Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psychiatry: Antidepressants
Psychiatry: Antidepressants
Uploaded by
Sok-Moi ChokCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dóczi - 2019 - An Overview of Conceptual Models and Theories of Lexical Representation in The Mental LexiconDocument20 pagesDóczi - 2019 - An Overview of Conceptual Models and Theories of Lexical Representation in The Mental LexiconAnthony RancourtNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant ChartDocument7 pagesAntidepressant Chartinher1tance100% (4)
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat Sheetfreecouch83% (6)
- Psychiatric Meds Excel WorksheetDocument8 pagesPsychiatric Meds Excel WorksheetDale Buckman100% (1)
- Medication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionFrom EverandMedication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsDocument7 pagesPsychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsBea Samonte100% (2)
- Antidepressant Medication ChartDocument2 pagesAntidepressant Medication Chartbabaran2No ratings yet
- Rheumatology: Differential Diagnoses of ArthritisDocument3 pagesRheumatology: Differential Diagnoses of ArthritisSok-Moi Chok100% (1)
- Why Mergers Fail and How To Prevent ItDocument4 pagesWhy Mergers Fail and How To Prevent ItAkshay RawatNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Pharmacology J. Psychiatry' AntidepressantsDocument9 pagesPsychiatry Pharmacology J. Psychiatry' AntidepressantssumithjalyNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry PharmacologyDocument2 pagesPsychiatry PharmacologyMegatFitriAziz100% (5)
- CHT Psyc AntidepressantDocument3 pagesCHT Psyc AntidepressantRicardo Lugon ArantesNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepine Comparison Chart - Commonly Available Sedative Hypnotic Anti Anxiety (Anxiolytic) Anti Epileptic MedicationsDocument2 pagesBenzodiazepine Comparison Chart - Commonly Available Sedative Hypnotic Anti Anxiety (Anxiolytic) Anti Epileptic MedicationsChristopher Chrysostom100% (3)
- Second and Third Generation Antipsychotics: A Comprehensive HandbookFrom EverandSecond and Third Generation Antipsychotics: A Comprehensive HandbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Art Direction Principles Including AssessmentsDocument5 pagesArt Direction Principles Including AssessmentsTerry FlewNo ratings yet
- Psych Drugs Info SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Info SheetPauline ChanNo ratings yet
- Psych Meds Review MaterialDocument2 pagesPsych Meds Review MaterialMary Romaine Dela Pasion100% (8)
- Psych Med ChartsDocument5 pagesPsych Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (7)
- Psychotropic Medication ReviewDocument7 pagesPsychotropic Medication ReviewAakash Shah100% (2)
- Psychiatry Grand NotesDocument10 pagesPsychiatry Grand NotesNathan T. CheungNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Medication: Generic Name Trade Name Indications Contraindications Drug Interaction Side Effects Nursing ImplicationDocument6 pagesAntipsychotic Medication: Generic Name Trade Name Indications Contraindications Drug Interaction Side Effects Nursing ImplicationJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Treatment Modalities For Mood DisordersDocument55 pagesTreatment Modalities For Mood DisordersGlory MimiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy in PschiatryDocument8 pagesPharmacotherapy in PschiatryygfhdgNo ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument5 pagesAntidepressantsUm HamoOd100% (2)
- Drug List PsychopharmDocument23 pagesDrug List PsychopharmGeorge HananiaNo ratings yet
- (Divalproate, CBZ, LTG) : Anxiety DisordersDocument3 pages(Divalproate, CBZ, LTG) : Anxiety DisordersGus AbellaNo ratings yet
- "Serotonin Syndrome Causes HARM": Psychiatry PharamacologyDocument9 pages"Serotonin Syndrome Causes HARM": Psychiatry Pharamacologytycobb63100% (4)
