Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oracle Processes
Oracle Processes
Uploaded by
Anonymous auWroiCjECopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Oracle Database Administration Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandOracle Database Administration Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Correction of EntryDocument5 pagesCorrection of EntryMineNo ratings yet
- Quick Oracle 9i Performance Tuning Tips & ScriptsDocument7 pagesQuick Oracle 9i Performance Tuning Tips & ScriptsEder CoutoNo ratings yet
- Ethics and TechnologyDocument42 pagesEthics and TechnologyZeeshanAhmad100% (1)
- Seismic Analysis of Concrete Gravity Dam-Reservoir-Foundation Interaction With Reservoir Bottom Absorption Effect PDFDocument10 pagesSeismic Analysis of Concrete Gravity Dam-Reservoir-Foundation Interaction With Reservoir Bottom Absorption Effect PDFSATYAJIT PALNo ratings yet
- Instance Background Processes: Redo Log BufferDocument2 pagesInstance Background Processes: Redo Log BufferMohammednazeer Nazeer UddinNo ratings yet
- Oracle Background ProcessesDocument3 pagesOracle Background ProcessesSatya RanimekalaNo ratings yet
- Background Processes in OracleDocument12 pagesBackground Processes in OracleGautam TrivediNo ratings yet
- Background Processes in OracleDocument37 pagesBackground Processes in OracleSraVanKuMarThadakamallaNo ratings yet
- Background Processes in OracleDocument11 pagesBackground Processes in OracleAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Oracle 8: Database Administration (Exam # 1Z0-013) : The SgaDocument16 pagesOracle 8: Database Administration (Exam # 1Z0-013) : The SgaAnonymous qPo1wFyH0ENo ratings yet
- 2 - Oracle OCP ExamDocument16 pages2 - Oracle OCP ExamAnonymous qPo1wFyH0ENo ratings yet
- DBA Interview Questions With Answers Part1Document134 pagesDBA Interview Questions With Answers Part1RajeshRajNo ratings yet
- 2 - Oracle 8 OCP Admin ExamDocument16 pages2 - Oracle 8 OCP Admin ExamAnonymous qPo1wFyH0ENo ratings yet
- DBA Interview Questions With Answers Part1Document134 pagesDBA Interview Questions With Answers Part1RajeshRaj100% (1)
- Pres4-Oracle Process StructureDocument21 pagesPres4-Oracle Process StructureAbdul WaheedNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA InterviewDocument73 pagesOracle DBA InterviewjaydevdangarNo ratings yet
- DBA Interview Questions With AnswersDocument104 pagesDBA Interview Questions With AnswersBirendra Padhi67% (3)
- Oracle 12c Multitnt ArchitectureDocument15 pagesOracle 12c Multitnt ArchitectureAzmath Tech TutsNo ratings yet
- Oracle Architecture Interview QuestionsDocument11 pagesOracle Architecture Interview QuestionsAnush Reddy100% (1)
- DBA Interview Questions With AnswersDocument118 pagesDBA Interview Questions With AnswersAnil DevNo ratings yet
- Database AdministrationDocument138 pagesDatabase AdministrationMir HusenNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA 11gR2 ArchitectureDocument9 pagesOracle DBA 11gR2 ArchitectureAzmath Tech TutsNo ratings yet
- QuestionaireDocument106 pagesQuestionairevenkatsainath06No ratings yet
- Oracle Background ProcessesDocument5 pagesOracle Background Processesalok_mishra4533No ratings yet
- ORACLE ClassDocument26 pagesORACLE Classssv pNo ratings yet
- 08.705 RTOS Module 3 NotesDocument19 pages08.705 RTOS Module 3 NotesAssini HussainNo ratings yet
- Db2 DBA Check ListDocument20 pagesDb2 DBA Check ListSarath RamineniNo ratings yet
- You Can See The Oracle Background Processes With This QueryDocument5 pagesYou Can See The Oracle Background Processes With This QueryAbdul NabiNo ratings yet
- What Are The Back Ground Processes in Oracle and What Are They?Document23 pagesWhat Are The Back Ground Processes in Oracle and What Are They?Sachin100% (1)
- Tricky PLSQL NotesDocument209 pagesTricky PLSQL NotesRanitha NairNo ratings yet
- Oracle BasicsDocument34 pagesOracle BasicsChakri ksNo ratings yet
- Sapinterview QuesDocument5 pagesSapinterview Quessatya1207No ratings yet
