Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 viewsHow A Bill Becomes A Law
How A Bill Becomes A Law
Uploaded by
legalfitzThis document outlines the process for how a bill becomes a law in the Senate and House of Representatives in the Philippines. It involves several steps including preparation and filing of the bill, committee consideration and action, plenary consideration and voting, reconciliation if different versions pass each chamber, enrollment, transmittal to the president, and it becoming law with the president's signature or overriding a veto. The process is similar in both chambers but with some differences in committee referrals and votes required.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Robert's Rules of Order (Revised for Deliberative Assemblies)From EverandRobert's Rules of Order (Revised for Deliberative Assemblies)No ratings yet
- Legislative Process FlowchartDocument3 pagesLegislative Process FlowchartHanna Quiambao100% (3)
- How A Bill Becomes Law in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes Law in The PhilippinesAngelina Villaver Reoja100% (1)
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument5 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawKevin KroytNo ratings yet
- Legislative Process - How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument6 pagesLegislative Process - How A Bill Becomes A LawFatzie Mendoza100% (2)
- How A Bill Becomes A Law AssignmentDocument2 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A Law Assignmenteduardo wapanioNo ratings yet
- 12 Steps Before A Bill Becomes A Law.Document4 pages12 Steps Before A Bill Becomes A Law.Racquel BatinoNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawSam B. PinedaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument3 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawclsNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument14 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawmimaymiNo ratings yet
- Bills and Parliamentary Procedure M2-1Document16 pagesBills and Parliamentary Procedure M2-1Deb DasNo ratings yet
- I. Law-Making Process in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesI. Law-Making Process in The PhilippinesNathaniel LepasanaNo ratings yet
- Statcon Bills OrdinancesDocument5 pagesStatcon Bills OrdinancesVic FrondaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument10 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawEve SaltNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A Law - SummarizedDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A Law - SummarizedNathaniel JosephNo ratings yet
- LawmakingDocument3 pagesLawmakingJaps PunoNo ratings yet
- Legislation 02042020 062141pmDocument3 pagesLegislation 02042020 062141pmHyder KhanNo ratings yet
- Chap02legislativeprocedureinpakistan 150706184115 Lva1 App6892Document3 pagesChap02legislativeprocedureinpakistan 150706184115 Lva1 App6892Hafsa SarfrazNo ratings yet
- BoL Notes-2Document15 pagesBoL Notes-2Rak kaurNo ratings yet
- PTT Steps in Passage of Bill in Philippine LegislatureDocument4 pagesPTT Steps in Passage of Bill in Philippine LegislatureMary Rose B. MendovaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument3 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawAurea Zambrano LibiranNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawMahri Rieanne Delle LangbisNo ratings yet
- Primrose Vien G. Ferolino July 30, 2019 Block 10 7:30-9:00 PM TTHDocument3 pagesPrimrose Vien G. Ferolino July 30, 2019 Block 10 7:30-9:00 PM TTHPrim Rose VienNo ratings yet
- Procedure of LegislationDocument8 pagesProcedure of LegislationSoomro KhanNo ratings yet
- Law Making Process or Legislative Procedure in PakistanDocument3 pagesLaw Making Process or Legislative Procedure in PakistanAbdullah FaizNo ratings yet
- Legislative Procedure in Pakistan: Parliamentairan System of PakistanDocument5 pagesLegislative Procedure in Pakistan: Parliamentairan System of PakistanKaneez FatimaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Become An ActDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Become An Actkaushal yadavNo ratings yet
- Legislative Process:: ConstitutionDocument4 pagesLegislative Process:: ConstitutionRameezNo ratings yet
- Legislation Process: How A Bill Becomes A Law 1. Preparation of The BillDocument3 pagesLegislation Process: How A Bill Becomes A Law 1. Preparation of The BillAngel SagubanNo ratings yet
