Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment Number: 04 Name of The Experiment
Experiment Number: 04 Name of The Experiment
Uploaded by
Towfiq Hossain Tasku0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesThis experiment involved standardizing an unknown concentration of sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3) solution using a standard potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) solution through titration. The reaction between K2Cr2O7 and iodide produces iodine, which is then reduced by Na2S2O3 in the presence of starch indicator. By calculating the volume of Na2S2O3 needed to reach the endpoint using the known concentration of K2Cr2O7, the concentration of Na2S2O3 was found to be 0.097 N with 1% error, possibly due to difficulty determining the endpoint visually.
Original Description:
Chemistry lab report
Original Title
Chemistry 04
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis experiment involved standardizing an unknown concentration of sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3) solution using a standard potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) solution through titration. The reaction between K2Cr2O7 and iodide produces iodine, which is then reduced by Na2S2O3 in the presence of starch indicator. By calculating the volume of Na2S2O3 needed to reach the endpoint using the known concentration of K2Cr2O7, the concentration of Na2S2O3 was found to be 0.097 N with 1% error, possibly due to difficulty determining the endpoint visually.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesExperiment Number: 04 Name of The Experiment
Experiment Number: 04 Name of The Experiment
Uploaded by
Towfiq Hossain TaskuThis experiment involved standardizing an unknown concentration of sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3) solution using a standard potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) solution through titration. The reaction between K2Cr2O7 and iodide produces iodine, which is then reduced by Na2S2O3 in the presence of starch indicator. By calculating the volume of Na2S2O3 needed to reach the endpoint using the known concentration of K2Cr2O7, the concentration of Na2S2O3 was found to be 0.097 N with 1% error, possibly due to difficulty determining the endpoint visually.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Experiment Number: 04
Name of the experiment:
Standardization of Sodium Thiosulphate solution with
standard Potassium Dichromate solution.
Course: Chem-114
Name: Atanu Kumar Saha
Roll: 0706125
Group: c1
Partners Roll:0706124
Department: E.E.E.
Date of Performance: 16-08-2008
Date of Submission: 23-08-2008
Objective:The objective of this experiment is to determine the strength of Sodium
Thiosulphate (Na2S2O3) with a standard Potassium Dichromate (K2Cr2O7)
solution. This experiment is based on oxidation and reduction reaction, as well as
iodometry. Sodium Thiosulphate has very important and huge industrial usage.
It is widely used in the photographic processing and to remove excess chlorine in
the bleaching industry. This examination is very useful to find out the percentage
of purity of Sodium Thiosulphate.
Theory:Standardization is the process by which the strength of a solution is
determined with the help of a standard solution. A solution of known
concentration is called a standard solution. This experiment is done by means of
titration. In presence of a suitable indicator, a chemical substance that detects the
end point of reaction by changing its color, the volumetric analysis in which a
standard solution is added in another solution (whose strength is unknown) to
reach its end point to determine the strength of that solution is called titration.
Titration involving iodine or dealing with liberated iodine in chemical
reaction is called iodometry and iodometry respectively. This reaction is
iodometry because iodine is obtained from KI.
The reactions of this experiment are:
6KI+14HCl+ K2Cr2O7 =2CrCl3+3I2 +7H2O+8KCl
(6 I- + 14 H+ + Cr2O7-2 + 6e- = 2 Cr+3 + 3 I2+ 7 H2O)
2Na2S2O3 + I2 = Na2S4O6 + 2NaI
(S2O3 2- + e- = S4O6 2- + I-)
Here K2Cr2O7 is an oxidizing agent and I- is a reducing agent. Again in the
second reaction I2 is an oxidizing agent and S2O3-- is a reducing agent.
In the 2nd Step of the reaction a specific indicator is used that is Starchwhich has a significant effect on iodine.
Starch+I2=Starch-Iodine (blue color)
Starch-Iodine+6S2O3--=Starch +6I- + 3S4 O6
If to a solution containing a little iodine, some starch solution is added and
Na2S2O3 is run in from the burette, the blue color of the starch-iodine complex
will disappear from the solution as soon as all the iodine has been reduced to
iodide ion.