- Process Management 3.1 What Is A ProcessDocument11 pagesProcess Management 3.1 What Is A ProcesspritiNo ratings yet
- PIA Training Centre Prime CommunicationsDocument14 pagesPIA Training Centre Prime CommunicationsArbabNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA Interview Questions and Answers From GeekInterviewDocument3 pagesOracle DBA Interview Questions and Answers From GeekInterviewPatti PrashanthNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database ArchitectureDocument7 pagesOracle Database ArchitecturearavinthNo ratings yet
- SCN and Instance RecoveryDocument9 pagesSCN and Instance RecoveryRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Operating System: Assighnment - 1Document6 pagesOperating System: Assighnment - 1NarayanaMunnaNo ratings yet
- Process Architecture: Open, Comprehensive, and Integrated Approach To Information Management. An OracleDocument13 pagesProcess Architecture: Open, Comprehensive, and Integrated Approach To Information Management. An OraclevishwasdeshkarNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument5 pagesOperating Systemsiddheshpatole153No ratings yet
- Problem ReviewDocument16 pagesProblem ReviewMoe Myintt Myintt50% (2)
- OS NotesDocument86 pagesOS Notesmyname2050No ratings yet
- Oracle Book-Final FormattedDocument168 pagesOracle Book-Final Formattedkranthi633100% (1)
- IBM DB2 UDB Versus Oracle Backup and RecoveryDocument62 pagesIBM DB2 UDB Versus Oracle Backup and Recoveryapi-2902935No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument83 pagesChapter 2 PDFMebratu AsratNo ratings yet
- Oracle-9: Unit - 9 (A) One Mark QuestionsDocument12 pagesOracle-9: Unit - 9 (A) One Mark QuestionsJonty BabaNo ratings yet
- Describe Oracle Architecture in Brief.: AnswerDocument8 pagesDescribe Oracle Architecture in Brief.: AnswersonijayminNo ratings yet
- SP01 - Spool Request Screen - Check For Spool That Are in Request For Over An HourDocument21 pagesSP01 - Spool Request Screen - Check For Spool That Are in Request For Over An HourdeepakNo ratings yet
- Oracle Rdbms KeypointsDocument1,439 pagesOracle Rdbms Keypointsdeepak1133100% (2)
- Operating Systems Lecture Notes Processes and Threads: Martin C. RinardDocument12 pagesOperating Systems Lecture Notes Processes and Threads: Martin C. RinardSandeep MinhasNo ratings yet
- Resources AllocationDocument10 pagesResources AllocationTedla MelekotNo ratings yet
- Study Material For OracleDocument197 pagesStudy Material For OracleSidharth SontiNo ratings yet
- Study Material For OracleDocument198 pagesStudy Material For OracleSarath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA ArchitectureDocument17 pagesOracle DBA ArchitectureDiwakar Reddy SNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument90 pagesUnit Iisk9271054No ratings yet
- Diagnosis For DB HungDocument5 pagesDiagnosis For DB Hungnu04330No ratings yet
- Operating System: COPE/Technical Test/Interview/Database Questions & AnswersDocument25 pagesOperating System: COPE/Technical Test/Interview/Database Questions & AnswersVasu DevanNo ratings yet
- DocDocument3 pagesDocDropdead OHNo ratings yet
- Background Processes 12cDocument12 pagesBackground Processes 12cPandiarajan DharmalingamNo ratings yet
- Oracle ArchitectureDocument5 pagesOracle ArchitectureVenu BabuNo ratings yet
- Instance: What Is An Oracle Database?Document7 pagesInstance: What Is An Oracle Database?Vinay GoddemmeNo ratings yet
- F Lecture o L 15 3 Documentation and Obtaining Consideration of Laws andDocument9 pagesF Lecture o L 15 3 Documentation and Obtaining Consideration of Laws andbehroz khanNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Subnet An Ipv4 Network: Addressing TableDocument5 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnet An Ipv4 Network: Addressing TableruriNo ratings yet
- Implications of The TrinityDocument6 pagesImplications of The TrinityTh3Lov3OfG0dNo ratings yet