- Psychiatry Made EasyDocument14 pagesPsychiatry Made EasyD. W. S JayarathnaNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument148 pagesPsychopharmacologyAsther Mantua100% (2)
- Notes On Psychiatry: TypesDocument17 pagesNotes On Psychiatry: TypesMAY100% (2)
- AntidepressantsDocument12 pagesAntidepressantsSubiVictorNo ratings yet
- PSYCH 1.2A Mood DisordersDocument22 pagesPSYCH 1.2A Mood DisordersZaza100% (1)
- PSYCHIATRY Course NotesDocument43 pagesPSYCHIATRY Course NotesNisha PillaiNo ratings yet
- DSM-IV Criteria MnemonicsDocument4 pagesDSM-IV Criteria Mnemonicsleonyap100% (2)
- Geriatric Giants - DR SeymourDocument108 pagesGeriatric Giants - DR SeymourSharon Mallia100% (1)
- Psychiatry History & Suicide Risk Assessment TemplatesDocument32 pagesPsychiatry History & Suicide Risk Assessment TemplatesDuncan Jackson100% (2)
- Psychiatry High Yield NotesDocument6 pagesPsychiatry High Yield Notesgregry2100% (3)
- Handy Hints When Prescribing Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (Ssris)Document3 pagesHandy Hints When Prescribing Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (Ssris)Mariya ZhekovaNo ratings yet
- 1: Adhd: Scientific Name Dose CommentsDocument4 pages1: Adhd: Scientific Name Dose CommentsSadiq Abdo92No ratings yet
- Psycho-Pharmacotherapy: Major Tranquilizers, D2 - Receptor Blockers and Anti - Schizophrenic DrugsDocument29 pagesPsycho-Pharmacotherapy: Major Tranquilizers, D2 - Receptor Blockers and Anti - Schizophrenic DrugsPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- Specific Drug Olanzapine (Classification IndicationDocument14 pagesSpecific Drug Olanzapine (Classification IndicationRIZZA JANE VELASCONo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - (5) Psychotic DrugsDocument8 pagesPharmacology - (5) Psychotic DrugsSamantha DiegoNo ratings yet
- Psychotropics NotesDocument5 pagesPsychotropics NotesJulianna Rheaven JoreNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageBipolar DisorderNur BalqisNo ratings yet
- Handy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For DepressionDocument2 pagesHandy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For Depressionrowanpurdy100% (4)
- ReferenceDocument2 pagesReferenceAaron Shokar100% (3)
- Psychotropic Medications: Dale Sanderson, PA-C Physician Assistant Seattle Mental HealthDocument72 pagesPsychotropic Medications: Dale Sanderson, PA-C Physician Assistant Seattle Mental HealthMichael Urrutia100% (2)
- Norepinephrine Acetylcholine (Ach)Document6 pagesNorepinephrine Acetylcholine (Ach)Jestoni Dulva Maniago100% (3)
- AntipsychoticsDocument4 pagesAntipsychoticsRana MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Provisional: Borderline Personality Disorder Differential DXDocument6 pagesProvisional: Borderline Personality Disorder Differential DXhernandez2812No ratings yet
- Psychiatric Work-Up Template For StudentsDocument2 pagesPsychiatric Work-Up Template For StudentsTommy FuNo ratings yet
- Psych DrugsDocument3 pagesPsych DrugsSwarna BanikNo ratings yet
- Anxiety/Depression: S AlprazolamDocument2 pagesAnxiety/Depression: S AlprazolamleesaNo ratings yet
- Psycho PharmaDocument8 pagesPsycho PharmaMark JosephNo ratings yet
- A) A/E of Moclobemide SNATCH: A) Pharmacology 1) Anti-DepressantsDocument10 pagesA) A/E of Moclobemide SNATCH: A) Pharmacology 1) Anti-DepressantsNur Atiqah Mohd AzliNo ratings yet
- Structured Approach To Acute Psychiatry EmergenciesDocument41 pagesStructured Approach To Acute Psychiatry EmergenciesRaimondo RomanazziNo ratings yet
- Drug List Psych Optho NeuroDocument22 pagesDrug List Psych Optho NeuroAshley BarrileNo ratings yet
- Commonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDocument2 pagesCommonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDragutin Petrić100% (1)
- PSYC - Medication TemplateDocument15 pagesPSYC - Medication TemplateM Henry100% (1)
- Blueprints PsychiatryDocument466 pagesBlueprints Psychiatrynoir100% (5)
