Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Sheet Diffraction
Tutorial Sheet Diffraction
Uploaded by
NsBhasinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- IATA EASA Cross-Reference List User Manual Ed 1Document37 pagesIATA EASA Cross-Reference List User Manual Ed 1Андрей Лубяницкий50% (2)
- Problems On DiffractionDocument2 pagesProblems On DiffractionBrajesh Kumar67% (3)
- Assignment Diffraction 2016Document3 pagesAssignment Diffraction 2016Ritesh MeelNo ratings yet
- Engineering OpticsDocument2 pagesEngineering OpticshsuyabNo ratings yet
- 7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDFDocument9 pages7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDFWakkuNo ratings yet
- Bangabasi College Kolkata NPTEL Local Chapter: Problems On OpticsDocument3 pagesBangabasi College Kolkata NPTEL Local Chapter: Problems On OpticsRajarsi ThakurNo ratings yet
- 01 Optics Part III Diffraction DHK Se AjwjejjsehDocument18 pages01 Optics Part III Diffraction DHK Se AjwjejjsehNareshNo ratings yet
- Phenomenon of Diffraction of LightDocument26 pagesPhenomenon of Diffraction of LightAditya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- AP 2 Module 3Document25 pagesAP 2 Module 3Anshuman NandanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Diffraction 2016Document3 pagesAssignment Diffraction 2016Mankush JainNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Modified Aug2011Document93 pagesDiffraction Modified Aug2011Shrinivas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Fraunhofer DiffractionDocument4 pagesFraunhofer DiffractionKshitij GulatiNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Grating: Condition For Maximum Intensity Double Slit Multiple Slits High Resolution Peak IntensitiesDocument8 pagesDiffraction Grating: Condition For Maximum Intensity Double Slit Multiple Slits High Resolution Peak IntensitiesGhannam MomoNo ratings yet
- Terahertz Diffractive Optics-Smart Control Over RaDocument24 pagesTerahertz Diffractive Optics-Smart Control Over RaHeberley Tobon MayaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4Adarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Optics, Set 2 Diffraction Gratings: D Detector ADocument20 pagesOptics, Set 2 Diffraction Gratings: D Detector ADaniel AdebayoNo ratings yet
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocument72 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsSIDDHARTHANo ratings yet
- Wireless Mohammed Abuhajar HW1Document6 pagesWireless Mohammed Abuhajar HW1mcsist1No ratings yet
- Q 1Document134 pagesQ 1Niessuh Ila0% (1)
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocument72 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDhyey DESAIIINo ratings yet
- 04 Propagation MechanismDocument35 pages04 Propagation MechanismHidayah Kamaludin100% (1)
- Lab Report Interferometer....Document14 pagesLab Report Interferometer....musabNo ratings yet
- QbankphyaaDocument33 pagesQbankphyaaSteven Brown100% (1)
- 2 DiffractdionDocument124 pages2 DiffractdionShrinivas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Rohini 24928786475Document12 pagesRohini 24928786475aswinvirat84No ratings yet
- 2014 EE170A Midterm ProblemsDocument3 pages2014 EE170A Midterm Problemssurv surveyNo ratings yet
- DiffractionDocument11 pagesDiffractionAnuj TomarNo ratings yet
- 11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitDocument4 pages11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitAliiAmiirNo ratings yet
- Diffraction of Light WavesDocument24 pagesDiffraction of Light Wavesbenjamin swokaNo ratings yet
- Waves&Optics Assignment PDFDocument4 pagesWaves&Optics Assignment PDFTanisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 3Document1 pageAssignment No 3ricchivedant07No ratings yet
- FTIRDocument12 pagesFTIRReemaNo ratings yet
- Fabry-Pérot Interferometer: TheoryDocument5 pagesFabry-Pérot Interferometer: TheorychandreshwarNo ratings yet
- 2 DiffractionDocument69 pages2 DiffractionChop DownNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Four-Wave Mixing in Optical Fiber Links With Non-Uniform Chromatic DispersionDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Four-Wave Mixing in Optical Fiber Links With Non-Uniform Chromatic DispersionjrosouzaNo ratings yet
