Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsDecision Support Applications Using Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Virtual Instrumentation
Decision Support Applications Using Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Virtual Instrumentation
Uploaded by
Julio CésarThis document describes a project to design a control system using statistical process control (SPC) and the virtual instrumentation program LabVIEW. The system monitors quality indicators for six departments at a hospital. LabVIEW was used to create interfaces to view the indicators and perform statistical analysis. Control charts and Pareto charts identified processes outside control limits. An expert system provided alerts and suggestions when limits were exceeded. The designed system aimed to monitor indicators and facilitate continuous process improvement at the hospital.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Parts Manual: C9 Generator SetDocument638 pagesParts Manual: C9 Generator SetAlex RamirezNo ratings yet
- Computational and Statistical Methods for Analysing Big Data with ApplicationsFrom EverandComputational and Statistical Methods for Analysing Big Data with ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Labview Based Control Software For Finger Force Sensor Instrumentation DesignDocument6 pagesLabview Based Control Software For Finger Force Sensor Instrumentation DesignJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Management SystemDocument66 pagesHealthcare Management Systemmanikmathi100% (1)
- TheoryDocument31 pagesTheoryGirraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Labview Based Three Phase Induction Motor Speed Control: 1 Literature SurveyDocument68 pagesLabview Based Three Phase Induction Motor Speed Control: 1 Literature Surveyhardikrananjay100% (1)
- Applications of The Microprocessor in The Behavioral Medicine LaboratoryDocument4 pagesApplications of The Microprocessor in The Behavioral Medicine LaboratoryRohini RajNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management System: ProjectDocument7 pagesHospital Management System: ProjectDreegyYTNo ratings yet
- Virtual Instrumentation For Bio-Medical ApplicationsDocument3 pagesVirtual Instrumentation For Bio-Medical Applicationssouvik5000No ratings yet
- An Application of Diagnostic Inference Modeling To Vehicle Health ManagementDocument12 pagesAn Application of Diagnostic Inference Modeling To Vehicle Health ManagementragothsunNo ratings yet
- 05 Computer Applications in Pharmacy Full Unit VDocument7 pages05 Computer Applications in Pharmacy Full Unit VSinh LuyenNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Apollo Hospitals Case Study by Akash PRDocument28 pagesToaz - Info Apollo Hospitals Case Study by Akash PRswamikollapudi7No ratings yet
- Medical Clinic Management Information SystemDocument10 pagesMedical Clinic Management Information Systemmarie france abilaNo ratings yet
- Application of DIALIFE System For Residual Life Time Assessment On Nuclear Power PlantsDocument8 pagesApplication of DIALIFE System For Residual Life Time Assessment On Nuclear Power Plantsamsk23456No ratings yet
- COVID 19 With HospitalDocument41 pagesCOVID 19 With HospitalInitz TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Covid-Tmp Project ReportDocument34 pagesCovid-Tmp Project ReportMariraju health centerNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument28 pagesHospital Management SystemMobin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Creating An IHE ATNA-Based Audit Repository: Bill Gregg, Horacio D - Agostino, and Eduardo Gonzalez ToledoDocument9 pagesCreating An IHE ATNA-Based Audit Repository: Bill Gregg, Horacio D - Agostino, and Eduardo Gonzalez ToledofebaumgratzNo ratings yet
- A Virtual Instrument For Data Acquisition and AnalysisDocument18 pagesA Virtual Instrument For Data Acquisition and AnalysiskamaleshNo ratings yet
- Ijesrt: International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research TechnologyDocument8 pagesIjesrt: International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research Technologyirshad ahmedNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease Detection ReportDocument10 pagesHeart Disease Detection Reportdummy dummyNo ratings yet
- Ban Application ProjDocument2 pagesBan Application ProjSmitha ShindeNo ratings yet
- Online Employee Health Care System-SynopsisDocument6 pagesOnline Employee Health Care System-SynopsisNageshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Retrospective Validation of A CDS Feb 99 PDFDocument9 pagesRetrospective Validation of A CDS Feb 99 PDFImran AsgharNo ratings yet
- Hosptial Management SystemDocument35 pagesHosptial Management Systemsahaniladri004No ratings yet
- Hospital Management System: DEPT OF CSE, Dr. A.I.T, 2014-2015Document18 pagesHospital Management System: DEPT OF CSE, Dr. A.I.T, 2014-2015tinaNo ratings yet
- Ai Powered Medical Diagnosis-Phase 3Document10 pagesAi Powered Medical Diagnosis-Phase 3faizalahamed345690No ratings yet
- Clinic SystemDocument5 pagesClinic Systemmanali chavan100% (1)
