram of the CO2+methane+ethane mixture at fixed T=220K and fixed
P=20 bar comparing the experimental data and the calculated data.
5. Confirm that the ternary phase diagram is correct by studying the binary information
previously obtained. Write a short summary (half a page maximim) of your conclusions.
In detail, you should complete the following tasks:
CO2+methane
1. Input all the experimental data provided in Excel and plot in Pxy form identifying the
liquid and gas phases.
2. Run a calculation in Aspen at the same fixed temperatures.
3. Plot the results of the Aspen calculation with the Peng-Robinson equation together with
the experimental data (usually experimental data is represented with symbols and
calculations with lines)
4. Perform a regression of the kij binary parameter at T=240K.
5. Use the new value of kij to run calculations at T=220K and T=240K again and compare
the new results with the experimental data and previous calculations.
Introduction to modelling the phase equilibria of fluids
Page 1 of 5
Department of Chemical Engineering
Elective CE433: Molecular Modelling of Fluids
CO2+ethane
Follow points 1-3 above.
Methane+ethane
Follow points 1-3 above.
CO2+methane+ethane
1. Input all the experimental data provided in Excel and plot in Pxy form identifying the
liquid and gas phases.
2. Perform a calculation in Aspen with the Peng-Robinson equation using your correlated
kij parameter for the CO2+methane mixture.
3. Plot the results of the Aspen calculation with the Peng-Robinson equation together with
the experimental data in a triangle plot.
2. Using Aspen:
Launch Aspen v8.4 using Application Jukebox
Create new simulation: File New Blank Simulation Create
The simulation opens automatically in Properties Components Specifications
1. Enter Component Ids:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Click Find
Enter component name and click Find Now
Highlight desired component in list proposed by Aspen
Click Add Selected Components
Repeat 2-4 until all components are entered, then click Close
Click on Next (the blue N in the Home menu). Aspen automatically moves to the next input
form. Fill in the following input forms:
2. Preparing an input:
1. Methods Specifications Global tab: Select Peng-Robinson property model under
Base method
2. Setup Specifications Global tab: Enter a title of your choice and select SI units
3. Write down in your notes all the parameters that appear in Methods Parameters
Binary Interaction PRKBV-1.
4. Click Next N to go to next and select Run Property Analysis/Setup to load
calculations with the parameters currently selected in the Parameters Table.
Introduction to modelling the phase equilibria of fluids
Page 2 of 5
Department of Chemical Engineering
Elective CE433: Molecular Modelling of Fluids
3. To run a binary phase equilibrium calculation
1. In the Analysis section of the Home menu, select Binary. This opens a new case which
appears in Properties Analysis.
2. In the Binary Analysis tab, under Analysis type select Txy. Specify the Valid phases,
Pressure, and Composition sections (calculate 50 data points).
3. Click on Run Analysis. A plot of the results is generated automatically. (To regenerate
the plot at a later time, go to the Results subsection of the analysis case and in the Plot
section of the Home menu select the Txy plot.)
4. To add experimental data
Inputting experimental data sets, for example Txy data:
1. Go to Properties Data, and click New
2. Name the data set and select data type MIXTURE.
3. In the Setup tab select the Components in the mixture, the Data type (TXY), the
Pressure, and the Composition Basis (Mole fraction).
4. In the Data tab enter the experimental data in the Excel file provided.
5. On the Plot section of the Home menu, click on T-xy to generate a plot of the data.
6. Repeat steps 1-5 for all data sets.
To plot the Txy experimental data alongside the Txy analysis calculations:
1. Plot the analysis results and the data set (see above), and keep both tabs open.
2. Go to the analysis results plot.
3. In the Design menu click on Merge Plot and select the data set plot from the drop-down
list. (If any other plots are open, the list will also include these.) The analysis results plot
will be updated to include the experimental data.
5. To perform a correlation of binary parameters
1. Select Regression from the Run Mode section of the Home menu.
2. Click on New and name the regression case.
3. In the Setup tab select the Method (PENG-ROB) and the Data set for regression by
clicking on the drop-down list.
4. In the Parameters tab set up the parameters to be regressed. For the CO2-Methane kij:
Type: Binary parameter
Name: PRKBV
Element: 1
Component or group: CO2, Methane
Usage: Regress
Set Aij=Aji: Yes.
