Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA Sequencing: How Do You Do It?
DNA Sequencing: How Do You Do It?
Uploaded by
jangam_rajesh1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
133 views12 pagesDNA sequencing determines the order of nucleotides in an organism's DNA. The most common method is dideoxy sequencing, which uses chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. DNA and a primer are mixed with normal nucleotides and one radioactively-labeled nucleotide in four separate tubes, each with a different dideoxynucleotide. DNA polymerase synthesizes new strands until a dideoxynucleotide is incorporated, terminating synthesis. Fragments of different lengths are separated by gel electrophoresis and visualized to determine the sequence. Modern automated sequencing uses fluorescent dyes instead of radioactivity.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lec 15 DNA Sequencing
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDNA sequencing determines the order of nucleotides in an organism's DNA. The most common method is dideoxy sequencing, which uses chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. DNA and a primer are mixed with normal nucleotides and one radioactively-labeled nucleotide in four separate tubes, each with a different dideoxynucleotide. DNA polymerase synthesizes new strands until a dideoxynucleotide is incorporated, terminating synthesis. Fragments of different lengths are separated by gel electrophoresis and visualized to determine the sequence. Modern automated sequencing uses fluorescent dyes instead of radioactivity.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
133 views12 pagesDNA Sequencing: How Do You Do It?
DNA Sequencing: How Do You Do It?
Uploaded by
jangam_rajesh123DNA sequencing determines the order of nucleotides in an organism's DNA. The most common method is dideoxy sequencing, which uses chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. DNA and a primer are mixed with normal nucleotides and one radioactively-labeled nucleotide in four separate tubes, each with a different dideoxynucleotide. DNA polymerase synthesizes new strands until a dideoxynucleotide is incorporated, terminating synthesis. Fragments of different lengths are separated by gel electrophoresis and visualized to determine the sequence. Modern automated sequencing uses fluorescent dyes instead of radioactivity.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
DNA Sequencing
How do you do it?
DNA Sequencing
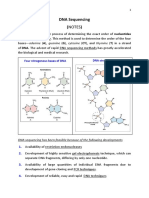
DNA sequencing – used to determine the
actual DNA sequence of an organism.
Using a computer, one can identify an organism,
and predict protein sequences and functions
based on the nucleic acid data.
The most commonly used sequencing method is
the dideoxy method.
This method uses dideoxynucleotide triphosphates(ddNTPs)
which have an H on the 3’ carbon of the ribose sugar instead
of the normal OH found in deoxynucleotide triphosphates
(dNTPs).
Dideoxynucleotides are chain terminators.
In a synthesis reaction, if a dideoxynucleotide is added instead
of the normal deoxynucleotide, the synthesis stops at that
point because the 3’OH necessary for the addition of the next
nucleotide is absent.
Deoxy versus dideoxy
DNA synthesis
DNA sequencing continued
In the dideoxy method of sequencing, the template DNA that
is to be sequenced is mixed with a primer complementary to
the template DNA and the four normal dNTPs, one of which
is radioactively labeled for subsequent visualization
purposes.
This mixture is then splint into four different tubes that are
labeled A, C, G, and T. Each tube is then “spiked” with a
different ddNTP (ddATP for tube A, ddCTP for tube C,
ddGTT for tube G, or ddTTP for tube T).
DNA polymerase is added and using the DNA template and
its’ complementary primer, the synthesis of new strands of
DNA complementary to the template begins.
Occasionally a dideoxynucleotide is added instead of the
normal deoxynucleotide and synthesis of that strand is
terminated at that point.
DNA sequencing continued
In the tube containing ddATP, some percentage of newly
synthesized molecules will get a ddATP in each place that
there is a T in the template DNA.
The result is a set of new DNA molecules in tube A, each of
which ends in an A.
A similar type of reaction occurs in the three other tubes to
result in molecules that end in C, G, and T in tubes C, G,
and T respectively.
After the synthesis reactions are complete, the products of
the four different tubes are loaded onto four adjacent lane of
a polyacrylamide gel and the different fragments are
separated by size.
The sequencing gel is able to resolve fragments that differ in
size from each other by only one base.