- Viva Voce: Division of The House Nominal VotingDocument3 pagesViva Voce: Division of The House Nominal VotingEmma SchultzNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes Law in The Philippines TetaDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes Law in The Philippines TetaJobel Sibal Capunfuerza100% (1)
- LAW-MAKING PROCESS: The Summary Example Bill of The SenateDocument3 pagesLAW-MAKING PROCESS: The Summary Example Bill of The SenateOliver PenalberNo ratings yet
- Climate 2Document12 pagesClimate 2boranihar34No ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument1 pageHow A Bill Becomes A LawNurseAmyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document5 pagesUnit 5Junard PajamaNo ratings yet
- Hand Out LegislativeDocument2 pagesHand Out LegislativeMarivic PuddunanNo ratings yet
- W10 CBMDocument2 pagesW10 CBMabhinaya24396No ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawJcarLo B AglibtNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument5 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A Lawshynah clarinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 B. LAW 20214Document3 pagesAssignment 01 B. LAW 20214Abdul RafayNo ratings yet
- Committee Consideration/Action - Committee Evaluate The Bill andDocument2 pagesCommittee Consideration/Action - Committee Evaluate The Bill andJennifer CamaNo ratings yet
- Legislative Procedure For Passing of Bills in State LegislatururesDocument12 pagesLegislative Procedure For Passing of Bills in State LegislatururesShreya VermaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument3 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawRoxanne LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Legislative ProcessDocument15 pagesLegislative ProcessfilodoxiaNo ratings yet
- Congress SDocument3 pagesCongress SGlencie PimentelNo ratings yet
- A Written Report in Political Science in Article VI: Legislative Department (Section 26 and 27)Document7 pagesA Written Report in Political Science in Article VI: Legislative Department (Section 26 and 27)Rohj EbreoNo ratings yet
- Statcon Review How Bill Becomes A Law To TolentinoDocument3 pagesStatcon Review How Bill Becomes A Law To Tolentinorose ann bulanNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument1 pageHow A Bill Becomes A Lawryanzafra30No ratings yet
- Summary of Report (grp.4 PA 141)Document7 pagesSummary of Report (grp.4 PA 141)Morthiza EmbongNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes Law in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageHow A Bill Becomes Law in The PhilippinesArt CrestFall ManlongatNo ratings yet
- Law Making ProcedureDocument13 pagesLaw Making Procedurekhushi guptaNo ratings yet
- Passage of Bill Into Law - House of RepresentativesDocument3 pagesPassage of Bill Into Law - House of RepresentativesFRANCHETTE FERNANDEZ SIMENENo ratings yet
- LegRes Legislative ProcessDocument17 pagesLegRes Legislative ProcessChandyNo ratings yet
- Legislative Process - Senate of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesLegislative Process - Senate of The PhilippinesJosephson AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- The Law Making Process in UgandaDocument4 pagesThe Law Making Process in UgandaremojamwaNo ratings yet
- The Legislative Process: Elaine Ruby B. Elihay Gr. 11-St. RitaDocument3 pagesThe Legislative Process: Elaine Ruby B. Elihay Gr. 11-St. RitaArlyn Apple ElihayNo ratings yet
- Legres Midterm NotesDocument13 pagesLegres Midterm NotesWater MelonNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance Week 2: Second QuarterDocument14 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance Week 2: Second QuarterLehanne BellenNo ratings yet
- Passage of BillDocument2 pagesPassage of BillErica Mae VistaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Henry M. Robert, Daniel H Honemann, Thomas J Balch, Daniel E. Seabold & Shmuel Gerber's Robert's Rules of OrderFrom EverandSummary of Henry M. Robert, Daniel H Honemann, Thomas J Balch, Daniel E. Seabold & Shmuel Gerber's Robert's Rules of OrderNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Constitutional Law 1Document23 pagesSyllabus For Constitutional Law 1Ashabe GuroNo ratings yet
