Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Section 4: Social Studies
Section 4: Social Studies
Uploaded by
Amanda-KoonsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 4: Social Studies
Section 4: Social Studies
Uploaded by
Amanda-KoonsCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 4: Social Studies
This section addresses Cognitive and Social Emotional Development through the content area of Social
Studies. The correlations are with the Kindergarten Curriculum Standards in Social Studies.
This section also correlates to Head Start Performance Standards:
1304.21(a)(3)(i)(A) Grantee and delegate agencies must support social and emotional development by:
Encouraging development which enhances each child’s strengths by: Building trust.
1304.21(a)(3)(i)(B) Fostering independence;
1304.21(a)(3)(i)(C) Encouraging self-control by setting clear, consistent limits, and having realistic
expectations;
1304.21(a)(3)(i)(D) Encouraging respect for the feelings and rights of others;
1304.21(b)(2)(i) Grantee and delegate agencies must support the social and emotional development of infants
and toddlers by promoting an environment that: Encourages the development of self-awareness, autonomy,
and self-expression;
1304.21(c)(1)(iv) Ensures that the program environment helps children develop emotional security and facility
in social relationships;
1304.21(c)(1)(v) Enhances each child’s understanding of self as an individual and as a member of a group;
1304.21(c)(1)(vi) Provides each child with opportunities for success to help develop feelings of competence,
self-esteem, and positive attitudes toward learning; and
1304.21(c)(1)(vii) Provides individual and small group experiences both indoors and outdoors.
Social Studies Page 1
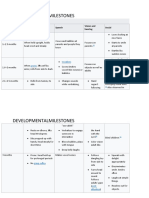
Social Studies for 0 through 4 months
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Gazes into caregiver's eyes while being fed
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
Turns head toward familiar voices
Responds to familiar Stops crying when familiar voice is heard
adults Begins to coo or smile when being talked to
Follows the caregiver with eyes
Fusses or cries to gain attention of familiar adults
Cuddles into a caregiver's shoulder when being held
Social Studies
Gazes passively, then begins to fuss when new persons move
Human close
Interactions/ Stops cooing and smiling when a new person tries to get her
Culture Shows awareness of attention
unfamiliar people Turns head into shoulder of caregiver when a new person
approaches
Stiffens and leans away when picked up by an unfamiliar person
Looks in direction of a nearby child
Shows awareness of Smiles and coos in response to an older child's attention
other children
Brightens and waves arms in response to a child's smiles
Social Studies Page 2
Social Studies for 5 through 8 months
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Babbles and coos to gain attention of someone nearby
Looks intently at the face when talked to by a familiar person
Smiles when someone familiar smiles or makes gentle, funny
faces
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
Engages with familiar Coos or smiles when talked to
adults Kicks legs or reaches with his arms when he sees a familiar
person approach
Bounces on the caregiver's lap to get attention
Makes loud noises as though trying to talk to someone
Relaxes when comforted by familiar persons
Social Studies
Hides face in familiar adult's shoulder when the adult is talking
with someone unfamiliar
Human
Looks curiously at someone who hasn't been around regularly,
Interactions/
Shows awareness of and clings to familiar adult
Culture Reaches to a familiar adult to be picked up when a stranger says
unfamiliar people
hello
Stops activity and stares at a new person entering the room
Cries when greeted by an unfamiliar person
Watches nearby children, and often reaches out
Looks toward a peer who is actively exploring an interesting
object
Shows awareness of Directs smiles and vocalizations toward other children
other children Kicks feet in excitement at the sight of other children
Uses hands to explore the face and hair of a peer
Watches with an expression of worry if another child cries; may
even cry herself
Social Studies Page 3
Social Studies for 9 through 12 months (9 months to 1 year)
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Actively clings or cries in response to a familiar person saying
"good-bye"
Shows great delight when playing peek-a-boo
Shows preference for Checks out the caregiver's reaction before deciding if he should
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
familiar adults act hurt
Coos or smiles when talked to
Tugs on caregiver or makes noise when feeling ignored
Reaches to the caregiver for comfort when upset or hurt
May cry inconsolably when left with a new or unfamiliar person
Plays comfortably in a new setting until the arrival of a new
Social Studies
person, then often needs to be comforted or be close to
Human someone familiar
Reacts to unfamiliar
Looks curiously at someone she hasn't seen for a long time, and
Interactions/ people holds on tightly
Culture Stops exploring or playing in order to watch intently when an
unfamiliar person enters the room
Demonstrates joy when the parent/guardian returns after being
away for a while
Watches older children play
Touches the face and hair of the peer next to him
