Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CNS Stimulant Summary
CNS Stimulant Summary
Uploaded by
ahmedOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CNS Stimulant Summary
CNS Stimulant Summary
Uploaded by
ahmedCopyright:
Available Formats
CNS Stimulant lecture Drug summary.
Done by Hnnen Al-Shikh, Kholoud Fallatah.
Pharmacology committee.
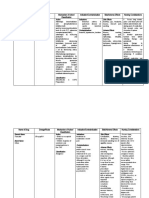
Psychomotor stimulants
Pharmacokinetics
Methylxanthines :
Theophylline
tea
Theobromine
cocoa
Caffeine
coffee
well absorbed
caffeine distributes
throughout the body
and to the fetus and
mothers milk
metabolized by liver
by CYP1A2 pathway
excreted in urine
Nicotine
Highly lipid soluble
cross BBB easily
Cross placenta and
reach mother milk
Metabolized in lung,
liver and urinary
excretion
Tolerance to the toxic
effect develops rapidly
cocaine
increases mental
awareness.
euphoria.
Hallucinations.
Stimulates the
Sympathetic nervous
system: tachycardia,
hypertension,
pupillary dilation.
Cocaine is the only
local anesthetic that
causes
vasoconstriction .
Action
Uses
CNS stimulation
Diuresis
Cardiac muscle
stimulation
Relaxation of smooth
muscle, especially
bronchial muscle
Stimulate HCL secretion
(peptic ulcers patients
should avoid them)
Nicotine receptors in CNS
where actions occur, such
as:
arousal and relaxation
(low doses)
respiratory paralysis
(high doses)
potentiates and
prolongs the CNS and
peripheral actions of
these catecholamines
Adverse effect
Caffeine + ergot alkaloid
(Ergotamine): treat migraine
headache
Theophylline: prophylaxis for
chronic asthma (bronchodilator)
Not used therapeutically
But secondary to caffeine as CNS
stimulant
Secondary to alcohol the most
abused drug (pharmacological
and behavioral therapy for
abusers)
Combined with tars and CO in
cigarette smoke
Not used
Short-Term:
Euphoria
Tachycardia
Respiration rate
Long-Term:
Agitation
Hypertension
Dyspnea
nasal collapse
Then:
seizure
Arrhythmias
Respiratory failure .
Pharmacokinetics
Action
Uses
Adverse effect
Psychomotor stimulants
indirect
elevation of the level of
catecholamine
transmitters in synaptic
spaces.
Amphetamine
o
methamphetamine
o Absorbed from GIT
100%
o Often administered
by IV or smoking.
o Metabolized by the
liver.
o excreted in the urine.
o The euphoria lasts 4
to 6 hours "its 4 to 8
times longer than
cocaine".
o Cause:
1. addictiondependence
2. tolerance
3. drug-seeking
behavior.
o
releasing intracellular
stores of
catecholamines.
also blocks
monoamine oxidase
(MAO).
1. Attention deficit syndrome.
Uses the derivative
methylphenidate
2. Narcolepsy.
a disorder marked by an
uncontrollable desire for sleep.
3. Appetite control
(suppresant)
CNS EFFECTs:
o stimulates the entire
cerebrospinal axis,
Overdoses of amphetamine are
cortex, brain stem, and
treated with chlorpromazine.
medulla.
o stimulates the entire
its -blocking effects on M2 ,H1,
cerebrospinal axis,
D1, D2, 1 receptors .
cortex, brain stem, and
medulla.
o This increased
alertness, decreased
fatigue, depressed
appetite, and
insomnia.
hypertension
insomnia
Anorexia
tremors
risk of exacerbating
schizophrenia
risk of dependence.
Cerebral
haemorrhage
long-term
psychological effects
psychotic symptoms
anxiety depression
cognitive impairment.
Pharmacokinetics
Action
Uses
Adverse effect
Psychomimetic Stimulants
Lysergic acid
diethylamide (LSD)
Tetrahydrocannabino:
From leaves of the
plant- Cannabis sativa
Hashish
Marijuana-
Sometimes high doses
causes:
produce long-lasting
psychotic changes in susceptible individuals.
