Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) : Wednesday, December 09, 2015 7:34 PM
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) : Wednesday, December 09, 2015 7:34 PM
Uploaded by
sda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pageseconomics lecture at uoft
Original Title
Lecture - economics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenteconomics lecture at uoft
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesGross Domestic Product (GDP) : Wednesday, December 09, 2015 7:34 PM
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) : Wednesday, December 09, 2015 7:34 PM
Uploaded by
sdaeconomics lecture at uoft
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Lecture
Wednesday, December 09, 2015
7:34 PM
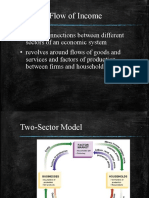
National Income Accounting
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
GDP = value of all final good produced in Canada during a period of time
1. Currently produced - not sales of used items
2. Market prices - at market prices, including indirect taxes
3. Exchanged in market - doesn't include illegal transactions
a. Imputed rent to owner's occupied houses
Measuring GDP
1. Production: value added in production
2. Expenditure: total expenditure on final goods and services
3. Income: total income earned by production
1. Production
Value of final goods and services produced in country (avoids double counting)
Value added = revenue selling product - amount paid for product
2. Expenditure
GDP = Consumption + Investment + Government + Net Exports
GDP = C + I + G + NX
Investment expenditure includes private investment but not gov. investment
Flow of net capital -> Gross Investment not net investment
Government expenditure includes investment, but not transfers and interest
3. Income
Value added in production = income
GDP includes indirect taxes - subsidies
Net Domestic Income
NDI = GDP - net indirect taxes - depreciation = part of GDP that goes to payment of owners
= salaries + profits + interest + rents + net income of unincorporated business
Also called Net Domestic Product at factor cost
Net Domestic Product at market prices = GDP - depreciation
Personal Income
Personal Income (PI) = NDI - profits + dividends + transfer payments + interest on govt. debt
Personal Disposable Income (PDI) = consumption expenditure + saving
GDP vs GNP
GDP = production within Canada of Canadian & non-resident production
GNP = production within & outside Canada of only Canadian production.
National Income of country
Real vs. Nominal GDP
Nominal GDP = value of output in current dollars (current period prices)
Changes because output and market price change
Real GDP = value of output in constant dollars (base period prices)
Only changes because output changes
Chapter 2 Page 1
Only changes because output changes
Chain Method of GDP
Averages price of current and previous year
GDP Deflator = GDP current prices / GDP base year prices x 100
CPI = consumer goods current prices / consumer goods base prices x 100
CPIX = CPI - volatile prices (i.e. oil, energy, etc.)
GDP vs. CPI
GDP is only domestic production, CPI is all purchases (domestic + foreign)
ASSUMPTIONS
1. Gross investment = net investment (no depreciation)
2. GDP = NDI (no indirect taxes/subsidies)
3. Y = GDP = NDI
IMPORTANT (1)
1. Taxes = Transfer payments = 0, Imports = Exports = 0, Profits = Dividends
2. Y = S + I
3. GDP = NDI = PI = PDI = Y = YD
4. Y = C + S
5. C + I = C + S
6. S = I
IMPORTANT (2)
1. GDP = NDI = GNP + Profits = Dividends
2. Y = C + I + G + NX
3. YD = Y - TA + TR = C + S
4. C = Y - TA + TR - S
5. Y = (Y -TA + TR - S) + I + G + NX
6. S = I + (G + TR - TA) + NX
G + TR - TA = government budget deficit
NX = net exports (trade surplus)
National Saving = Private Saving + Public Saving
NS = S + PS (or Government Budget Surplus - BS)
Chapter 2 Page 2
You might also like
- Charles Stevenson - On What Is PoemDocument35 pagesCharles Stevenson - On What Is PoemFilip Nikolić100% (1)
- Discerning of Spirits - Francis FrangipaneDocument32 pagesDiscerning of Spirits - Francis FrangipaneOgoo Honysco100% (7)
- Eco 200 - Principles of Macroeconomics: Chapter 6: National Income AccountingDocument10 pagesEco 200 - Principles of Macroeconomics: Chapter 6: National Income AccountingElaine MateoNo ratings yet
- Eco 200 - Principles of Macroeconomics: Chapter 6: National Income AccountingDocument10 pagesEco 200 - Principles of Macroeconomics: Chapter 6: National Income AccountingKate BernalNo ratings yet
- Economic Environment of Business-GdpDocument42 pagesEconomic Environment of Business-GdpBalajiNo ratings yet
- GDP, Saving and ConsumptionDocument38 pagesGDP, Saving and ConsumptionBhawna KhoslaNo ratings yet
- What Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeDocument3 pagesWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeWhat Is National IncomeSmitha RajNo ratings yet
- CH 2 MacroeconomicsDocument63 pagesCH 2 MacroeconomicsYidid GetachewNo ratings yet