- 4 - Separation of Powers - Check and BalanceDocument13 pages4 - Separation of Powers - Check and BalanceBhuwan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stat ConDocument7 pagesStat ConJC TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Ang NARS vs. Executive Secretary DigestDocument2 pagesAng NARS vs. Executive Secretary DigestevgciikNo ratings yet
- Con Law OutlineDocument26 pagesCon Law OutlineABC_1234_LAW100% (1)
- In Re Cunanan 94 PHIL. 534, MARCH 18, 1954 FactsDocument2 pagesIn Re Cunanan 94 PHIL. 534, MARCH 18, 1954 FactsMagr EscaNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law Case ReviewDocument73 pagesAdministrative Law Case ReviewthriftydigNo ratings yet
- Bar Questions and Answers Political LawDocument228 pagesBar Questions and Answers Political LawDee Why100% (4)
- Dahl PowerDocument15 pagesDahl PowerCatalin SamoilNo ratings yet
- 1.president Rodrigo Duterte Vetoed The Anti Endo Bill Which Is Beneficial For Workers.Document53 pages1.president Rodrigo Duterte Vetoed The Anti Endo Bill Which Is Beneficial For Workers.tiffany shyn raloNo ratings yet
- Bengzon vs. Drilon (208 SCRA 133)Document23 pagesBengzon vs. Drilon (208 SCRA 133)Mak FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ongsuco vs. MalonesDocument1 pageOngsuco vs. Malonesxx_stripped52100% (1)
- An Analysis of The Rights of Minority Shareholders and The Remedies Available To Them in Case of Oppression Done by The Majority ShareholdersDocument14 pagesAn Analysis of The Rights of Minority Shareholders and The Remedies Available To Them in Case of Oppression Done by The Majority ShareholdersIpkshita SinghNo ratings yet
- United States v. Bull, G.R. No. L-5270, 15 January 1910Document12 pagesUnited States v. Bull, G.R. No. L-5270, 15 January 1910Dominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument23 pagesSeparation of PowersLubna Iftikhar 4506-FSL/LLB/F15No ratings yet
- Legislative Process - Senate of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesLegislative Process - Senate of The Philippinescharles batagaNo ratings yet
- Veto Power of The MayorDocument3 pagesVeto Power of The MayoredcelquibenNo ratings yet
- Department of The Interior and Local GovernmentDocument3 pagesDepartment of The Interior and Local Governmentruss8dikoNo ratings yet
- The US Constitution PowerPointDocument100 pagesThe US Constitution PowerPointe_29No ratings yet
- Effect of Laws - RAC and LGCDocument5 pagesEffect of Laws - RAC and LGCErica Mae VistaNo ratings yet
- Semester-1: Powers and Functions of Indian PresidentDocument25 pagesSemester-1: Powers and Functions of Indian PresidentRohit VardhanNo ratings yet
- Stat Con RecitDocument141 pagesStat Con RecitJhon Allain HisolaNo ratings yet
- Parliamentary DemocracyDocument4 pagesParliamentary DemocracyLucky MalhotraNo ratings yet
- 1928 Congressional RecordsDocument17 pages1928 Congressional RecordsNomadFamily Shabazz-ElNo ratings yet
- Proposed Amended Constitution Federation of Student Governments Negros Oriental State UniversityDocument24 pagesProposed Amended Constitution Federation of Student Governments Negros Oriental State UniversityJohn Kenneth BoholNo ratings yet
- Raw Consti Module 8Document19 pagesRaw Consti Module 8Ryan Derrick GacayanNo ratings yet
- Project Assignment Topics Ps 1Document21 pagesProject Assignment Topics Ps 1Rupesh 1312No ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument15 pagesSeparation of PowersYusuph kiswagerNo ratings yet
- Doctrines in Constitutional Law: This Study Resource WasDocument8 pagesDoctrines in Constitutional Law: This Study Resource WasVeah CaabayNo ratings yet
- President: Election of The PresidentDocument8 pagesPresident: Election of The PresidentDhruva Chandra PandeyNo ratings yet
How A Bill Becomes A Law
How A Bill Becomes A Law
Uploaded by
legalfitz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesThis document outlines the process for how a bill becomes a law in the Senate and House of Representatives in the Philippines. It involves several steps including preparation and filing of the bill, committee consideration and action, plenary consideration and voting, reconciliation if different versions pass each chamber, enrollment, transmittal to the president, and it becoming law with the president's signature or overriding a veto. The process is similar in both chambers but with some differences in committee referrals and votes required.