- Laser and Fibre Optics Assignment-1Document2 pagesLaser and Fibre Optics Assignment-1Paras VermaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 StudentDocument15 pagesLecture 4 StudentJanine NaluzNo ratings yet
- Part A University Questions2019 2020Document9 pagesPart A University Questions2019 2020thiruvengadam cNo ratings yet
- The Spectrum Analyzer and The Mode Structure of A LaserDocument7 pagesThe Spectrum Analyzer and The Mode Structure of A LasertenpointerNo ratings yet
- Que Bank Optics PDFDocument4 pagesQue Bank Optics PDFLeenaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics Sixth EditionDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Physics Sixth EditionQahtan Al-zaidiNo ratings yet
- Fiberoptic NotesDocument8 pagesFiberoptic NotesFurqan WarisNo ratings yet
- Intensitas Difraksi Beberapa Celah Dan GridDocument6 pagesIntensitas Difraksi Beberapa Celah Dan GridzoelfadillhNo ratings yet
- Session:: Class: IST YEARDocument9 pagesSession:: Class: IST YEARAppuGappu10% (1)
- Optical FiberDocument16 pagesOptical FiberRinju DuttNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightDocument30 pagesApplied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightWilliam MartinezNo ratings yet
- Laser DiodesDocument11 pagesLaser DiodesMireiaNo ratings yet
- Interference McqsDocument15 pagesInterference McqsJerry Johnson88% (8)
- JSL - Lecture 35-18-04-18 - Optical Fiber Arrays and Refractive Index MeasurementsDocument24 pagesJSL - Lecture 35-18-04-18 - Optical Fiber Arrays and Refractive Index MeasurementsVishweshRaviShrimaliNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument10 pagesNew Text DocumentTanuja MagarNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightDocument28 pagesApplied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightADARSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Physical Optics and Modern OpticsDocument31 pagesPhysical Optics and Modern Opticsammavan akNo ratings yet
- Basics of Optical Data Communication: 1.1 Light Propagation in Optical Fibers and WaveguidesDocument35 pagesBasics of Optical Data Communication: 1.1 Light Propagation in Optical Fibers and WaveguidesMarilene MachadoNo ratings yet
- Four-Wave Mixing in Optical Fibers and Its ApplicationsDocument6 pagesFour-Wave Mixing in Optical Fibers and Its Applicationsgjohnson1968No ratings yet
- Week8 InterferometersDocument84 pagesWeek8 InterferometersArijit PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Concept of Resolving Power in The FabryPerot Interferometer Using A Digital Simulation Ejp6 5 010Document9 pagesUnderstanding The Concept of Resolving Power in The FabryPerot Interferometer Using A Digital Simulation Ejp6 5 010Rousse AldavaNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpaceFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpaceNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility: Analysis and Case Studies in TransportationFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility: Analysis and Case Studies in TransportationNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsFrom EverandDigital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Quiz Contsts Questions ChemistryDocument49 pagesQuiz Contsts Questions ChemistryNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalDocument6 pagesPhysics PracticalNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatics PDFDocument13 pagesHydrostatics PDFNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Lab AllWeeksDocument9 pagesLab AllWeeksNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension PDFDocument7 pagesSurface Tension PDFNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) AcknowledgementPageDocument1 pageJEE (Main) AcknowledgementPageNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument14 pagesSolutionsNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Kvpy Paper 2014Document25 pagesKvpy Paper 2014Avinash PalNo ratings yet
- Portable Boring MachineDocument2 pagesPortable Boring Machinesexmanijak100% (1)
- School Form 5A (SF 5A)Document3 pagesSchool Form 5A (SF 5A)Ijherafel Baliola YusophNo ratings yet
- Exadata and Database Machine Administration Workshop PDFDocument316 pagesExadata and Database Machine Administration Workshop PDFusman newtonNo ratings yet