DNA sequencing continued
After electrophoresis to separate the fragments by
size, the fragments are visualized to exposing the
gel to photographic film (Remember that one
nucleotide was radioactively labeled).
All fragments in lane A will end in an A, fragments
in lane C will all end in a C, fragments in lane G
will all end in a G, and fragments in lane T will all
end in a T.
The sequence of the DNA is read from the gel by
starting at the bottom and reading upward.
Dideoxy DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing
Automated DNA sequencing – in automated DNA
sequencing a radioactive deoxynucleotide is not used
and all four dideoxy reactions are done in a single
tube.
This is possible because each ddNTPs is labeled with
a different flourescent dye.
Therefore the dye present in each synthesized
fragment corresponds to the dye attached to the
dideoxynucleotide that was added to terminate the
synthesis of that particular fragment.
The contents of the single tube reaction are loaded
onto a single lane of a gel and electrophoresis is
done.
DNA Sequencing
A flourimeter and computer are hooked up to
the gel and they detect and record the dye
attached to the fragments as they come off
the gel.
The sequence is determined by the order of
the dyes coming off the gel.
Automated DNA sequencing
You might also like
- Molecular Biology ExperimentDocument6 pagesMolecular Biology ExperimentWalwin Hare100% (1)
- E-Book No.05 On Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)Document32 pagesE-Book No.05 On Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)sriram100% (1)
- Quality Assessment of Commercial Sandcrete Blocks in Minna Metroplosis Nigerstate-2Document75 pagesQuality Assessment of Commercial Sandcrete Blocks in Minna Metroplosis Nigerstate-2Victor OmotoriogunNo ratings yet
- Tack Welding PowerPointDocument94 pagesTack Welding PowerPointCheerag100% (1)
- DNA SequencingDocument34 pagesDNA Sequencingmnouma1612No ratings yet
- Techniques of DNA Sequencing (ASSIGNMENT)Document6 pagesTechniques of DNA Sequencing (ASSIGNMENT)Speech's ClubNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencin2Document2 pagesDNA Sequencin2praneeth06No ratings yet
- What Is DNA SequencingDocument8 pagesWhat Is DNA SequencingjosephineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document19 pagesLecture 2MuhammadFakhriAimi100% (1)
- DNA Sequencing NCBIDocument2 pagesDNA Sequencing NCBIMostafa55 662No ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument8 pagesDNA SequencingAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- SEQUENCING ATU OnlineDocument39 pagesSEQUENCING ATU Onlinemaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Genome Sequencing: Sanger Sequencing: The Chain Termination MethodDocument5 pagesGenome Sequencing: Sanger Sequencing: The Chain Termination MethodansahNo ratings yet
- Dna Sequencing PDFDocument5 pagesDna Sequencing PDFMarcelino CalataNo ratings yet
- DNA TechnologyDocument27 pagesDNA TechnologyIM CTNo ratings yet
- Sanger Sequence Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesSanger Sequence Lecture NotesneelamysrNo ratings yet
- Sanger SequencingDocument4 pagesSanger SequencingMilka RahmanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic - Biotechnology - Forensic Biology and - Biological SystematicsDocument5 pagesDiagnostic - Biotechnology - Forensic Biology and - Biological SystematicsAngelle Loise EstanteNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument21 pagesDNA SequencingAsfoor gake1100% (1)
- Dna Sequencing (Sanger's Method)Document12 pagesDna Sequencing (Sanger's Method)Ajay KumarNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Chapter 4 - DNA SequencingDocument20 pages4.3 Chapter 4 - DNA SequencingShafiqahFazyaziqahNo ratings yet
- Dna Sequence 2024Document11 pagesDna Sequence 2024Mohab EhabNo ratings yet
- Dna Sequencing MethodsDocument29 pagesDna Sequencing MethodsWilson Anandaraj92% (13)
- Sanger Method of DNA SequencingDocument15 pagesSanger Method of DNA SequencingDipesh karnNo ratings yet