Original Description:
Legislative Procedure
Original Title
How a Bill Becomes a Law
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the process for how a bill becomes a law in the Senate and House of Representatives in the Philippines. It involves several steps including preparation and filing of the bill, committee consideration and action, plenary consideration and voting, reconciliation if different versions pass each chamber, enrollment, transmittal to the president, and it becoming law with the president's signature or overriding a veto. The process is similar in both chambers but with some differences in committee referrals and votes required.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A Law
How A Bill Becomes A Law
Uploaded by
legalfitzThis document outlines the process for how a bill becomes a law in the Senate and House of Representatives in the Philippines. It involves several steps including preparation and filing of the bill, committee consideration and action, plenary consideration and voting, reconciliation if different versions pass each chamber, enrollment, transmittal to the president, and it becoming law with the president's signature or overriding a veto. The process is similar in both chambers but with some differences in committee referrals and votes required.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
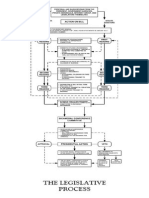
HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW
SENATE
1
Preparation of bill
HOUSE
1
> Drafting of bill by the Senator (through
either his staff or a proponent)
> Drafting of bill by the Representative (through
either his staff or a proponent)
> Filing of bill
> Filing of bill
* the bill is assigned a number
* the bill is assigned a number
First Reading in Plenary
> Committee Referral
3
Preparation of bill
Committee consideration/action
First Reading in Plenary
> Committee Referral
Committee consideration/action
> Committee Hearing(s)
> Committee Hearing(s)
> Technical Working Group (if necessary
to consolidate several versions)
> Technical Working Group (if necessary to
consolidate several versions)
* The hearing is conducted by the Mother
Committee (primary committee
referral) then by the Committee on Appropriation
and Ways and Means Committee if there are
pertinent approrpriatiion provision and provisions
that will impact on government revenues,
respectively.
> Drafting of Committee Report
> Drafting of Committee Report
> Filing of Committee Report (after
aproval by majority of Members)
> Filing of Committee Report (after aproval by
majority of Members)
* the Committee Report/ Substitute bill is
assigned a number
* the Committee Report/ Substitute bill is assigned
a number
Plenary consideration/ Second Reading
Plenary consideration/ Second Reading
> Sponsorship of Committee Chairperson
and co-authors/co-sponsors
> Sponsorship of Committee Chairperson and coauthors/co-sponsors
> Interpellations by members of Senate
> Interpellations by members of the House of
Representatives
> Period of Amendments
> Period of Amendments
Committee amendments
Committee amendments
Individual amendments
Individual amendments
> Second reading through voting by
members of Senate
> Second reading through voting by members of
the House of Representatives
* Second reading approval may be reconsidered to allow perfecting/
* Second reading approval may be re-considered
to allow perfecting/
additional amendments in plenary or CR
may be re-committed to the
additional amendments in plenary or CR may be
re-committed to the
Mother Committee
Mother Committee
Plenary consideration/ Third Reading
> Third reading of the bill through voting
by members of Senate
> Third reading of the bill through voting by
members of the House of Representatives
* Approval on Third Reading takes place 3
session days after distribution of copies of
approved on Second reading version to
the Members except if the
* Approval on Third Reading takes place 3 session
days after distribution of copies of approved on
Second reading version to the Members except if
the
bill was certified urgent by the President in
which case the 3 days is dispensed with.
bill was certified urgent by the President in which
case the 3 days is dispensed with.