Tries to imitate playing with a toy after watching another person
play with it
Shows awareness of
Cries when hearing another child cry
other children Plays with a toy when sitting beside another child who is also
playing with a toy
Crawls into an adult's lap if the adult is still and interacting with
other children
Social Studies Page 4
Social Studies for 13 through 18 months (1 year to 1-1/2 years)
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Explores and experiments with new materials, such as play
dough, when the caregiver is using the materials nearby
Relies on the presence Will crawl or walk through a confined area to reach a familiar
person
of familiar adults to try Momentarily stops play to touch base with a familiar adult, and
things then resumes play when given a reassuring smile or
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
encouraging word by the caregiver
Goes to a trusted adult with words or gestures
Hides behind his parent but peeks out when a new person says
"Hello"
Moves to the other side of the room when an unfamiliar person
enters the room
Social Studies
Shows awareness of Cries when she sees a face that is very different from what she
is used to -- a beard or mustache (Santa Claus) or a clown
Human unfamiliar adults
Interactions/ Cries when the parent leaves but will slowly settle down with the
help of familiar adult
Culture
Allows a stranger to approach when the stranger does
something familiar such as wave or play peek-a-boo
Looks in the direction of other children playing nearby
Reaches out and tugs at another child's hair
Offers a toy to another child
Hits a child when that child tries to take the toy he is playing with
Interacts with other
Plays with an older child by following the activities that the older
children
child suggests
Reacts with a frown or turns to look when another child cries
Plays with a toy when sitting beside another child who is also
playing with a toy/ will try to offer the other child the toy or take
that child's toy
Social Studies Page 5
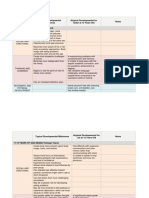
Social Studies for 19 through 24 months (1-1/2 years to 2 years)
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Moves toward a toy, but comes back to adult for reassurance
before going to the toy; seeks adult contact during time he is
playing with an object
Seeks the support of Pulls the face of a caregiver toward her when the adult begins to
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
familiar adults to try talk to someone else
things Cautiously watches the familiar adult talk to a new person, and
then slowly begins to interact with the new adult
Acts shy at parties or larger gatherings, and wants to hold onto
familiar adult when entering a new group
Human
Acts cautiously around Keeps one eye on the stranger and does not respond to friendly
Interactions/ efforts by the stranger
unfamiliar adults
Social Studies
Culture
Plays next to a child for brief periods, but goes back to own play
Watches and begins to play briefly with other children, but tends
Interacts with other to become demanding and needs adult redirection of attention
children Imitates peers' behavior for short periods of time (can copy
hopping like a frog or making sounds like a fire engine)
Makes compromises occasionally, but taking turns is very
difficult
Begins to recognize Shows increasing memory for details and routines (remembers
routines and to where things go, goes to wash hands when meal time is
History categorize time intervals announced, gets special item for naptime)
Recognizes the changes
Responds with "bye" when reminded that someone is leaving
in environment
Social Studies Page 6
Social Studies for 25 through 30 months (2 years to 2-1/2 years)
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Holds on tight to adult in new setting but gradually lets go to
explore the environment
Shows need for familiar Attempts a new behavior but looks to the adult to watch and
affirm efforts (climbs to top of slide but wants the adult to watch
adult's approval before sliding down)
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
Turns to adult for comfort after falling, but goes back to play
Approaches a new person after familiar adult has talked with the
Shows cautious interest new person a while
Human in unfamiliar adults Looks away when a new person talks to her
Interactions/ Joins a small group in an area and plays for a brief period
without a disruption, but mostly plays independently
Social Studies
Culture
Can play beside another child in a center for longer periods of
time without trying to take the other child's toys
Plays beside other
children Can say "no" or "stop" to a child who is taking something he
does not want him to, rather than hitting or using physical force
Can help other children pick up toys for short time span
Uses words to ask another child to play
Insists on doing things "by myself" but needs adult assurance
Begins to act
(tries to dress himself and may have things on backward, but
independently refuses help)
Knows when it is snack time or meal time
Identifies common
Begins to pick up on clues to the routine (puts on coat before
events and routines going outside)
History Begins to categorize time Begins to understand that some events follow a pattern (nap
intervals time comes after meal time)
Recognizes the changes Recognizes weather (sees snow and runs to put on coat; sees