- Index: Economics For FinanceDocument32 pagesIndex: Economics For FinanceJoseph PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 GDP, Inflation and UnemplyementDocument61 pagesChapter-2 GDP, Inflation and Unemplyementpapia rahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document35 pagesChapter 8Danial NorazmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document14 pagesChapter 22naolfekadu8No ratings yet
- UNIT II: National Income Concepts & MeasurementDocument30 pagesUNIT II: National Income Concepts & MeasurementPooza SunuwarNo ratings yet
- CH - 8 NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING - FINALDocument35 pagesCH - 8 NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING - FINALdeepakNo ratings yet
- Income AccountingDocument18 pagesIncome AccountingNikhil KasatNo ratings yet
- The Formula To Calculate The Components of GNP Is: Y C + I + G + X + ZDocument4 pagesThe Formula To Calculate The Components of GNP Is: Y C + I + G + X + ZUme Aima ayubNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument46 pagesNational Income AccountingMohamed AbdiNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument16 pagesNational Incomejyoti pillayNo ratings yet
- Measuring The EconomyDocument40 pagesMeasuring The EconomyTiffany Gayle bNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: National Income AccountingDocument20 pagesChapter Seven: National Income AccountingMeron GetahunNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Income &Document40 pagesCircular Flow of Income &Kunal Uddhavrao GaradNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Gross National Product (GNPDocument3 pagesGross Domestic Product (GDP) and Gross National Product (GNPJitendraNo ratings yet
- CHap. 2Document36 pagesCHap. 2ZeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6: The National Income Accounting: GDP and GNP: An OverviewDocument10 pagesMODULE 6: The National Income Accounting: GDP and GNP: An OverviewLeigh CabritoNo ratings yet
- Text BookDocument10 pagesText BookHayamnotNo ratings yet
- CPI-GNP Approaches-1Document36 pagesCPI-GNP Approaches-1Reida DelmasNo ratings yet
- National Income FinalDocument28 pagesNational Income FinalRajesh MahatoNo ratings yet
- Unit II National Income AccountingDocument61 pagesUnit II National Income Accountinggeeta neupaneNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Lecture 3: GDP: Components and MeasurementDocument12 pagesMacroeconomics: Lecture 3: GDP: Components and Measurementrahul sharmaNo ratings yet
- The Related Aggregates of National Income AreDocument12 pagesThe Related Aggregates of National Income Aretransport bassNo ratings yet
- NSS Exploring Economics 5 (3 Edition) : Revision NotesDocument2 pagesNSS Exploring Economics 5 (3 Edition) : Revision NotesinkeNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting AbelDocument12 pagesNational Income Accounting AbelKushagra AroraNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting Reference - Chapter 5Document13 pagesNational Income Accounting Reference - Chapter 5hannah_clariceNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Eco211Document67 pagesCHAPTER 2 Eco211Amalin IlyanaNo ratings yet
- The Circular-Flow Diagram: The Equality of Income and Expenditure Can Be Illustrated With TheDocument40 pagesThe Circular-Flow Diagram: The Equality of Income and Expenditure Can Be Illustrated With TheAsif WarsiNo ratings yet
- Lec 15. National Income Accounting V3 REVISEDDocument33 pagesLec 15. National Income Accounting V3 REVISEDAbhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Lecturer: Mr. AllicockDocument32 pagesMacroeconomics: Lecturer: Mr. AllicockPrecious MarksNo ratings yet
- Measuring National Output and National Income-Chapter 2Document48 pagesMeasuring National Output and National Income-Chapter 2madanNo ratings yet
- National Income: Submitted byDocument85 pagesNational Income: Submitted byShrutiNo ratings yet
- BDevs Macro National Income PDFDocument11 pagesBDevs Macro National Income PDFSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Gross National Product (GNP)Document3 pagesGross National Product (GNP)jitendra.jgec8525No ratings yet
- Me Unit-5Document7 pagesMe Unit-5Anuj YadavNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument23 pagesNational Income AccountingAmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1 MacroeconomicsDocument42 pages1 MacroeconomicsMahmoud IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Eco Quick RevisionDocument42 pagesEco Quick RevisionRitesh RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document6 pagesChapter 12bellavdbergNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument30 pagesNational IncomeTaruna Dureja BangaNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes On Unit 9Document4 pagesAdditional Notes On Unit 9Bhavna JoseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-5-6 National Income Accounting1Document37 pagesLecture 4-5-6 National Income Accounting1Deepak KapaNo ratings yet
- MTP Session 4 Reading 1. This Set of Slides 2. From Blanchard 6 Ed.: Chapter 2 - Page 40 - 45, 49 - 51Document25 pagesMTP Session 4 Reading 1. This Set of Slides 2. From Blanchard 6 Ed.: Chapter 2 - Page 40 - 45, 49 - 51DevbratRathNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - STDocument20 pagesLecture 2 - STzaim ilyasaNo ratings yet