- 23112020213036-DNA Sequencing PPTDocument23 pages23112020213036-DNA Sequencing PPTgundlapalli.2023No ratings yet
- 23112020213036-DNA Sequencing PPTDocument23 pages23112020213036-DNA Sequencing PPTgundlapalli.2023No ratings yet
- Biotech Group 5Document6 pagesBiotech Group 5CarminexxxNo ratings yet
- DNA Isolation, PCR & Sequencing: Dr. Dr. Mgs. Irsan Saleh, M.BiomedDocument22 pagesDNA Isolation, PCR & Sequencing: Dr. Dr. Mgs. Irsan Saleh, M.BiomedUmiieg MiansyahNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing:: Sanger Method (Dideoxynucleotide Chain Termination)Document4 pagesDNA Sequencing:: Sanger Method (Dideoxynucleotide Chain Termination)Nitu ThulasidharanNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument60 pagesDNA Sequencingabimbolagrace356No ratings yet
- The Sanger Method: Background InformationDocument5 pagesThe Sanger Method: Background InformationSâthí SàthîNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing SlidesDocument64 pagesDNA Sequencing SlideskittyngameNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - 2023 - DNA SequencingDocument67 pagesLecture 3 - 2023 - DNA SequencingChen ZhonghaoNo ratings yet
- GENETICSDocument37 pagesGENETICSJohn KennedyNo ratings yet
- Dna Sequence (Lab Activity)Document2 pagesDna Sequence (Lab Activity)Jane Valine BalinoNo ratings yet
- Lec-9 DNA SequencingDocument31 pagesLec-9 DNA SequencingRabiul IslamNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology 8Document17 pagesBiotechnology 8Angelle Loise EstanteNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing pptb2.0Document22 pagesDNA Sequencing pptb2.0Muhammad Touseef TahirNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing & ApplicationDocument15 pagesDNA Sequencing & Applicationshamidr99No ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument9 pagesDNA SequencingDr Sanjeeb Kumar Dey BaidyaNo ratings yet
- 14.2 DNA Structure and SequencingDocument7 pages14.2 DNA Structure and SequencingJoanna Maurene SalimbotNo ratings yet
- Science of LIVING SYSTEM AB (Part of Unit 2)Document46 pagesScience of LIVING SYSTEM AB (Part of Unit 2)himanshu_agraNo ratings yet
- Dna Sequencing: by - Kanika 1603Document75 pagesDna Sequencing: by - Kanika 1603biotechengineer100% (1)
- Dna SeqDocument2 pagesDna SeqGup RatNo ratings yet
- PCR Crime Scene ReportDocument16 pagesPCR Crime Scene ReportAdibah Ahmad100% (1)
- Sequencing NotesDocument14 pagesSequencing NotesRASHINo ratings yet
- Bio101 2 DnaSequencingDocument6 pagesBio101 2 DnaSequencingdmjuncalNo ratings yet
- Methods Molecular Cardiology:n: The Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument7 pagesMethods Molecular Cardiology:n: The Polymerase Chain ReactionmarcelsNo ratings yet
- Up 2Document1 pageUp 2Hannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Sanger Sequencing - WikipediaDocument35 pagesSanger Sequencing - WikipediamuhammadfaiztrueNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesDNA Replication: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Melanie Joy Arellano Bsmt2-Set2 Explain How Nucleotides Joined Into Two Chains Form The Strands of A DNA MoleculeDocument3 pagesMelanie Joy Arellano Bsmt2-Set2 Explain How Nucleotides Joined Into Two Chains Form The Strands of A DNA MoleculeMelanie Joy ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Group ProjDocument21 pagesBiochem Group ProjYves Christian PineNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument31 pagesDNA Sequencingmymobile502100% (1)
- Dna Replication - Dna RepairDocument27 pagesDna Replication - Dna Repairnokate konkoorNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing PosterDocument1 pageDNA Sequencing PosterTapasNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids NOTESDocument8 pagesNucleic Acids NOTESelaineNo ratings yet
- Genome Acquisition - Sangers's SequencingDocument30 pagesGenome Acquisition - Sangers's SequencingMohana Priya AchuthanNo ratings yet