- Yamuna Biodiversity Park Yamuna Biodiversity ParkDocument37 pagesYamuna Biodiversity Park Yamuna Biodiversity ParkAnsh SagrohaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FictionDocument7 pagesIntroduction To FictionParlin PardedeNo ratings yet
- Promark 500: Multi-Constellation Gnss ReceiverDocument4 pagesPromark 500: Multi-Constellation Gnss Receiverdummy_officeNo ratings yet
- Schaeffler Technical Pocket Guide PDFDocument716 pagesSchaeffler Technical Pocket Guide PDFStoica ValentinNo ratings yet
- JumpchainDocument28 pagesJumpchainKavin VishmikaNo ratings yet
- Satanic Panic - The Creation of - Victor, Jeffrey S-153-350Document198 pagesSatanic Panic - The Creation of - Victor, Jeffrey S-153-350BRUNNA FELKL DO NASCIMENTONo ratings yet
- Sectional Title Ownership Podcast SummaryDocument4 pagesSectional Title Ownership Podcast SummaryannNo ratings yet
- Chess and NutritionDocument6 pagesChess and NutritionAnonymous pTZCrF7No ratings yet
- Jurnal EndometriosisDocument17 pagesJurnal Endometriosisiduy cantikNo ratings yet
- Geagonia Vs CADocument7 pagesGeagonia Vs CADanielle Ray V. VelascoNo ratings yet
- PikeDocument8 pagesPikeJamieDuncanNo ratings yet
- Comercial BanksDocument21 pagesComercial BanksSanto AntonyNo ratings yet
- Reconstructing The Origin of Andaman IslandersDocument1 pageReconstructing The Origin of Andaman IslandersCulture HeritageNo ratings yet
- Macroscript For Interactive PowerpointDocument2 pagesMacroscript For Interactive PowerpointAldrin PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- Tindahan Pinoy NG Laguna Business PlanDocument15 pagesTindahan Pinoy NG Laguna Business PlanRica Kathrine Reyes AustriaNo ratings yet
- Paley CommentaryDocument746 pagesPaley CommentaryTrivia Tatia Moonson100% (2)
- The Natural Setting and Its People 1. How The Earth Was in The BeginningDocument20 pagesThe Natural Setting and Its People 1. How The Earth Was in The Beginningcharls xyrhen BalangaNo ratings yet
- ICA Notes For Telegram 1646048676072Document18 pagesICA Notes For Telegram 1646048676072Aditi JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Art Lesson Plan - PrintmakingDocument5 pagesArt Lesson Plan - PrintmakingLloyd Zeta PeranteNo ratings yet
- Influence of Motivation On Teachers Performance in A Local Government Area in NigeriaDocument7 pagesInfluence of Motivation On Teachers Performance in A Local Government Area in NigeriaJay GalangNo ratings yet
- Around The WorldDocument6 pagesAround The WorldNEOFIX ServiceNo ratings yet
- Figure Description TM254 Practice Examination Paper SolutionsDocument22 pagesFigure Description TM254 Practice Examination Paper Solutionsmelissa taylorNo ratings yet
- Customer Delight ServiceDocument4 pagesCustomer Delight Service79ImtiyazNo ratings yet
Oracle Processes
Oracle Processes
Uploaded by
Anonymous auWroiCjEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oracle Processes
Oracle Processes
Uploaded by
Anonymous auWroiCjECopyright:
Available Formats
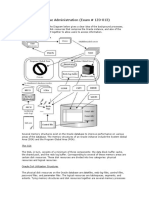
Oracle Processes
Three
types
of
processes
are
part
Background
processes are
involved
in
running
the
Server
processes negotiate
the
actions
User processes commonly work outside the database server itself
accesses the database.
of
the
instance:
Oracle
software
itself.
of
the
users.
to run the application that
Background processes
PMON : The process monitor manages the systems server processes. It cleans up failed
processes by releasing resources and rolling back uncommitted data
SMON : The system monitor is primarily responsible for instance recovery. If the database
crashes and redo information must be read and applied, the SMON takes care of it. It also cleans and
releases temporary space.
DBWn : The database writers sole job is taking dirty blocks from the dirty list and writing them to
disk. There can be up to 20 of them, hence the n. It starts as DBW0 and continues with DBW1, DBW2,
and so on. After DBW9, it continues with DBWa through DBWj. An average system wont see more than a
few of these.