5. Click on Next N and select Run Data Regression cases.
Introduction to modelling the phase equilibria of fluids
Page 3 of 5
Department of Chemical Engineering
Elective CE433: Molecular Modelling of Fluids
6. When the regression is complete, you can change the existing kij with the regressed one
by clicking yes on the pop-up window which appears. Otherwise it can be changed
manually by going to Methods Parameters Binary Interaction PRKBV-1.
To see the result of the correlation, go to the Results subsection of the regression case. Note
that the parameter describing the CO2-methane interactions is different from the original one
provided by Aspen. Write the value in your notes. Select the new parameter in the parameter
table (see step 6 above) and follow Part 3 above to perform a new analysis calculation with the
new parameter.
6. To calculate phase equilibria in multicomponent systems
In the case of calculations with more than two components, Aspen requires information of
which properties should be calculated (the Property Set). We shall perform constant pressure
and constant temperature flash calculations. The outputs are the compositions of the three
components in the liquid and vapour phases.
First ensure all the input corresponding to the relevant three components and chosen kij is
complete.
Go to Properties Property Sets, select New and provide a name.
In the Properties tab select mole fraction under Physical properties.
In Qualifiers tab create two columns and select vapour and liquid phases.
To carry out a flash calculation follow: Run Mode Analysis New and provide a
name.
5. Select type GENERIC.
6. In the System tab:
- Select Points along a flash curve.
- Specify the Valid phases as Vapour-Liquid
- Select an initial composition of flow for each component (be careful that your total
composition is inside the expected coexistence region)
7. In the Variables tab:
- Specify the pressure and temperature conditions
- In the Adjusted variables section, specify mole fraction of CO2.
- Click on Rage/List and select Specify Limits: calculate for mole fractions from 0 to 1
using 20 points.
1.
2.
3.
4.
8. In the Tabulate tab select your Property Set.
9. Click on Next N and select Run Property Analysis to carry out the calculation.
10. Go to the Results subsection of the analysis case and transfer the data to Excel for
plotting.
Introduction to modelling the phase equilibria of fluids
Page 4 of 5
Elective CE433: Molecular Modelling of Fluids
Department of Chemical Engineering
7. To build-up a triangle phase diagram in Excel.
In a triangular phase diagram each of the axes corresponds to the mole fraction of one of the
components. The experimental and calculated compositions need to be scaled in order for the
points to follow triangular geometry. Each of the points along the coexisting vapour and liquid
phase can be transformed to be given by (X,Y) which can then be plotted directly. Follow:
X = 1 xmethane - xco2/2
Y = xco2*cos(/6)
Following this transformation the vortices of the phase diagram are:
CO2
Methane
Ethane
Introduction to modelling the phase equilibria of fluids
Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- Detailed Layout Plan of 100 KLD STP PackageDocument1 pageDetailed Layout Plan of 100 KLD STP PackageRavindraSatpute100% (5)
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15From EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15No ratings yet
- EES TutorialDocument6 pagesEES TutorialKiran RajNo ratings yet
- Aspenplustm IbuprofenDocument10 pagesAspenplustm IbuprofensinghuchNo ratings yet
- Patran Excercise3Document18 pagesPatran Excercise3Karthick MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Assignment (Plate and Frame Filter Press) Group A-8)Document22 pagesAssignment (Plate and Frame Filter Press) Group A-8)Sajjad Rasool Chaudhry0% (4)
- JetMax Software Installation GuideDocument24 pagesJetMax Software Installation Guideforumid2697No ratings yet
- Stoichiometric Reactors ASPENDocument9 pagesStoichiometric Reactors ASPENRafique Ahmed Abro100% (1)