- Review of Antipsychotic DrugsDocument15 pagesReview of Antipsychotic DrugsTuanthonBoonlue100% (1)
- AntipsychoticsDocument10 pagesAntipsychoticswawing16No ratings yet
- Psychiatry Practice Boosters 2016: Insights from research to enhance your clinical workFrom EverandPsychiatry Practice Boosters 2016: Insights from research to enhance your clinical workNo ratings yet
- O&G: Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument3 pagesO&G: Sexually Transmitted InfectionsSok-Moi ChokNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry: DementiaDocument3 pagesPsychiatry: DementiaSok-Moi Chok100% (2)
- Psychiatry: Mental State ExaminationDocument3 pagesPsychiatry: Mental State ExaminationSok-Moi Chok100% (5)
- Judith Gardiner - Female MasculinityDocument28 pagesJudith Gardiner - Female MasculinityDimitria HerreraNo ratings yet
- The Play First Summit - 1Document7 pagesThe Play First Summit - 1Valentina ZackriasNo ratings yet
- III 1 RomanticismDocument15 pagesIII 1 Romanticismrickishe100% (3)
- Reading Response InformationDocument2 pagesReading Response InformationĐức BùiNo ratings yet
- Critical Summary of The ArticleDocument3 pagesCritical Summary of The ArticleEdsel AlapagNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - 13t - Gary DesslerDocument39 pagesHuman Resource Management - 13t - Gary Desslerhayelom0% (2)
- The Mindful Athlete by George MumfordDocument7 pagesThe Mindful Athlete by George Mumfordsimas100% (1)
- APD506 Asignment Rev 10.5Document4 pagesAPD506 Asignment Rev 10.5Sandeep NairNo ratings yet
- Film Guide CluelessDocument8 pagesFilm Guide CluelessValeria GomezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Sea Change PosterDocument7 pagesLesson 3 - Sea Change Posterapi-323655794No ratings yet
- Respiratory Biofeedback FinalDocument5 pagesRespiratory Biofeedback FinalGareth Thomas100% (2)
- ASD Early Intervention TablesDocument3 pagesASD Early Intervention Tablesjuliepipip23100% (1)
- The Success and Failure of International BusinessDocument8 pagesThe Success and Failure of International BusinessToniEltoniNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For BleedingDocument1 pageNCP Risk For BleedingJen Garzo75% (4)
- How To Really Learn SpanishDocument47 pagesHow To Really Learn Spanishlightjp171% (7)
- Mikey Newman - Objective EssayDocument6 pagesMikey Newman - Objective Essayapi-607529399No ratings yet
- WWWWMDocument36 pagesWWWWMRude Gal SheenaNo ratings yet
- Teacher Resource - The Ongoing Percentage Grade in PTGBDocument11 pagesTeacher Resource - The Ongoing Percentage Grade in PTGBapi-202232251No ratings yet
- 10 Effective Teaching StrategiesDocument5 pages10 Effective Teaching StrategiesfranceloiseNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument4 pagesReaction PaperJam Knows RightNo ratings yet
- Hawa Latifzai - Pedagogical Theory Paper FinalDocument10 pagesHawa Latifzai - Pedagogical Theory Paper Finalapi-272324384No ratings yet
- Healing Anxiety PeruDocument8 pagesHealing Anxiety Peruayahuascaassociation100% (1)
- AT3U4Document1 pageAT3U4Julio LópezNo ratings yet
- History of Management Trend - Stephen RobbinsDocument24 pagesHistory of Management Trend - Stephen Robbinstrucanh1803No ratings yet
- Introduction of Sustainable Low-Cost Housing in Ethiopia - An Innovation Diffusion PerspectiveDocument7 pagesIntroduction of Sustainable Low-Cost Housing in Ethiopia - An Innovation Diffusion PerspectiveninashiroNo ratings yet
- Nightingale PDFDocument2 pagesNightingale PDFLawrence CezarNo ratings yet
- Sip - Planning WorksheetsDocument5 pagesSip - Planning WorksheetsEr MaNo ratings yet
Psychiatry: Antidepressants
Psychiatry: Antidepressants
Uploaded by
Sok-Moi ChokCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Psychiatry: Antidepressants
Psychiatry: Antidepressants
Uploaded by
Sok-Moi ChokCopyright:
Available Formats
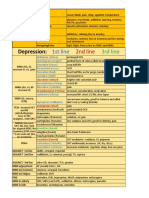
PSYCHIATRY: DEPRESSION Tx| S.M.