- Eco - EnglishDocument15 pagesEco - EnglishSharmila RijalNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic ProductDocument5 pagesGross Domestic ProductabdallahmachiliNo ratings yet
- UNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationDocument15 pagesUNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationanushreeNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument37 pagesNational Income Accountingnavya.cogni21No ratings yet
- The Measurement and Structure of The National Economy: Abel, Bernanke and Croushore (Chapter 2)Document21 pagesThe Measurement and Structure of The National Economy: Abel, Bernanke and Croushore (Chapter 2)Fahad TanveerNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting-1Document30 pagesNational Income Accounting-1Manu ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic Product: Group 6 Yifan Du Chi Yan Jim Samson Wong Jany LimpiyachartDocument12 pagesGross Domestic Product: Group 6 Yifan Du Chi Yan Jim Samson Wong Jany LimpiyachartJanyaporn LimpiyachartNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP: References: Ch. 7, Macroeconomics, Roger A. ArnoldDocument12 pagesMacroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP: References: Ch. 7, Macroeconomics, Roger A. ArnoldLeonilaEnriquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI Macroeconomics PartDocument44 pagesChapter VI Macroeconomics PartBereket MuniyeNo ratings yet
- Answer The Question Below by Choosing The Right Answer Among A, B, C, or DDocument3 pagesAnswer The Question Below by Choosing The Right Answer Among A, B, C, or DAgus SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Compliance Factors Associated With Contact Lens-Related Dry EyeDocument6 pagesCompliance Factors Associated With Contact Lens-Related Dry EyeAlda Gitu RahmaNo ratings yet
- Objective in ResearchDocument7 pagesObjective in ResearchNIMSHI MCCNo ratings yet
- Ed 242 Activity Creating Online FormDocument3 pagesEd 242 Activity Creating Online FormJane Marie Albios TevesNo ratings yet
- AIIMS PG Solved Paper 1999Document3 pagesAIIMS PG Solved Paper 1999Beta ReaderNo ratings yet
- Fallacies in ReasoningDocument3 pagesFallacies in ReasoningJames Clarenze VarronNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors WordDocument64 pagesTata Motors WordSayon Das100% (1)
- Assessment Speaking & ListeningDocument26 pagesAssessment Speaking & ListeningSelvita Márquez MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Problems of Parenthood + Leadership Functions + Security Tips in The SchoolDocument8 pagesProblems of Parenthood + Leadership Functions + Security Tips in The SchoolAminu SaniNo ratings yet
- Bryan Hloom: Address: 1234 Park Avenue, Redwood City, CA 94063Document2 pagesBryan Hloom: Address: 1234 Park Avenue, Redwood City, CA 94063aykutNo ratings yet
- 18 Making Math Meaningful For Students With Learning Problems Powerful Teaching Strategies That WorkDocument79 pages18 Making Math Meaningful For Students With Learning Problems Powerful Teaching Strategies That WorkFroilan TinduganNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric SymptomsDocument65 pagesPsychiatric SymptomsEslam HamadaNo ratings yet
- NDA PeroranganDocument2 pagesNDA PeroranganAdi SusenoNo ratings yet
- Seares Vs Alzate DigestDocument1 pageSeares Vs Alzate DigestlirioNo ratings yet
- The Professional CPA Review SchoolDocument23 pagesThe Professional CPA Review SchoolGray JavierNo ratings yet
- 03 Horace Walpole, Ann Radcliffe HandoutDocument15 pages03 Horace Walpole, Ann Radcliffe HandoutDaniraKucevicNo ratings yet
- Indian Gaming Regulatory Act: HearingDocument214 pagesIndian Gaming Regulatory Act: HearingScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- தசம பின்னம் ஆண்டு 4Document22 pagesதசம பின்னம் ஆண்டு 4Jessica BarnesNo ratings yet
- Response Sheet For SCQDocument7 pagesResponse Sheet For SCQChandresh Gambhir100% (1)
- Solomon Concert ReviewDocument4 pagesSolomon Concert ReviewBrianWeathersNo ratings yet
- What Is The Poet's Appeal To The People? Ans. The Poet Appeals To All TheDocument35 pagesWhat Is The Poet's Appeal To The People? Ans. The Poet Appeals To All Thecbs123abcNo ratings yet
- English 8 Course OutlineDocument7 pagesEnglish 8 Course OutlineYhel LantionNo ratings yet
- 1997 Hidalgo, J. Investigacion Educat Iva - Una Estrategia ConstructivistaDocument23 pages1997 Hidalgo, J. Investigacion Educat Iva - Una Estrategia ConstructivistaKarla FaNo ratings yet
- ASHA Statement On CASDocument3 pagesASHA Statement On CASAGSpeechLPNo ratings yet
- Cwts - Module - 1st Semester A.Y 2022-2023Document71 pagesCwts - Module - 1st Semester A.Y 2022-2023Jae Ashlie BernabeNo ratings yet
- SEC AssignmentDocument5 pagesSEC AssignmentChandra Prakash DixitNo ratings yet
- Dustin Hoffman Masterclass NotesDocument5 pagesDustin Hoffman Masterclass NotesDorian BasteNo ratings yet
- TCRP REPORT 178. A National Training and Certification Program For Transit Vehicle Maintenance Instructors TRANSIT COOPERATIVE RESEARCH PROGRAMDocument114 pagesTCRP REPORT 178. A National Training and Certification Program For Transit Vehicle Maintenance Instructors TRANSIT COOPERATIVE RESEARCH PROGRAMkrristinNo ratings yet