- Apollo Hospitals Case Study by AkashDocument28 pagesApollo Hospitals Case Study by AkashVishwa Sourab Brungi0% (2)
- E (OTDA: O T D A) : Valuation of An Operating Theatre Design by A Software Program Perating Heatre Esign NalyzerDocument8 pagesE (OTDA: O T D A) : Valuation of An Operating Theatre Design by A Software Program Perating Heatre Esign NalyzerOlim AriyaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument17 pagesHospital Management SystemhyklassNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Evaluation of AI Assisted SystemsDocument21 pagesGuidance For Evaluation of AI Assisted SystemsManas MishraNo ratings yet
- Health Monitorig and DetectionDocument2 pagesHealth Monitorig and DetectionAnusree k vNo ratings yet
- Building Your Medical Expert System-Do It Yourself: Irosh@sltnet - LKDocument5 pagesBuilding Your Medical Expert System-Do It Yourself: Irosh@sltnet - LKHimanshu RathoreNo ratings yet
- GNUmed Introduction v4Document14 pagesGNUmed Introduction v4trabajadosNo ratings yet
- A Software Architecture and Data Model For CommuniDocument5 pagesA Software Architecture and Data Model For CommuniAlfie Frankie DiezNo ratings yet
- Epi Info GuideDocument93 pagesEpi Info GuideAgus FitrianggaNo ratings yet
- Parvender Gusain SynopsisDocument15 pagesParvender Gusain SynopsisNageshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Computer in Pharm. Technology 97Document9 pagesComputer in Pharm. Technology 97Ram C DhakarNo ratings yet
- IOT Based Calorie Calculator For Healthcare SystemDocument4 pagesIOT Based Calorie Calculator For Healthcare SystemVicente Rap Anderson Azabache GrandaNo ratings yet
- PCBI - WholeDocument10 pagesPCBI - WholeSucharitha PathipatiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management Report FinalDocument38 pagesHospital Management Report FinalAnkush Garg0% (1)
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument7 pagesIlovepdf MergedAshutoshNo ratings yet
- A Blockchain Based System For Healthcare Digital TwinDocument54 pagesA Blockchain Based System For Healthcare Digital Twinbvishal27No ratings yet
- 17bce0578 Dai IipDocument16 pages17bce0578 Dai IipChinmay Soni50% (4)
- Multiple Disease Prediction Using Different Machine Learning Algorithms ComparativelyDocument5 pagesMultiple Disease Prediction Using Different Machine Learning Algorithms ComparativelyNeha BhatiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument18 pagesHospital Management Systemzamirul2islamNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Part - 2concept of Information Systems and SoftwareDocument30 pagesUnit - 1 Part - 2concept of Information Systems and SoftwareDhaval TelangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Systems Introduction: 1.1 Description of The ProjectDocument52 pagesChapter 1. Systems Introduction: 1.1 Description of The ProjectRupesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Daily Time Record Keeping SystemDocument6 pagesDaily Time Record Keeping SystemVickram JainNo ratings yet
- Automated Cause Effect Analysis For Process PlantsDocument7 pagesAutomated Cause Effect Analysis For Process PlantsAkg WorldNo ratings yet
- Human Pulse Detection SystemDocument19 pagesHuman Pulse Detection SystemFakorede Akinwande alexNo ratings yet
- Automate Statistical AnalysisDocument6 pagesAutomate Statistical Analysisnishu_aminNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease Risk Predictor: Rashmi Mishra, Pooja Saharan, Amrita JyotiDocument5 pagesHeart Disease Risk Predictor: Rashmi Mishra, Pooja Saharan, Amrita Jyotishital shermaleNo ratings yet
- PurposeDocument2 pagesPurposeSmitha DanielNo ratings yet
- A Home-Based Functional Hand-Extremity Assessment System For Stroke RehabilitationDocument2 pagesA Home-Based Functional Hand-Extremity Assessment System For Stroke Rehabilitationwijaya ajaaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument62 pagesHospital Management Systemmaverick_apoc100% (1)
- Health Care Management System ProjectDocument3 pagesHealth Care Management System ProjectRajesh MandalNo ratings yet
- Framework For A Smart Data Analytics Platform Towards Process Monitoring and Alarm ManagementDocument31 pagesFramework For A Smart Data Analytics Platform Towards Process Monitoring and Alarm Managementjluis98No ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document4 pagesLesson 10Roland OpleNo ratings yet