- Introduction To Aspen Plus - 2014Document214 pagesIntroduction To Aspen Plus - 2014Moy GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Batch Distillation W 10Document6 pagesBatch Distillation W 10Junaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Properties: Chapter TwoDocument15 pagesProperties: Chapter TwoOscar ReynosoNo ratings yet
- Appendix B - Descriptions of Computer Programs and Computer Aids For Use With This BookDocument13 pagesAppendix B - Descriptions of Computer Programs and Computer Aids For Use With This BookVitor MuzulonNo ratings yet
- Chemsep Tutorial: Distillation With Hypothetical ComponentsDocument25 pagesChemsep Tutorial: Distillation With Hypothetical ComponentsErving MJNo ratings yet
- Taller Aspen TermodinámicaDocument3 pagesTaller Aspen TermodinámicaJuanda BarbosaNo ratings yet
- How To Model Vapor-Liquid Equilibria (Vle) Data With ChemsepDocument10 pagesHow To Model Vapor-Liquid Equilibria (Vle) Data With ChemsepJazmin Flores MondragónNo ratings yet
- Short Project On T-NavigatorDocument26 pagesShort Project On T-Navigatorirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Presenting The Results From Factor AnalysisDocument2 pagesPresenting The Results From Factor AnalysisCristina ValentinaNo ratings yet
- How To Model Vapor-Liquid Equilibria (Vle) Data With ChemsepDocument12 pagesHow To Model Vapor-Liquid Equilibria (Vle) Data With ChemsepDaniel Giraldo PerezNo ratings yet
- Cse T Scds Kolonne enDocument16 pagesCse T Scds Kolonne enDeborah S. FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2Document2 pagesAssignment #2Ayush DubeyNo ratings yet
- Process Simulation Essentials - Example Book PDFDocument60 pagesProcess Simulation Essentials - Example Book PDFhamzashafiq1100% (1)
- Use of Aspen Plus and SPLIT To Calculate Phase Equilibria and Ternary Residue CurvesDocument2 pagesUse of Aspen Plus and SPLIT To Calculate Phase Equilibria and Ternary Residue CurvesMARK LESTER REALNo ratings yet
- Aspen HYSYS Training: Module 4: Logical OperationsDocument50 pagesAspen HYSYS Training: Module 4: Logical OperationsMohamed RjebNo ratings yet
- Binary Vapor Liquid Equilibrium (Vle) Calculator PDFDocument11 pagesBinary Vapor Liquid Equilibrium (Vle) Calculator PDFSalman ZafarNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Reacting Gas Property Calculations: Seitzman - Gatech.edu/classes/ae6050/homeworkformat - HTMLDocument1 pageEquilibrium Reacting Gas Property Calculations: Seitzman - Gatech.edu/classes/ae6050/homeworkformat - HTMLcheongyuchanNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometric Reactor (Updated 8/3/05) : Problem StatementDocument9 pagesStoichiometric Reactor (Updated 8/3/05) : Problem StatementTugyam Irem EsNo ratings yet
- HM4 Salikhov AmirDocument7 pagesHM4 Salikhov Amirsalikhovamir77No ratings yet
- Simulation of Distillation Column On Aspen HysysDocument8 pagesSimulation of Distillation Column On Aspen HysysAMOL RASTOGI 19BCM00120% (1)
- Models - Chem.activation EnergyDocument10 pagesModels - Chem.activation EnergyBilal BELMEKKINo ratings yet
- Transient Thermal Analysis TutDocument19 pagesTransient Thermal Analysis TutFlyNarutoFly27No ratings yet
- Calculation of Vapor-Liquid-Liquid Equilibria For The Fischer-Tropsch Reactor Effluents Using Modified Peng-Robinson Equation of StateDocument31 pagesCalculation of Vapor-Liquid-Liquid Equilibria For The Fischer-Tropsch Reactor Effluents Using Modified Peng-Robinson Equation of StatekenymorenoNo ratings yet
- 2021 CIR310 Sem Test 2 With AnswersDocument13 pages2021 CIR310 Sem Test 2 With Answersu21589969No ratings yet
- Peng RobinsonDocument7 pagesPeng Robinsonjunkhead254No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: TitleDocument22 pagesExperiment No. 1: TitleRashail AshasNo ratings yet
- Well Test Course ExecirsesDocument4 pagesWell Test Course ExecirsesBambang AriyantoNo ratings yet
- VTT Processes GTT Technologies: Use of For Thermochemical CalculationsDocument21 pagesVTT Processes GTT Technologies: Use of For Thermochemical CalculationsThaigroup CementNo ratings yet
- Manual For Computational Experiments - M.Sc. 1Document6 pagesManual For Computational Experiments - M.Sc. 1yusuf230395bhimaniNo ratings yet
- L4 HYSYS Tutorial - PART IDocument25 pagesL4 HYSYS Tutorial - PART IThilina GunawardhanaNo ratings yet