Sent to House of Representatives for
concurrence
> if House of Rep still has no counterpart
bill that has been acted on, then this bill
undergoes the usual process of legislation
7
Consolidation of Senate and House version
Sent to the Senate for concurrence
> if Senate still has no counterpart bill that has
been acted on, then this bill undergoes the usual
process of legislation
Consolidation of House and Senate version
> if compatible, then versions are
consolidated into one enrolled bill
> if compatible, then versions are consolidated
into one enrolled bill
> if there are differences, a BICAMERAL
CONFERENCE COMMITTEE is formed to
reconcile conflicting provisions*
> if there are differences, a BICAMERAL
CONFERENCE COMMITTEE is formed to reconcile
conflicting provisions
Filing/ Ratification of Conference
Committee Report by both Chambers
Preparation and Printing of Enrolled Bill
10
Plenary consideration/ Third Reading
Filing/ Ratification of Conference Committee
Report by both Chambers
Transmittal of Enrolled Bill to the President for approval
> if signed, then bill becomes LAW
> if vetoed, then bill is returned to Congress
if Senate decides to override veto, then a 2/3 vote of all members must be obtained, PROVIDED
that the House of Representatives likewise follows this condition
> if President fails to communicate his veto of the bill within 30 days after receipt thereof, the bill
shall lapse into law
* Note: Bicam Committee can come up with a bill different from the Senate and the House
(Tolentino vs. Sec. of Finance)
You might also like
- Robert's Rules of Order (Revised for Deliberative Assemblies)From EverandRobert's Rules of Order (Revised for Deliberative Assemblies)No ratings yet
- Legislative Process FlowchartDocument3 pagesLegislative Process FlowchartHanna Quiambao100% (3)
- How A Bill Becomes Law in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes Law in The PhilippinesAngelina Villaver Reoja100% (1)
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument5 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawKevin KroytNo ratings yet
- Legislative Process - How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument6 pagesLegislative Process - How A Bill Becomes A LawFatzie Mendoza100% (2)
- How A Bill Becomes A Law AssignmentDocument2 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A Law Assignmenteduardo wapanioNo ratings yet
- 12 Steps Before A Bill Becomes A Law.Document4 pages12 Steps Before A Bill Becomes A Law.Racquel BatinoNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawSam B. PinedaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument3 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawclsNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument14 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawmimaymiNo ratings yet
- Bills and Parliamentary Procedure M2-1Document16 pagesBills and Parliamentary Procedure M2-1Deb DasNo ratings yet
- I. Law-Making Process in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesI. Law-Making Process in The PhilippinesNathaniel LepasanaNo ratings yet
- Statcon Bills OrdinancesDocument5 pagesStatcon Bills OrdinancesVic FrondaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument10 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawEve SaltNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A Law - SummarizedDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A Law - SummarizedNathaniel JosephNo ratings yet
- LawmakingDocument3 pagesLawmakingJaps PunoNo ratings yet
- Legislation 02042020 062141pmDocument3 pagesLegislation 02042020 062141pmHyder KhanNo ratings yet
- Chap02legislativeprocedureinpakistan 150706184115 Lva1 App6892Document3 pagesChap02legislativeprocedureinpakistan 150706184115 Lva1 App6892Hafsa SarfrazNo ratings yet
- BoL Notes-2Document15 pagesBoL Notes-2Rak kaurNo ratings yet
- PTT Steps in Passage of Bill in Philippine LegislatureDocument4 pagesPTT Steps in Passage of Bill in Philippine LegislatureMary Rose B. MendovaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument3 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawAurea Zambrano LibiranNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawMahri Rieanne Delle LangbisNo ratings yet
- Primrose Vien G. Ferolino July 30, 2019 Block 10 7:30-9:00 PM TTHDocument3 pagesPrimrose Vien G. Ferolino July 30, 2019 Block 10 7:30-9:00 PM TTHPrim Rose VienNo ratings yet