- GM2018 MediaKit 9 21 2017 1Document4 pagesGM2018 MediaKit 9 21 2017 1Julio CésarNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Generation SystemsDocument8 pagesRenewable Energy Generation SystemsJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Research On Technology of Traffic Video Incidents Detection Under Highway ConditionDocument5 pagesResearch On Technology of Traffic Video Incidents Detection Under Highway ConditionJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Labview Based Control Software For Finger Force Sensor Instrumentation DesignDocument6 pagesLabview Based Control Software For Finger Force Sensor Instrumentation DesignJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Modelling & Software: Yolanda Bolea, Vicenç Puig, Joaquim BlesaDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Modelling & Software: Yolanda Bolea, Vicenç Puig, Joaquim BlesaJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Modelling & Software: R. Rivas-Perez, V. Feliu-Batlle, F.J. Castillo-Garcia, A. Linares-SaezDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Modelling & Software: R. Rivas-Perez, V. Feliu-Batlle, F.J. Castillo-Garcia, A. Linares-SaezJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Road Surveillance System: A Proposed Model For Vehicle Detection and Traffic Signal ControlDocument8 pagesAutonomous Road Surveillance System: A Proposed Model For Vehicle Detection and Traffic Signal ControlJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1568494609000908 Main PDFDocument35 pages1 s2.0 S1568494609000908 Main PDFJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect SciencedirectDocument8 pagesSciencedirect SciencedirectJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- PESTR18Document390 pagesPESTR18Julio CésarNo ratings yet
- Design of The Measurement System of The Pump Based On LabviewDocument4 pagesDesign of The Measurement System of The Pump Based On LabviewJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Smart Approach To Traffic Management Using Labview: Manan Temani, Rohank Agarwal, Rhythm Kohli, Mrinal SenDocument4 pagesSmart Approach To Traffic Management Using Labview: Manan Temani, Rohank Agarwal, Rhythm Kohli, Mrinal SenJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Virtual Instrumentation Interface For SRRC Control System: The Is AsDocument3 pagesVirtual Instrumentation Interface For SRRC Control System: The Is AsJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Transportation Research Part C: Sohail Zangenehpour, Luis F. Miranda-Moreno, Nicolas SaunierDocument16 pagesTransportation Research Part C: Sohail Zangenehpour, Luis F. Miranda-Moreno, Nicolas SaunierJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- PC Based Monitoring and Fault Prediction For Small Hydroelectric PlantsDocument4 pagesPC Based Monitoring and Fault Prediction For Small Hydroelectric PlantsJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory Model For Harmonic Measurements Windpowcr: in GeneratorsDocument2 pagesA Laboratory Model For Harmonic Measurements Windpowcr: in GeneratorsJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Transportation Research Part C: Mauro Dell'Orco, Mario Marinelli, Mehmet Ali SilguDocument13 pagesTransportation Research Part C: Mauro Dell'Orco, Mario Marinelli, Mehmet Ali SilguJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- AFSD ReviewDocument14 pagesAFSD ReviewKinesys TechsolutionsNo ratings yet
- CSP 520N 1BDocument18 pagesCSP 520N 1BfredtornayNo ratings yet
- Linux OSDocument10 pagesLinux OSAhamed ShahasNo ratings yet
- UENR2631-01 CDocument15 pagesUENR2631-01 CShanmuga PrakashNo ratings yet
- Schema IBM R60Document92 pagesSchema IBM R60Eva Beti PetreNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Set 3Document6 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Set 3MUSKAN PRNNo ratings yet
- Weekly RM Call Log During COVID Roster-2021: BranchDocument2 pagesWeekly RM Call Log During COVID Roster-2021: Brancharzu tabassumNo ratings yet
- MMM Friocell 22p - enDocument2 pagesMMM Friocell 22p - enmaawsNo ratings yet
- Freezer 50 TR Online Manual: Arcc - deDocument1 pageFreezer 50 TR Online Manual: Arcc - deMiraziz AliyevNo ratings yet
- BJ2 Ch7Document4 pagesBJ2 Ch7Shivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Agilent X-Series Signal Analyzer: N9030A PXA Specifications GuideDocument402 pagesAgilent X-Series Signal Analyzer: N9030A PXA Specifications GuideMichelle Ysa ValeraNo ratings yet
- MainBridge - Design ReportDocument18 pagesMainBridge - Design ReportWan100% (1)
- 2018 Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic Actuators With Muscle-Like PerformanceDocument6 pages2018 Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic Actuators With Muscle-Like PerformanceJack LeeNo ratings yet
- Form Pengukuran GroundingDocument2 pagesForm Pengukuran GroundingghooestiepNo ratings yet
- Gymnasium DesignDocument3 pagesGymnasium DesignjimmyboyjrNo ratings yet
- Strength Requirement: (1) - Pile Shear CapacityDocument4 pagesStrength Requirement: (1) - Pile Shear CapacityAlma M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual For Spin CoaterDocument3 pagesOperating Manual For Spin CoaterKhursheed Ahmed CheshttiNo ratings yet
- Autocom FAQ - Доработка IVECO 30pinDocument3 pagesAutocom FAQ - Доработка IVECO 30pinAvs Electron100% (1)
- Venturi Medium Sized (VMS) : ApplicationDocument8 pagesVenturi Medium Sized (VMS) : ApplicationChn TutkunNo ratings yet
- Mysql WorkshopDocument197 pagesMysql WorkshopNaser NaseerNo ratings yet
- DatabasesDocument20 pagesDatabaseslokenders801No ratings yet
- Introduction To Multisim 12Document11 pagesIntroduction To Multisim 12Madhuri RoyNo ratings yet
- Aws D1.3-D1.3M 2018Document6 pagesAws D1.3-D1.3M 2018Lee Chong EeNo ratings yet
