Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electricity Questions
Electricity Questions
Uploaded by
sanat kr pratiharOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electricity Questions
Electricity Questions
Uploaded by
sanat kr pratiharCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 1
Aluminium is manufactured by the electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide which is obtained from
the ore bauxite.
(i)
Explain why the aluminium has to be in the molten form for the electrolysis to take place.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
om
(ii) Pure aluminium oxide melts at 2045oC. Name the substance to which the aluminium oxide is added in
order that the melting point is reduced to below 1000oC.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
e.c
(iii) Explain the reason why aluminium is extracted from its oxide by means of electrolysis rather than
a chemical reducing agent such as carbon.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
ctiv
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iv) Name the substance that the positive electrode is made of.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
ma
(v) Name the gas given off at the positive electrode.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
I.
he
(vi) Give a balanced symbol equation for the reactions taking place at the positive and negative electrode.
At the positive electrode.
ww
w.c
..............................................................................................................................................................................
II. At the negative electrode.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
[4]
(vii) Explain why the positive electrodes must be replaced on a regular basis.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 11
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 2
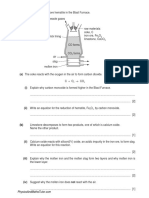
The following diagram shows the apparatus that could be used to investigate the electrolysis of molten lead(II)
bromide. Molten lead(II) bromide is an electrolyte. Both electrodes are made from graphite.
om
battery
positive
electrode
e.c
negative
electrode
lead
molten lead
bromide
ctiv
bubbles of
gas
dish
Give the meaning of the terms:
ma
(i)
heat
I. electrode .................................................................................................................................................
he
......................................................................................................................................................................
ww
w.c
II. electrolyte ..............................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................
[2]
(ii) State why the dish was heated during the experiment.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Give the symbols for the two ions present in the molten lead bromide.
and
.........................................................................................................................................................................
[2]
(iv) Give the colour of the vapour released around the positive electrode.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
QUESTIONSHEET 2 CONTINUED
(v) The word equation for the reaction that took place at the negative is:
lead ion
electrons
lead atom
Give the balanced symbol equation for this reaction.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
Produced at the positive
electrode
Produced at the negative
electrode
e.c
Molten compound
om
(vi) This experiment can be repeated using different substances. Predict the products of electrolysis of the
following two molten compounds by completing the table.
Sodium chloride
[2]
ww
w.c
he
ma
ctiv
Lithium sulphide
TOTAL / 10
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 3
If two different metals are placed in salt solution, electricity can be made as shown.
V
Metal B
(a)
e.c
om
Metal A
Name two metals which, when used in the apparatus, would give a reading on the voltmeter.
(b)
What everyday use is made of this process?
ctiv
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
How can this experiment be used to work out a reactivity series of metals?
ma
(c)
..............................................................................................................................................................................
(d)
he
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
Why does this process eventually stop working?
(e)
ww
w.c
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
List three ways in which the voltage of the cell could be increased.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 4
om
The chemical A is sodium chloride.
Write the formula for A.
e.c
(a)
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(i)
When electricity is passed though A, what is produced at
the anode?
ctiv
(b)
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) the cathode?
(i)
Write a half equation showing the reaction at
the anode.
he
(c)
ma
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) the cathode.
ww
w.c
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d) (i)
If A were molten, what mass of chlorine would be produced if 2.3 g of sodium were formed?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(ii) What volume will this gas occupy at room temperature?
(The molar volume of a gas at room temperature is 24 dm3)
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 12
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 5
The diagram shows electricity being passed into sodium chloride solution.
(a)
Gas A
-
om
Gas B
Sodium
hydroxide
solution
e.c
Brine
in
Give the names of gas A and gas B.
ctiv
Gas A. .......................................................................................................................................................
Gas B..........................................................................................................................................................
[2]
What four ions are present in sodium chloride solution?
ma
(b)
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(i)
he
Use equations to explain what happens
at the anode
ww
w.c
(c)
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) at the cathode
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 6
Electricity is passed through molten sodium chloride.