CHOK (Manchester Medical School)
ANTIDEPRESSANTS
SSRIs
SNRIs
TCAs
MAOIs
Mechanism of
Action
block the reuptake of serotonin in the
brain
block the reuptake of noradrenaline &
serotonin by the presynaptic nerves
inhibition of noradrenaline and
serotonin reuptake
inhibit monoamine oxidase, causing
accumulation of amine
neurotransmitters
Examples
duloxetine
venlafaxine
desvenlafaxine
amitriptyline
clomipramine
imipramine
lofepramine
nortriptyline
Recommendation
1st line Tx for depression
better tolerated, safer in overdose
patients with severe depression may
older type of antidepressant
respond better to an SNRI
SE and toxicity in overdosage are
lower risk of drug-to-drug interactions
problems
older type of antidepressant
dangerous interactions with some
foods and drugs
Contraindication
cautions: patients with epilepsy,
cardiac disease, DM, angle-closeure
glaucoma, Hx of mania or bleeding
disorder
should not be used if patient enters a
manic phase
cautions: cardiac disease (HPTN and
arrhythmias), DM, Hx of epilepsy or
mania, angle-closure glaucoma,
bleeding disorders or concomitant
use of drugs that risk of bleeding
MI, arrhythmias
manic phase of bipolar
acute porphyria
should not be started until 2/52 after
stopping MAOIs
should not be started until 2/52 after
a TCAs/a previous MAOIs has been
stopped
other antidepressants should not be
started for 2/52 after MAOIs has
been stopped
pressor effects of tyramine (in some
foods) may cause a dangerous BP
Withdrawal
Symptoms
dizziness
flu-like symptomes
anxiety
urinary urgency
diarrhoea
influenza-like symptoms
insomnia
vivid dreams
movement disorders
mania
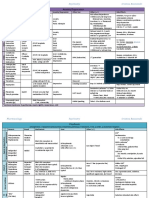
Citalopram
Escitalopram
Fluoxetine
Paroxetine
Sertraline
GI disturbances
headache
anxiety
dizziness
paraesthesia
electric shock sensation in the head,
neck and spine
tinnitus
sleep disturbances
fatigue
influenza-like symptoms
Overdosage
cardiovascular and
epileptogenic effects
phenelzine
tranylcypromine
isocarboxazid
moclobemide
agitation
irritability
ataxia
movement disorders
insomnia
drowsiness
vivid dreams
cognitive impairment
slowed speech
hallucination
paranoid delusions
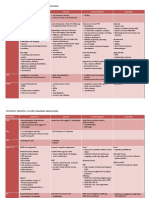
PSYCHIATRY: DEPRESSION Tx| S.M.CHOK (Manchester Medical School)
SSRIs
Side Effects
SNRIs
less sedative, fewer cardiotoxic and
antimuscarinic SE than TCAs
Venlafaxine/Desvenlafaxine BP
Duloxetine may worsen liver problem
GI SE
nausea, vomiting, abdo pain,
dyspepsia, weight loss (anorexia) or
weight gain (appetite),
constipation, diarrhoea
Serotonin Syndrome
(if used with other antidepressants,
certain pain or headache meds, and
herbal supplement St.John's wort)
anxiety
agitation
sweating
confusion
tremors
restlessness
lack of coordination
tachycardia
Hypersensitivity Reaction
rash, urticaria, angioedema,
anaphylaxis, arthralgia, myalgia,
photosensitivity
CNS SE
headache, insomnia, tremor,
dizziness, hallucination, mania or
hypomania, drowsiness, anxiety,
convulsions, suicidal behaviour
Other SE
dry mouth
movement disorders
visual disturbances
bleeding disorders
hyponatraemia
GI SE
risk of GI bleeding
nausea
changes in appetite
constipation
dry mouth
Other SE
arrhythmias
insomnia
dizziness
fluid retention
difficulty with micturition
urinary incontinence
sensory disturbances
sexual dysfunction
tinnitus
alopecia
rash, photosensitivity
TCAs
Cardiovascular SE
arrhythmias and heart block
postural HPTN
tachycardia
ECG changes
CNS SE
anxiety, confusion, sleep
disturbances, dizziness, agitation,
irritability
Antimuscarinic SE
dry mouth, blurred vision,
constipation, urinary retention
Endocrine SE
breast enlargement
gynaecomastia
galactorrhoea
weight gain (appetite)
hyponatraemia (elderly)
Other SE
nausea, vomiting
taste disturbances
tinnitus
rash, urticaria, pruritis
photosensitivity
alopecia
sweating