- PRELIMINARY (CMP) - Comprehensive Master Planning Report / ChecklistDocument7 pagesPRELIMINARY (CMP) - Comprehensive Master Planning Report / ChecklistNikki CalumaNo ratings yet
- Filtro Fino - Rsl0287 - Cut - FboDocument2 pagesFiltro Fino - Rsl0287 - Cut - Fbotomeu_vanrell100% (1)
- Quotation 132kv CT PT 33kv PTDocument5 pagesQuotation 132kv CT PT 33kv PTSharafat AliNo ratings yet
- C13TE3ADocument2 pagesC13TE3AAhmed Sherif CupoNo ratings yet
- Speed Modeling of DC Motorcusing Tacho GeneratorDocument7 pagesSpeed Modeling of DC Motorcusing Tacho GeneratorAbanoub Malak SelemNo ratings yet
- THIELE Lashing ProductsDocument28 pagesTHIELE Lashing ProductsNixNo ratings yet
Decision Support Applications Using Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Virtual Instrumentation
Decision Support Applications Using Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Virtual Instrumentation
Uploaded by
Julio César0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThis document describes a project to design a control system using statistical process control (SPC) and the virtual instrumentation program LabVIEW. The system monitors quality indicators for six departments at a hospital. LabVIEW was used to create interfaces to view the indicators and perform statistical analysis. Control charts and Pareto charts identified processes outside control limits. An expert system provided alerts and suggestions when limits were exceeded. The designed system aimed to monitor indicators and facilitate continuous process improvement at the hospital.
Original Description:
labview
Original Title
00842377
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes a project to design a control system using statistical process control (SPC) and the virtual instrumentation program LabVIEW. The system monitors quality indicators for six departments at a hospital. LabVIEW was used to create interfaces to view the indicators and perform statistical analysis. Control charts and Pareto charts identified processes outside control limits. An expert system provided alerts and suggestions when limits were exceeded. The designed system aimed to monitor indicators and facilitate continuous process improvement at the hospital.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesDecision Support Applications Using Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Virtual Instrumentation
Decision Support Applications Using Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Virtual Instrumentation
Uploaded by
Julio CésarThis document describes a project to design a control system using statistical process control (SPC) and the virtual instrumentation program LabVIEW. The system monitors quality indicators for six departments at a hospital. LabVIEW was used to create interfaces to view the indicators and perform statistical analysis. Control charts and Pareto charts identified processes outside control limits. An expert system provided alerts and suggestions when limits were exceeded. The designed system aimed to monitor indicators and facilitate continuous process improvement at the hospital.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Decision Support Applications using Statistical Process Control (SPC)
and Virtual Instrumentation (VI)
Izabella A. Gieras, BS, Eric Rosow, MS, Joseph Adam, MS, Chris Roth, BS, and John D. Enderle, PhD
Hartford Hospital, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hartford, CT
Premise Development Corporation, Avon, CT
University of Connecticut, Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering, Storrs, CT 06269-2 157
LabVIEW requires 16 MB RAM, 32 MB
recommended, Pentium recommended and 500-MB hard
disk space, SVGA monitor, CD-ROM and 3.5-inch floppy
disk [2]. The objective in VI is to use a general-purpose
computer to mimic real instruments with their dedicated
controls and displays, but with added versatility that comes
with this software [3].
Main front panel was designed in LabVIEW as
displayed in Figure 1 below. It consists of a list of 6
different departments and their corresponding indicators.
When the VI is run, the panel is activated and where out
of range signals have been detected, visual alarm will be
triggered by red blinking light informing the user that this
indicator needs to be investigated further. The green
blinking light indicates a stable process.
Abstract- Healthcare is an ever-changing environment and
it is essential for each medical institution to be prepared to
face and consequently conquer the future advancements in
technology. This task can be accomplished by the
implementation of appropriate healthcare performance and
quality measures, namely indicators, within a control system.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) together with a Virtual
Instrumentation (VI) programming environment called
LabVIEW (National Instruments), was used to develop the
necessary system.
I. INTRODUCTION
The primary objective of this project was to design and
develop a control system for the implementation of
different quality and performance indicators in healthcare.