(a)
What ions are present in molten sodium chloride?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
Use equations to explain what happens
(i)
om
(b)
at the anode
(ii) at the cathode
e.c
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
ctiv
What is the safety problem with this experiment?
he
ma
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
ww
w.c
(c)
TOTAL / 7
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 7
Electricity is passed into nickel nitrate solution using nickel electrodes as shown in the diagram.
e.c
om
Nickel
nitrate
solution
(a)
Give the formulae of all the ions that are in nickel nitrate solution.
ctiv
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
Write an equation for the deposition of nickel ions at the cathode.
ma
(b)
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
0.1 g of nickel was deposited in 60 minutes with a current of 0.1 A.
(i)
Calculate the quantity of electricity in coulombs.
he
(c)
ww
w.c
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) How much electricity is needed to deposit 1 mole of nickel (59 g)?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 6
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 8
The diagram shows how aluminium can be manufactured by electricity.
+
Carbon
anodes
om
Carbon lining
(cathode)
Tap
What is the formula of aluminium oxide?
ctiv
(a)
e.c
Molten aluminium
oxide and cryolite
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
Why is the aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite?
ma
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
Write the equation for what happens at the cathode.
he
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d)
Why is it possible to tap off the aluminium at the bottom?
(e) (i)
ww
w.c
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
What is the other product of the process?
....................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Explain why it is not possible to collect this product at the anode.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(f)
Give two major uses for the aluminium extracted by this process.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
QUESTIONSHEET 9
Medium Demand Questions
(a) (i)
Describe an experiment that could be carried out to investigate whether aluminium conducts electricity
or not. You may do this by means of a diagram if you wish.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
Complete the following table of conductors and non-conductors by placing each substance from
the box below into the correct column. One example has been done for you.
copper
aluminium
he
[2]
The apparatus shown in the diagram below may be used to distinguish between an electrolyte and
a non-electrolyte.
ww
w.c
(b)
Non-conductor
ma
Conductor
aluminium
sulphur
ctiv
polythene
graphite
e.c
(ii)
om
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
battery
bulb
liquid/solution
Describe how the same equipment could be used to distinguish between strong and weak electrolytes.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
QUESTIONSHEET 9 CONTINUED
One important use of electrolysis is seen in electroplating. A nickel spoon can be silver plated by using
the equipment shown below.
om
electrode A
e.c
nickel spoon
silver nitrate
solution
ctiv
(i) Give the name of the metal from which electrode A is made.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
ma
(ii) Silver ions, Ag+, are deposited on the nickel spoon.
Place a tick (3) in the box next to the correct answer.
The spoon is the:
positive electrode
he
negative electrode
[1]
ww
w.c
(c)
(iii) Give the symbol equation for the change that takes place at the surface of the nickel spoon.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 10
(a)
The following box contains six substances.
carbon
molten wax
copper
molten aluminium oxide
sulphur
silver
om
Choose only substances from the box to answer the following questions
Each substance can be used once, more than once or not at all.
Name the substance which is a:
(ii)
non metal that does not conduct electricity
(iii)
compound that conducts electricity
(iv)
metal used in electrical cables
(v)
non metal found in a dry cell (torch battery)
......................................................... [1]
e.c
metal that allows electricity to pass
........................................................... [1]
ma
ctiv
........................................................ [1]
.......................................................... [1]
......................................................... [1]
The apparatus drawn below can be used to investigate the electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid.
he
bulb
ww
w.c
(b)
(i)
electrode
dilute sulphuric
acid
bubbles of
gas
(i) Name the apparatus labelled A. ............................................................................................................. [1]
(ii) How would you know that electricity is flowing through the apparatus?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii)
How would you know that electrolysis is taking place?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
QUESTIONSHEET 11
A solid chemical X is burned in a green gas Y to form a white solid P. The solid P does not conduct electricity
in the solid state. P dissolves in water and when the solution is crystallised cubic crystals are formed.
(a)
Suggest names for: -
(i)
Solid X
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
om
(ii) Gas Y
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
e.c
(iii) Chemical P
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
How would melting P affect its ability to conduct electricity?
ctiv
(b)
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
ma
Write a balanced equation for the reaction of X and Y.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
he
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
ww
w.c
(c)
TOTAL / 7
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
QUESTIONSHEET 12
Medium Demand Questions
om
The diagram shows the process of electrolysis.