Serotonin (5-HT) agonist
True dependence is
activity at presynaptic
rare.
receptors in the midbrain,
Haloperidol and other
binding to both 5-HT 1 and 5neuroleptics can block the
HT 2 receptors.
hallucinatory action of LSD
Activation of the sympathetic
nervous system
smoking THC effect:
Euphoria
Uncontrolled laughing
Feeling of relaxation
Altered time sense
Dream like state.
impairs short-term
memory.
mental activity .
decreases muscle
strength.
impairs highly skilled
motor activity "driving a
car".
THC receptors found
endogenously on presynaptic
nerve terminals that interact
synaptically with pyramidal
neurons.
Hyper-reflexia.
Nausea.
muscular weakness.
Haloperidol and other
neuroleptics can block the
hallucinatory action of LSD
and quickly abort the
syndrome.
Dronabinol - CB
(cannabinoid)
receptor agonist:
AIDS patient who
are losing weight.
cancer patients
severe emesis
Rimonabant - CB
(cannabinoid)
receptor antagonists
Obesity treatment
by decrease appetite
and body weight.
An increased heart rate,
Decreased blood
pressure, and a
Reddening of the
conjunctiva.
At high doses, a toxic
psychosis develops.
Tolerance and mild
physical dependence
occur with continued
frequent use of the drug.
You might also like
- Clinical Pks Anticoagulation Manual PDFDocument128 pagesClinical Pks Anticoagulation Manual PDFJosephine YauviraNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant Drugs: Presented By-K.Vinod Dept. of PharmacologyDocument38 pagesAntidepressant Drugs: Presented By-K.Vinod Dept. of PharmacologyVinod GuruNo ratings yet
- CNS Stimulants and PsychotomimeticsDocument29 pagesCNS Stimulants and Psychotomimeticsatom paul100% (1)
- Cns Stimulants: (MOA and Uses)Document39 pagesCns Stimulants: (MOA and Uses)Mirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Drugs Effecting On Endocrine System: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, PharmdDocument26 pagesDrugs Effecting On Endocrine System: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, PharmdRtxGaming Zone 73No ratings yet
- Drugs Interaction: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFK & DR - Dr.Tri Widyawati MSCDocument39 pagesDrugs Interaction: DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFK & DR - Dr.Tri Widyawati MSCpsyNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument56 pagesAnxiolyticsjabari.baraNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Active Emergence From Propofol General Anesthesia Is Induced by MethylphenidateDocument16 pagesNIH Public Access: Active Emergence From Propofol General Anesthesia Is Induced by Methylphenidate'-dooublleaiienn Itouehh IinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9: Drugs Effecting Function of UterusDocument22 pagesLecture 9: Drugs Effecting Function of UterusRtxGaming Zone 73No ratings yet
- Anti Allergic Drugs: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, PharmdDocument21 pagesAnti Allergic Drugs: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, PharmdRtxGaming Zone 73No ratings yet
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: DR Tarek M Nasrallah Al - AzharDocument97 pagesNonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: DR Tarek M Nasrallah Al - AzharTarek NasrallahNo ratings yet
- Mayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingDocument50 pagesMayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingmayraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8: Antigout DrugsDocument20 pagesLecture 8: Antigout DrugsRtxGaming Zone 73No ratings yet
- Digoxin PharmacokineticsDocument15 pagesDigoxin PharmacokineticsLama SaudNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMonica Gagarin CortezNo ratings yet
- Hypnotics and Sedatives PDFDocument35 pagesHypnotics and Sedatives PDFSayan Nag100% (1)
- Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Autonomic PharmacologyPranalosaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: BenzodiazepineDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: BenzodiazepineAriadne MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Drug Interactions: Pharmacodynamics and PharmacokineticsDocument4 pagesMechanisms of Drug Interactions: Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokineticsgowepa9266No ratings yet
- PenicillinDocument21 pagesPenicillinnadar shahNo ratings yet
- Drugs Effecting On Thyroid Gland: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, PharmdDocument22 pagesDrugs Effecting On Thyroid Gland: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, PharmdRtxGaming Zone 73No ratings yet