in environment rain and runs to get umbrella)
Social Studies Page 7
Social Studies for 31 through 36 months (2-1/2 years to 3 years)
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Acts out different "settings/events" that have happened at home
Reflects attitudes and
behaviors of familiar Uses language -- appropriate or inappropriate -- that adults
adults around her use
Tries to do silly things to engage familiar adults
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
Shows cautious interest
Talks to new person if familiar adult is nearby
in unfamiliar adults
Human Joins a small group in an area and plays for a short time; will
Interactions/ interact with the persons in the area
Culture Has capacity to play Begins to participate in simple group activities (like follow the
cooperatively with other leader)
Has a better understanding of waiting a moment and taking
children
Social Studies
turns; can play with another child and not take the materials
Talks with a peer using shortened sentence structure, but has
ability to communicate his wants and needs
Begins to act Enjoys doing things independently ( can pick up trash and throw
independently it away without help); seeks recognition of successes
Identifies common Recognizes routines; following the routines becomes very
events and routines important
Begins to categorize time Comprehends the details of the daily routines and is aware when
History the details are not followed
intervals
Recognizes the changes
Points out that something is missing from a table, puzzle, etc.
in environment
Recognizes environmental symbols and print (arches are
McDonalds and Wal-Mart sign means going shopping)
Begins to understand
Geography and recognize familiar Associates riding in different vehicles with arriving at different
localities destinations (a ride in the car means going to the store; the
school bus ride means going to "school")
Social Studies Page 8
Social Studies for 36 through 48 months (3 years to 4 years)
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Begins to recognize likenesses and differences in others
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
Discriminates individual, Begins to understand family structures and roles
culture and community Draws self, usually with head and not much detail
Acts out family roles in dramatic play center
Human Develops growing
Interactions/ awareness of jobs and
Participates in classroom jobs
Culture what is required to
Social Studies
perform them
Follows simple class rules
Begins to understand the Participates in class clean-up or group activities
reason for rules Understands that there is no hitting because it hurts
Learns to wait (for a short period of time) for her turn
Knows when it is snack time or meal time
Identifies Common
Recognizes routines of washing hands before eating or brushing
Events and Routines teeth after meals or before bed time
Begins to categorize time Uses the word "today," or "day" and "night" to talk about time of
History
intervals day; sometimes uses the wrong term
Recognizes the changes
Recognizes that it is rainy, sunny, hot and cold
in environment
Social Studies Page 9
Social Studies for 49 through 60 months (4 years to 5 years)
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Recognizes own gender
Discriminates individual, Begins to understand family structures and roles
culture and community Notices similarities and differences in people
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
Social Studies K.5.0, K.1.01
Plays and acts out family roles in dramatic play center
Develops growing Participates in classroom jobs
awareness of jobs and
Human Looks at books and identifies jobs of persons
what is required to
Interactions/
perform them Chooses "leader" or "boss" for activity
Culture
Helps make and follows class rules
Social Studies
Places personal symbol at interest area to denote her place
Begins to understand the Participates in class clean-up or group activities
reason for rules Can state a rule and simply explain the "why" of rule, e.g., Don't
push because someone will fall.
Learns to wait (for longer periods of time) for his turn
Understands that the day follows a schedule
Identifies common
Social Studies K.3.02;
Understands and can predict the next events that will happen in
events and routines
the day
Math K.4.1.c/d
Begins to categorize time Uses terms "today." "tomorrow," "next time" with some accuracy
History intervals Begins to understand concepts of before and after
Recognizes that it is rainy, sunny, cool, hot
Recognizes the changes
in environment Begins to recognize seasons (if he lives in a place where
seasonal differences are apparent)
Social Studies Page 10
Social Studies for 49 through 60 months (4 years to 5 years)
Correlations
Learning
Domain
Area of
Learning Expectations Performance Indicators (examples)
Component
(examples) By the end of age span
Recognizes common features in his immediate environment
COGNITIVE / SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL
Social Studies K.3.01
Begins to express and (playground, library, restroom)
understand concepts and Creates drawings of home, school, etc.; can make simple map
of home to show different areas and talk about what is in those
language of geography in
areas (stove in kitchen)
the context of her Identifies important or familiar landmarks (fire house, grocery
Geography classroom, home and store, etc.)