- Presented By, Raihanathus Sahdhiyya A, I M.Sc. MicrobiologyDocument14 pagesPresented By, Raihanathus Sahdhiyya A, I M.Sc. MicrobiologyKhoid DiamNo ratings yet
- Denaturing High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (DHPLC) For Nucleic Acid AnalysisDocument18 pagesDenaturing High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (DHPLC) For Nucleic Acid AnalysisLydie Praxede EkoboNo ratings yet
- Understanding Praziquantel: By:Karl SchoelerDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Praziquantel: By:Karl Schoelerhmalikn7581100% (1)
- Oral Controlled Drug DeliveryDocument23 pagesOral Controlled Drug DeliveryMergu Bala RajuNo ratings yet
- Establishment Categorization Checklist FormDocument2 pagesEstablishment Categorization Checklist FormAngelika CalingasanNo ratings yet
- Casquillos INADocument55 pagesCasquillos INAFrancisco PalomeroNo ratings yet
- Pe AaDocument5 pagesPe AanedalllNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Introduction To Basic Microbiology Laboratory PracticesDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 Introduction To Basic Microbiology Laboratory PracticesCesarHarrisonNo ratings yet
- Allied Chemistry SyllabusDocument6 pagesAllied Chemistry SyllabushyutoyrNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument2 pagesCHAPTER - 2 - Acids, Bases and Saltsshuchi guptaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field & Its Applications (EE30012)Document1 pageElectromagnetic Field & Its Applications (EE30012)rohan9643No ratings yet
- KAL Pathippagam - Diploma - Heat Power Engineering (Tamil) - 2 & 3 Marks - Important Questions - DOTE - TamilnaduDocument48 pagesKAL Pathippagam - Diploma - Heat Power Engineering (Tamil) - 2 & 3 Marks - Important Questions - DOTE - TamilnaduKal Pathippagam85% (47)
- Isorapid277HM (De) EG GHS SDB (En) 20190322Document6 pagesIsorapid277HM (De) EG GHS SDB (En) 20190322José MtvNo ratings yet
- Exide Industries LimitedDocument2 pagesExide Industries Limitedmanikanda7prabu7sNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Extra Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesChapter Three Extra Practice Problemsleaveme07No ratings yet
- DSC ImDocument9 pagesDSC Imapi-242743683No ratings yet
- Extraction of Essential Oils From Citrus By-Products Using Microwave Steam DistillationDocument12 pagesExtraction of Essential Oils From Citrus By-Products Using Microwave Steam DistillationKiesa Mae LeenNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0013935121019435 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0013935121019435 MainEsmeralda SouzaNo ratings yet
- SA JER AG221 DALM 649001 - Rev04Document26 pagesSA JER AG221 DALM 649001 - Rev04Srihari KodimelaNo ratings yet
- 5 Question Bank 1 DOM 2161901 Even 2019Document3 pages5 Question Bank 1 DOM 2161901 Even 2019FuxNo ratings yet
- Lúcio, V.J.G. Silva, A.M.S. "Design Models For Footings of Precast Concrete Structures" The Second International Symposium On Prefabrication, Helsínquia, 2000.Document6 pagesLúcio, V.J.G. Silva, A.M.S. "Design Models For Footings of Precast Concrete Structures" The Second International Symposium On Prefabrication, Helsínquia, 2000.Válter LúcioNo ratings yet
- Adsorption of Selected Pesticides From Aqueous Solutions Using Cost Effective Walnut ShellsDocument14 pagesAdsorption of Selected Pesticides From Aqueous Solutions Using Cost Effective Walnut ShellsIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- 05 Expiremental Approach - Affecting Retention TimeDocument28 pages05 Expiremental Approach - Affecting Retention Timejonida88No ratings yet
- Science5 Q4 Mod1 HowRocksTurnIntoSoil v2Document19 pagesScience5 Q4 Mod1 HowRocksTurnIntoSoil v2Chester Allan EduriaNo ratings yet
- Cromgard C21Document3 pagesCromgard C21Sonu KumarNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Is 13445 1 1992Document14 pagesIs 13445 1 1992kalgithNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1040 Chapter 1Document2 pagesCHEM 1040 Chapter 1rijzNo ratings yet
- Coal Mill PartDocument59 pagesCoal Mill PartHazem DiabNo ratings yet