(a)(i) On the diagram, label the cathode and anode.
e.c
[2]
ctiv
(ii) At which electrode will metals always be discharged?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Why are non-metallic ions known as anions?
ma
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)(i) What is the general name given to liquids such as A?
he
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) What is the essential property of liquid A?
(c)
ww
w.c
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
If liquid A is molten potassium bromide, name the products at the two electrodes.
(i)
anode
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) cathode
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
QUESTIONSHEET 13
Medium Demand Questions
Copper has many important uses, including electrical wires, since it is a very good conductor of electricity.
For copper to be used in this way it needs to be very pure. Copper is purified by using electrolysis. The
diagram below shows how the metal is purified.
om
battery
positive
electrode
e.c
negative
electrode
impure
copper
ctiv
pure
copper
blue solution
B
substance
(i)
What is substance A?
ma
(ii) Name the blue solution B.
he
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
ww
w.c
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) State and explain two changes you would see during this electrolysis.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(iv) State what would happen to the blue colour of the solution B during electrolysis.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(v) Copper is a shiny, colourful and malleable metal. Give one use of copper that relies on all three
properties of the metal.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 6
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
QUESTIONSHEET 14
Medium Demand Questions
The diagram shows a fuel cell of the type taken into space by astronauts.
fuel
oxygen
water + other
products
e.c
om
FUEL
CELL
ctiv
electricity
In the Apollo spacecraft, the fuel was hydrogen and the electrolyte was potassium hydroxide.
(a) (i)
Why is a fuel cell particularly suitable for supplying power in space?
ma
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
he
(ii) What does the cell also produce which is of use to the astronauts?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
Suggest one other source of power that could have been taken into space.
ww
w.c
(b)
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
Give a reason in each case to explain why each of the following power cells was rejected for
use in space.
(i)
a dry cell
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) a car battery
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) a hearing aid type of cell
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 7
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
QUESTIONSHEET 15
Medium Demand Questions
(a)
Complete the table below to show the electrolyte and the anode and cathode products in the cells.
electrolyte
sodium chloride solution
dilute sulphuric acid
molten lead(II) bromide
magnesium sulphate solution
anode product
chlorine
cathode product
hydrogen
chlorine
copper
oxygen
om
cell
A
B
C
D
E
(b)
[6]
Explain why hydrogen is collected at the cathode in cell A instead of sodium.
e.c
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
(c)(i)
ctiv
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
What is the name of the process occurring in each cell?
(ii) What does this name mean?
ma
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
ww
w.c
he
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 10
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
QUESTIONSHEET 16
Medium Demand Questions
Many metal objects that we use are electroplated with another metal.
(a)
Give two reasons for electroplating metals.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
The diagram below shows a ring being plated with nickel.
om
(b)
e.c
dc
supply
ctiv
ring
ma
nickel sulphate
solution
(i) From what material would the anode be made? Give a reason for your answer.
he
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
ww
w.c
(ii) Why is the ring attached to the negative terminal of the dc supply?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(c)
List three objects that are often electroplated, and name the plating metal in each case.
1. .........................................................................................................................................................................
2. .........................................................................................................................................................................
3. .................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 17
The diagram below shows a dry cell.
graphite
zinc casing
om
electrolyte
paste
steel outer
casing
e.c
insulator
ctiv
A Dry Cell
(a)
Explain why the cell cannot be totally dry, despite its name.
ma
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(i)
Name the materials of
the anode
he
(b)
(ii) the cathode
ww
w.c
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
On the diagram, draw an arrow to show the direction of flow of the electrons.
(d)
Why does the dry cell eventually stop working?
[1]
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(e)
State two everyday uses of dry cells.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 18
A lead-acid cell consists of two pieces of lead dipping into a solution of sulphuric acid.
lead
Why would this cell not produce any electricity?
ctiv
(a)
e.c
sulphuric
acid
om
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
When a dc power supply is connected at X, the piece of lead attached to the positive terminal
turns brown.