community Identifies common features of local landscape (houses, streets,
Social Studies
buildings)
Begins to understand that people need nutritious food
Begins to understand
Understands that he must put on a coat and warm shoes in cold
that people need food,
Social Studies K.2.01/03,
weather
clothing and shelter Understands that people need a place to live
Begins to understand
Hlth K.4.0
Understands that fire fighters help others in many ways
what services the
Understands that police officers help people in different ways
community workers Begins to understand that there are other community workers
Economics provide that help his community
Understands that money can buy items
Begins to understand the
concept of money Understands that some items cost more than others
Social Studies Page 11
You might also like
- Pragmatic Language Chart PDFDocument1 pagePragmatic Language Chart PDFShawn StevensNo ratings yet
- Disabilities Categories and IDEA Docx-1 Matrix Assignment Due 11Document30 pagesDisabilities Categories and IDEA Docx-1 Matrix Assignment Due 11Denise BryantNo ratings yet
- Understanding Body Language and Facial ExpressionsDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Body Language and Facial ExpressionsFellipe Lima100% (1)
- DLL - Math 7 - Q3 - W2Document5 pagesDLL - Math 7 - Q3 - W2Kevin Bermudez Atienza100% (6)
- Robert Daniel School Counselor Cover LetterDocument1 pageRobert Daniel School Counselor Cover Letterapi-512429614No ratings yet
- DONE MYLENE JOY GALAMITON - ECE-16-Course-File-M1-L2-Activity1Document2 pagesDONE MYLENE JOY GALAMITON - ECE-16-Course-File-M1-L2-Activity1Mylene Joy Cabariban GalamitonNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestones Eylf Nqs Document Divided Into Ages and Stages - Ver - 4Document8 pagesDevelopmental Milestones Eylf Nqs Document Divided Into Ages and Stages - Ver - 4claire.sykesNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestones: Age Motor Speech Vision and Hearing SocialDocument6 pagesDevelopmental Milestones: Age Motor Speech Vision and Hearing SocialAdnan RezaNo ratings yet
- Theorist-Chart Fall 2010Document11 pagesTheorist-Chart Fall 2010ianptaylorNo ratings yet
- PROFEDDocument3 pagesPROFEDhgvabalosNo ratings yet
- Social DevelopmentDocument75 pagesSocial DevelopmentAjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Section 2: Early LiteracyDocument22 pagesSection 2: Early LiteracyAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Stages Emotional Social Mental Physical: Infancy (Birth - 2° Week)Document2 pagesStages Emotional Social Mental Physical: Infancy (Birth - 2° Week)Mark Vertiz CernaNo ratings yet
- Physical Cogniti Ve Langua Ge Social/ Emotion Al Moral: Yea RsDocument8 pagesPhysical Cogniti Ve Langua Ge Social/ Emotion Al Moral: Yea RsVanTaneoNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal Entry 1 Edph 366Document4 pagesReflective Journal Entry 1 Edph 366api-357915760No ratings yet
- ECCDDocument88 pagesECCDHazel HhetNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTIONARY DEVELOPMENT OF THE CHILD InfographicDocument3 pagesEVOLUTIONARY DEVELOPMENT OF THE CHILD InfographicScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Flinto@Home Brochure v1.2Document9 pagesFlinto@Home Brochure v1.2fredrickleanasNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document3 pagesActivity 5DELMARK MIENNo ratings yet
- Parental Tips Skills That Are Learnt in Physical DomainDocument2 pagesParental Tips Skills That Are Learnt in Physical DomainShellyNo ratings yet
- Parental TipsDocument2 pagesParental TipsShellyNo ratings yet
- Social Awareness CompetencyDocument30 pagesSocial Awareness CompetencyudaykumarNo ratings yet
- Math & ScienceDocument18 pagesMath & ScienceAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Early Indicators of Developmental Delays-2Document31 pagesEarly Indicators of Developmental Delays-2shai gestNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentalMatrix YapparconDocument3 pagesDevelopmentalMatrix YapparconantoNo ratings yet
- Slides Social InteractionsDocument17 pagesSlides Social InteractionsFernandaNo ratings yet
- Typical and Atypical Development ListDocument2 pagesTypical and Atypical Development ListKenneth EchonNo ratings yet
- CV5EI Modulo 025001Document39 pagesCV5EI Modulo 025001Jorge JuniorNo ratings yet