- Chemotherapy: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, Pharmd International Medical UniversityDocument26 pagesChemotherapy: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, Pharmd International Medical UniversityRtxGaming Zone 73No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Drug Delivery: DR Mohammad IssaDocument39 pagesPulmonary Drug Delivery: DR Mohammad IssaWika'deKaka'UtomoNo ratings yet
- By Ashutosh Gupta From BIT Mesra RanchiDocument31 pagesBy Ashutosh Gupta From BIT Mesra Ranchiexcel pro100% (1)
- 4853 Medication Worksheet: Student NameDocument8 pages4853 Medication Worksheet: Student Nameapi-546817891No ratings yet
- Antifungal DrugsDocument43 pagesAntifungal DrugsMohammed WasimNo ratings yet
- Psychoactive Drug UseDocument1 pagePsychoactive Drug UsePisay Shehannah Grail MedinaNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability & BioequivalenceDocument39 pagesBioavailability & BioequivalencePrathamesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Beta Lactam AntibioticsVishaal BhatNo ratings yet
- Antiobiotics Concept MapDocument6 pagesAntiobiotics Concept MapTricia Mae FarinNo ratings yet
- Endocannabinoid-CB Receptor SystemDocument7 pagesEndocannabinoid-CB Receptor SystemRobert DinuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GalaponDocument4 pagesDrug Study GalaponSheryl DiazNo ratings yet
- Penicillins: Presented By, DR Noor JahanDocument58 pagesPenicillins: Presented By, DR Noor JahanSally PujaNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside & VancomycinDocument10 pagesAminoglycoside & VancomycinKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial FinalDocument227 pagesAntimicrobial FinalAbdulrhman MekawyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacovigilance Related Questions - 1585456120320Document10 pagesPharmacovigilance Related Questions - 1585456120320Saravanan RamNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument25 pagesAntifungal AgentsCham MontimanNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside Dosage Adjustment - Group 4Document27 pagesAminoglycoside Dosage Adjustment - Group 4katrinNo ratings yet
- Sedative - HypnoticsDocument60 pagesSedative - HypnoticsNurul AinNo ratings yet
- Concept of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring TDMDocument33 pagesConcept of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring TDMWalaa YousefNo ratings yet
- 1introDocument158 pages1introDea MaharanisNo ratings yet
- Case 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCase 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument27 pagesSedative HypnoticsPrecious FulgarinasNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Adrenrgic Nervous System: Presented byDocument63 pagesDrugs Acting On Adrenrgic Nervous System: Presented byKiranNo ratings yet
- Drug Bioavailability - Clinical Pharmacology - MSD Manual Professional Edition PDFDocument2 pagesDrug Bioavailability - Clinical Pharmacology - MSD Manual Professional Edition PDFRutuja BhujbalNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDocument30 pagesBacterial Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsBYAWELE JAIRUS WANGUSANo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsDocument27 pagesAnxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsEjaj SumitNo ratings yet
- Beta Lactams LectureDocument59 pagesBeta Lactams Lecturexmd6787qpqNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Chapter # 7Document69 pagesNervous System: Chapter # 7saddam ud dinNo ratings yet
- CNS DepressantsDocument69 pagesCNS DepressantsMicah Lou Calamba100% (1)
- A Pharmceutico Analytical Study of Amavatari Rasa - A Herbal FormulationDocument7 pagesA Pharmceutico Analytical Study of Amavatari Rasa - A Herbal FormulationArutpa SundaramNo ratings yet
- Clin PK 1-4Document105 pagesClin PK 1-4Klye SahagunNo ratings yet
- Drug Delivery Through NanohydrogelsDocument11 pagesDrug Delivery Through NanohydrogelsPrabhat BistNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Inhibitors - Pharmacology 3 - Frank SsengoobaDocument16 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors - Pharmacology 3 - Frank SsengoobaVhugala AudreyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Sedative-Hypnotics: DR - Datten Bangun, MSC, SPFK Dept - Farmakologi & Terapetik Fak - Kedokteran Uhn MedanDocument49 pagesPharmacology of Sedative-Hypnotics: DR - Datten Bangun, MSC, SPFK Dept - Farmakologi & Terapetik Fak - Kedokteran Uhn MedanGeorge AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Revized 5 - Antifungal Medications - 2021Document28 pagesRevized 5 - Antifungal Medications - 2021احمد علىNo ratings yet