- Procedure of LegislationDocument8 pagesProcedure of LegislationSoomro KhanNo ratings yet
- Law Making Process or Legislative Procedure in PakistanDocument3 pagesLaw Making Process or Legislative Procedure in PakistanAbdullah FaizNo ratings yet
- Legislative Procedure in Pakistan: Parliamentairan System of PakistanDocument5 pagesLegislative Procedure in Pakistan: Parliamentairan System of PakistanKaneez FatimaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Become An ActDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Become An Actkaushal yadavNo ratings yet
- Legislative Process:: ConstitutionDocument4 pagesLegislative Process:: ConstitutionRameezNo ratings yet
- Legislation Process: How A Bill Becomes A Law 1. Preparation of The BillDocument3 pagesLegislation Process: How A Bill Becomes A Law 1. Preparation of The BillAngel SagubanNo ratings yet
- Viva Voce: Division of The House Nominal VotingDocument3 pagesViva Voce: Division of The House Nominal VotingEmma SchultzNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes Law in The Philippines TetaDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes Law in The Philippines TetaJobel Sibal Capunfuerza100% (1)
- LAW-MAKING PROCESS: The Summary Example Bill of The SenateDocument3 pagesLAW-MAKING PROCESS: The Summary Example Bill of The SenateOliver PenalberNo ratings yet
- Climate 2Document12 pagesClimate 2boranihar34No ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument1 pageHow A Bill Becomes A LawNurseAmyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document5 pagesUnit 5Junard PajamaNo ratings yet
- Hand Out LegislativeDocument2 pagesHand Out LegislativeMarivic PuddunanNo ratings yet
- W10 CBMDocument2 pagesW10 CBMabhinaya24396No ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument4 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawJcarLo B AglibtNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument5 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A Lawshynah clarinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 B. LAW 20214Document3 pagesAssignment 01 B. LAW 20214Abdul RafayNo ratings yet
- Committee Consideration/Action - Committee Evaluate The Bill andDocument2 pagesCommittee Consideration/Action - Committee Evaluate The Bill andJennifer CamaNo ratings yet
- Legislative Procedure For Passing of Bills in State LegislatururesDocument12 pagesLegislative Procedure For Passing of Bills in State LegislatururesShreya VermaNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument3 pagesHow A Bill Becomes A LawRoxanne LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Legislative ProcessDocument15 pagesLegislative ProcessfilodoxiaNo ratings yet
- Congress SDocument3 pagesCongress SGlencie PimentelNo ratings yet
- A Written Report in Political Science in Article VI: Legislative Department (Section 26 and 27)Document7 pagesA Written Report in Political Science in Article VI: Legislative Department (Section 26 and 27)Rohj EbreoNo ratings yet
- Statcon Review How Bill Becomes A Law To TolentinoDocument3 pagesStatcon Review How Bill Becomes A Law To Tolentinorose ann bulanNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes A LawDocument1 pageHow A Bill Becomes A Lawryanzafra30No ratings yet
- Summary of Report (grp.4 PA 141)Document7 pagesSummary of Report (grp.4 PA 141)Morthiza EmbongNo ratings yet
- How A Bill Becomes Law in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageHow A Bill Becomes Law in The PhilippinesArt CrestFall ManlongatNo ratings yet
- Law Making ProcedureDocument13 pagesLaw Making Procedurekhushi guptaNo ratings yet
- Passage of Bill Into Law - House of RepresentativesDocument3 pagesPassage of Bill Into Law - House of RepresentativesFRANCHETTE FERNANDEZ SIMENENo ratings yet
- LegRes Legislative ProcessDocument17 pagesLegRes Legislative ProcessChandyNo ratings yet
- Legislative Process - Senate of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesLegislative Process - Senate of The PhilippinesJosephson AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- The Law Making Process in UgandaDocument4 pagesThe Law Making Process in UgandaremojamwaNo ratings yet
- The Legislative Process: Elaine Ruby B. Elihay Gr. 11-St. RitaDocument3 pagesThe Legislative Process: Elaine Ruby B. Elihay Gr. 11-St. RitaArlyn Apple ElihayNo ratings yet