The following five indicators were selected in the
Biomedical Engineering Department at Hartford Hospital:
number of medical equipment breakdowns, total number of
work orders, average hours and cost per service call and
percentage of completed preventive maintenance
inspections. These indicators were measured in the
following six departments, namely Anesthesia, Biomedical
Engineering, Hemodialysis, Operating Rooms, Radiology
and Respiratory Care. This data was taken from the
biomedical engineering medical equipment database,
WOSYST (St. Croix System) and stored in MS Excel.
With the use of LabVIEW, appropriate indicators were
modeled with various statistical tools, such as control and
Pareto charts and histograms. With the use of expert
system designed in LabVIEW, the user can be notified of
any potential problems, just in time to implement various
techniques for their improvement.
Application of Statistical Process Control (SPC) was
used in LabVIEW in order to graphically display the
predefined indicators. SPC is a method of monitoring,
controlling and, ideally, improving a process through
statistical analysis. It includes the following steps:
measuring the process, eliminating variances in the process
to make it consistent, monitoring the process, and
improving the process to its best target value [ 11.
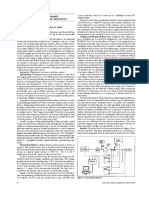
Fig. 1. Main front panel in LabVIEW accessing
indicators in all 6 departments
Another front panel was created for the graphical data
display and analysis. This is shown in Figure 2. Each
indicator data is read from MS Excel for the individual
department. Control Chart of type c was used and upper,
central and lower control limits were set accordingly to
monitor the data. Pareto chart, displaying the data in
descending order and thus concentrating primarily on the
11. DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION
0-7803-6341-8/00/$10.00 02000 IEEE
57
left side of the chart, constituted another statistical data
analysis method.
Fig. 3. Expert System in LabVIEW - pop-up dialog box
IV. CONCLUSIONS
Fig. 2. Design of SPC Front Panel in LabVIEW
111. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A. SPC System in LabVIEW
The design process mentioned in section 2 was implemented
in all 6 departments. The capability indexes, standard deviations
and means were calculated in LabVIEW. These were indicative
of the range of variability present within each indicator process.
With the use of an add-on package, MS QI (Lifestar, Inc.),
the data will be further analyzed for detection of trends and
patterns.
B. Experf System
With the design of statistical process control
applications in LabVIEW, it is essential to have the user
notified when the monitored process has gone over the
predefined limits. This was done with an implementation
of pop-up dialog boxes in LabVIEW acting as an expert
system. An expert system acted as a computer program that
simulated the judgement and behavior of a human that has
expert knowledge and experience in a particular field [4].
The dialog boxes not only alarm the user of changes
occurring within a process but also provide some intuitive
suggestions on how the user can go about rectifying the
existing problem. Figure 3 displays a sample dialog box.
With the designed control system, the biomedical
engineering department at Hartford Hospital will be
capable of constantly monitoring the predefined indicators
and make appropriate changes where necessary in order to
avoid any potential losses. This is especially applicable to
the medical equipment breakdown and cost per service call
indicators. The designed system will work closely with the
medical equipment database, WOSYST, for real-time data
input. This system will also have the capability of being
extended for the implementation of other indicators from
different databases.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Special thanks would like to be extended to Eric
Rosow, Joe Adam, Chris Roth for their help and expertise
in LabVJEW as well as Dr Bronzino and Dr Enderle for
their academic guidance.
REFERENCES
[ l ] Duncan W.J., Ginter P.M., Swayne L.E. (1998).
Handbook of Health Care Management. Oxford:
Blackwell Publishers.
LabVIEW Catalogue, 1999. National Instruments, TX.
Johnson, G.W.,
LabVIEW Graphical Programming
Practical Applications in Instrumentation and
Control. McGraw-Hill, 1997.