- Paediatric PsychologyDocument10 pagesPaediatric PsychologyHaa HaaaNo ratings yet
- Asd, Adhd, Di, GiftedDocument30 pagesAsd, Adhd, Di, GiftedRamaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Delay PosterDocument1 pageDevelopmental Delay PosterwiwiNo ratings yet
- Elementary School Middle School High School: Emotional Red FlagsDocument1 pageElementary School Middle School High School: Emotional Red FlagsJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Newborn and InfantDocument4 pagesNewborn and InfantTeddy leyianNo ratings yet
- Group 9 - PPT ReportDocument32 pagesGroup 9 - PPT ReportWest QuijadaNo ratings yet
- MTW 2016 Understanding Social Communication 2Document9 pagesMTW 2016 Understanding Social Communication 2Asmaa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Activity 4Document5 pagesActivity 4Stephanie Angel OmpadNo ratings yet
- Developmentalmilestones: Developmental Milestones Age Motor Speech Vision and Hearing SocialDocument9 pagesDevelopmentalmilestones: Developmental Milestones Age Motor Speech Vision and Hearing SocialDevsya DodiaNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022 2 1Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022 2 1api-621033980No ratings yet
- Dir 101Document59 pagesDir 101rafaelfrizzocallegaroNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Lifespan DevelopmentDocument30 pagesTopic 5 Lifespan DevelopmentKaibin LowNo ratings yet
- (Ch. 3) Coaching Toddlers' Social and Emotional Competence - Incredible Toddlers (Webster-Stratton)Document48 pages(Ch. 3) Coaching Toddlers' Social and Emotional Competence - Incredible Toddlers (Webster-Stratton)ppeixinhoNo ratings yet
- Child Care & DevelopmentDocument36 pagesChild Care & DevelopmentDesireeNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed ReviewerDocument11 pagesProf Ed ReviewerMarissa EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2Document6 pagesAssignment 1 2Tharien OosthuizenNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestone Matrix - Sample FormatDocument16 pagesDevelopmental Milestone Matrix - Sample FormatArchien Espaldon Cassion100% (1)
- Child Language Aquisition Revision NotesDocument31 pagesChild Language Aquisition Revision NotesPat BagnallNo ratings yet
- Positive Approach To Child Discipline FrameworkDocument11 pagesPositive Approach To Child Discipline FrameworkJohn Philip G. NavaNo ratings yet
- Teaching EFL Across Different Ages and Levels.Document1 pageTeaching EFL Across Different Ages and Levels.Natalia CantorNo ratings yet
- Development Milestone of ChildrenDocument13 pagesDevelopment Milestone of ChildrenJonnel GadinganNo ratings yet
- Social DevelopmentDocument3 pagesSocial DevelopmentAshley Co TingNo ratings yet
- Articol AsdDocument13 pagesArticol AsdAna Isabella SimionNo ratings yet
- 9 To 13 Years OldDocument3 pages9 To 13 Years OldAnthansia McllianNo ratings yet
- IGNOU DECE-01 Unit 10Document14 pagesIGNOU DECE-01 Unit 10kanishkayadav60No ratings yet
- Standard 1Document6 pagesStandard 1api-525123857No ratings yet
- Child Language - Learning To Talk: (Skinner)Document41 pagesChild Language - Learning To Talk: (Skinner)HayeonNo ratings yet
- Personal Development WLP Week2Document5 pagesPersonal Development WLP Week2Herson MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Perdev W2Document5 pagesPerdev W2Herson MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestones: © 2019 Kids OT Help - All Rights ReservedDocument6 pagesDevelopmental Milestones: © 2019 Kids OT Help - All Rights ReservedZainab Abizer Merchant100% (1)
- Perdev W3Document5 pagesPerdev W3Herson MadrigalNo ratings yet
- PDF Child Development Milestone Chart Finals DL PDFDocument2 pagesPDF Child Development Milestone Chart Finals DL PDFChristelle AbaoNo ratings yet
- Hitos Del DesarrolloDocument16 pagesHitos Del DesarrolloCarmen BustillosNo ratings yet
- Supporting Children's Social Development: Positive Relationships in the Early YearsFrom EverandSupporting Children's Social Development: Positive Relationships in the Early YearsNo ratings yet