This is called charging the cell.
ma
(b)
he
What is the piece of lead which turns brown known as?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
A single lead-acid cell produces 2 volts.
ww
w.c
(c) (i)
A car battery consists of six of these cells linked together.
What is the voltage of a car battery?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Name two things that need power from the battery in a car.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(iii) Why does a car battery lose its charge more quickly in winter?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d)
What is the main danger from car batteries?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRICITY IN CHEMISTRY
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 19
Match the list of power cells in the list on the left with the uses in the right hand list.
dry cell
hearing aid
mercury cell (or button cell)
personal stereo
lead-acid cell
heart pacemaker
rechargeable cell
invalid car
lithium cell (reliable, long-lasting, expensive)
space station
om
(a)
solar cell
(i)
Give reasons for your choices of cell for
[6]
e.c
(b)
mobile phone
heart pacemakers
ctiv
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) space stations
ww
w.c
he
ma
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
ELECTRCITY IN CHEMISTRY
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 20
Fill in the missing words in the following sentences.
The electrodes in cells are made from _______ or from _______.
The negative electrode is called the _______ and the positive one is the _______.
_______ and _______ form at the cathode, whilst _______ form at the anode.
The liquid which conducts the electricity is called the _______. It must contain _______.
ww
w.c
he
ma
ctiv
e.c
om
Two ways to make solid salt conduct electricity are to _______ it in _______ or to _______ it.
TOTAL / 12
You might also like
- Chapter 15-Basics of Electrical Systems: True/FalseDocument190 pagesChapter 15-Basics of Electrical Systems: True/FalsewesamNo ratings yet
- PETRONAS Fuel Oil 80: Safety Data SheetDocument10 pagesPETRONAS Fuel Oil 80: Safety Data SheetJaharudin JuhanNo ratings yet
- Delta Planer ManualDocument44 pagesDelta Planer ManualstiellNo ratings yet
- Chem 11Document1 pageChem 11yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Electricity CoverworkDocument19 pagesElectricity CoverworktechnabooksNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 2 QPDocument10 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 2 QPValerine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry QuestionsDocument24 pagesElectricity & Chemistry QuestionsIsaa gabNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Reactivity of Metals 3 QPDocument16 pages4.1 Reactivity of Metals 3 QPDumpsterFireGamingNo ratings yet
- Igcse Electrochemistry Review PDFDocument7 pagesIgcse Electrochemistry Review PDFbilly ogadaNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 2 QPDocument10 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 2 QPaangijain646No ratings yet
- Bonding - Structuce 3 QPDocument14 pagesBonding - Structuce 3 QPtertianerima101No ratings yet
- Electrolysis PPDocument12 pagesElectrolysis PPshamsur.rehman.khatriNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 2Document5 pagesElectrolysis 2trickster jonasNo ratings yet
- Topical Questions For ElectrolysisDocument6 pagesTopical Questions For Electrolysisokguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- RP 3 - Electrolysis QPDocument6 pagesRP 3 - Electrolysis QPChisom OsuntaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistrysalmanismart123No ratings yet
- 21.4_manufacture_and_uses-_includes_sulfur_dioxide_questions__qp_-_igcse_cie_chemistry_-_extended_theory_paperDocument9 pages21.4_manufacture_and_uses-_includes_sulfur_dioxide_questions__qp_-_igcse_cie_chemistry_-_extended_theory_paperSamson YauNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 3 QPDocument14 pagesElectrolysis 3 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- Igcse Test CH 2 To 6 PDFDocument17 pagesIgcse Test CH 2 To 6 PDFkashishhagarwalNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument14 pagesBondingMuizzudin AzaliNo ratings yet
