Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Zero Conditional
The Zero Conditional
Uploaded by
KahnMéndezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Inglês - Me and My Family 5º AnoDocument4 pagesInglês - Me and My Family 5º Anodalilaramos76% (21)
- Ngữ Pháp Quangbao Đề CươngDocument3 pagesNgữ Pháp Quangbao Đề CươngNga PhanNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyFrom EverandEnglish Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishapi-278092100No ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument5 pagesThe Zero ConditionalEduard Hernan Cardona VillamilNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Conditional: If Clause Main ClauseDocument3 pagesType 1 Conditional: If Clause Main ClauseDian daniNo ratings yet
- Amanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalDocument4 pagesAmanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalGeraldine SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Conditional If PDF To Be SharedDocument21 pagesConditional If PDF To Be SharedMiandy CelestinnNo ratings yet
- Name:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesName:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentenceshosearoinaldoNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence TypeDocument6 pagesConditional Sentence TypeHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument3 pagesConditionalSalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseStancu AlinNo ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument4 pagesThe Zero ConditionalKim SeorinNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument95 pagesCONDITIONALmmmmmNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": ConditionalsDocument3 pages"The Unreal Past": ConditionalsLuisa Fernanda Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- Conditional EF GlobalDocument1 pageConditional EF GlobalMARINA SARAHY HERNANDEZ OROZCONo ratings yet
- G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Conditional SentencesDocument10 pagesG5+8 - Ms. Amara - Conditional SentencesHadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Conditional - English Grammar - EFDocument2 pagesConditional - English Grammar - EFNameless 00No ratings yet
- Clasa A VIII A B ConditionalsDocument9 pagesClasa A VIII A B ConditionalsLiliana GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument7 pagesConditional SentenceAbhieey Choi Soo Hyun100% (1)
- CONDITIONALDocument25 pagesCONDITIONALShiella Mae Vispo100% (1)
- Conditional Sentences G 9 ENGDocument3 pagesConditional Sentences G 9 ENGEnas MujaliNo ratings yet
- Conditional If Type 0, 1 & 2Document3 pagesConditional If Type 0, 1 & 2obengNo ratings yet
- If Conditional: With Reza and FaisaDocument9 pagesIf Conditional: With Reza and FaisaSyifaa ZuchrufNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseDocument8 pages2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseArmeliaNo ratings yet
- InggrisDocument4 pagesInggrisZhong XinaNo ratings yet
- Kel. 11 Conditonal SentenceDocument15 pagesKel. 11 Conditonal SentenceNu FaNo ratings yet
- Conditional 2pagesDocument2 pagesConditional 2pagesTechArea GamingNo ratings yet
- Conditional: "The Unreal Past"Document23 pagesConditional: "The Unreal Past"Liyan SusantoNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesRekaman IstiNo ratings yet
- Conditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFDocument15 pagesConditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFUmu NeroNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: ClauseDocument4 pagesConditionals: ClauseAhmed RubelNo ratings yet
- Summary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationDocument6 pagesSummary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationJaime G. MendozaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsPetra StefanescuNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument2 pagesConditional SentenceBunnarin ChrunNo ratings yet
- Conditional TenseDocument19 pagesConditional Tenseecardnyl25No ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument8 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: English For Level IvDocument4 pagesConditionals: English For Level IvJuan Felipe SalazarNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument8 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument27 pagesCONDITIONALBjp MishraNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Conditional: If + Simple Present Simple FutureDocument7 pagesType 2 Conditional: If + Simple Present Simple FutureJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument8 pagesConditional SentenceShim HanelNo ratings yet
- Conditional TenseDocument19 pagesConditional Tenseecardnyl25No ratings yet
- The 'Zero' Conditional: 1. FormDocument14 pagesThe 'Zero' Conditional: 1. Formhima67No ratings yet
- IF ClauseDocument5 pagesIF ClauseJuliette Viveros UlibarryNo ratings yet
- Conditianal - If ClausesDocument15 pagesConditianal - If ClausesJbour LaithNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Conditional Sentences-Rules You Need To KnowDocument3 pagesGrammar: Conditional Sentences-Rules You Need To Knowgilca.monicaluizaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesRoxana Alexandru100% (1)
- ConditionalDocument22 pagesConditionalMae CabanasNo ratings yet