Apparatus:1. Conical flask,
2. Burette ,
4. Volumetric flask , 5. Stand,
3. Pipette ,
6. Funnel
Chemicals:-
1. Na2S2O3 , 2. K2Cr2O7 , 3. KI , 4. NaHCO3
5. HCl (Concentrated) , 6. Starch (Indicator)
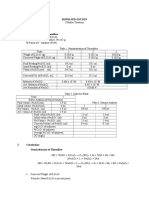
Data:-
Standardization of Na2S2O3 solution with standard K2Cr2O7 solution
No. of
obs.
1.
2.
3.
Volume
of
K2Cr2O7
(ml)
10
10
10
Burette reading
Initial
(ml)
Final
(ml)
0
10.3
20.7
10.3
20.7
31.1
Volume of
Na2S2O3
Calculation:We know, Vred X Sred = Vox X Sox
Here,
VK2Cr2O7 = 10 ml ,
VNa2S2O4 = 10.4 ml
SK2Cr2O7 = 0.1 N
SNa2S2O4 =?
SNa2S2O4 = (10 X 0.1)/10.4
=0.097 N
Result:-
Determined strength of Na2S2O3 solution is = 0.097 N
(ml)
10.3
10.4
10.4
Average
(Volume of
Na2S2O3)
(ml)
10.4
Error Analysis:-
Percentage of error = (known value ~observed value) X 100 known value
= (0.098 0.097) X 100 / 0.098
= 1%
Discussion:-
As the color change of the titration of Na2S2O3 with K2Cr2O7 is very
confusing, the end point of the titration may not have been properly
determined. This may be the cause of error.
You might also like
- AWS D17.1 D17.1M 2017 - Fusion WeldingDocument111 pagesAWS D17.1 D17.1M 2017 - Fusion Weldingbenkendimbizzat56No ratings yet
- Laboratory Report: Universiti Teknologi MaraDocument6 pagesLaboratory Report: Universiti Teknologi MaraYulNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation For ScaffoldingDocument12 pagesDesign Calculation For Scaffoldinganwar50% (2)
- Experiment 5 - Oxidation-Reduction Titration IodimetryDocument3 pagesExperiment 5 - Oxidation-Reduction Titration IodimetryAlma Pabilane75% (12)
- Clock RX N KineticsDocument7 pagesClock RX N KineticsYutrat Ratyut0% (2)
- Synthesis of Lidocaine 2Document12 pagesSynthesis of Lidocaine 2Johan Ahlström100% (2)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionFrom EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction To Chemical Synthesis Processes Analysis Solutions Chapter05Document95 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Synthesis Processes Analysis Solutions Chapter05lastlandingNo ratings yet
- Sessional-4 Sodium Thiosulphate and Potassium DicromateDocument4 pagesSessional-4 Sodium Thiosulphate and Potassium DicromateAftab S. MirzaNo ratings yet
- Chem 04Document4 pagesChem 04Farhatul Abrar AnandaNo ratings yet
- Dissolved OxygenDocument4 pagesDissolved OxygenMohd Zafar100% (1)
- Engineering Chemistry Lab ManualDocument57 pagesEngineering Chemistry Lab ManualRemusNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Analysis: UNIT IV Oxidation & ReductionDocument19 pagesPharmaceutical Analysis: UNIT IV Oxidation & ReductionRahul SawarkarNo ratings yet
- Reduction-Oxidation Titration 2Document21 pagesReduction-Oxidation Titration 2Caitlene Lee Uy0% (1)
- Lab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetDocument5 pagesLab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetMd Afif AbrarNo ratings yet
- Yodimetria, Yodometria Yodatometria - 2014-IIDocument47 pagesYodimetria, Yodometria Yodatometria - 2014-IIGabby Novillo PillacaNo ratings yet
- E-Manual, Engg - ChemistryDocument28 pagesE-Manual, Engg - ChemistryTanvi BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- 2013 H2 Redox Titration (Iodometric Titration) Teachers'Document4 pages2013 H2 Redox Titration (Iodometric Titration) Teachers'csanjeevanNo ratings yet
- Exp 6Document6 pagesExp 6MsShu93100% (1)
- Unit 1 Cape Chemistry Lab Manual2013 14Document18 pagesUnit 1 Cape Chemistry Lab Manual2013 14Nick MillerNo ratings yet
- IodometriDocument13 pagesIodometriNinik SunardiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document6 pagesExperiment 4232449045No ratings yet