- 5070 Mock 1 P2 - 2024Document10 pages5070 Mock 1 P2 - 2024ShamsaNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCoLYySoFuGkrumBZij5zb9gwokYrliSeCR7cP9bawK2ZtTGiDqPZ7erW0oiiZYUnvM7tM18fSl kfWoltWryBpLIu4aJeCs86igjQdiNJfFUGBFTSV9 IyeSXflALiZHqz8BOV2vTFVYq9Document4 pagesACFrOgCoLYySoFuGkrumBZij5zb9gwokYrliSeCR7cP9bawK2ZtTGiDqPZ7erW0oiiZYUnvM7tM18fSl kfWoltWryBpLIu4aJeCs86igjQdiNJfFUGBFTSV9 IyeSXflALiZHqz8BOV2vTFVYq9Sinead MulumbaNo ratings yet
- Metals mj2020Document6 pagesMetals mj2020FenNo ratings yet
- Name Class:10-IGCSE Date: Assignment: Formative Assessment Topic: Electricity and Chemistry AO: Demonstrate Knowledge and Understanding ofDocument2 pagesName Class:10-IGCSE Date: Assignment: Formative Assessment Topic: Electricity and Chemistry AO: Demonstrate Knowledge and Understanding ofnamrata maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Part 2 Question 2Document4 pagesElectrolysis Part 2 Question 2danielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Hieu Le (10040) - Sulphuric Acid Qu'sDocument8 pagesKami Export - Hieu Le (10040) - Sulphuric Acid Qu'sHieu Le (10040)No ratings yet
- Electro - Stochio-Redox - A GradeDocument15 pagesElectro - Stochio-Redox - A GradeRayaan MerchantNo ratings yet
- Because Involving Reduction and Oxidation That Occurs at The Same Time/ SimultaneouslyDocument8 pagesBecause Involving Reduction and Oxidation That Occurs at The Same Time/ SimultaneouslySiti AinaNo ratings yet
- Worksheeth - Extraction of MetalDocument4 pagesWorksheeth - Extraction of MetalSindhu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Reactivity of Metals 3 QPDocument16 pagesReactivity of Metals 3 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- Mixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionDocument23 pagesMixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionYaakkwNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen 240128 145942Document11 pagesNitrogen 240128 145942omarkbkb2007suiNo ratings yet
- 9c ElectroDocument10 pages9c ElectrodR SHAMMIR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 1 QP Test 1Document11 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 1 QP Test 1TAONANo ratings yet
- Balanced Equations & Associated Calc's 10 QPDocument8 pagesBalanced Equations & Associated Calc's 10 QPjade.davis0019No ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 1 QPDocument11 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 1 QPValerine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- SE1 Chemistry Final Exam2022 Paper4 QDocument9 pagesSE1 Chemistry Final Exam2022 Paper4 QDerron LimNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen & Fertilisers 1 QPDocument10 pagesNitrogen & Fertilisers 1 QPwembley1629No ratings yet
- 10 This Question Is About Chemicals Made From Sodium Chloride. (A) ADocument15 pages10 This Question Is About Chemicals Made From Sodium Chloride. (A) AFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics 3 QPDocument12 pagesChemical Energetics 3 QPSrijita RoyNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Homework PupilDocument8 pagesElectrolysis Homework Pupilnicole.fiorentini.almeidaNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Topic 6 - Redox, Group 2 and Group 7 Assessed HomeworkDocument10 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Topic 6 - Redox, Group 2 and Group 7 Assessed HomeworkSumathi GanasenNo ratings yet
- TestDocument10 pagesTestElizabethNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals 3 QPDocument8 pagesProperties of Metals 3 QPValerine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- 0654 s16 QP 33Document36 pages0654 s16 QP 33lynguyentbNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structuure and BondingDocument6 pagesAtomic Structuure and BondingHarshika Prasanganie Abeydeera100% (1)
- Riepriw (Riw (Irs (If (SifDocument12 pagesRiepriw (Riw (Irs (If (SifFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Chem 4Document33 pagesChem 4S 9K32No ratings yet
- Metals, Electrolysis, Energy Change Topical TestDocument5 pagesMetals, Electrolysis, Energy Change Topical TestCharles Allon YapNo ratings yet
