Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ex 4 Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity
Ex 4 Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity
Uploaded by
Rochel CaduyacCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Emg Lab ReportDocument12 pagesEmg Lab ReportKelly Mason Walker60% (5)
- Biofuels Formal Lab Report RevisedDocument9 pagesBiofuels Formal Lab Report RevisedVeronica ChangNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Action Testing Catalase Activity Lab ReportDocument4 pagesEnzyme Action Testing Catalase Activity Lab ReportAnthony100% (3)
- NMR Kinetics: Study of A Reversible Hydrolysis ReactionDocument8 pagesNMR Kinetics: Study of A Reversible Hydrolysis ReactionOldbooklover100% (2)
- Statistics Data ProjectDocument16 pagesStatistics Data Projectapi-250861401No ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab Report FinalDocument6 pagesEnzyme Lab Report Finalrsenser2100% (2)
- Determination of Enzymatic Activity of Salivary Amylase Depending On The Effect of Temperature and PHDocument11 pagesDetermination of Enzymatic Activity of Salivary Amylase Depending On The Effect of Temperature and PHAmberValentineNo ratings yet
- Kinetics LabDocument12 pagesKinetics LabJesseNo ratings yet
- Effect of Substrate Concentration on α -AmylaseDocument26 pagesEffect of Substrate Concentration on α -Amylasepriyaa100% (5)
- CHEM 160 Formal Lab Report IDocument10 pagesCHEM 160 Formal Lab Report IDatoya BrownNo ratings yet
- Biology Enzyme Lab ReportDocument2 pagesBiology Enzyme Lab Reportapi-273494632No ratings yet
- CIROS Production Handout - ENDocument121 pagesCIROS Production Handout - ENĐặng Xuân Hồng100% (1)
- Henry Tam - MGI CaseDocument3 pagesHenry Tam - MGI CasejayjNo ratings yet
- CCP v2.1Document52 pagesCCP v2.1bhuwan_vijayNo ratings yet
- Catalase Enzyme Lab RevisedDocument4 pagesCatalase Enzyme Lab RevisedIda FaridaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Core PracticalDocument7 pagesEnzyme Core PracticalJackHowley123No ratings yet
- Effect ofDocument8 pagesEffect ofAriadna Zatyuri Zuñiga LlanosNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Substrate Concentration PracDocument4 pagesThe Effect of Substrate Concentration PracjimslibraryNo ratings yet
- Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity Lab 3Document8 pagesEffect of PH On Enzyme Activity Lab 3api-340907023No ratings yet
- How Do Different PH Values Affect The Enzyme Catalase's Activity in The Decomposition of Hydrogen PeroxideDocument1 pageHow Do Different PH Values Affect The Enzyme Catalase's Activity in The Decomposition of Hydrogen PeroxideAnanya PunyamurtulaNo ratings yet
- AP Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis LabDocument4 pagesAP Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Labpointweb50% (2)
- Optimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationDocument6 pagesOptimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Amylase A Sample EnzymeDocument10 pagesAmylase A Sample EnzymeJulioNo ratings yet
- Amylase Assay 2Document9 pagesAmylase Assay 2Rahman ImudaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp.6Document8 pagesLab Report Exp.6Qj B PdkhNo ratings yet
- Joshua Haholongan - Science Rate of Reaction ReportDocument13 pagesJoshua Haholongan - Science Rate of Reaction ReportJoshua HaholonganNo ratings yet
- Investigating An Enzyme Controlled Reaction - Catalase and Hydrogen PeroxideDocument4 pagesInvestigating An Enzyme Controlled Reaction - Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxidevictoria.crausazNo ratings yet
- Antacid Analysisrty4Document4 pagesAntacid Analysisrty4Melced BenasasNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument13 pagesEnzyme KineticsalicjadzNo ratings yet
- Biology ExperimentDocument4 pagesBiology ExperimentKasyfur Rif'at Raduan0% (1)
- Enzymes and PH - The Effect of PH On The Activity of The Enzyme CatalaseDocument1 pageEnzymes and PH - The Effect of PH On The Activity of The Enzyme Catalasear404100% (1)
- The Effect of Temperature On The Activity of The Enzyme AmylaseDocument12 pagesThe Effect of Temperature On The Activity of The Enzyme AmylaseNathaniel Hammo50% (2)
- Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesDocument3 pagesTitration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesMatthew Runyon50% (2)
- Chemistry Lab Report 1 Titration 2012Document9 pagesChemistry Lab Report 1 Titration 2012VeiliLookNo ratings yet
- Amylase Enzyme and Temperature LabDocument4 pagesAmylase Enzyme and Temperature LabJames DaurayNo ratings yet
- Sample Kinetics ExperimentDocument7 pagesSample Kinetics ExperimentVenus PondevidaNo ratings yet
- An Alternative Method of Milk TreatmentDocument9 pagesAn Alternative Method of Milk TreatmentA.M.ANo ratings yet
- Chem Lab - A Velocity Constant TitrationDocument6 pagesChem Lab - A Velocity Constant TitrationMiguel Ackah-Yensu50% (2)
- Biology - Enzyme Lab ConclusionDocument4 pagesBiology - Enzyme Lab ConclusionlanichungNo ratings yet
- Lab Report For AntacidsDocument4 pagesLab Report For Antacidsapi-24584273567% (3)
- Enzyme Lab ReportDocument3 pagesEnzyme Lab Reportapi-299729019No ratings yet
- Core Practical 4Document4 pagesCore Practical 4AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Lab ReportDocument23 pagesEnzymes Lab ReportHelenNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Biochem Lab KGDocument13 pagesEnzyme Biochem Lab KGKimberly George-Balgobin50% (2)
- Factors That Influence Enzyme Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesFactors That Influence Enzyme Lab ActivityDaniel BelnapNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Enzyme Lab ReportDocument3 pagesAP Biology Enzyme Lab ReportPatrick100% (6)
- AP Chemistry - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesDocument5 pagesAP Chemistry - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesJonathan Chen100% (2)
- Enyzmatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument6 pagesEnyzmatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseGio Punsalan50% (2)
- Rate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidDocument6 pagesRate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidSimon WayneNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Unit 3: DurationDocument30 pagesAS Biology Unit 3: DurationShamaNo ratings yet
- LDH Purification Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLDH Purification Lab ReportShivalee Gujarathi75% (4)
- Ap Cellular Respiration LabDocument8 pagesAp Cellular Respiration Labapi-382372564No ratings yet
- Amylase Experiment Lab ReportDocument7 pagesAmylase Experiment Lab ReportCHLOE IANNAH CALVADORESNo ratings yet
- Digestion LabDocument7 pagesDigestion LabnicewanNo ratings yet
- Spinach Chromatography Lab 1Document7 pagesSpinach Chromatography Lab 1api-392376456No ratings yet
- Bio ReportDocument8 pagesBio ReportTharshini_Indr_6713No ratings yet
- DCPIP Write UpDocument2 pagesDCPIP Write UpHashim Chishty0% (1)
- Experiment 3: Le Chatelier's PrincipleDocument4 pagesExperiment 3: Le Chatelier's PrinciplespaghetticurlersNo ratings yet
- Assays For Determination of Protein ConcentrationDocument29 pagesAssays For Determination of Protein ConcentrationSam Joshva100% (1)
- UTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp12Document7 pagesUTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp12Izykiel EdwardNo ratings yet
- Expt.1 BiochemDocument4 pagesExpt.1 BiochemMc de RamosNo ratings yet
- Membranes for Life SciencesFrom EverandMembranes for Life SciencesKlaus-Viktor PeinemannNo ratings yet
- Causes of Job SatisfactionDocument2 pagesCauses of Job SatisfactionBishawnath RoyNo ratings yet
- Communications: Unit I India - PositionDocument125 pagesCommunications: Unit I India - PositionvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Synergos 2002 Annual ReportDocument23 pagesSynergos 2002 Annual ReportSynergos InstituteNo ratings yet
- Self Reflection Exercise Myers Briggs Online1Document5 pagesSelf Reflection Exercise Myers Briggs Online1Asad BilalNo ratings yet
- Data Types in Ms-AccessDocument3 pagesData Types in Ms-AccessUmeshSharmaNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of Logarithms: Rewrite Each Equation in Exponential FormDocument4 pagesThe Meaning of Logarithms: Rewrite Each Equation in Exponential FormSh HoxhaNo ratings yet
