Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsPhysics
Physics
Uploaded by
Shankar Rao Asipiiitjee syllabus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Sambungan Chapter 2.2Document57 pagesSambungan Chapter 2.2iffahNo ratings yet
- Kim Evelyn - Viscosity of Dextrose SolutionsDocument6 pagesKim Evelyn - Viscosity of Dextrose SolutionsMatteo AgenoNo ratings yet
- Blame Game Erupts in UP Over RiotsDocument2 pagesBlame Game Erupts in UP Over RiotsShankar Rao AsipiNo ratings yet
- 2019 08 24 15 36 22 554 - 1566641182554 - XXXPR5688X - Itrv PDFDocument1 page2019 08 24 15 36 22 554 - 1566641182554 - XXXPR5688X - Itrv PDFShankar Rao AsipiNo ratings yet
- 8 IIT JEE Books Every Aspirant Should Have: Get Free AppDocument14 pages8 IIT JEE Books Every Aspirant Should Have: Get Free AppShankar Rao AsipiNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge Current GKDocument114 pagesGeneral Knowledge Current GKShankar Rao Asipi100% (2)
- SongDocument3 pagesSongShankar Rao AsipiNo ratings yet
- SOF Level 2 IMO Class 3Document5 pagesSOF Level 2 IMO Class 3Shankar Rao Asipi73% (11)
- Gas Dynamics Book (Dr. El-Sayed M. Marzouk)Document173 pagesGas Dynamics Book (Dr. El-Sayed M. Marzouk)Karim SalesNo ratings yet
- CRC Advanced Classical Mechanics B071HLBNQDDocument272 pagesCRC Advanced Classical Mechanics B071HLBNQDAndrew HucekNo ratings yet
- Pretest and PosttestDocument7 pagesPretest and PosttestKeiNo ratings yet
- Eng1001 Vectors ExamplesDocument2 pagesEng1001 Vectors ExamplesAhza JufriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Tacoma Narrows BridgeDocument18 pagesChapter 7 Tacoma Narrows BridgeFernando SmithNo ratings yet
- Time PeriodDocument40 pagesTime PeriodRabi Dhakal100% (1)
- Machine Design Tutorials - Week 10Document51 pagesMachine Design Tutorials - Week 10Yunsu LeeNo ratings yet
- 6.23 Equation of State Prediction of Carbon Dioxide PropertiesDocument70 pages6.23 Equation of State Prediction of Carbon Dioxide Propertiessaulatlone100% (1)
- Scalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andDocument10 pagesScalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andFazlina MustafaNo ratings yet
- Cut and CoverDocument8 pagesCut and CoverAkshay DuggalNo ratings yet
- 2016 ENGSTRU Castellaro Et Al PDFDocument13 pages2016 ENGSTRU Castellaro Et Al PDFsaurabh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Fluids - Lecture 12 Notes: Stream FunctionDocument4 pagesFluids - Lecture 12 Notes: Stream Functionnellai kumarNo ratings yet
- Albert Einstein (: GermanDocument2 pagesAlbert Einstein (: GermanBrian Hesús Ambrocio MirandaNo ratings yet
- Shear StudsDocument4 pagesShear StudsmaricusiaNo ratings yet
- Space and TimeDocument36 pagesSpace and TimeravindraNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology RourkelaDocument2 pagesNational Institute of Technology RourkelaMrinalPattnaikNo ratings yet
- 18 - Timoshenko-Beam-Based Response of Existing Tunnel To Single TunnelingDocument18 pages18 - Timoshenko-Beam-Based Response of Existing Tunnel To Single TunnelingIsabella DuarteNo ratings yet
- Basics of Turbomachinery BalanceDocument14 pagesBasics of Turbomachinery BalanceSuthan RNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - Plastic Deformation (1) - VDocument14 pagesTutorial 5 - Plastic Deformation (1) - Vwoongs73No ratings yet
- Interview Questions For Structural EngineersDocument8 pagesInterview Questions For Structural EngineersPml PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mech103 Tut ch14Document16 pagesMech103 Tut ch14wallidhgsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41jad obaidNo ratings yet
- Op-029. Interpretation of Ciu Test: Work Instructions For EngineersDocument7 pagesOp-029. Interpretation of Ciu Test: Work Instructions For EngineersNadeem AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Kinematics of A ParticleDocument75 pagesChapter 12 Kinematics of A ParticleMuhammad Ahmad Khan LodhiNo ratings yet
- EXP-MN-SI120-EN-R0 - Metering PDFDocument263 pagesEXP-MN-SI120-EN-R0 - Metering PDFبوطالب خالد براهمي100% (1)
- Assignment 5 Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment 5 Solutions PDFMuhammad IdrisNo ratings yet
- Tips On Playing Tumbang Preso: Physical ActivityDocument2 pagesTips On Playing Tumbang Preso: Physical Activityalliah valenciaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Fourth Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesScience 9 Fourth Quarter ExamEncluna Lindon JayNo ratings yet
Physics
Physics
Uploaded by
Shankar Rao Asipi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesiitjee syllabus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentiitjee syllabus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesPhysics
Physics
Uploaded by
Shankar Rao Asipiiitjee syllabus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
PHYSICS
Units and dimensions, dimensional analysis; least count, significant figures;
Methods of measurement and error analysis for physical quantities pertaining
to the following experiments: Experiments based on using Verniercalipers
and screw gauge (micrometer), Determination of g using simple pendulum,
Youngs modulus by Searles method, Specific heat of a liquid using
calorimeter, focal length of a concave mirror and a convex lens using u-v
method, Speed of sound using resonance column, Verification of Ohms law
using voltmeter and ammeter, and specific resistance of the material of a
wire using meter bridge and post office box.