MAOIs
hepatic impairment
risk of neonatal malformation
hypotension
insomnia
weight gain
nausea
agitation
You might also like
- Dóczi - 2019 - An Overview of Conceptual Models and Theories of Lexical Representation in The Mental LexiconDocument20 pagesDóczi - 2019 - An Overview of Conceptual Models and Theories of Lexical Representation in The Mental LexiconAnthony RancourtNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant ChartDocument7 pagesAntidepressant Chartinher1tance100% (4)
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat Sheetfreecouch83% (6)
- Psychiatric Meds Excel WorksheetDocument8 pagesPsychiatric Meds Excel WorksheetDale Buckman100% (1)
- Medication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionFrom EverandMedication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsDocument7 pagesPsychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsBea Samonte100% (2)
- Antidepressant Medication ChartDocument2 pagesAntidepressant Medication Chartbabaran2No ratings yet
- Rheumatology: Differential Diagnoses of ArthritisDocument3 pagesRheumatology: Differential Diagnoses of ArthritisSok-Moi Chok100% (1)
- Why Mergers Fail and How To Prevent ItDocument4 pagesWhy Mergers Fail and How To Prevent ItAkshay RawatNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Pharmacology J. Psychiatry' AntidepressantsDocument9 pagesPsychiatry Pharmacology J. Psychiatry' AntidepressantssumithjalyNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry PharmacologyDocument2 pagesPsychiatry PharmacologyMegatFitriAziz100% (5)
- CHT Psyc AntidepressantDocument3 pagesCHT Psyc AntidepressantRicardo Lugon ArantesNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepine Comparison Chart - Commonly Available Sedative Hypnotic Anti Anxiety (Anxiolytic) Anti Epileptic MedicationsDocument2 pagesBenzodiazepine Comparison Chart - Commonly Available Sedative Hypnotic Anti Anxiety (Anxiolytic) Anti Epileptic MedicationsChristopher Chrysostom100% (3)
- Second and Third Generation Antipsychotics: A Comprehensive HandbookFrom EverandSecond and Third Generation Antipsychotics: A Comprehensive HandbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Art Direction Principles Including AssessmentsDocument5 pagesArt Direction Principles Including AssessmentsTerry FlewNo ratings yet
- Psych Drugs Info SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Info SheetPauline ChanNo ratings yet
- Psych Meds Review MaterialDocument2 pagesPsych Meds Review MaterialMary Romaine Dela Pasion100% (8)
- Psych Med ChartsDocument5 pagesPsych Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (7)
- Psychotropic Medication ReviewDocument7 pagesPsychotropic Medication ReviewAakash Shah100% (2)
- Psychiatry Grand NotesDocument10 pagesPsychiatry Grand NotesNathan T. CheungNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Medication: Generic Name Trade Name Indications Contraindications Drug Interaction Side Effects Nursing ImplicationDocument6 pagesAntipsychotic Medication: Generic Name Trade Name Indications Contraindications Drug Interaction Side Effects Nursing ImplicationJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Treatment Modalities For Mood DisordersDocument55 pagesTreatment Modalities For Mood DisordersGlory MimiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy in PschiatryDocument8 pagesPharmacotherapy in PschiatryygfhdgNo ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument5 pagesAntidepressantsUm HamoOd100% (2)
- Drug List PsychopharmDocument23 pagesDrug List PsychopharmGeorge HananiaNo ratings yet
- (Divalproate, CBZ, LTG) : Anxiety DisordersDocument3 pages(Divalproate, CBZ, LTG) : Anxiety DisordersGus AbellaNo ratings yet
- "Serotonin Syndrome Causes HARM": Psychiatry PharamacologyDocument9 pages"Serotonin Syndrome Causes HARM": Psychiatry Pharamacologytycobb63100% (4)