- General Music: Kindergarten: Standard 1.0 SingingDocument7 pagesGeneral Music: Kindergarten: Standard 1.0 SingingAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten: Embedded Inquiry: Conceptual Strand Guiding QuestionDocument11 pagesKindergarten: Embedded Inquiry: Conceptual Strand Guiding QuestionAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Standard 1.0: Computer Technology: Literacy and Usage KindergartenDocument7 pagesStandard 1.0: Computer Technology: Literacy and Usage KindergartenAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Reading - First Grade: Content Standard: 1.0Document4 pagesReading - First Grade: Content Standard: 1.0Amanda-Koons100% (1)
- MA Grade KDocument3 pagesMA Grade KAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- School Counseling & Career Guidance: Grades 3-5Document10 pagesSchool Counseling & Career Guidance: Grades 3-5Amanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Tennessee Mathematics Standards 2009-2010 Implementation Grade One Mathematics Standard 1 - Mathematical ProcessesDocument3 pagesTennessee Mathematics Standards 2009-2010 Implementation Grade One Mathematics Standard 1 - Mathematical ProcessesAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten Dance Curriculum Standards: Standard 1.0 Elements and SkillsDocument10 pagesKindergarten Dance Curriculum Standards: Standard 1.0 Elements and SkillsAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- 1st Grade Dance Curriculum StandardsDocument10 pages1st Grade Dance Curriculum StandardsAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Social Studies - Kindergarten: Culture Content Standard: 1.0Document6 pagesSocial Studies - Kindergarten: Culture Content Standard: 1.0Amanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- General Music: 1st Grade: Standard 1.0 SingingDocument9 pagesGeneral Music: 1st Grade: Standard 1.0 SingingAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Theatre Grade K Standard 1.0 Script WritingDocument7 pagesTheatre Grade K Standard 1.0 Script WritingAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Theatre Grade 1 Standard 1.0 Script WritingDocument8 pagesTheatre Grade 1 Standard 1.0 Script WritingAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Tennessee Mathematics Standards 2009-2010 Implementation Grade Two Mathematics Standard 1 - Mathematical ProcessesDocument3 pagesTennessee Mathematics Standards 2009-2010 Implementation Grade Two Mathematics Standard 1 - Mathematical ProcessesAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Standard 1.0: Computer Technology: Literacy and Usage First GradeDocument8 pagesStandard 1.0: Computer Technology: Literacy and Usage First GradeAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Reading - Third Grade: Content Standard: 1.0Document7 pagesReading - Third Grade: Content Standard: 1.0Amanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Tennessee Mathematics Standards 2009-2010 Implementation Grade Three Mathematics Standard 1 - Mathematical ProcessesDocument4 pagesTennessee Mathematics Standards 2009-2010 Implementation Grade Three Mathematics Standard 1 - Mathematical ProcessesAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Reading - Second Grade: Content Standard 1.0Document4 pagesReading - Second Grade: Content Standard 1.0Amanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- General Music: 2nd Grade: Standard 1.0 SingingDocument9 pagesGeneral Music: 2nd Grade: Standard 1.0 SingingAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Tennessee English Language Arts Standards Effective 2009-2010 Grade 1 Standard 1 - LanguageDocument7 pagesTennessee English Language Arts Standards Effective 2009-2010 Grade 1 Standard 1 - LanguageAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Theatre Grade 2 Standard 1.0 Script WritingDocument8 pagesTheatre Grade 2 Standard 1.0 Script WritingAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Social Studies - First Grade: Culture Content Standard: 1.0Document6 pagesSocial Studies - First Grade: Culture Content Standard: 1.0Amanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 Dance Curriculum Standards: Standard 1.0 Elements and SkillsDocument10 pagesGrade 2 Dance Curriculum Standards: Standard 1.0 Elements and SkillsAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Visual Art: Second Grade: Standard 1.0 Media, Techniques, and ProcessesDocument7 pagesVisual Art: Second Grade: Standard 1.0 Media, Techniques, and ProcessesAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Grades K - 2: The