- 3 Dissolved OxygenDocument12 pages3 Dissolved OxygenatharvaNo ratings yet
- Let'S Begin!: Course OverviewDocument20 pagesLet'S Begin!: Course OverviewNur-aine HajijulNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Final 1Document18 pagesOrganic Chemistry Final 1Tenny AbioyeNo ratings yet
- Winkler TitrationDocument6 pagesWinkler TitrationMarivic BarandaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report SolubilityDocument5 pagesLaboratory Report SolubilityIndraNo ratings yet
- Sessional-5 Estimation of Copper by Iodometric MethodDocument5 pagesSessional-5 Estimation of Copper by Iodometric Methodsakib1994100% (1)
- Exp 3 (Prep - of Na2S2O3.5H2O) & 4 (Excercise)Document12 pagesExp 3 (Prep - of Na2S2O3.5H2O) & 4 (Excercise)photocopy photocopyNo ratings yet
- Name: Mahmood Knaan EX - No:08 Ex. Name: Volumetric Analysis (II) : Redox Titration Analysis of Bleach. Date:2008.4.14Document6 pagesName: Mahmood Knaan EX - No:08 Ex. Name: Volumetric Analysis (II) : Redox Titration Analysis of Bleach. Date:2008.4.14شركة العاصمة لخدمات التنظيفNo ratings yet
- Lab1 3Document5 pagesLab1 3Izzat Arif33% (3)
- Experiment No. 4: Standardization of Sodium Thiosulphate Solution With A Standard Potassium Dichromate SolutionDocument20 pagesExperiment No. 4: Standardization of Sodium Thiosulphate Solution With A Standard Potassium Dichromate Solutionshiam50% (2)
- Iodometry and IodimetryDocument3 pagesIodometry and Iodimetrysungupta5763% (8)
- Experiment 7 - Determination of Bleaching Power by IodimetryDocument5 pagesExperiment 7 - Determination of Bleaching Power by Iodimetryeldeee143100% (5)
- (Saurov Karati) Chem-236Document78 pages(Saurov Karati) Chem-236Shadab DipNo ratings yet
- Chem 27.1 Experiment 5 Oxidation Reduction Titration IodimetryDocument3 pagesChem 27.1 Experiment 5 Oxidation Reduction Titration IodimetryNathaniel John JumalonNo ratings yet
- Reboquio - experiment4.OxidationReductionReactions M7 C1Document9 pagesReboquio - experiment4.OxidationReductionReactions M7 C1Denampo Ivan MikhaelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Oxidation-Reduction Titration Determination of Bleaching Power by IodometryDocument3 pagesExperiment 7 Oxidation-Reduction Titration Determination of Bleaching Power by IodometryJobel De PedroNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Lab 3Document8 pagesInorganic Chemistry Lab 3LinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- Iodometric TitrationDocument30 pagesIodometric TitrationCapsanneNo ratings yet
- The Analysis of Groupi Cations (Ag, HG, PB)Document11 pagesThe Analysis of Groupi Cations (Ag, HG, PB)Hussein ShakirNo ratings yet
- Iodometry: Iodometry, Known As Iodometric Titration, Is A Method ofDocument4 pagesIodometry: Iodometry, Known As Iodometric Titration, Is A Method oftaysi tafriNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Redox Analysis of BleachDocument9 pagesExperiment 8 Redox Analysis of BleachUzo Paul NwabuisiNo ratings yet
- Chem 3BDocument3 pagesChem 3BWahid Salauddin DiptaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Basic Water Properties 1 Group Class: EH2202ADocument23 pagesExperiment 4: Basic Water Properties 1 Group Class: EH2202AAnonymous dJYic9XNo ratings yet
- Exp 6 - Copper EstimationDocument45 pagesExp 6 - Copper Estimationabiranjum035No ratings yet
- Revision:Edexcel Chemistry Unit 3B - Laboratory Techniques - Group 1 and 2 ReactionsDocument4 pagesRevision:Edexcel Chemistry Unit 3B - Laboratory Techniques - Group 1 and 2 ReactionsAhmed ViaamNo ratings yet
- CHM 131 Exp 4Document7 pagesCHM 131 Exp 4Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Iodometry (1) - Read-OnlyDocument9 pagesIodometry (1) - Read-Onlyananyapandey6582No ratings yet