- Unesco Four Pillars With CommentsDocument25 pagesUnesco Four Pillars With Commentslaurice hermanes100% (1)
- MagicDraw UserManualDocument1,171 pagesMagicDraw UserManualLorenzo RossiNo ratings yet
- MSC AdamsDocument16 pagesMSC Adamskuldeepsingh055100% (1)
- 2010 TnuDocument90 pages2010 TnuFerdinand SiahaanNo ratings yet
- TE040 System Test ScriptDocument10 pagesTE040 System Test ScriptPrasad RajashekarNo ratings yet
- FDP Brochure 2018Document2 pagesFDP Brochure 2018anoop13No ratings yet
- M-Class Mark II M-4206Document76 pagesM-Class Mark II M-4206sebax1982No ratings yet
- Step 3 - Argumentative Essay Outline WorksheetDocument2 pagesStep 3 - Argumentative Essay Outline WorksheetAlejandro TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Environmental Protection in Outer SpaceDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Protection in Outer SpaceHarman SainiNo ratings yet
- Natural Perfume MaterialsDocument362 pagesNatural Perfume MaterialsAlan Miller100% (5)
- GSM Planning v2Document7 pagesGSM Planning v2Hassan HafezNo ratings yet
- Gkindiaonline.comDocument19 pagesGkindiaonline.comVarun Yadav100% (1)
- 2A - Lean Six Sigma Airplane Simulation PDFDocument8 pages2A - Lean Six Sigma Airplane Simulation PDFBalaji SNo ratings yet
- Cisco Smart Software Manager Satellite: Q A Q A Q ADocument3 pagesCisco Smart Software Manager Satellite: Q A Q A Q AMahmoud RamadanNo ratings yet
- Laptop Components IdentifyDocument4 pagesLaptop Components IdentifyTanishsadan ANo ratings yet
- Syllabus Break Test Series (Part-I) Regular S-2: Superior College PattokiDocument1 pageSyllabus Break Test Series (Part-I) Regular S-2: Superior College PattokiAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Vehicle Dynamics 1 PDFDocument10 pagesLecture On Vehicle Dynamics 1 PDFSuryo mubarokNo ratings yet
- Paper P6 Advanced Taxation Complete Text: Finance Act 2015 For September 2016 To March 2017 Examination SittingsDocument8 pagesPaper P6 Advanced Taxation Complete Text: Finance Act 2015 For September 2016 To March 2017 Examination SittingsShahbano BangashNo ratings yet
- T22Document13 pagesT22Juan Daniel Rojas PalmaNo ratings yet
- Viton DS - Downloaded - 90 ShoreDocument1 pageViton DS - Downloaded - 90 ShoreazadeazNo ratings yet
- Capstone Final ReflectionDocument5 pagesCapstone Final Reflectionapi-345147949No ratings yet
Ex 4 Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity
Ex 4 Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity
Uploaded by
Rochel CaduyacOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ex 4 Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity
Ex 4 Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity
Uploaded by
Rochel CaduyacCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 4: Enzymes
Effect of pH on Enzyme Activity
Methods:
Three (3) test tubes were labeled #1, #2, and #3. Each test tube were marked off 2
cm and 7cm from the bottom, with the 2 marks being distinguishable from each
other. Three cubes of 1cm3 potato was collected and then macerated using a mortar
& pestle. Test tube #1 was added with distilled water up toe first mark and 1cm 3 of
macerated potato. Test tube #2 was added with HCl up to the first mark and
another 1cm3 of macerated potato was added. Test tube #3 was added with NaOH
up to the first mark and 1 cm 3 of macerated potato was added. After 3 minutes, all
test tubes were added with H2O2 up to the second mark.
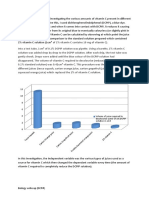
Results:
Test Tube
1
Contents
H2O, macerated
potato, H2O2
Results
+++
HCl, macerated
potato, H2O2
NaOH, macerated
potato, H2O2
++
Explanation
Catalase works
best at a pH of 7
or neutral pH
Catalase does not
work/less likely to
work at an acidic
pH
Catalase is less
effective at a basic
pH compared at a
neutral pH but
more effective
than at an acidic
pH
Discussion:
pH is a measure of the acidity or hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. It is
measured on a scale of 0-14 with pH values below 7 being acidic, values above 7
being alkaline and a value of 7 being neutral. Changes are produced in the weak
interactions that maintain the shape of the enzyme molecule resulting in a change
in shape that denatures the enzyme and decreases the enzyme activity.