- Catatan Kelompok 4 GrammarDocument6 pagesCatatan Kelompok 4 GrammarIkhlas PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument3 pagesConditional SentenceRegina MagdaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument7 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- How To Use Zero Conditional SentencesDocument5 pagesHow To Use Zero Conditional SentencesLast-Mov 20thNo ratings yet
- Form and Meaning: Zero ConditionalDocument2 pagesForm and Meaning: Zero ConditionalHampnie HambertNo ratings yet
- 1st and Zero - ConditionalsDocument3 pages1st and Zero - ConditionalsDarkCreeper13No ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument5 pagesConditional SentenceUjjawal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument6 pagesConditional Sentencesmigue714100% (1)
- The Hypothetical ConstructionsDocument22 pagesThe Hypothetical ConstructionsComan AlexandraNo ratings yet
- The 'Zero' ConditionalDocument2 pagesThe 'Zero' ConditionalMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- If A Certain Condition Is True, Then A Particular Result HappensDocument6 pagesIf A Certain Condition Is True, Then A Particular Result HappensNhật ChungNo ratings yet
- Kisi-Kisi Tugas Bing 1Document4 pagesKisi-Kisi Tugas Bing 1ratnasariNo ratings yet
- 9313 - Presentasi InggrisDocument6 pages9313 - Presentasi InggrisDINAYUKUNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Small Words - Big Trouble-PrepositionsDocument37 pagesPresentation - Small Words - Big Trouble-PrepositionsAndrea Alvendia Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Volume II Grammar E-BookDocument101 pagesVolume II Grammar E-BookAhmad Bik ElhaysNo ratings yet
- Adjective: ExampleDocument8 pagesAdjective: ExampleMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Constantino The Sentence Patterns of 26 Philippine LanguagesDocument54 pagesConstantino The Sentence Patterns of 26 Philippine LanguagesCarol GalleonNo ratings yet
- Regens English WorkbookDocument68 pagesRegens English WorkbookrockNo ratings yet
- Prova de Inglês 2005 EfommDocument6 pagesProva de Inglês 2005 EfommGabriel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Where Are You From?: Vocabulary ComprehensionDocument22 pagesWhere Are You From?: Vocabulary Comprehension:DNo ratings yet
- Why Clauses-Lexico GrammarDocument16 pagesWhy Clauses-Lexico GrammarAmalia Rahma FirdausNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument5 pagesPronounMannan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Cuadro de LinkersDocument4 pagesCuadro de LinkersCONNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Theories and Sentence 2Document8 pagesGrammatical Theories and Sentence 2Bimpe KofoNo ratings yet
- Kannada Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesKannada Parts of SpeechNarayanan Kannan SubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Understanding PronounsDocument41 pagesUnderstanding PronounsNilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument14 pagesParts of SpeechSampada SawantNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast ContinuousILy SofiaNo ratings yet
- Falcon Crest Public SchoolDocument11 pagesFalcon Crest Public Schoolsanjay tomarNo ratings yet
- Conjunction NotesDocument3 pagesConjunction NotesThwayyiba PKNo ratings yet
- Ch-1, QA, XII, Communication SkillDocument8 pagesCh-1, QA, XII, Communication Skillmuhammed zidanNo ratings yet
- The Use of Articles With Some Semantic Groups of NounsDocument3 pagesThe Use of Articles With Some Semantic Groups of NounsValeriya VoytehovskayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Asking Questions & Talking Regular ActivitiesDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Asking Questions & Talking Regular ActivitiesVega Nanda ArtianiNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - The Possessive Case Versus The Genitive CaseDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammar - The Possessive Case Versus The Genitive CaseMauricio BarrosNo ratings yet
- What Are Participles?: Clause Clause/reduced Relative ClauseDocument3 pagesWhat Are Participles?: Clause Clause/reduced Relative ClauseAnna VilellaNo ratings yet
- Demo GrammarDocument10 pagesDemo GrammarAbby YambaoNo ratings yet
- SoalDocument5 pagesSoalZharotul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Adverbial Phrases of TimeDocument2 pagesAdverbial Phrases of TimeGemma HSNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Direct - Indirect Speech)Document14 pagesReported Speech (Direct - Indirect Speech)Roy SihombingNo ratings yet
The Zero Conditional
The Zero Conditional
Uploaded by
KahnMéndezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Zero Conditional
The Zero Conditional
Uploaded by
KahnMéndezCopyright:
Available Formats
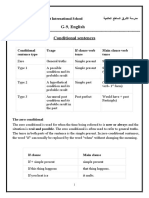
CONDITIONAL
Conditional tenses are used to speculate about what could happen, what might have happened, and what
we wish would happen. In English, most sentences using the conditional contain the word if. Many
conditional forms in English are used in sentences that include verbs in one of the past tenses. This usage
is referred to as "the unreal past" because we use a past tense but we are not actually referring to
something that happened in the past. There are five main ways of constructing conditional sentences in
English. In all cases, these sentences are made up of an if clause and a main clause. In many negative
conditional sentences, there is an equivalent sentence construction using "unless" instead of "if".