LGWR : The log writer process flushes the redo log buffer. It writes the redo entries to disk and
signals a completion.
CKPT : The checkpoint process is responsible for initiating check points. A check point is when
the system periodically dumps all the dirty buffers to disk. Most commonly, this occurs when the database
receives a shutdown command. It also updates the data file headers and the control files with the
check point information so the SMON know where to start recovery in the event of a system crash.
The above mentioned 5 processes are mandatory processes that are must required for any Oracle
Instance to run properly. Any one process missing can bring down the whole instance.
The rest of the processes are optional processes. They may or may not be present in the system
depending
upon
the
additional
functionality
assigned
to
the
DB
instance.
ARCn : Up to 30 archiver processes (09, at) are responsible for copying filled redo logs to the
archived redo storage area. If your database isnt running in archive mode, this process shuts down.
CJQ0 : The job queue coordinator checks for scheduled tasks within the database. These jobs
can be set up by the user or can be internal jobs for maintenance. When it finds a job that must be run it
spawns the following goodie.
J000 : A job queue process slave actually runs the job. There can be up to 1,000 of them (000
999).
DIA0 : The diagnosability process resolves deadlock situations and investigates hanging issues.
VKTM : The virtual keeper of time sounds like a fantasy game character but simply provides a
time reference within the database.
You might also like
- Oracle Database Administration Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandOracle Database Administration Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Correction of EntryDocument5 pagesCorrection of EntryMineNo ratings yet
- Quick Oracle 9i Performance Tuning Tips & ScriptsDocument7 pagesQuick Oracle 9i Performance Tuning Tips & ScriptsEder CoutoNo ratings yet
- Ethics and TechnologyDocument42 pagesEthics and TechnologyZeeshanAhmad100% (1)
- Seismic Analysis of Concrete Gravity Dam-Reservoir-Foundation Interaction With Reservoir Bottom Absorption Effect PDFDocument10 pagesSeismic Analysis of Concrete Gravity Dam-Reservoir-Foundation Interaction With Reservoir Bottom Absorption Effect PDFSATYAJIT PALNo ratings yet
- Instance Background Processes: Redo Log BufferDocument2 pagesInstance Background Processes: Redo Log BufferMohammednazeer Nazeer UddinNo ratings yet
- Oracle Background ProcessesDocument3 pagesOracle Background ProcessesSatya RanimekalaNo ratings yet
- Background Processes in OracleDocument12 pagesBackground Processes in OracleGautam TrivediNo ratings yet
- Background Processes in OracleDocument37 pagesBackground Processes in OracleSraVanKuMarThadakamallaNo ratings yet
- Background Processes in OracleDocument11 pagesBackground Processes in OracleAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Oracle 8: Database Administration (Exam # 1Z0-013) : The SgaDocument16 pagesOracle 8: Database Administration (Exam # 1Z0-013) : The SgaAnonymous qPo1wFyH0ENo ratings yet
- 2 - Oracle OCP ExamDocument16 pages2 - Oracle OCP ExamAnonymous qPo1wFyH0ENo ratings yet
- DBA Interview Questions With Answers Part1Document134 pagesDBA Interview Questions With Answers Part1RajeshRajNo ratings yet
- 2 - Oracle 8 OCP Admin ExamDocument16 pages2 - Oracle 8 OCP Admin ExamAnonymous qPo1wFyH0ENo ratings yet
- DBA Interview Questions With Answers Part1Document134 pagesDBA Interview Questions With Answers Part1RajeshRaj100% (1)
- Pres4-Oracle Process StructureDocument21 pagesPres4-Oracle Process StructureAbdul WaheedNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA InterviewDocument73 pagesOracle DBA InterviewjaydevdangarNo ratings yet
- DBA Interview Questions With AnswersDocument104 pagesDBA Interview Questions With AnswersBirendra Padhi67% (3)
- Oracle 12c Multitnt ArchitectureDocument15 pagesOracle 12c Multitnt ArchitectureAzmath Tech TutsNo ratings yet