- Gas Properties, Flowrate and Conditions: Reciprocating Compressor Calculation SheetDocument5 pagesGas Properties, Flowrate and Conditions: Reciprocating Compressor Calculation SheetNaqqash Sajid0% (2)
- Consultants/Contractors Confirmation Check List: Consultant/Contractor UndertakingDocument1 pageConsultants/Contractors Confirmation Check List: Consultant/Contractor Undertakingfishy18No ratings yet
- Lingerie Insight February 2011Document52 pagesLingerie Insight February 2011gab20100% (2)
- Chain Surveying Obstacles PPT DownloadDocument24 pagesChain Surveying Obstacles PPT DownloadKreesthu Reddy100% (1)
- 11 RECT TANK 4.0M X 3.0M X 3.3M H - Flocculator PDFDocument3 pages11 RECT TANK 4.0M X 3.0M X 3.3M H - Flocculator PDFaaditya chopadeNo ratings yet
- The Great Gatsby (1925)Document100 pagesThe Great Gatsby (1925)Radu-Alexandru BulaiNo ratings yet
- Igs NT 2.6.5Document6 pagesIgs NT 2.6.5Luis JesusNo ratings yet
- Sic Mos Trench SJ Micromachines-13-01770-V2Document12 pagesSic Mos Trench SJ Micromachines-13-01770-V2terry chenNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Electrostatic Precipitator Performance and Comparison With Existing Theoretical Prediction ModelsDocument23 pagesExperimental Study of Electrostatic Precipitator Performance and Comparison With Existing Theoretical Prediction ModelssamactrangNo ratings yet
- Communication Protocol For T300CDocument14 pagesCommunication Protocol For T300CChristian Vásquez SánchezNo ratings yet
- Leaf 2Document5 pagesLeaf 2Mannu GuptaNo ratings yet
- RF Wmhi14ds DF NDocument8 pagesRF Wmhi14ds DF NTabletaUnicaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan: Teacher: Blessie Jean A. YbañezDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan: Teacher: Blessie Jean A. YbañezJENNIFER YBAÑEZNo ratings yet
- Contaminants in Oils and Fats: Li D Lti Analysis and RegulationsDocument30 pagesContaminants in Oils and Fats: Li D Lti Analysis and RegulationsediasianagriNo ratings yet
- U5 - Ultrasonic InspectionDocument83 pagesU5 - Ultrasonic InspectionSuraj B SNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Chanting of Sacred Sound Om (Aum) As A Healing PracticeDocument6 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Chanting of Sacred Sound Om (Aum) As A Healing Practicejayesh rajputNo ratings yet
- Olivicultura de PrecisionDocument13 pagesOlivicultura de PrecisionJT546No ratings yet
- Dorothea Orem Theory Slideshow TranscriptDocument5 pagesDorothea Orem Theory Slideshow TranscriptpambeheraNo ratings yet
- Synchro Studio 8: Getting Started and What's New in Version 8Document35 pagesSynchro Studio 8: Getting Started and What's New in Version 8Fernando Luis FerrerNo ratings yet
- Program For Live Streaming NG Buwan NG Wika 2022Document2 pagesProgram For Live Streaming NG Buwan NG Wika 2022Timosa TeyobNo ratings yet
- Vendor Security Due Diligence ChecklistDocument9 pagesVendor Security Due Diligence ChecklistSukhveer SinghNo ratings yet
- STARS (SHE Tracking Analysis Reporting System) Plant ViewDocument18 pagesSTARS (SHE Tracking Analysis Reporting System) Plant ViewrajatNo ratings yet
- Guide To Supply Chain Management RemediationV2Document26 pagesGuide To Supply Chain Management RemediationV2Andrada-DianaFilipciucNo ratings yet
- Student Handout Carbon CycleDocument6 pagesStudent Handout Carbon CycleKaveen DNo ratings yet
- MFG Procedure ManualDocument46 pagesMFG Procedure ManualAdinanNo ratings yet
- De Thi Thu TN THPT 2024 Tieng Anh So GD Ha NoiDocument23 pagesDe Thi Thu TN THPT 2024 Tieng Anh So GD Ha NoiQuang Lê Hồ DuyNo ratings yet
Tutorial Sheet Diffraction
Tutorial Sheet Diffraction
Uploaded by
NsBhasinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Sheet Diffraction
Tutorial Sheet Diffraction
Uploaded by
NsBhasinCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS BBDNIIT
B. TECH. FIRST SEMESTER 2014-2015
UNIT III: WAVE OPTICS (DIFRACTION)
Q.1
Q.2
Q.3
Q.4
Q.5
Q.6
Q.7
Q.8
Q.9
Q.10
Q.11
Q.12
Q.13
Q.14
Q.15
Q.16
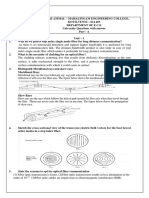
What is meant by diffraction of light? Distinguish between Fresnels and Fraunhofer classes of
diffraction.
Discuss Fraunhofer diffraction due to single slit Derive an expression for intensity distribution and
show that the intensities of the successive maximum are nearly 1:4/92:4/25 2:4/492.