Conditional sentence type
Zero
Type 1
Type 2
Type 3
Mixed type
Usage
General truths
A possible condition and its probable result
A hypothetical condition and its probable result
An unreal past condition and its probable result in the past
An unreal past condition and its probable result in the
present
If clause verb te
Simple present
Simple present
Simple past
Past perfect
Past perfect
THE ZERO CONDITIONAL
The zero conditional is used for when the time being referred to is now or always and the situation is real
and possible. The zero conditional is often used to refer to general truths. The tense in both parts of the
sentence is the simple present. In zero conditional sentences, the word "if" can usually be replaced by the
word "when" without changing the meaning.
If clause
Main clause
If + simple present
simple present
If this thing happens
that thing happens.
If you heat ice
it melts.
If it rains
the grass gets wet.
TYPE 1 CONDITIONAL
The type 1 conditional is used to refer to the present or future where the situation is real. The type 1
conditional refers to a possible condition and its probable result. In these sentences the if clause is in the
simple present, and the main clause is in the simple future.
If clause
Main clause
If + simple present
simple future
If this thing happens
that thing will happen.
If you don't hurry
you will miss the train.
If it rains today
you will get wet.
TYPE 2 CONDITIONAL
The type 2 conditional is used to refer to a time that is now or any time, and a situation that is unreal.
These sentences are not based on fact. The type 2 conditional is used to refer to a hypothetical condition
and its probable result. In type 2 conditional sentences, the if clause uses the simple past, and the main
clause uses the present conditional.
If clause
Main clause
If + simple past
present conditional or present continuous conditional
If this thing happened
that thing would happen. (but I'm not sure this thing will happ
that thing would be happening.
If you went to bed earlier
you would not be so tired.
If it rained
you would get wet.
If I spoke Italian
I would be working in Italy.
TYPE 3 CONDITIONAL
The type 3 conditional is used to refer to a time that is in the past, and a situation that is contrary to
reality. The facts they are based on are the opposite of what is expressed. The type 3 conditional is used
to refer to an unreal past condition and its probable past result. In type 3 conditional sentences, the if
clause uses the past perfect, and the main clause uses the perfect conditional.
If clause
Main clause
If + past perfect
perfect conditional or perfect continuous conditional
If this thing had happened
that thing would have happened. (but neither of those thing
that thing would have been happening.
If you had studied harder
you would have passed the exam.
If it had rained
you would have gotten wet.
If I had accepted that promotion
I would have been working in Milan.
MIXED TYPE CONDITIONAL
The mixed type conditional is used to refer to a time that is in the past, and a situation that is ongoing
into the present. The facts they are based on are the opposite of what is expressed. The mixed type
conditional is used to refer to an unreal past condition and its probable result in the present. In mixed type
conditional sentences, the if clause uses the past perfect, and the main clause uses the present
conditional.
If clause
Main clause
If + past perfect or simple past
present conditional or perfect conditional
If this thing had happened
that thing would happen. (but this thing didn't happen so th
If I had worked harder at school
I would have a better job now.
If we had looked at the map
we wouldn't be lost.
If you weren't afraid of spiders
you would have picked it up and put it outside.