- Legres Midterm NotesDocument13 pagesLegres Midterm NotesWater MelonNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance Week 2: Second QuarterDocument14 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance Week 2: Second QuarterLehanne BellenNo ratings yet
- Passage of BillDocument2 pagesPassage of BillErica Mae VistaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Henry M. Robert, Daniel H Honemann, Thomas J Balch, Daniel E. Seabold & Shmuel Gerber's Robert's Rules of OrderFrom EverandSummary of Henry M. Robert, Daniel H Honemann, Thomas J Balch, Daniel E. Seabold & Shmuel Gerber's Robert's Rules of OrderNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Constitutional Law 1Document23 pagesSyllabus For Constitutional Law 1Ashabe GuroNo ratings yet
- 4 - Separation of Powers - Check and BalanceDocument13 pages4 - Separation of Powers - Check and BalanceBhuwan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stat ConDocument7 pagesStat ConJC TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Ang NARS vs. Executive Secretary DigestDocument2 pagesAng NARS vs. Executive Secretary DigestevgciikNo ratings yet
- Con Law OutlineDocument26 pagesCon Law OutlineABC_1234_LAW100% (1)
- In Re Cunanan 94 PHIL. 534, MARCH 18, 1954 FactsDocument2 pagesIn Re Cunanan 94 PHIL. 534, MARCH 18, 1954 FactsMagr EscaNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law Case ReviewDocument73 pagesAdministrative Law Case ReviewthriftydigNo ratings yet
- Bar Questions and Answers Political LawDocument228 pagesBar Questions and Answers Political LawDee Why100% (4)
- Dahl PowerDocument15 pagesDahl PowerCatalin SamoilNo ratings yet
- 1.president Rodrigo Duterte Vetoed The Anti Endo Bill Which Is Beneficial For Workers.Document53 pages1.president Rodrigo Duterte Vetoed The Anti Endo Bill Which Is Beneficial For Workers.tiffany shyn raloNo ratings yet
- Bengzon vs. Drilon (208 SCRA 133)Document23 pagesBengzon vs. Drilon (208 SCRA 133)Mak FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ongsuco vs. MalonesDocument1 pageOngsuco vs. Malonesxx_stripped52100% (1)
- An Analysis of The Rights of Minority Shareholders and The Remedies Available To Them in Case of Oppression Done by The Majority ShareholdersDocument14 pagesAn Analysis of The Rights of Minority Shareholders and The Remedies Available To Them in Case of Oppression Done by The Majority ShareholdersIpkshita SinghNo ratings yet
- United States v. Bull, G.R. No. L-5270, 15 January 1910Document12 pagesUnited States v. Bull, G.R. No. L-5270, 15 January 1910Dominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument23 pagesSeparation of PowersLubna Iftikhar 4506-FSL/LLB/F15No ratings yet
- Legislative Process - Senate of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesLegislative Process - Senate of The Philippinescharles batagaNo ratings yet
- Veto Power of The MayorDocument3 pagesVeto Power of The MayoredcelquibenNo ratings yet
- Department of The Interior and Local GovernmentDocument3 pagesDepartment of The Interior and Local Governmentruss8dikoNo ratings yet
- The US Constitution PowerPointDocument100 pagesThe US Constitution PowerPointe_29No ratings yet
- Effect of Laws - RAC and LGCDocument5 pagesEffect of Laws - RAC and LGCErica Mae VistaNo ratings yet
- Semester-1: Powers and Functions of Indian PresidentDocument25 pagesSemester-1: Powers and Functions of Indian PresidentRohit VardhanNo ratings yet
- Stat Con RecitDocument141 pagesStat Con RecitJhon Allain HisolaNo ratings yet
- Parliamentary DemocracyDocument4 pagesParliamentary DemocracyLucky MalhotraNo ratings yet
- 1928 Congressional RecordsDocument17 pages1928 Congressional RecordsNomadFamily Shabazz-ElNo ratings yet
- Proposed Amended Constitution Federation of Student Governments Negros Oriental State UniversityDocument24 pagesProposed Amended Constitution Federation of Student Governments Negros Oriental State UniversityJohn Kenneth BoholNo ratings yet
- Raw Consti Module 8Document19 pagesRaw Consti Module 8Ryan Derrick GacayanNo ratings yet
- Project Assignment Topics Ps 1Document21 pagesProject Assignment Topics Ps 1Rupesh 1312No ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument15 pagesSeparation of PowersYusuph kiswagerNo ratings yet
- Doctrines in Constitutional Law: This Study Resource WasDocument8 pagesDoctrines in Constitutional Law: This Study Resource WasVeah CaabayNo ratings yet
- President: Election of The PresidentDocument8 pagesPresident: Election of The PresidentDhruva Chandra PandeyNo ratings yet