- DP-1 Test Paper For Unit 1 2 3 H LDocument7 pagesDP-1 Test Paper For Unit 1 2 3 H Lwama ojhaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionslNo ratings yet
- Redox HLDocument19 pagesRedox HLmikeasmith404No ratings yet
- Electrolysis 2 QPDocument21 pagesElectrolysis 2 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument19 pagesRedoxHamna BilalNo ratings yet
- Revision Exer 8Document6 pagesRevision Exer 8killer boyNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals 9 QPDocument12 pagesProperties of Metals 9 QPAmogh KothariNo ratings yet
- Topic 06 ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesTopic 06 Electrochemistryzafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Electron Structure PDFDocument13 pagesElectron Structure PDFSunnyNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration 2 QPDocument9 pagesElectron Configuration 2 QP303341No ratings yet
- Module 5A Electrochemistry IDocument6 pagesModule 5A Electrochemistry IMohd HafiezNo ratings yet
- Review Pack 1st Term (23-24)Document21 pagesReview Pack 1st Term (23-24)Teck TieNo ratings yet
- What You Must Know About Chemistry Paper 3: Diagram 1 Shows Two Electrolytic CellsDocument5 pagesWhat You Must Know About Chemistry Paper 3: Diagram 1 Shows Two Electrolytic CellsZainudin Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- By Prince Singh Solid State Chemical Bonding: Final Touch Revision For Iit Jee Main Physical & Inorganic ChemistryDocument13 pagesBy Prince Singh Solid State Chemical Bonding: Final Touch Revision For Iit Jee Main Physical & Inorganic Chemistrysanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- (TGX) Downloaded FromDocument1 page(TGX) Downloaded Fromsanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- (TGX) Downloaded From Torrentgalaxy - ToDocument1 page(TGX) Downloaded From Torrentgalaxy - Topavan kurapatiNo ratings yet
- DPP Conic Sections-385Document21 pagesDPP Conic Sections-385sanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- প্রবাহী তড়িতDocument4 pagesপ্রবাহী তড়িতsanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- Merchant VeniceDocument173 pagesMerchant Venicereader_no_junk73% (11)
- T. R. Form No. 26 (T.R. 4.135 Sub-Rule (1) and Explanation 1 and T.R. 4.137)Document5 pagesT. R. Form No. 26 (T.R. 4.135 Sub-Rule (1) and Explanation 1 and T.R. 4.137)sanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- Class X ICSE Exam 2016: English Paper 2 (English Literature) (Don Bosco)Document3 pagesClass X ICSE Exam 2016: English Paper 2 (English Literature) (Don Bosco)sanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- Item 0 20180516015421505Document8 pagesItem 0 20180516015421505sanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- ResPaper ICSE Prelims 2016 English Paper 2 English Literature Mahavir Institute of Education and Research MIER KolkataDocument4 pagesResPaper ICSE Prelims 2016 English Paper 2 English Literature Mahavir Institute of Education and Research MIER Kolkatasanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- ResPaper ICSE Prelims 2016 English Paper 2 English Literature Hiranandani Foundation School HFS Powai MumbaiDocument4 pagesResPaper ICSE Prelims 2016 English Paper 2 English Literature Hiranandani Foundation School HFS Powai Mumbaisanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- ResPaper ICSE Prelims 2016 English Paper 2 English Literature The Chanda Devi Saraf School CDS NagpurDocument5 pagesResPaper ICSE Prelims 2016 English Paper 2 English Literature The Chanda Devi Saraf School CDS Nagpursanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- ResPaper ICSE Prelims 2016 English Paper 2 English Literature Deepti Convent School KoraputDocument4 pagesResPaper ICSE Prelims 2016 English Paper 2 English Literature Deepti Convent School Koraputsanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- The Shri Ram School Aravali ICSE Revision Paper 2015: LiteratureDocument16 pagesThe Shri Ram School Aravali ICSE Revision Paper 2015: Literaturesanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- Language of Chemistry' PDFDocument13 pagesLanguage of Chemistry' PDFsanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- Lilavatibai Podar ICSE: English Literature Prelim Paper 