- Psychiatry Made EasyDocument14 pagesPsychiatry Made EasyD. W. S JayarathnaNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument148 pagesPsychopharmacologyAsther Mantua100% (2)
- Notes On Psychiatry: TypesDocument17 pagesNotes On Psychiatry: TypesMAY100% (2)
- AntidepressantsDocument12 pagesAntidepressantsSubiVictorNo ratings yet
- PSYCH 1.2A Mood DisordersDocument22 pagesPSYCH 1.2A Mood DisordersZaza100% (1)
- PSYCHIATRY Course NotesDocument43 pagesPSYCHIATRY Course NotesNisha PillaiNo ratings yet
- DSM-IV Criteria MnemonicsDocument4 pagesDSM-IV Criteria Mnemonicsleonyap100% (2)
- Geriatric Giants - DR SeymourDocument108 pagesGeriatric Giants - DR SeymourSharon Mallia100% (1)
- Psychiatry History & Suicide Risk Assessment TemplatesDocument32 pagesPsychiatry History & Suicide Risk Assessment TemplatesDuncan Jackson100% (2)
- Psychiatry High Yield NotesDocument6 pagesPsychiatry High Yield Notesgregry2100% (3)
- Handy Hints When Prescribing Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (Ssris)Document3 pagesHandy Hints When Prescribing Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (Ssris)Mariya ZhekovaNo ratings yet
- 1: Adhd: Scientific Name Dose CommentsDocument4 pages1: Adhd: Scientific Name Dose CommentsSadiq Abdo92No ratings yet
- Psycho-Pharmacotherapy: Major Tranquilizers, D2 - Receptor Blockers and Anti - Schizophrenic DrugsDocument29 pagesPsycho-Pharmacotherapy: Major Tranquilizers, D2 - Receptor Blockers and Anti - Schizophrenic DrugsPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- Specific Drug Olanzapine (Classification IndicationDocument14 pagesSpecific Drug Olanzapine (Classification IndicationRIZZA JANE VELASCONo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - (5) Psychotic DrugsDocument8 pagesPharmacology - (5) Psychotic DrugsSamantha DiegoNo ratings yet
- Psychotropics NotesDocument5 pagesPsychotropics NotesJulianna Rheaven JoreNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageBipolar DisorderNur BalqisNo ratings yet
- Handy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For DepressionDocument2 pagesHandy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For Depressionrowanpurdy100% (4)
- ReferenceDocument2 pagesReferenceAaron Shokar100% (3)
- Psychotropic Medications: Dale Sanderson, PA-C Physician Assistant Seattle Mental HealthDocument72 pagesPsychotropic Medications: Dale Sanderson, PA-C Physician Assistant Seattle Mental HealthMichael Urrutia100% (2)
- Norepinephrine Acetylcholine (Ach)Document6 pagesNorepinephrine Acetylcholine (Ach)Jestoni Dulva Maniago100% (3)
- AntipsychoticsDocument4 pagesAntipsychoticsRana MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Provisional: Borderline Personality Disorder Differential DXDocument6 pagesProvisional: Borderline Personality Disorder Differential DXhernandez2812No ratings yet
- Psychiatric Work-Up Template For StudentsDocument2 pagesPsychiatric Work-Up Template For StudentsTommy FuNo ratings yet
- Psych DrugsDocument3 pagesPsych DrugsSwarna BanikNo ratings yet
- Anxiety/Depression: S AlprazolamDocument2 pagesAnxiety/Depression: S AlprazolamleesaNo ratings yet
- Psycho PharmaDocument8 pagesPsycho PharmaMark JosephNo ratings yet
- A) A/E of Moclobemide SNATCH: A) Pharmacology 1) Anti-DepressantsDocument10 pagesA) A/E of Moclobemide SNATCH: A) Pharmacology 1) Anti-DepressantsNur Atiqah Mohd AzliNo ratings yet
- Structured Approach To Acute Psychiatry EmergenciesDocument41 pagesStructured Approach To Acute Psychiatry EmergenciesRaimondo RomanazziNo ratings yet
- Drug List Psych Optho NeuroDocument22 pagesDrug List Psych Optho NeuroAshley BarrileNo ratings yet
- Commonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDocument2 pagesCommonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDragutin Petrić100% (1)