- Oracle Architecture Interview QuestionsDocument11 pagesOracle Architecture Interview QuestionsAnush Reddy100% (1)
- DBA Interview Questions With AnswersDocument118 pagesDBA Interview Questions With AnswersAnil DevNo ratings yet
- Database AdministrationDocument138 pagesDatabase AdministrationMir HusenNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA 11gR2 ArchitectureDocument9 pagesOracle DBA 11gR2 ArchitectureAzmath Tech TutsNo ratings yet
- QuestionaireDocument106 pagesQuestionairevenkatsainath06No ratings yet
- Oracle Background ProcessesDocument5 pagesOracle Background Processesalok_mishra4533No ratings yet
- ORACLE ClassDocument26 pagesORACLE Classssv pNo ratings yet
- 08.705 RTOS Module 3 NotesDocument19 pages08.705 RTOS Module 3 NotesAssini HussainNo ratings yet
- Db2 DBA Check ListDocument20 pagesDb2 DBA Check ListSarath RamineniNo ratings yet
- You Can See The Oracle Background Processes With This QueryDocument5 pagesYou Can See The Oracle Background Processes With This QueryAbdul NabiNo ratings yet
- What Are The Back Ground Processes in Oracle and What Are They?Document23 pagesWhat Are The Back Ground Processes in Oracle and What Are They?Sachin100% (1)
- Tricky PLSQL NotesDocument209 pagesTricky PLSQL NotesRanitha NairNo ratings yet
- Oracle BasicsDocument34 pagesOracle BasicsChakri ksNo ratings yet
- Sapinterview QuesDocument5 pagesSapinterview Quessatya1207No ratings yet
- Process Management 3.1 What Is A ProcessDocument11 pagesProcess Management 3.1 What Is A ProcesspritiNo ratings yet
- PIA Training Centre Prime CommunicationsDocument14 pagesPIA Training Centre Prime CommunicationsArbabNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA Interview Questions and Answers From GeekInterviewDocument3 pagesOracle DBA Interview Questions and Answers From GeekInterviewPatti PrashanthNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database ArchitectureDocument7 pagesOracle Database ArchitecturearavinthNo ratings yet
- SCN and Instance RecoveryDocument9 pagesSCN and Instance RecoveryRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Operating System: Assighnment - 1Document6 pagesOperating System: Assighnment - 1NarayanaMunnaNo ratings yet
- Process Architecture: Open, Comprehensive, and Integrated Approach To Information Management. An OracleDocument13 pagesProcess Architecture: Open, Comprehensive, and Integrated Approach To Information Management. An OraclevishwasdeshkarNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument5 pagesOperating Systemsiddheshpatole153No ratings yet
- Problem ReviewDocument16 pagesProblem ReviewMoe Myintt Myintt50% (2)
- OS NotesDocument86 pagesOS Notesmyname2050No ratings yet
- Oracle Book-Final FormattedDocument168 pagesOracle Book-Final Formattedkranthi633100% (1)
- IBM DB2 UDB Versus Oracle Backup and RecoveryDocument62 pagesIBM DB2 UDB Versus Oracle Backup and Recoveryapi-2902935No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument83 pagesChapter 2 PDFMebratu AsratNo ratings yet
- Oracle-9: Unit - 9 (A) One Mark QuestionsDocument12 pagesOracle-9: Unit - 9 (A) One Mark QuestionsJonty BabaNo ratings yet
- Describe Oracle Architecture in Brief.: AnswerDocument8 pagesDescribe Oracle Architecture in Brief.: AnswersonijayminNo ratings yet
- SP01 - Spool Request Screen - Check For Spool That Are in Request For Over An HourDocument21 pagesSP01 - Spool Request Screen - Check For Spool That Are in Request For Over An HourdeepakNo ratings yet
- Oracle Rdbms KeypointsDocument1,439 pagesOracle Rdbms Keypointsdeepak1133100% (2)
- Operating Systems Lecture Notes Processes and Threads: Martin C. RinardDocument12 pagesOperating Systems Lecture Notes Processes and Threads: Martin C. RinardSandeep MinhasNo ratings yet
- Resources AllocationDocument10 pagesResources AllocationTedla MelekotNo ratings yet
- Study Material For OracleDocument197 pagesStudy Material For OracleSidharth SontiNo ratings yet