- Estimation of Cu (II) Using Sodium Thiosulphate Solution (Iodometrically)Document11 pagesEstimation of Cu (II) Using Sodium Thiosulphate Solution (Iodometrically)Gayatri Govind NairNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Analyte, Sodium Thiosulfate, Starch TS, Potassium Iodate, Mohr Buret, Reduction-Oxidation Reaction, Titration, Iodimetry, IodometryDocument1 pageKeywords: Analyte, Sodium Thiosulfate, Starch TS, Potassium Iodate, Mohr Buret, Reduction-Oxidation Reaction, Titration, Iodimetry, IodometryAlfie Benedict EspedidoNo ratings yet
- Exp No-5Document15 pagesExp No-5shiamNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction TitrationDocument5 pagesOxidation Reduction TitrationElena LlasosNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 3B Notes 6CH07Document14 pagesChemistry Unit 3B Notes 6CH07RG_penNo ratings yet
- Iodometry TitrationDocument15 pagesIodometry TitrationNur Halimah75% (4)
- Iodometry CapistranoFuentesDocument11 pagesIodometry CapistranoFuentesJordanNo ratings yet
- LR5 Group4Document5 pagesLR5 Group4Ramil Joshua TrabadoNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Cu & ZNDocument7 pagesEstimation of Cu & ZNjhfgh100% (2)
- Practical Manual of Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandPractical Manual of Analytical ChemistryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Sol-Gel Handbook, 3 Volume Set: Synthesis, Characterization, and ApplicationsFrom EverandThe Sol-Gel Handbook, 3 Volume Set: Synthesis, Characterization, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Iridium(III) in Optoelectronic and Photonics ApplicationsFrom EverandIridium(III) in Optoelectronic and Photonics ApplicationsEli Zysman-ColmanNo ratings yet
- Water AnalysisDocument19 pagesWater AnalysisTowfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 Chem 1 .Document4 pagesExpt 1 Chem 1 .Towfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument2 pagesBangladesh University of Engineering and TechnologyTowfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- References/Bibliography Harvard Style: What Is Referencing?Document9 pagesReferences/Bibliography Harvard Style: What Is Referencing?Towfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 Chem 1 .Document4 pagesExpt 1 Chem 1 .Towfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Oil AnalysisDocument11 pagesOil AnalysisTowfiq Hossain Tasku100% (1)
- Bangladesh University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument1 pageBangladesh University of Engineering and TechnologyTowfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ferrous Ion in A Solution by Standard Potassium Permanganate (Kmno) SolutionDocument3 pagesDetermination of Ferrous Ion in A Solution by Standard Potassium Permanganate (Kmno) SolutionTowfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Che 400 - Thesis ProjectDocument15 pagesObjectives:: Che 400 - Thesis ProjectTowfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number06Document5 pagesExperiment Number06Towfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ferrous Ion in A Solution by Standard Potassium Permanganate (Kmno) SolutionDocument3 pagesDetermination of Ferrous Ion in A Solution by Standard Potassium Permanganate (Kmno) SolutionTowfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 02Document6 pagesChemistry 02Towfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- My Chem 08Document3 pagesMy Chem 08Towfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Specifition-Sheet For Evaporator 1. Customer Details A. B. C. D. E. 2. Data Required For EvaporatorDocument2 pagesSpecifition-Sheet For Evaporator 1. Customer Details A. B. C. D. E. 2. Data Required For EvaporatorTowfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- The Walk Passive Solar Food DryerDocument2 pagesThe Walk Passive Solar Food DryerTowfiq Hossain TaskuNo ratings yet