Expert System, (1999). httD://whatis.com/expertsy.htm
You might also like
- Parts Manual: C9 Generator SetDocument638 pagesParts Manual: C9 Generator SetAlex RamirezNo ratings yet
- Computational and Statistical Methods for Analysing Big Data with ApplicationsFrom EverandComputational and Statistical Methods for Analysing Big Data with ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Labview Based Control Software For Finger Force Sensor Instrumentation DesignDocument6 pagesLabview Based Control Software For Finger Force Sensor Instrumentation DesignJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Management SystemDocument66 pagesHealthcare Management Systemmanikmathi100% (1)
- TheoryDocument31 pagesTheoryGirraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Labview Based Three Phase Induction Motor Speed Control: 1 Literature SurveyDocument68 pagesLabview Based Three Phase Induction Motor Speed Control: 1 Literature Surveyhardikrananjay100% (1)
- Applications of The Microprocessor in The Behavioral Medicine LaboratoryDocument4 pagesApplications of The Microprocessor in The Behavioral Medicine LaboratoryRohini RajNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management System: ProjectDocument7 pagesHospital Management System: ProjectDreegyYTNo ratings yet
- Virtual Instrumentation For Bio-Medical ApplicationsDocument3 pagesVirtual Instrumentation For Bio-Medical Applicationssouvik5000No ratings yet
- An Application of Diagnostic Inference Modeling To Vehicle Health ManagementDocument12 pagesAn Application of Diagnostic Inference Modeling To Vehicle Health ManagementragothsunNo ratings yet
- 05 Computer Applications in Pharmacy Full Unit VDocument7 pages05 Computer Applications in Pharmacy Full Unit VSinh LuyenNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Apollo Hospitals Case Study by Akash PRDocument28 pagesToaz - Info Apollo Hospitals Case Study by Akash PRswamikollapudi7No ratings yet
- Medical Clinic Management Information SystemDocument10 pagesMedical Clinic Management Information Systemmarie france abilaNo ratings yet
- Application of DIALIFE System For Residual Life Time Assessment On Nuclear Power PlantsDocument8 pagesApplication of DIALIFE System For Residual Life Time Assessment On Nuclear Power Plantsamsk23456No ratings yet
- COVID 19 With HospitalDocument41 pagesCOVID 19 With HospitalInitz TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Covid-Tmp Project ReportDocument34 pagesCovid-Tmp Project ReportMariraju health centerNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument28 pagesHospital Management SystemMobin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Creating An IHE ATNA-Based Audit Repository: Bill Gregg, Horacio D - Agostino, and Eduardo Gonzalez ToledoDocument9 pagesCreating An IHE ATNA-Based Audit Repository: Bill Gregg, Horacio D - Agostino, and Eduardo Gonzalez ToledofebaumgratzNo ratings yet
- A Virtual Instrument For Data Acquisition and AnalysisDocument18 pagesA Virtual Instrument For Data Acquisition and AnalysiskamaleshNo ratings yet
- Ijesrt: International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research TechnologyDocument8 pagesIjesrt: International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research Technologyirshad ahmedNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease Detection ReportDocument10 pagesHeart Disease Detection Reportdummy dummyNo ratings yet
- Ban Application ProjDocument2 pagesBan Application ProjSmitha ShindeNo ratings yet
- Online Employee Health Care System-SynopsisDocument6 pagesOnline Employee Health Care System-SynopsisNageshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Retrospective Validation of A CDS Feb 99 PDFDocument9 pagesRetrospective Validation of A CDS Feb 99 PDFImran AsgharNo ratings yet
- Hosptial Management SystemDocument35 pagesHosptial Management Systemsahaniladri004No ratings yet
- Hospital Management System: DEPT OF CSE, Dr. A.I.T, 2014-2015Document18 pagesHospital Management System: DEPT OF CSE, Dr. A.I.T, 2014-2015tinaNo ratings yet
- Ai Powered Medical Diagnosis-Phase 3Document10 pagesAi Powered Medical Diagnosis-Phase 3faizalahamed345690No ratings yet
- Clinic SystemDocument5 pagesClinic Systemmanali chavan100% (1)
- Apollo Hospitals Case Study by AkashDocument28 pagesApollo Hospitals Case Study by AkashVishwa Sourab Brungi0% (2)
- E (OTDA: O T D A) : Valuation of An Operating Theatre Design by A Software Program Perating Heatre Esign NalyzerDocument8 pagesE (OTDA: O T D A) : Valuation of An Operating Theatre Design by A Software Program Perating Heatre Esign NalyzerOlim AriyaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument17 pagesHospital Management SystemhyklassNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Evaluation of AI Assisted SystemsDocument21 pagesGuidance For Evaluation of AI Assisted SystemsManas MishraNo ratings yet
- Health Monitorig and DetectionDocument2 pagesHealth Monitorig and DetectionAnusree k vNo ratings yet