MECHANICS
Kinematics in one and two dimensions (Cartesian coordinates only),
projectiles; Uniform Circular motion; Relative velocity.
Newtons laws of motion; Inertial and uniformly accelerated frames of
reference; Static and dynamic friction; Kinetic and potential energy; Work
and power; Conservation of linear momentum and mechanical energy.
Systems of particles; Centre of mass and its motion; Impulse; Elastic and
inelastic collisions.
Law of gravitation; Gravitational potential and field; Acceleration due to
gravity; Motion of planets and satellites in circular orbits; Escape velocity.
Rigid body, moment of inertia, parallel and perpendicular axes theorems,
moment of inertia of uniform bodies with simple geometrical shapes; Angular
momentum; Torque; Conservation of angular momentum; Dynamics of rigid
bodies with fixed axis of rotation; Rolling without slipping of rings, cylinders
and spheres; Equilibrium of rigid bodies; Collision of point masses with rigid
bodies.
Linear and angular simple harmonic motions.
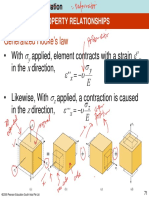
Hookes law, Youngs modulus.
Pressure in a fluid; Pascals law; Buoyancy; Surface energy and surface
tension, capillary rise; Viscosity (Poiseuilles equation excluded), Stokes law;
Terminal velocity, Streamline flow, equation of continuity, Bernoullis
theorem and its applications.
Wave motion (plane waves only), longitudinal and transverse waves,
superposition of waves; Progressive and stationary waves; Vibration of
strings and air columns; Resonance; Beats; Speed of sound in gases;
Doppler effect (in sound).
THERMAL
Thermal expansion of solids, liquids and gases; Calorimetry, latent heat;
Heat conduction in one dimension; Elementary concepts of convection and
radiation; Newtons law of cooling; Ideal gas laws; Specific heats (Cv and Cp
for monoatomic and diatomic gases); Isothermal and adiabatic processes,
bulk modulus of gases; Equivalence of heat and work; First law of
thermodynamics and its applications (only for ideal gases); Blackbody
radiation: absorptive and emissive powers; Kirchhoffs law; Wiens
displacement law, Stefans law.
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
Coulombs law; Electric field and potential; Electrical potential energy of a
system of point charges and of electrical dipoles in a uniform electrostatic
field; Electric field lines; Flux of electric field; Gausss law and its application
in simple cases, such as, to find field due to infinitely long straight wire,
uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical
shell.
Capacitance; Parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectrics; Capacitors
in series and parallel; Energy stored in a capacitor.
Electric current; Ohms law; Series and parallel arrangements of resistances
and cells; Kirchhoffs laws and simple applications; Heating effect of current.
BiotSavarts law and Amperes law; Magnetic field near a current-carrying
straight wire, along the axis of a circular coil and inside a long straight
solenoid; Force on a moving charge and on a current-carrying wire in a
uniform magnetic field.
Magnetic moment of a current loop; Effect of a uniform magnetic field on a
current loop; Moving coil galvanometer, voltmeter, ammeter and their
conversions.
Electromagnetic induction: Faradays law, Lenzs law; Self and mutual
inductance; RC, LR and LC circuits with d.c. and a.c. sources.
OPTICS
Rectilinear propagation of light; Reflection and refraction at plane and
spherical surfaces; Total internal reflection; Deviation and dispersion of light
by a prism; Thin lenses; Combinations of mirrors and thin lenses;
Magnification.
Wave nature of light: Huygens principle, interference limited to Youngs
double-slit experiment.
MODERN PHYSICS
Atomic nucleus; , and radiations; Law of radioactive decay; Decay
constant; Half-life and mean life; Binding energy and its calculation; Fission
and fusion processes; Energy calculation in these processes.