You might also like
- Inglês - Me and My Family 5º AnoDocument4 pagesInglês - Me and My Family 5º Anodalilaramos76% (21)
- Ngữ Pháp Quangbao Đề CươngDocument3 pagesNgữ Pháp Quangbao Đề CươngNga PhanNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyFrom EverandEnglish Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishapi-278092100No ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument5 pagesThe Zero ConditionalEduard Hernan Cardona VillamilNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Conditional: If Clause Main ClauseDocument3 pagesType 1 Conditional: If Clause Main ClauseDian daniNo ratings yet
- Amanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalDocument4 pagesAmanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalGeraldine SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Conditional If PDF To Be SharedDocument21 pagesConditional If PDF To Be SharedMiandy CelestinnNo ratings yet
- Name:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesName:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentenceshosearoinaldoNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence TypeDocument6 pagesConditional Sentence TypeHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument3 pagesConditionalSalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseStancu AlinNo ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument4 pagesThe Zero ConditionalKim SeorinNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument95 pagesCONDITIONALmmmmmNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": ConditionalsDocument3 pages"The Unreal Past": ConditionalsLuisa Fernanda Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- Conditional EF GlobalDocument1 pageConditional EF GlobalMARINA SARAHY HERNANDEZ OROZCONo ratings yet
- G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Conditional SentencesDocument10 pagesG5+8 - Ms. Amara - Conditional SentencesHadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Conditional - English Grammar - EFDocument2 pagesConditional - English Grammar - EFNameless 00No ratings yet
- Clasa A VIII A B ConditionalsDocument9 pagesClasa A VIII A B ConditionalsLiliana GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument7 pagesConditional SentenceAbhieey Choi Soo Hyun100% (1)
- CONDITIONALDocument25 pagesCONDITIONALShiella Mae Vispo100% (1)
- Conditional Sentences G 9 ENGDocument3 pagesConditional Sentences G 9 ENGEnas MujaliNo ratings yet
- Conditional If Type 0, 1 & 2Document3 pagesConditional If Type 0, 1 & 2obengNo ratings yet
- If Conditional: With Reza and FaisaDocument9 pagesIf Conditional: With Reza and FaisaSyifaa ZuchrufNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseDocument8 pages2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseArmeliaNo ratings yet
- InggrisDocument4 pagesInggrisZhong XinaNo ratings yet
- Kel. 11 Conditonal SentenceDocument15 pagesKel. 11 Conditonal SentenceNu FaNo ratings yet
- Conditional 2pagesDocument2 pagesConditional 2pagesTechArea GamingNo ratings yet
- Conditional: "The Unreal Past"Document23 pagesConditional: "The Unreal Past"Liyan SusantoNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesRekaman IstiNo ratings yet
- Conditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFDocument15 pagesConditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFUmu NeroNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: ClauseDocument4 pagesConditionals: ClauseAhmed RubelNo ratings yet
- Summary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationDocument6 pagesSummary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationJaime G. MendozaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsPetra StefanescuNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument2 pagesConditional SentenceBunnarin ChrunNo ratings yet
- Conditional TenseDocument19 pagesConditional Tenseecardnyl25No ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument8 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: English For Level IvDocument4 pagesConditionals: English For Level IvJuan Felipe SalazarNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument8 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument27 pagesCONDITIONALBjp MishraNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Conditional: If + Simple Present Simple FutureDocument7 pagesType 2 Conditional: If + Simple Present Simple FutureJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument8 pagesConditional SentenceShim HanelNo ratings yet
- Conditional TenseDocument19 pagesConditional Tenseecardnyl25No ratings yet
- The 'Zero' Conditional: 1. FormDocument14 pagesThe 'Zero' Conditional: 1. Formhima67No ratings yet
- IF ClauseDocument5 pagesIF ClauseJuliette Viveros UlibarryNo ratings yet