- Building Your Medical Expert System-Do It Yourself: Irosh@sltnet - LKDocument5 pagesBuilding Your Medical Expert System-Do It Yourself: Irosh@sltnet - LKHimanshu RathoreNo ratings yet
- GNUmed Introduction v4Document14 pagesGNUmed Introduction v4trabajadosNo ratings yet
- A Software Architecture and Data Model For CommuniDocument5 pagesA Software Architecture and Data Model For CommuniAlfie Frankie DiezNo ratings yet
- Epi Info GuideDocument93 pagesEpi Info GuideAgus FitrianggaNo ratings yet
- Parvender Gusain SynopsisDocument15 pagesParvender Gusain SynopsisNageshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Computer in Pharm. Technology 97Document9 pagesComputer in Pharm. Technology 97Ram C DhakarNo ratings yet
- IOT Based Calorie Calculator For Healthcare SystemDocument4 pagesIOT Based Calorie Calculator For Healthcare SystemVicente Rap Anderson Azabache GrandaNo ratings yet
- PCBI - WholeDocument10 pagesPCBI - WholeSucharitha PathipatiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management Report FinalDocument38 pagesHospital Management Report FinalAnkush Garg0% (1)
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument7 pagesIlovepdf MergedAshutoshNo ratings yet
- A Blockchain Based System For Healthcare Digital TwinDocument54 pagesA Blockchain Based System For Healthcare Digital Twinbvishal27No ratings yet
- 17bce0578 Dai IipDocument16 pages17bce0578 Dai IipChinmay Soni50% (4)
- Multiple Disease Prediction Using Different Machine Learning Algorithms ComparativelyDocument5 pagesMultiple Disease Prediction Using Different Machine Learning Algorithms ComparativelyNeha BhatiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument18 pagesHospital Management Systemzamirul2islamNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Part - 2concept of Information Systems and SoftwareDocument30 pagesUnit - 1 Part - 2concept of Information Systems and SoftwareDhaval TelangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Systems Introduction: 1.1 Description of The ProjectDocument52 pagesChapter 1. Systems Introduction: 1.1 Description of The ProjectRupesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Daily Time Record Keeping SystemDocument6 pagesDaily Time Record Keeping SystemVickram JainNo ratings yet
- Automated Cause Effect Analysis For Process PlantsDocument7 pagesAutomated Cause Effect Analysis For Process PlantsAkg WorldNo ratings yet
- Human Pulse Detection SystemDocument19 pagesHuman Pulse Detection SystemFakorede Akinwande alexNo ratings yet
- Automate Statistical AnalysisDocument6 pagesAutomate Statistical Analysisnishu_aminNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease Risk Predictor: Rashmi Mishra, Pooja Saharan, Amrita JyotiDocument5 pagesHeart Disease Risk Predictor: Rashmi Mishra, Pooja Saharan, Amrita Jyotishital shermaleNo ratings yet
- PurposeDocument2 pagesPurposeSmitha DanielNo ratings yet
- A Home-Based Functional Hand-Extremity Assessment System For Stroke RehabilitationDocument2 pagesA Home-Based Functional Hand-Extremity Assessment System For Stroke Rehabilitationwijaya ajaaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument62 pagesHospital Management Systemmaverick_apoc100% (1)
- Health Care Management System ProjectDocument3 pagesHealth Care Management System ProjectRajesh MandalNo ratings yet
- Framework For A Smart Data Analytics Platform Towards Process Monitoring and Alarm ManagementDocument31 pagesFramework For A Smart Data Analytics Platform Towards Process Monitoring and Alarm Managementjluis98No ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document4 pagesLesson 10Roland OpleNo ratings yet
- GM2018 MediaKit 9 21 2017 1Document4 pagesGM2018 MediaKit 9 21 2017 1Julio CésarNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Generation SystemsDocument8 pagesRenewable Energy Generation SystemsJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Research On Technology of Traffic Video Incidents Detection Under Highway ConditionDocument5 pagesResearch On Technology of Traffic Video Incidents Detection Under Highway ConditionJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Labview Based Control Software For Finger Force Sensor Instrumentation DesignDocument6 pagesLabview Based Control Software For Finger Force Sensor Instrumentation DesignJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Modelling & Software: Yolanda Bolea, Vicenç Puig, Joaquim BlesaDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Modelling & Software: Yolanda Bolea, Vicenç Puig, Joaquim BlesaJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Modelling & Software: R. Rivas-Perez, V. Feliu-Batlle, F.J. Castillo-Garcia, A. Linares-SaezDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Modelling & Software: R. Rivas-Perez, V. Feliu-Batlle, F.J. Castillo-Garcia, A. Linares-SaezJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Road Surveillance System: A Proposed Model For Vehicle Detection and Traffic Signal ControlDocument8 pagesAutonomous Road Surveillance System: A Proposed Model For Vehicle Detection and Traffic Signal ControlJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1568494609000908 Main PDFDocument35 pages1 s2.0 S1568494609000908 Main PDFJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect SciencedirectDocument8 pagesSciencedirect SciencedirectJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- PESTR18Document390 pagesPESTR18Julio CésarNo ratings yet