A single slit is illuminated by light composed of two wavelengths 1 and 2.One observes that due
to fraunhofer diffraction the first minima obtained for 1 coincides with second diffraction minima
of 2.What is the relation between 1 and 2.
In Fraunhofer diffraction due to a single slit, the screen is placed 2m away from the slit. If the slit
width is 0.2 mm and the first minima lies 5mm on either side of the central maxima, find the
wavelength of incident light.
Calculate the angle at which the first dark band and the next bright band are formed in the
Fraunhofer diffraction pattern of a slit of 0.3 mm width with monochromatic light of wavelength
6000.
A lens whose focal length is 50 cm. forms a Fraunhofer diffraction of a single slit of 0.3 mm.
width. Calculate the distances of the first dark band and of the next bright band on either side of the
central maximum. The wavelength of light used is 5890.
What do you understand by dispersive power of a plane transmission grating? Derive the
expression for it.
What do you understand by missing order spectrum? Show that only first order is possible if the
width of a grating element is less than twice the wavelength of light.
Show that the angular half width of a principal maximum in a plane transmission grating does not
depend upon the number of lines per unit length, but it depends on the total number of lines present
on the grating.
A diffraction grating used at normal incidence gives a yellow line ( =6000) in a certain special
order superimposed on a blue line ( =4800) of the next higher order. If the angle of diffraction is
sin-1(3/4), calculate the grating element.
How many orders will be visible, if the wavelength of the incident radiation is 5000 and the
number of lines on the grating is 2620 per inch.
In a grating spectrum, which spectral line in 5th order will overlap with 4th order line of 5890?
What is meant by the resolving power of an optical instrument? Explain Rayleighs criterion for
just resolution. Define limit of resolution and resolving power.
What do you understand by resolving power of a grating? Derive the necessary expression for it.
Calculate the minimum number of lines in a grating which will just resolve the lines of
wavelengths 5890 and 5896 in the second order.
A grating has 6,000 lines per cm drawn on it. If its width is 10 cm, calculate
A. The resolving power in the second order.
B. The smallest wavelength that can be resolved in the third order in 6000 wavelength region.
You might also like
- IATA EASA Cross-Reference List User Manual Ed 1Document37 pagesIATA EASA Cross-Reference List User Manual Ed 1Андрей Лубяницкий50% (2)
- Problems On DiffractionDocument2 pagesProblems On DiffractionBrajesh Kumar67% (3)
- Assignment Diffraction 2016Document3 pagesAssignment Diffraction 2016Ritesh MeelNo ratings yet
- Engineering OpticsDocument2 pagesEngineering OpticshsuyabNo ratings yet
- 7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDFDocument9 pages7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDFWakkuNo ratings yet
- Bangabasi College Kolkata NPTEL Local Chapter: Problems On OpticsDocument3 pagesBangabasi College Kolkata NPTEL Local Chapter: Problems On OpticsRajarsi ThakurNo ratings yet
- 01 Optics Part III Diffraction DHK Se AjwjejjsehDocument18 pages01 Optics Part III Diffraction DHK Se AjwjejjsehNareshNo ratings yet
- Phenomenon of Diffraction of LightDocument26 pagesPhenomenon of Diffraction of LightAditya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- AP 2 Module 3Document25 pagesAP 2 Module 3Anshuman NandanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Diffraction 2016Document3 pagesAssignment Diffraction 2016Mankush JainNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Modified Aug2011Document93 pagesDiffraction Modified Aug2011Shrinivas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Fraunhofer DiffractionDocument4 pagesFraunhofer DiffractionKshitij GulatiNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Grating: Condition For Maximum Intensity Double Slit Multiple Slits High Resolution Peak IntensitiesDocument8 pagesDiffraction Grating: Condition For Maximum Intensity Double Slit Multiple Slits High Resolution Peak IntensitiesGhannam MomoNo ratings yet
- Terahertz Diffractive Optics-Smart Control Over RaDocument24 pagesTerahertz Diffractive Optics-Smart Control Over RaHeberley Tobon MayaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4Adarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Optics, Set 2 Diffraction Gratings: D Detector ADocument20 pagesOptics, Set 2 Diffraction Gratings: D Detector ADaniel AdebayoNo ratings yet