- Study Material For OracleDocument198 pagesStudy Material For OracleSarath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA ArchitectureDocument17 pagesOracle DBA ArchitectureDiwakar Reddy SNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument90 pagesUnit Iisk9271054No ratings yet
- Diagnosis For DB HungDocument5 pagesDiagnosis For DB Hungnu04330No ratings yet
- Operating System: COPE/Technical Test/Interview/Database Questions & AnswersDocument25 pagesOperating System: COPE/Technical Test/Interview/Database Questions & AnswersVasu DevanNo ratings yet
- DocDocument3 pagesDocDropdead OHNo ratings yet
- Background Processes 12cDocument12 pagesBackground Processes 12cPandiarajan DharmalingamNo ratings yet
- Oracle ArchitectureDocument5 pagesOracle ArchitectureVenu BabuNo ratings yet
- Instance: What Is An Oracle Database?Document7 pagesInstance: What Is An Oracle Database?Vinay GoddemmeNo ratings yet
- F Lecture o L 15 3 Documentation and Obtaining Consideration of Laws andDocument9 pagesF Lecture o L 15 3 Documentation and Obtaining Consideration of Laws andbehroz khanNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Subnet An Ipv4 Network: Addressing TableDocument5 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnet An Ipv4 Network: Addressing TableruriNo ratings yet
- Implications of The TrinityDocument6 pagesImplications of The TrinityTh3Lov3OfG0dNo ratings yet
- Yamuna Biodiversity Park Yamuna Biodiversity ParkDocument37 pagesYamuna Biodiversity Park Yamuna Biodiversity ParkAnsh SagrohaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FictionDocument7 pagesIntroduction To FictionParlin PardedeNo ratings yet
- Promark 500: Multi-Constellation Gnss ReceiverDocument4 pagesPromark 500: Multi-Constellation Gnss Receiverdummy_officeNo ratings yet
- Schaeffler Technical Pocket Guide PDFDocument716 pagesSchaeffler Technical Pocket Guide PDFStoica ValentinNo ratings yet
- JumpchainDocument28 pagesJumpchainKavin VishmikaNo ratings yet
- Satanic Panic - The Creation of - Victor, Jeffrey S-153-350Document198 pagesSatanic Panic - The Creation of - Victor, Jeffrey S-153-350BRUNNA FELKL DO NASCIMENTONo ratings yet
- Sectional Title Ownership Podcast SummaryDocument4 pagesSectional Title Ownership Podcast SummaryannNo ratings yet
- Chess and NutritionDocument6 pagesChess and NutritionAnonymous pTZCrF7No ratings yet
- Jurnal EndometriosisDocument17 pagesJurnal Endometriosisiduy cantikNo ratings yet
- Geagonia Vs CADocument7 pagesGeagonia Vs CADanielle Ray V. VelascoNo ratings yet
- PikeDocument8 pagesPikeJamieDuncanNo ratings yet
- Comercial BanksDocument21 pagesComercial BanksSanto AntonyNo ratings yet
- Reconstructing The Origin of Andaman IslandersDocument1 pageReconstructing The Origin of Andaman IslandersCulture HeritageNo ratings yet
- Macroscript For Interactive PowerpointDocument2 pagesMacroscript For Interactive PowerpointAldrin PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- Tindahan Pinoy NG Laguna Business PlanDocument15 pagesTindahan Pinoy NG Laguna Business PlanRica Kathrine Reyes AustriaNo ratings yet
- Paley CommentaryDocument746 pagesPaley CommentaryTrivia Tatia Moonson100% (2)
- The Natural Setting and Its People 1. How The Earth Was in The BeginningDocument20 pagesThe Natural Setting and Its People 1. How The Earth Was in The Beginningcharls xyrhen BalangaNo ratings yet
- ICA Notes For Telegram 1646048676072Document18 pagesICA Notes For Telegram 1646048676072Aditi JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Art Lesson Plan - PrintmakingDocument5 pagesArt Lesson Plan - PrintmakingLloyd Zeta PeranteNo ratings yet
- Influence of Motivation On Teachers Performance in A Local Government Area in NigeriaDocument7 pagesInfluence of Motivation On Teachers Performance in A Local Government Area in NigeriaJay GalangNo ratings yet
- Around The WorldDocument6 pagesAround The WorldNEOFIX ServiceNo ratings yet
- Figure Description TM254 Practice Examination Paper SolutionsDocument22 pagesFigure Description TM254 Practice Examination Paper Solutionsmelissa taylorNo ratings yet
- Customer Delight ServiceDocument4 pagesCustomer Delight Service79ImtiyazNo ratings yet