- Design of The Measurement System of The Pump Based On LabviewDocument4 pagesDesign of The Measurement System of The Pump Based On LabviewJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Smart Approach To Traffic Management Using Labview: Manan Temani, Rohank Agarwal, Rhythm Kohli, Mrinal SenDocument4 pagesSmart Approach To Traffic Management Using Labview: Manan Temani, Rohank Agarwal, Rhythm Kohli, Mrinal SenJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Virtual Instrumentation Interface For SRRC Control System: The Is AsDocument3 pagesVirtual Instrumentation Interface For SRRC Control System: The Is AsJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Transportation Research Part C: Sohail Zangenehpour, Luis F. Miranda-Moreno, Nicolas SaunierDocument16 pagesTransportation Research Part C: Sohail Zangenehpour, Luis F. Miranda-Moreno, Nicolas SaunierJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- PC Based Monitoring and Fault Prediction For Small Hydroelectric PlantsDocument4 pagesPC Based Monitoring and Fault Prediction For Small Hydroelectric PlantsJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory Model For Harmonic Measurements Windpowcr: in GeneratorsDocument2 pagesA Laboratory Model For Harmonic Measurements Windpowcr: in GeneratorsJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- Transportation Research Part C: Mauro Dell'Orco, Mario Marinelli, Mehmet Ali SilguDocument13 pagesTransportation Research Part C: Mauro Dell'Orco, Mario Marinelli, Mehmet Ali SilguJulio CésarNo ratings yet
- AFSD ReviewDocument14 pagesAFSD ReviewKinesys TechsolutionsNo ratings yet
- CSP 520N 1BDocument18 pagesCSP 520N 1BfredtornayNo ratings yet
- Linux OSDocument10 pagesLinux OSAhamed ShahasNo ratings yet
- UENR2631-01 CDocument15 pagesUENR2631-01 CShanmuga PrakashNo ratings yet
- Schema IBM R60Document92 pagesSchema IBM R60Eva Beti PetreNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Set 3Document6 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Set 3MUSKAN PRNNo ratings yet
- Weekly RM Call Log During COVID Roster-2021: BranchDocument2 pagesWeekly RM Call Log During COVID Roster-2021: Brancharzu tabassumNo ratings yet
- MMM Friocell 22p - enDocument2 pagesMMM Friocell 22p - enmaawsNo ratings yet
- Freezer 50 TR Online Manual: Arcc - deDocument1 pageFreezer 50 TR Online Manual: Arcc - deMiraziz AliyevNo ratings yet
- BJ2 Ch7Document4 pagesBJ2 Ch7Shivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Agilent X-Series Signal Analyzer: N9030A PXA Specifications GuideDocument402 pagesAgilent X-Series Signal Analyzer: N9030A PXA Specifications GuideMichelle Ysa ValeraNo ratings yet
- MainBridge - Design ReportDocument18 pagesMainBridge - Design ReportWan100% (1)
- 2018 Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic Actuators With Muscle-Like PerformanceDocument6 pages2018 Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic Actuators With Muscle-Like PerformanceJack LeeNo ratings yet
- Form Pengukuran GroundingDocument2 pagesForm Pengukuran GroundingghooestiepNo ratings yet
- Gymnasium DesignDocument3 pagesGymnasium DesignjimmyboyjrNo ratings yet
- Strength Requirement: (1) - Pile Shear CapacityDocument4 pagesStrength Requirement: (1) - Pile Shear CapacityAlma M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual For Spin CoaterDocument3 pagesOperating Manual For Spin CoaterKhursheed Ahmed CheshttiNo ratings yet
- Autocom FAQ - Доработка IVECO 30pinDocument3 pagesAutocom FAQ - Доработка IVECO 30pinAvs Electron100% (1)
- Venturi Medium Sized (VMS) : ApplicationDocument8 pagesVenturi Medium Sized (VMS) : ApplicationChn TutkunNo ratings yet
- Mysql WorkshopDocument197 pagesMysql WorkshopNaser NaseerNo ratings yet
- DatabasesDocument20 pagesDatabaseslokenders801No ratings yet
- Introduction To Multisim 12Document11 pagesIntroduction To Multisim 12Madhuri RoyNo ratings yet
- Aws D1.3-D1.3M 2018Document6 pagesAws D1.3-D1.3M 2018Lee Chong EeNo ratings yet
- PRELIMINARY (CMP) - Comprehensive Master Planning Report / ChecklistDocument7 pagesPRELIMINARY (CMP) - Comprehensive Master Planning Report / ChecklistNikki CalumaNo ratings yet
- Filtro Fino - Rsl0287 - Cut - FboDocument2 pagesFiltro Fino - Rsl0287 - Cut - Fbotomeu_vanrell100% (1)
- Quotation 132kv CT PT 33kv PTDocument5 pagesQuotation 132kv CT PT 33kv PTSharafat AliNo ratings yet
- C13TE3ADocument2 pagesC13TE3AAhmed Sherif CupoNo ratings yet
- Speed Modeling of DC Motorcusing Tacho GeneratorDocument7 pagesSpeed Modeling of DC Motorcusing Tacho GeneratorAbanoub Malak SelemNo ratings yet
- THIELE Lashing ProductsDocument28 pagesTHIELE Lashing ProductsNixNo ratings yet