- Lab Boyles LawDocument3 pagesLab Boyles Lawblackwellbert100% (1)
- Technical Engineering College Energy Department Course:: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics ClassDocument7 pagesTechnical Engineering College Energy Department Course:: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics ClassAbdla DoskiNo ratings yet
- Pressure Temperature PhETDocument6 pagesPressure Temperature PhETMiNH HayatNo ratings yet
- Hysys For Aspen Plus Users PDFDocument11 pagesHysys For Aspen Plus Users PDFKarim KholeifNo ratings yet
- QPA TrainingDocument13 pagesQPA TrainingsenthilkumarNo ratings yet
- CO2SYS Macro InstructionsDocument5 pagesCO2SYS Macro InstructionsHadiwijaya Lesmana SalimNo ratings yet
- Dise No de Procesos: Estimation of Properties For Simulation PurposesDocument2 pagesDise No de Procesos: Estimation of Properties For Simulation PurposesAnyury LatorreNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Basic Program Functionality: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 - Basic Program Functionality: ObjectivesJaime HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chemsep Tutorial: Pcdmanager: Ross Taylor and Harry Kooijman Updated For Version 6.8, August 1, 2011Document37 pagesChemsep Tutorial: Pcdmanager: Ross Taylor and Harry Kooijman Updated For Version 6.8, August 1, 2011joseNo ratings yet
- ENGR131 Fall14 Exam1 ExcelPracticalDocument38 pagesENGR131 Fall14 Exam1 ExcelPracticalJason LeeNo ratings yet
- Lab: Pressure - Temperature Relationship in Gases: NSU Physics ExperimentDocument6 pagesLab: Pressure - Temperature Relationship in Gases: NSU Physics Experimenterick salgadoNo ratings yet
- Final Stage For Cocomo Using PCADocument8 pagesFinal Stage For Cocomo Using PCAVikas MahurkarNo ratings yet
- A Step by Step Guide To Use Pvti (Geoquest)Document49 pagesA Step by Step Guide To Use Pvti (Geoquest)13670319No ratings yet
- Exercise Property Phase DiagramDocument5 pagesExercise Property Phase DiagramRizkatul Amriah ANo ratings yet
- Lab # 15Document13 pagesLab # 15Kashaf TehreemNo ratings yet
- CSTRDocument14 pagesCSTRVLADYRONNo ratings yet
- Heat & Mass BalanceDocument26 pagesHeat & Mass BalanceAbhiyan Anala ArvindNo ratings yet
- CHE 372 Project ReportDocument12 pagesCHE 372 Project ReportGonzalo Jose SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Guidlines For LE2Document8 pagesGuidlines For LE2Fatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Combined Cooling, Heating, and Power Systems: Modeling, Optimization, and OperationFrom EverandCombined Cooling, Heating, and Power Systems: Modeling, Optimization, and OperationNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Experimental Data Microsoft®Excel or Spss??! Sharing of Experience English Version: Book 3From EverandAnalysis of Experimental Data Microsoft®Excel or Spss??! Sharing of Experience English Version: Book 3No ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Kinetics: Concepts, Methods and Case StudiesFrom EverandChemical Reaction Kinetics: Concepts, Methods and Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- Reading ListDocument1 pageReading Listraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
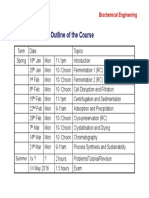
- Outline of The Course: Biochemical EngineeringDocument1 pageOutline of The Course: Biochemical Engineeringraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- What Is FatcaDocument1 pageWhat Is Fatcaraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- London: Imperial Insulin CoDocument2 pagesLondon: Imperial Insulin Coraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- Imperial Fine Chemicals LTD.: Ibuprofen ProjectDocument3 pagesImperial Fine Chemicals LTD.: Ibuprofen Projectraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- 16-25 Railcard Application FormDocument1 page16-25 Railcard Application Formraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- Edible Vaccines BriefDocument3 pagesEdible Vaccines Briefraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- Green Banking: Maja Drobnjaković, PHD Student University of Novi Sad, SerbiaDocument10 pagesGreen Banking: Maja Drobnjaković, PHD Student University of Novi Sad, Serbiaraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- Access To Employment 2015: Application FormDocument2 pagesAccess To Employment 2015: Application Formraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- $R0VOZ6PDocument3 pages$R0VOZ6Praneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- Traffic Light MatrixDocument27 pagesTraffic Light Matrixraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- Plate and Frame Filter PressDocument16 pagesPlate and Frame Filter Pressraneshkumar19920% (1)