- Adrenoceptor - Activating Other Sympathomimetic Drugs PDFDocument43 pagesAdrenoceptor - Activating Other Sympathomimetic Drugs PDFRupal RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- CNS Stimulants 2023Document10 pagesCNS Stimulants 2023ManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Cns StimulantsDocument41 pagesCns StimulantsYIKI ISAACNo ratings yet
- Cns Stimulants: DR Laith M Abbas Al-Huseini M.B.CH.B, M.SC., M.Res., PH.DDocument38 pagesCns Stimulants: DR Laith M Abbas Al-Huseini M.B.CH.B, M.SC., M.Res., PH.DHemantNo ratings yet
- Portable Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in Drug TestingDocument4 pagesPortable Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in Drug Testingthor888888No ratings yet
- Antidepressants MaterialDocument5 pagesAntidepressants MaterialxyzNo ratings yet
- Clinical AssignmentDocument22 pagesClinical AssignmentKeziah GillNo ratings yet
- DEPRESSANTSDocument18 pagesDEPRESSANTSElisha Arwynne Postrero RomaNo ratings yet
- Indiana OTC Drug List PDFDocument422 pagesIndiana OTC Drug List PDFPaulNo ratings yet
- Full PDFDocument93 pagesFull PDFPrints BindingsNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology of Antipsychotic AgentsDocument29 pagesBasic Pharmacology of Antipsychotic AgentsZane PhillipNo ratings yet
- Narcan InfographicDocument1 pageNarcan InfographicAnonymous C7bFTkrd5No ratings yet
- Law and Ethics QuizDocument62 pagesLaw and Ethics QuizElisa Quiambao PalmesNo ratings yet
- TITLE-5-Article-190-193 Revised-Penal-CodeDocument12 pagesTITLE-5-Article-190-193 Revised-Penal-CodeJohnson YaplinNo ratings yet
- Queen - My Melancholy Blues (Piano Sheet Music)Document27 pagesQueen - My Melancholy Blues (Piano Sheet Music)Kamil Iżykowski0% (3)
- LUBBOCK COUNTY - Idalou ISD - 2002 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseDocument10 pagesLUBBOCK COUNTY - Idalou ISD - 2002 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseTexas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseNo ratings yet
- Drug Crimes StatisticsDocument5 pagesDrug Crimes StatisticsRituNo ratings yet
- New Materi Pretest Skill Blok 10Document3 pagesNew Materi Pretest Skill Blok 10asabri yunisNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 1 Unit 5 Psycho Pharma Cological Agents Notes by MahendraDocument39 pagesPharmacology 1 Unit 5 Psycho Pharma Cological Agents Notes by MahendraKim Nicole Villaflores0% (1)
- Hemp Oil Vs CBD OilDocument16 pagesHemp Oil Vs CBD Oilfelix reyesNo ratings yet
- Spesialit Asma, Batuk, DekongestanDocument4 pagesSpesialit Asma, Batuk, DekongestanS AnindahYaniNo ratings yet
- Colorado: Drug Threat AssessmentDocument42 pagesColorado: Drug Threat AssessmentlosangelesNo ratings yet
- Dll-Health9 Q2 Week7Document3 pagesDll-Health9 Q2 Week7Uricca Mari Briones Sarmiento100% (1)
- BEE COUNTY - Beeville Isd - 2009 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseDocument249 pagesBEE COUNTY - Beeville Isd - 2009 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol Use2009 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseNo ratings yet
- Research Paper - Drug Addiction and AbusDocument5 pagesResearch Paper - Drug Addiction and AbusAvel BadilloNo ratings yet
- Psychopathology by Maanya DuaDocument7 pagesPsychopathology by Maanya DuaMaanya DuaNo ratings yet
- (Lecture 5) Vice, Drug Education and ControlDocument25 pages(Lecture 5) Vice, Drug Education and ControlJohnpatrick DejesusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 ProblemsDocument4 pagesChapter 13 Problemswalt richardsNo ratings yet
- Opiate Abuse PaperDocument7 pagesOpiate Abuse Paperapi-272576949No ratings yet
- Drug Education and Vice ControlDocument7 pagesDrug Education and Vice ControlJovie MasongsongNo ratings yet
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act-1985Document20 pagesNarcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act-1985Gunji Venkata LokeshNo ratings yet
- Criminology: Vice & Drug Education and ControlDocument17 pagesCriminology: Vice & Drug Education and Controldynamic_edgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Psychoactive Drugs: Classification and HistoryDocument24 pagesChapter 1 - Psychoactive Drugs: Classification and HistoryrayNo ratings yet