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocument72 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsSIDDHARTHANo ratings yet
- Wireless Mohammed Abuhajar HW1Document6 pagesWireless Mohammed Abuhajar HW1mcsist1No ratings yet
- Q 1Document134 pagesQ 1Niessuh Ila0% (1)
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocument72 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDhyey DESAIIINo ratings yet
- 04 Propagation MechanismDocument35 pages04 Propagation MechanismHidayah Kamaludin100% (1)
- Lab Report Interferometer....Document14 pagesLab Report Interferometer....musabNo ratings yet
- QbankphyaaDocument33 pagesQbankphyaaSteven Brown100% (1)
- 2 DiffractdionDocument124 pages2 DiffractdionShrinivas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Rohini 24928786475Document12 pagesRohini 24928786475aswinvirat84No ratings yet
- 2014 EE170A Midterm ProblemsDocument3 pages2014 EE170A Midterm Problemssurv surveyNo ratings yet
- DiffractionDocument11 pagesDiffractionAnuj TomarNo ratings yet
- 11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitDocument4 pages11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitAliiAmiirNo ratings yet
- Diffraction of Light WavesDocument24 pagesDiffraction of Light Wavesbenjamin swokaNo ratings yet
- Waves&Optics Assignment PDFDocument4 pagesWaves&Optics Assignment PDFTanisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 3Document1 pageAssignment No 3ricchivedant07No ratings yet
- FTIRDocument12 pagesFTIRReemaNo ratings yet
- Fabry-Pérot Interferometer: TheoryDocument5 pagesFabry-Pérot Interferometer: TheorychandreshwarNo ratings yet
- 2 DiffractionDocument69 pages2 DiffractionChop DownNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Four-Wave Mixing in Optical Fiber Links With Non-Uniform Chromatic DispersionDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Four-Wave Mixing in Optical Fiber Links With Non-Uniform Chromatic DispersionjrosouzaNo ratings yet
- Laser and Fibre Optics Assignment-1Document2 pagesLaser and Fibre Optics Assignment-1Paras VermaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 StudentDocument15 pagesLecture 4 StudentJanine NaluzNo ratings yet
- Part A University Questions2019 2020Document9 pagesPart A University Questions2019 2020thiruvengadam cNo ratings yet
- The Spectrum Analyzer and The Mode Structure of A LaserDocument7 pagesThe Spectrum Analyzer and The Mode Structure of A LasertenpointerNo ratings yet
- Que Bank Optics PDFDocument4 pagesQue Bank Optics PDFLeenaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics Sixth EditionDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Physics Sixth EditionQahtan Al-zaidiNo ratings yet
- Fiberoptic NotesDocument8 pagesFiberoptic NotesFurqan WarisNo ratings yet
- Intensitas Difraksi Beberapa Celah Dan GridDocument6 pagesIntensitas Difraksi Beberapa Celah Dan GridzoelfadillhNo ratings yet
- Session:: Class: IST YEARDocument9 pagesSession:: Class: IST YEARAppuGappu10% (1)
- Optical FiberDocument16 pagesOptical FiberRinju DuttNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightDocument30 pagesApplied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightWilliam MartinezNo ratings yet
- Laser DiodesDocument11 pagesLaser DiodesMireiaNo ratings yet
- Interference McqsDocument15 pagesInterference McqsJerry Johnson88% (8)
- JSL - Lecture 35-18-04-18 - Optical Fiber Arrays and Refractive Index MeasurementsDocument24 pagesJSL - Lecture 35-18-04-18 - Optical Fiber Arrays and Refractive Index MeasurementsVishweshRaviShrimaliNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument10 pagesNew Text DocumentTanuja MagarNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightDocument28 pagesApplied Physics - I Question Bank - 1 Topic: Interference of LightADARSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Physical Optics and Modern OpticsDocument31 pagesPhysical Optics and Modern Opticsammavan akNo ratings yet
- Basics of Optical Data Communication: 1.1 Light Propagation in Optical Fibers and WaveguidesDocument35 pagesBasics of Optical Data Communication: 1.1 Light Propagation in Optical Fibers and WaveguidesMarilene MachadoNo ratings yet
- Four-Wave Mixing in Optical Fibers and Its ApplicationsDocument6 pagesFour-Wave Mixing in Optical Fibers and Its Applicationsgjohnson1968No ratings yet