- A Filter PressDocument0 pagesA Filter Pressraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- Please See Diagram and ChartsDocument2 pagesPlease See Diagram and Chartsraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- Needs Needs Are Needs To Fulfil Customers Need, We Must SurveyDocument1 pageNeeds Needs Are Needs To Fulfil Customers Need, We Must Surveyraneshkumar1992No ratings yet
- Cite It Right PDFDocument58 pagesCite It Right PDFOlga LazarevicNo ratings yet
- TCE 5107 Course OutlineDocument4 pagesTCE 5107 Course OutlinekudaNo ratings yet
- EndNote For MacDocument18 pagesEndNote For Macdtlee95No ratings yet
- Transaction Process System AisDocument3 pagesTransaction Process System AisGem BaguinonNo ratings yet
- CS F342-11 PDFDocument24 pagesCS F342-11 PDFsky_davisNo ratings yet
- Indicators of Tursiops Truncatus Cognition Level Review PaperDocument4 pagesIndicators of Tursiops Truncatus Cognition Level Review PaperCharlene RiveraNo ratings yet
- List of Computer Sindh Board of Technical EducationDocument17 pagesList of Computer Sindh Board of Technical Educationmuhamedshuaibbhai50% (2)
- Use of Recycled Aggregates From Construction and DemolitionDocument15 pagesUse of Recycled Aggregates From Construction and DemolitionWagner TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- The Body of Light in The Western Esoteric Tradition - Mark StavishDocument9 pagesThe Body of Light in The Western Esoteric Tradition - Mark StavishMorya DomNo ratings yet
- Smith - Lesson Plan FinalDocument2 pagesSmith - Lesson Plan Finalapi-429426959No ratings yet
- Rohan (2000) - A Rose by Any Name?? The Values ConstructDocument23 pagesRohan (2000) - A Rose by Any Name?? The Values ConstructHelen HENo ratings yet
- Manual IDEC FC5A AdvancedDocument343 pagesManual IDEC FC5A AdvancedJoako FilipovichNo ratings yet
- QMM Assignment 2Document2 pagesQMM Assignment 2Ambika Sharma0% (1)
- Toshiba Placement PaperDocument12 pagesToshiba Placement Paperpanakkaltino100% (1)
- Bruce Wilkinson 7 Laws of The Learner: Law 4a - RetentionDocument31 pagesBruce Wilkinson 7 Laws of The Learner: Law 4a - RetentionrichardNo ratings yet
- Phy Chapter Wise P1 P3Document277 pagesPhy Chapter Wise P1 P3sidharthNo ratings yet
- TMC Role Play ScriptDocument12 pagesTMC Role Play Scriptsittinorsimah nasirNo ratings yet
- MGT1102E - Consumer Behavior - Chapter 4Document16 pagesMGT1102E - Consumer Behavior - Chapter 4Tiến Lê NgọcNo ratings yet
- Master's Thesis - Quaternion-Based Control For Aggressive Trajectory Tracking With A Micro-Quadrotor UAVDocument113 pagesMaster's Thesis - Quaternion-Based Control For Aggressive Trajectory Tracking With A Micro-Quadrotor UAVMarcus LimaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary TeachingDocument44 pagesVocabulary TeachingNi Made Ivana Swastiana100% (1)
- Multiple ChoiceDocument26 pagesMultiple Choiceedgar_chieyahoocomNo ratings yet
- Quantum Compatibility RulesDocument4 pagesQuantum Compatibility RulesAbel AndradaNo ratings yet
- Brady Cronin 2001Document17 pagesBrady Cronin 2001Tamires ToniotiNo ratings yet
- Select Quant Individual AssignmentDocument3 pagesSelect Quant Individual AssignmentNatnael Belay0% (1)
- Bedanking ThesisDocument6 pagesBedanking Thesisafkodkedr100% (2)
- New Welding Technologies in The ShipbuildingDocument2 pagesNew Welding Technologies in The ShipbuildingTahsinul Haque TasifNo ratings yet
- Core Java PDFDocument177 pagesCore Java PDFpratikshaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines and EquipmentDocument76 pagesElectrical Machines and EquipmentsirageldeenNo ratings yet
- Narco Analysis and Brain MappingDocument17 pagesNarco Analysis and Brain MappingManbaniKaurOhriNo ratings yet