Photoelectric effect; Bohrs theory of hydrogen-like atoms; Characteristic and
continuous X-rays, Moseleys law; de Broglie wavelength of matter waves
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Sambungan Chapter 2.2Document57 pagesSambungan Chapter 2.2iffahNo ratings yet
- Kim Evelyn - Viscosity of Dextrose SolutionsDocument6 pagesKim Evelyn - Viscosity of Dextrose SolutionsMatteo AgenoNo ratings yet
- Blame Game Erupts in UP Over RiotsDocument2 pagesBlame Game Erupts in UP Over RiotsShankar Rao AsipiNo ratings yet
- 2019 08 24 15 36 22 554 - 1566641182554 - XXXPR5688X - Itrv PDFDocument1 page2019 08 24 15 36 22 554 - 1566641182554 - XXXPR5688X - Itrv PDFShankar Rao AsipiNo ratings yet
- 8 IIT JEE Books Every Aspirant Should Have: Get Free AppDocument14 pages8 IIT JEE Books Every Aspirant Should Have: Get Free AppShankar Rao AsipiNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge Current GKDocument114 pagesGeneral Knowledge Current GKShankar Rao Asipi100% (2)
- SongDocument3 pagesSongShankar Rao AsipiNo ratings yet
- SOF Level 2 IMO Class 3Document5 pagesSOF Level 2 IMO Class 3Shankar Rao Asipi73% (11)
- Gas Dynamics Book (Dr. El-Sayed M. Marzouk)Document173 pagesGas Dynamics Book (Dr. El-Sayed M. Marzouk)Karim SalesNo ratings yet
- CRC Advanced Classical Mechanics B071HLBNQDDocument272 pagesCRC Advanced Classical Mechanics B071HLBNQDAndrew HucekNo ratings yet
- Pretest and PosttestDocument7 pagesPretest and PosttestKeiNo ratings yet
- Eng1001 Vectors ExamplesDocument2 pagesEng1001 Vectors ExamplesAhza JufriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Tacoma Narrows BridgeDocument18 pagesChapter 7 Tacoma Narrows BridgeFernando SmithNo ratings yet
- Time PeriodDocument40 pagesTime PeriodRabi Dhakal100% (1)
- Machine Design Tutorials - Week 10Document51 pagesMachine Design Tutorials - Week 10Yunsu LeeNo ratings yet
- 6.23 Equation of State Prediction of Carbon Dioxide PropertiesDocument70 pages6.23 Equation of State Prediction of Carbon Dioxide Propertiessaulatlone100% (1)
- Scalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andDocument10 pagesScalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andFazlina MustafaNo ratings yet
- Cut and CoverDocument8 pagesCut and CoverAkshay DuggalNo ratings yet
- 2016 ENGSTRU Castellaro Et Al PDFDocument13 pages2016 ENGSTRU Castellaro Et Al PDFsaurabh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Fluids - Lecture 12 Notes: Stream FunctionDocument4 pagesFluids - Lecture 12 Notes: Stream Functionnellai kumarNo ratings yet
- Albert Einstein (: GermanDocument2 pagesAlbert Einstein (: GermanBrian Hesús Ambrocio MirandaNo ratings yet
- Shear StudsDocument4 pagesShear StudsmaricusiaNo ratings yet
- Space and TimeDocument36 pagesSpace and TimeravindraNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology RourkelaDocument2 pagesNational Institute of Technology RourkelaMrinalPattnaikNo ratings yet
- 18 - Timoshenko-Beam-Based Response of Existing Tunnel To Single TunnelingDocument18 pages18 - Timoshenko-Beam-Based Response of Existing Tunnel To Single TunnelingIsabella DuarteNo ratings yet
- Basics of Turbomachinery BalanceDocument14 pagesBasics of Turbomachinery BalanceSuthan RNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - Plastic Deformation (1) - VDocument14 pagesTutorial 5 - Plastic Deformation (1) - Vwoongs73No ratings yet
- Interview Questions For Structural EngineersDocument8 pagesInterview Questions For Structural EngineersPml PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mech103 Tut ch14Document16 pagesMech103 Tut ch14wallidhgsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41jad obaidNo ratings yet
- Op-029. Interpretation of Ciu Test: Work Instructions For EngineersDocument7 pagesOp-029. Interpretation of Ciu Test: Work Instructions For EngineersNadeem AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Kinematics of A ParticleDocument75 pagesChapter 12 Kinematics of A ParticleMuhammad Ahmad Khan LodhiNo ratings yet
- EXP-MN-SI120-EN-R0 - Metering PDFDocument263 pagesEXP-MN-SI120-EN-R0 - Metering PDFبوطالب خالد براهمي100% (1)
- Assignment 5 Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment 5 Solutions PDFMuhammad IdrisNo ratings yet
- Tips On Playing Tumbang Preso: Physical ActivityDocument2 pagesTips On Playing Tumbang Preso: Physical Activityalliah valenciaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Fourth Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesScience 9 Fourth Quarter ExamEncluna Lindon JayNo ratings yet