2015Document4 pagesLilavatibai Podar ICSE: English Literature Prelim Paper 2015sanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- ResPaper ICSE Prelims 2015 English Paper 2 English Literature SMT Lilavatibai Podar High School LPHS MumbaiDocument4 pagesResPaper ICSE Prelims 2015 English Paper 2 English Literature SMT Lilavatibai Podar High School LPHS Mumbaisanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- 10th Acid Base and Salt Cbse Test Paper - 03Document1 page10th Acid Base and Salt Cbse Test Paper - 03sanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Continuous Reactors: 8.4.1 Steady-State Chemostat (CHEMOSTA)Document33 pages8.4 Continuous Reactors: 8.4.1 Steady-State Chemostat (CHEMOSTA)Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- (5).pptDocument15 pages(5).pptAKINYEMI ADISA KAMORUNo ratings yet
- 09 em 002Document6 pages09 em 002Zelva ChileNo ratings yet
- Emergency Preparedness For Severe WeatherDocument2 pagesEmergency Preparedness For Severe WeatherRandy PedrozaNo ratings yet
- 016 Alhambra Cigar and Cigarette Manufacturing, Co. v. CollectorDocument1 page016 Alhambra Cigar and Cigarette Manufacturing, Co. v. CollectorDexter GasconNo ratings yet
- Moving To A World Beyond P 0 05Document20 pagesMoving To A World Beyond P 0 05Frank LopezNo ratings yet
- NCP StrokeDocument6 pagesNCP StrokeIrish TatelNo ratings yet
- Aluminium GMAW GuideDocument32 pagesAluminium GMAW GuideDaniel Salinas100% (2)
- 44.1.16 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 906.03 in Vert Sugar in Sugars and SyrupsDocument1 page44.1.16 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 906.03 in Vert Sugar in Sugars and Syrupsc2haNo ratings yet
- Aboras MM 2015 Type of Failure in PFM RestorationDocument2 pagesAboras MM 2015 Type of Failure in PFM RestorationSopan SinamoNo ratings yet
- Team 3 Group InsuranceDocument42 pagesTeam 3 Group InsuranceAnonymous Ua8mvPkNo ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio ES12-25WADocument38 pagesManual de Servicio ES12-25WARonald PiedrahitaNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Organic Fertilizers On The Yield and Quality of WatermelonsDocument3 pagesThe Influence of Organic Fertilizers On The Yield and Quality of WatermelonsresearchparksNo ratings yet
- (NCRP Report No. 174 - ) - Preconception and Prenatal Radiation Exposure - Health Effects and Protective Guidance-National Council On Radiation (2014) PDFDocument386 pages(NCRP Report No. 174 - ) - Preconception and Prenatal Radiation Exposure - Health Effects and Protective Guidance-National Council On Radiation (2014) PDFIulia ChiriacNo ratings yet
- Flanges Table: ANSI B16.5 #150Document17 pagesFlanges Table: ANSI B16.5 #150Gaurav SalujaNo ratings yet
- Epojet 270Document4 pagesEpojet 270Yudi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Management Report 2012Document41 pagesManagement Report 2012Daniela AlimanNo ratings yet
- Long Term LiabilitiesDocument21 pagesLong Term Liabilitiesnioriatti8924No ratings yet
- Phy Investigatory Project Tangent GalvanDocument11 pagesPhy Investigatory Project Tangent Galvankomal mahelaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesFinal Exam QuestionsAndil MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Brick Work JSA HSE ProfessionalsDocument1 pageBrick Work JSA HSE ProfessionalsStansilous Tatenda NyagomoNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence ReflectionDocument5 pagesEmotional Intelligence Reflectionapi-336005635No ratings yet
- 1 - Ne - b2 Sety Leksykalne U7iDocument1 page1 - Ne - b2 Sety Leksykalne U7iAneta WalejewskaNo ratings yet
- Occlusion in Complete DentureDocument12 pagesOcclusion in Complete DentureNadeemNo ratings yet
- Clinical Nutrition: Paediatric Nutrition Risk Scores in Clinical Practice: Children With Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument4 pagesClinical Nutrition: Paediatric Nutrition Risk Scores in Clinical Practice: Children With Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseMaggie S HungNo ratings yet
- EcoDocument7 pagesEcoSushma YonzenNo ratings yet
- Office of The Secretary: TransmissionDocument8 pagesOffice of The Secretary: TransmissionFranchise AlienNo ratings yet