Catalase is found in a cell organelle called the peroxisome. Its purpose is to destroy
toxic substances which may be introduced into cells. Also, some cells use catalase
to destroy cellular debris or worn out organelles. Hydrogen peroxide is a normal byproduct of cellular metabolism but, it is also toxic to cells. Under normal conditions
organisms produce the enzyme catalase that quickly changes hydrogen peroxide
into two harmless substances, oxygen and water. However, the function of the
enzyme is affected by changes in the environment. Catalase works to break down
hydrogen peroxide by the following chemical reaction:
2 H2O2 ------------------>2 H2O+ O2
The rate of reaction was recorded by the amount of bubbles present in the test tube
after a given amount of time, which was around 7 minutes. Catalase works best at a
neutral pH of 7, exhibited by H2O, which is the optimum pH of the enzyme. Catalase
is less likely/does not produce products when exposed to an environment which is
acidic but would still react at a basic medium.
References:
The Effect of pH on the Activity of Catalase :: Papers. (n.d.). Retrieved December 4,
2015, from http://www.123helpme.com/view.asp?id=147736
The Effect of pH on Catalase - GCSE Science - Marked by Teachers.com. (n.d.).
Retrieved December 4, 2015, from
http://www.markedbyteachers.com/gcse/science/the-effect-of-ph-on-catalase.html
You might also like
- Emg Lab ReportDocument12 pagesEmg Lab ReportKelly Mason Walker60% (5)
- Biofuels Formal Lab Report RevisedDocument9 pagesBiofuels Formal Lab Report RevisedVeronica ChangNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Action Testing Catalase Activity Lab ReportDocument4 pagesEnzyme Action Testing Catalase Activity Lab ReportAnthony100% (3)
- NMR Kinetics: Study of A Reversible Hydrolysis ReactionDocument8 pagesNMR Kinetics: Study of A Reversible Hydrolysis ReactionOldbooklover100% (2)
- Statistics Data ProjectDocument16 pagesStatistics Data Projectapi-250861401No ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab Report FinalDocument6 pagesEnzyme Lab Report Finalrsenser2100% (2)
- Determination of Enzymatic Activity of Salivary Amylase Depending On The Effect of Temperature and PHDocument11 pagesDetermination of Enzymatic Activity of Salivary Amylase Depending On The Effect of Temperature and PHAmberValentineNo ratings yet
- Kinetics LabDocument12 pagesKinetics LabJesseNo ratings yet
- Effect of Substrate Concentration on α -AmylaseDocument26 pagesEffect of Substrate Concentration on α -Amylasepriyaa100% (5)
- CHEM 160 Formal Lab Report IDocument10 pagesCHEM 160 Formal Lab Report IDatoya BrownNo ratings yet
- Biology Enzyme Lab ReportDocument2 pagesBiology Enzyme Lab Reportapi-273494632No ratings yet
- CIROS Production Handout - ENDocument121 pagesCIROS Production Handout - ENĐặng Xuân Hồng100% (1)
- Henry Tam - MGI CaseDocument3 pagesHenry Tam - MGI CasejayjNo ratings yet
- CCP v2.1Document52 pagesCCP v2.1bhuwan_vijayNo ratings yet
- Catalase Enzyme Lab RevisedDocument4 pagesCatalase Enzyme Lab RevisedIda FaridaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Core PracticalDocument7 pagesEnzyme Core PracticalJackHowley123No ratings yet
- Effect ofDocument8 pagesEffect ofAriadna Zatyuri Zuñiga LlanosNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Substrate Concentration PracDocument4 pagesThe Effect of Substrate Concentration PracjimslibraryNo ratings yet
- Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity Lab 3Document8 pagesEffect of PH On Enzyme Activity Lab 3api-340907023No ratings yet
- How Do Different PH Values Affect The Enzyme Catalase's Activity in The Decomposition of Hydrogen PeroxideDocument1 pageHow Do Different PH Values Affect The Enzyme Catalase's Activity in The Decomposition of Hydrogen PeroxideAnanya PunyamurtulaNo ratings yet
- AP Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis LabDocument4 pagesAP Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis Labpointweb50% (2)
- Optimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationDocument6 pagesOptimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Amylase A Sample EnzymeDocument10 pagesAmylase A Sample EnzymeJulioNo ratings yet
- Amylase Assay 2Document9 pagesAmylase Assay 2Rahman ImudaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp.6Document8 pagesLab Report Exp.6Qj B PdkhNo ratings yet
- Joshua Haholongan - Science Rate of Reaction ReportDocument13 pagesJoshua Haholongan - Science Rate of Reaction ReportJoshua HaholonganNo ratings yet
- Investigating An Enzyme Controlled Reaction - Catalase and Hydrogen PeroxideDocument4 pagesInvestigating An Enzyme Controlled Reaction - Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxidevictoria.crausazNo ratings yet
- Antacid Analysisrty4Document4 pagesAntacid Analysisrty4Melced BenasasNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument13 pagesEnzyme KineticsalicjadzNo ratings yet
- Biology ExperimentDocument4 pagesBiology ExperimentKasyfur Rif'at Raduan0% (1)
- Enzymes and PH - The Effect of PH On The Activity of The Enzyme CatalaseDocument1 pageEnzymes and PH - The Effect of PH On The Activity of The Enzyme Catalasear404100% (1)
- The Effect of Temperature On The Activity of The Enzyme AmylaseDocument12 pagesThe Effect of Temperature On The Activity of The Enzyme AmylaseNathaniel Hammo50% (2)
- Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesDocument3 pagesTitration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesMatthew Runyon50% (2)
- Chemistry Lab Report 1 Titration 2012Document9 pagesChemistry Lab Report 1 Titration 2012VeiliLookNo ratings yet
- Amylase Enzyme and Temperature LabDocument4 pagesAmylase Enzyme and Temperature LabJames DaurayNo ratings yet
- Sample Kinetics ExperimentDocument7 pagesSample Kinetics ExperimentVenus PondevidaNo ratings yet
- An Alternative Method of Milk TreatmentDocument9 pagesAn Alternative Method of Milk TreatmentA.M.ANo ratings yet
- Chem Lab - A Velocity Constant TitrationDocument6 pagesChem Lab - A Velocity Constant TitrationMiguel Ackah-Yensu50% (2)
- Biology - Enzyme Lab ConclusionDocument4 pagesBiology - Enzyme Lab ConclusionlanichungNo ratings yet
- Lab Report For AntacidsDocument4 pagesLab Report For Antacidsapi-24584273567% (3)
- Enzyme Lab ReportDocument3 pagesEnzyme Lab Reportapi-299729019No ratings yet
- Core Practical 4Document4 pagesCore Practical 4AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Lab ReportDocument23 pagesEnzymes Lab ReportHelenNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Biochem Lab KGDocument13 pagesEnzyme Biochem Lab KGKimberly George-Balgobin50% (2)
- Factors That Influence Enzyme Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesFactors That Influence Enzyme Lab ActivityDaniel BelnapNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Enzyme Lab ReportDocument3 pagesAP Biology Enzyme Lab ReportPatrick100% (6)
- AP Chemistry - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesDocument5 pagesAP Chemistry - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesJonathan Chen100% (2)
- Enyzmatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument6 pagesEnyzmatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseGio Punsalan50% (2)
- Rate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidDocument6 pagesRate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidSimon WayneNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Unit 3: DurationDocument30 pagesAS Biology Unit 3: DurationShamaNo ratings yet
- LDH Purification Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLDH Purification Lab ReportShivalee Gujarathi75% (4)
- Ap Cellular Respiration LabDocument8 pagesAp Cellular Respiration Labapi-382372564No ratings yet
- Amylase Experiment Lab ReportDocument7 pagesAmylase Experiment Lab ReportCHLOE IANNAH CALVADORESNo ratings yet
- Digestion LabDocument7 pagesDigestion LabnicewanNo ratings yet