- Conditianal - If ClausesDocument15 pagesConditianal - If ClausesJbour LaithNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Conditional Sentences-Rules You Need To KnowDocument3 pagesGrammar: Conditional Sentences-Rules You Need To Knowgilca.monicaluizaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesRoxana Alexandru100% (1)
- ConditionalDocument22 pagesConditionalMae CabanasNo ratings yet
- Catatan Kelompok 4 GrammarDocument6 pagesCatatan Kelompok 4 GrammarIkhlas PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument3 pagesConditional SentenceRegina MagdaNo ratings yet
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocument7 pagesClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- How To Use Zero Conditional SentencesDocument5 pagesHow To Use Zero Conditional SentencesLast-Mov 20thNo ratings yet
- Form and Meaning: Zero ConditionalDocument2 pagesForm and Meaning: Zero ConditionalHampnie HambertNo ratings yet
- 1st and Zero - ConditionalsDocument3 pages1st and Zero - ConditionalsDarkCreeper13No ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument5 pagesConditional SentenceUjjawal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument6 pagesConditional Sentencesmigue714100% (1)
- The Hypothetical ConstructionsDocument22 pagesThe Hypothetical ConstructionsComan AlexandraNo ratings yet
- The 'Zero' ConditionalDocument2 pagesThe 'Zero' ConditionalMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- If A Certain Condition Is True, Then A Particular Result HappensDocument6 pagesIf A Certain Condition Is True, Then A Particular Result HappensNhật ChungNo ratings yet
- Kisi-Kisi Tugas Bing 1Document4 pagesKisi-Kisi Tugas Bing 1ratnasariNo ratings yet
- 9313 - Presentasi InggrisDocument6 pages9313 - Presentasi InggrisDINAYUKUNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Small Words - Big Trouble-PrepositionsDocument37 pagesPresentation - Small Words - Big Trouble-PrepositionsAndrea Alvendia Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Volume II Grammar E-BookDocument101 pagesVolume II Grammar E-BookAhmad Bik ElhaysNo ratings yet
- Adjective: ExampleDocument8 pagesAdjective: ExampleMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Constantino The Sentence Patterns of 26 Philippine LanguagesDocument54 pagesConstantino The Sentence Patterns of 26 Philippine LanguagesCarol GalleonNo ratings yet
- Regens English WorkbookDocument68 pagesRegens English WorkbookrockNo ratings yet
- Prova de Inglês 2005 EfommDocument6 pagesProva de Inglês 2005 EfommGabriel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Where Are You From?: Vocabulary ComprehensionDocument22 pagesWhere Are You From?: Vocabulary Comprehension:DNo ratings yet
- Why Clauses-Lexico GrammarDocument16 pagesWhy Clauses-Lexico GrammarAmalia Rahma FirdausNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument5 pagesPronounMannan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Cuadro de LinkersDocument4 pagesCuadro de LinkersCONNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Theories and Sentence 2Document8 pagesGrammatical Theories and Sentence 2Bimpe KofoNo ratings yet
- Kannada Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesKannada Parts of SpeechNarayanan Kannan SubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Understanding PronounsDocument41 pagesUnderstanding PronounsNilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument14 pagesParts of SpeechSampada SawantNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast ContinuousILy SofiaNo ratings yet
- Falcon Crest Public SchoolDocument11 pagesFalcon Crest Public Schoolsanjay tomarNo ratings yet
- Conjunction NotesDocument3 pagesConjunction NotesThwayyiba PKNo ratings yet
- Ch-1, QA, XII, Communication SkillDocument8 pagesCh-1, QA, XII, Communication Skillmuhammed zidanNo ratings yet
- The Use of Articles With Some Semantic Groups of NounsDocument3 pagesThe Use of Articles With Some Semantic Groups of NounsValeriya VoytehovskayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Asking Questions & Talking Regular ActivitiesDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Asking Questions & Talking Regular ActivitiesVega Nanda ArtianiNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - The Possessive Case Versus The Genitive CaseDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammar - The Possessive Case Versus The Genitive CaseMauricio BarrosNo ratings yet
- What Are Participles?: Clause Clause/reduced Relative ClauseDocument3 pagesWhat Are Participles?: Clause Clause/reduced Relative ClauseAnna VilellaNo ratings yet
- Demo GrammarDocument10 pagesDemo GrammarAbby YambaoNo ratings yet
- SoalDocument5 pagesSoalZharotul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Adverbial Phrases of TimeDocument2 pagesAdverbial Phrases of TimeGemma HSNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Direct - Indirect Speech)Document14 pagesReported Speech (Direct - Indirect Speech)Roy SihombingNo ratings yet