- Cement Plant Design-1Document14 pagesCement Plant Design-1Towfiq Hossain Tasku100% (2)
- Combined PDF TensionBushesDocument6 pagesCombined PDF TensionBusheslogan95No ratings yet
- Information About The Fire TriangleDocument5 pagesInformation About The Fire TriangleJey RhyNo ratings yet
- Soil Nailing AbridgeDocument10 pagesSoil Nailing AbridgeMarcelo QuisbertNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials (SOM) : at Internal AssessmentDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials (SOM) : at Internal AssessmentAli Jarrar JafriNo ratings yet
- iNORGANIC Salt AnalysisDocument12 pagesiNORGANIC Salt AnalysisNishant KaushikNo ratings yet
- Tubería AWWA C900Document3 pagesTubería AWWA C900ErickNo ratings yet
- E 1300 - 02 - Rtezmdatmdi - PDFDocument58 pagesE 1300 - 02 - Rtezmdatmdi - PDFMauricio Antonio SalgadoNo ratings yet
- CHW Pipe Support SampleDocument19 pagesCHW Pipe Support SamplesyedmuzafferNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rate PMGSY Bridge-2021Document344 pagesAnalysis of Rate PMGSY Bridge-2021Abhishek Choudhary100% (1)
- Thermo1 Chapter 04Document110 pagesThermo1 Chapter 04Yasser Hijji80% (15)
- Mini Project Report: Infrared HeadphoneDocument25 pagesMini Project Report: Infrared HeadphoneMadhu SekharNo ratings yet
- S-000-53A0-001 - 5 Surface Preparation Painting Lettering O-611Document43 pagesS-000-53A0-001 - 5 Surface Preparation Painting Lettering O-611Midhun K ChandraboseNo ratings yet
- 5500 Dynamics Colorwave Accent Rings Core ConceptDocument8 pages5500 Dynamics Colorwave Accent Rings Core Conceptlandworth2450No ratings yet
- Sound TransmissionDocument2 pagesSound TransmissionKristoffer Jose AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- DPP-13 (Coordination Compound) PDFDocument3 pagesDPP-13 (Coordination Compound) PDFAvishek BiswasNo ratings yet
- The Practicing Engineer's Guide To Designing by Strut and Tie Modeling (ACI 318-14)Document6 pagesThe Practicing Engineer's Guide To Designing by Strut and Tie Modeling (ACI 318-14)jabh311No ratings yet
- Ductility of BitumenDocument4 pagesDuctility of BitumenArpita MulikNo ratings yet
- For Proof Only: Bored and Driven Pile Testing in Bangkok Sub-SoilsDocument8 pagesFor Proof Only: Bored and Driven Pile Testing in Bangkok Sub-SoilsakanagesNo ratings yet
- FeltDocument8 pagesFeltadhityaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Chapter 3 - Mechanical, Electrical and Thermal PropertiesDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 Chapter 3 - Mechanical, Electrical and Thermal PropertiesHafizatul AqmarNo ratings yet
- Dura. Grout: Non-Shrink Cementitious GroutDocument2 pagesDura. Grout: Non-Shrink Cementitious GroutANILNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Practicals (Qualitative Analysis)Document5 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Practicals (Qualitative Analysis)Ravibabu BoddaNo ratings yet
- PGE 361, HW 5, Ideal Answer, 1442Document6 pagesPGE 361, HW 5, Ideal Answer, 1442urmomNo ratings yet
- Group 16Document12 pagesGroup 16api-460406046No ratings yet
- ScreensDocument10 pagesScreensCloud WtafNo ratings yet
- VERNO Products For DLS ApprovalDocument5 pagesVERNO Products For DLS ApprovalsumonislambdNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Euee 2011/2019 Answer Sponserd by Qubee AcademyDocument15 pagesChemistry Euee 2011/2019 Answer Sponserd by Qubee AcademyIsmael NuredinNo ratings yet