- Spinach Chromatography Lab 1Document7 pagesSpinach Chromatography Lab 1api-392376456No ratings yet
- Bio ReportDocument8 pagesBio ReportTharshini_Indr_6713No ratings yet
- DCPIP Write UpDocument2 pagesDCPIP Write UpHashim Chishty0% (1)
- Experiment 3: Le Chatelier's PrincipleDocument4 pagesExperiment 3: Le Chatelier's PrinciplespaghetticurlersNo ratings yet
- Assays For Determination of Protein ConcentrationDocument29 pagesAssays For Determination of Protein ConcentrationSam Joshva100% (1)
- UTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp12Document7 pagesUTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp12Izykiel EdwardNo ratings yet
- Expt.1 BiochemDocument4 pagesExpt.1 BiochemMc de RamosNo ratings yet
- Membranes for Life SciencesFrom EverandMembranes for Life SciencesKlaus-Viktor PeinemannNo ratings yet
- Causes of Job SatisfactionDocument2 pagesCauses of Job SatisfactionBishawnath RoyNo ratings yet
- Communications: Unit I India - PositionDocument125 pagesCommunications: Unit I India - PositionvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Synergos 2002 Annual ReportDocument23 pagesSynergos 2002 Annual ReportSynergos InstituteNo ratings yet
- Self Reflection Exercise Myers Briggs Online1Document5 pagesSelf Reflection Exercise Myers Briggs Online1Asad BilalNo ratings yet
- Data Types in Ms-AccessDocument3 pagesData Types in Ms-AccessUmeshSharmaNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of Logarithms: Rewrite Each Equation in Exponential FormDocument4 pagesThe Meaning of Logarithms: Rewrite Each Equation in Exponential FormSh HoxhaNo ratings yet
- Unesco Four Pillars With CommentsDocument25 pagesUnesco Four Pillars With Commentslaurice hermanes100% (1)
- MagicDraw UserManualDocument1,171 pagesMagicDraw UserManualLorenzo RossiNo ratings yet
- MSC AdamsDocument16 pagesMSC Adamskuldeepsingh055100% (1)
- 2010 TnuDocument90 pages2010 TnuFerdinand SiahaanNo ratings yet
- TE040 System Test ScriptDocument10 pagesTE040 System Test ScriptPrasad RajashekarNo ratings yet
- FDP Brochure 2018Document2 pagesFDP Brochure 2018anoop13No ratings yet
- M-Class Mark II M-4206Document76 pagesM-Class Mark II M-4206sebax1982No ratings yet
- Step 3 - Argumentative Essay Outline WorksheetDocument2 pagesStep 3 - Argumentative Essay Outline WorksheetAlejandro TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Environmental Protection in Outer SpaceDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Protection in Outer SpaceHarman SainiNo ratings yet
- Natural Perfume MaterialsDocument362 pagesNatural Perfume MaterialsAlan Miller100% (5)
- GSM Planning v2Document7 pagesGSM Planning v2Hassan HafezNo ratings yet
- Gkindiaonline.comDocument19 pagesGkindiaonline.comVarun Yadav100% (1)
- 2A - Lean Six Sigma Airplane Simulation PDFDocument8 pages2A - Lean Six Sigma Airplane Simulation PDFBalaji SNo ratings yet
- Cisco Smart Software Manager Satellite: Q A Q A Q ADocument3 pagesCisco Smart Software Manager Satellite: Q A Q A Q AMahmoud RamadanNo ratings yet
- Laptop Components IdentifyDocument4 pagesLaptop Components IdentifyTanishsadan ANo ratings yet
- Syllabus Break Test Series (Part-I) Regular S-2: Superior College PattokiDocument1 pageSyllabus Break Test Series (Part-I) Regular S-2: Superior College PattokiAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Vehicle Dynamics 1 PDFDocument10 pagesLecture On Vehicle Dynamics 1 PDFSuryo mubarokNo ratings yet
- Paper P6 Advanced Taxation Complete Text: Finance Act 2015 For September 2016 To March 2017 Examination SittingsDocument8 pagesPaper P6 Advanced Taxation Complete Text: Finance Act 2015 For September 2016 To March 2017 Examination SittingsShahbano BangashNo ratings yet
- T22Document13 pagesT22Juan Daniel Rojas PalmaNo ratings yet
- Viton DS - Downloaded - 90 ShoreDocument1 pageViton DS - Downloaded - 90 ShoreazadeazNo ratings yet
- Capstone Final ReflectionDocument5 pagesCapstone Final Reflectionapi-345147949No ratings yet