- PSYC - Medication TemplateDocument15 pagesPSYC - Medication TemplateM Henry100% (1)
- Blueprints PsychiatryDocument466 pagesBlueprints Psychiatrynoir100% (5)
- Review of Antipsychotic DrugsDocument15 pagesReview of Antipsychotic DrugsTuanthonBoonlue100% (1)
- AntipsychoticsDocument10 pagesAntipsychoticswawing16No ratings yet
- Psychiatry Practice Boosters 2016: Insights from research to enhance your clinical workFrom EverandPsychiatry Practice Boosters 2016: Insights from research to enhance your clinical workNo ratings yet
- O&G: Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument3 pagesO&G: Sexually Transmitted InfectionsSok-Moi ChokNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry: DementiaDocument3 pagesPsychiatry: DementiaSok-Moi Chok100% (2)
- Psychiatry: Mental State ExaminationDocument3 pagesPsychiatry: Mental State ExaminationSok-Moi Chok100% (5)
- Judith Gardiner - Female MasculinityDocument28 pagesJudith Gardiner - Female MasculinityDimitria HerreraNo ratings yet
- The Play First Summit - 1Document7 pagesThe Play First Summit - 1Valentina ZackriasNo ratings yet
- III 1 RomanticismDocument15 pagesIII 1 Romanticismrickishe100% (3)
- Reading Response InformationDocument2 pagesReading Response InformationĐức BùiNo ratings yet
- Critical Summary of The ArticleDocument3 pagesCritical Summary of The ArticleEdsel AlapagNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - 13t - Gary DesslerDocument39 pagesHuman Resource Management - 13t - Gary Desslerhayelom0% (2)
- The Mindful Athlete by George MumfordDocument7 pagesThe Mindful Athlete by George Mumfordsimas100% (1)
- APD506 Asignment Rev 10.5Document4 pagesAPD506 Asignment Rev 10.5Sandeep NairNo ratings yet
- Film Guide CluelessDocument8 pagesFilm Guide CluelessValeria GomezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Sea Change PosterDocument7 pagesLesson 3 - Sea Change Posterapi-323655794No ratings yet
- Respiratory Biofeedback FinalDocument5 pagesRespiratory Biofeedback FinalGareth Thomas100% (2)
- ASD Early Intervention TablesDocument3 pagesASD Early Intervention Tablesjuliepipip23100% (1)
- The Success and Failure of International BusinessDocument8 pagesThe Success and Failure of International BusinessToniEltoniNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For BleedingDocument1 pageNCP Risk For BleedingJen Garzo75% (4)
- How To Really Learn SpanishDocument47 pagesHow To Really Learn Spanishlightjp171% (7)
- Mikey Newman - Objective EssayDocument6 pagesMikey Newman - Objective Essayapi-607529399No ratings yet
- WWWWMDocument36 pagesWWWWMRude Gal SheenaNo ratings yet
- Teacher Resource - The Ongoing Percentage Grade in PTGBDocument11 pagesTeacher Resource - The Ongoing Percentage Grade in PTGBapi-202232251No ratings yet
- 10 Effective Teaching StrategiesDocument5 pages10 Effective Teaching StrategiesfranceloiseNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument4 pagesReaction PaperJam Knows RightNo ratings yet
- Hawa Latifzai - Pedagogical Theory Paper FinalDocument10 pagesHawa Latifzai - Pedagogical Theory Paper Finalapi-272324384No ratings yet
- Healing Anxiety PeruDocument8 pagesHealing Anxiety Peruayahuascaassociation100% (1)
- AT3U4Document1 pageAT3U4Julio LópezNo ratings yet
- History of Management Trend - Stephen RobbinsDocument24 pagesHistory of Management Trend - Stephen Robbinstrucanh1803No ratings yet
- Introduction of Sustainable Low-Cost Housing in Ethiopia - An Innovation Diffusion PerspectiveDocument7 pagesIntroduction of Sustainable Low-Cost Housing in Ethiopia - An Innovation Diffusion PerspectiveninashiroNo ratings yet
- Nightingale PDFDocument2 pagesNightingale PDFLawrence CezarNo ratings yet
- Sip - Planning WorksheetsDocument5 pagesSip - Planning WorksheetsEr MaNo ratings yet