Student WillDocument8 pagesPhysical Education: Grades K - 2: The Student WillAmanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Social Studies - Third Grade: Culture Content Standard: 1.0Document14 pagesSocial Studies - Third Grade: Culture Content Standard: 1.0Amanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- School Counseling & Career Guidance: Grades K-2Document16 pagesSchool Counseling & Career Guidance: Grades K-2Amanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Health 3 5Document21 pagesHealth 3 5Amanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Modern Languages-Elementary K-5 (Beginning)Document7 pagesModern Languages-Elementary K-5 (Beginning)Amanda-KoonsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Geometrical Applications of CalculusDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Geometrical Applications of CalculusRhea0% (1)
- 1036Document108 pages1036Adarsha Vidyalaya DaminiNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Library Research ProjectDocument10 pagesAssignment-Library Research ProjectDi TiểuNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 - Curriculum Defined: Reflection #5Document9 pagesACTIVITY 1 - Curriculum Defined: Reflection #5clara dupitasNo ratings yet
- Annual Report of Eco-Care Club Activities 2021-2022Document5 pagesAnnual Report of Eco-Care Club Activities 2021-2022NANDHINI SNo ratings yet
- Implementation ReportDocument10 pagesImplementation ReportRenita Eclar LaranangNo ratings yet
- Chapter Fifteen: Understanding and Using Standardized TestsDocument21 pagesChapter Fifteen: Understanding and Using Standardized TestsMorgan ArnoldNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Our Solar System 20150701 Wednesday PrepositionsDocument1 pageUnit 9 Our Solar System 20150701 Wednesday PrepositionsAsh AngelNo ratings yet
- CV - Manuel Castells 2006Document47 pagesCV - Manuel Castells 2006openid_Mtc4LtrUNo ratings yet
- Slo Presentation March 15Document44 pagesSlo Presentation March 15api-223530755No ratings yet
- Addressing The Causes That Hinder Effective English Language Teaching in Saudi Universities: A Case StudyDocument36 pagesAddressing The Causes That Hinder Effective English Language Teaching in Saudi Universities: A Case StudyChoudhary Zahid JavidNo ratings yet
- TOEFL 80 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTOEFL 80 QuestionsJom-Jom Fong RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The National CurriculumDocument7 pagesLesson 1 The National CurriculumDreik ArpinoNo ratings yet
- Fractions Final ProjectDocument10 pagesFractions Final Projectapi-291564354No ratings yet
- CADAC Accom. Report Final FinalDocument37 pagesCADAC Accom. Report Final FinalizzatericNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument35 pagesResearch PaperRUCHINo ratings yet
- The Aditya Birla Public School, Adityanaagr ANNUAL REPORT 2013-2014Document8 pagesThe Aditya Birla Public School, Adityanaagr ANNUAL REPORT 2013-2014Harsh BardhanNo ratings yet
- Teaching Young Children Briody McGarryDocument4 pagesTeaching Young Children Briody McGarryvmeederNo ratings yet
- W5 - Ilpm - Aral Pan 8Document1 pageW5 - Ilpm - Aral Pan 8Llemor Soled SeyerNo ratings yet
- Gender Stereotype and Children's LitDocument45 pagesGender Stereotype and Children's LitIrinaNo ratings yet
- Individualized Education ProgramDocument13 pagesIndividualized Education ProgramkpodomNo ratings yet
- (UDISE+) : Data Capture FormatDocument24 pages(UDISE+) : Data Capture FormatShivamNo ratings yet
- BISRAT EJIGU-returns To ScaleDocument89 pagesBISRAT EJIGU-returns To ScaleTesfahun tegegnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Read About Some Different People's JobsDocument2 pagesLesson 3 Read About Some Different People's JobsАнђелка ГемовићNo ratings yet
- Test Taker Score Report: February 28, 2020 Test Date Scores ScoresDocument2 pagesTest Taker Score Report: February 28, 2020 Test Date Scores ScoresISHAK BULJUBASICNo ratings yet
- Tylers RationaleDocument4 pagesTylers RationaleCarlo Zebedee Reyes GualvezNo ratings yet
- March Scheme - El BanqueteDocument11 pagesMarch Scheme - El BanquetececiliawolmanNo ratings yet
- PIL On TET Sent To Supreme Court by Vijay Kumar HeerDocument26 pagesPIL On TET Sent To Supreme Court by Vijay Kumar HeerVIJAY KUMAR HEERNo ratings yet