- Week8 InterferometersDocument84 pagesWeek8 InterferometersArijit PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Concept of Resolving Power in The FabryPerot Interferometer Using A Digital Simulation Ejp6 5 010Document9 pagesUnderstanding The Concept of Resolving Power in The FabryPerot Interferometer Using A Digital Simulation Ejp6 5 010Rousse AldavaNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpaceFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpaceNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility: Analysis and Case Studies in TransportationFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility: Analysis and Case Studies in TransportationNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsFrom EverandDigital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Quiz Contsts Questions ChemistryDocument49 pagesQuiz Contsts Questions ChemistryNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalDocument6 pagesPhysics PracticalNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatics PDFDocument13 pagesHydrostatics PDFNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Lab AllWeeksDocument9 pagesLab AllWeeksNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension PDFDocument7 pagesSurface Tension PDFNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) AcknowledgementPageDocument1 pageJEE (Main) AcknowledgementPageNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument14 pagesSolutionsNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Kvpy Paper 2014Document25 pagesKvpy Paper 2014Avinash PalNo ratings yet
- Portable Boring MachineDocument2 pagesPortable Boring Machinesexmanijak100% (1)
- School Form 5A (SF 5A)Document3 pagesSchool Form 5A (SF 5A)Ijherafel Baliola YusophNo ratings yet
- Exadata and Database Machine Administration Workshop PDFDocument316 pagesExadata and Database Machine Administration Workshop PDFusman newtonNo ratings yet
- Gas Properties, Flowrate and Conditions: Reciprocating Compressor Calculation SheetDocument5 pagesGas Properties, Flowrate and Conditions: Reciprocating Compressor Calculation SheetNaqqash Sajid0% (2)
- Consultants/Contractors Confirmation Check List: Consultant/Contractor UndertakingDocument1 pageConsultants/Contractors Confirmation Check List: Consultant/Contractor Undertakingfishy18No ratings yet
- Lingerie Insight February 2011Document52 pagesLingerie Insight February 2011gab20100% (2)
- Chain Surveying Obstacles PPT DownloadDocument24 pagesChain Surveying Obstacles PPT DownloadKreesthu Reddy100% (1)
- 11 RECT TANK 4.0M X 3.0M X 3.3M H - Flocculator PDFDocument3 pages11 RECT TANK 4.0M X 3.0M X 3.3M H - Flocculator PDFaaditya chopadeNo ratings yet
- The Great Gatsby (1925)Document100 pagesThe Great Gatsby (1925)Radu-Alexandru BulaiNo ratings yet
- Igs NT 2.6.5Document6 pagesIgs NT 2.6.5Luis JesusNo ratings yet
- Sic Mos Trench SJ Micromachines-13-01770-V2Document12 pagesSic Mos Trench SJ Micromachines-13-01770-V2terry chenNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Electrostatic Precipitator Performance and Comparison With Existing Theoretical Prediction ModelsDocument23 pagesExperimental Study of Electrostatic Precipitator Performance and Comparison With Existing Theoretical Prediction ModelssamactrangNo ratings yet
- Communication Protocol For T300CDocument14 pagesCommunication Protocol For T300CChristian Vásquez SánchezNo ratings yet
- Leaf 2Document5 pagesLeaf 2Mannu GuptaNo ratings yet
- RF Wmhi14ds DF NDocument8 pagesRF Wmhi14ds DF NTabletaUnicaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan: Teacher: Blessie Jean A. YbañezDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan: Teacher: Blessie Jean A. YbañezJENNIFER YBAÑEZNo ratings yet
- Contaminants in Oils and Fats: Li D Lti Analysis and RegulationsDocument30 pagesContaminants in Oils and Fats: Li D Lti Analysis and RegulationsediasianagriNo ratings yet
- U5 - Ultrasonic InspectionDocument83 pagesU5 - Ultrasonic InspectionSuraj B SNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Chanting of Sacred Sound Om (Aum) As A Healing PracticeDocument6 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Chanting of Sacred Sound Om (Aum) As A Healing Practicejayesh rajputNo ratings yet
- Olivicultura de PrecisionDocument13 pagesOlivicultura de PrecisionJT546No ratings yet
- Dorothea Orem Theory Slideshow TranscriptDocument5 pagesDorothea Orem Theory Slideshow TranscriptpambeheraNo ratings yet
- Synchro Studio 8: Getting Started and What's New in Version 8Document35 pagesSynchro Studio 8: Getting Started and What's New in Version 8Fernando Luis FerrerNo ratings yet
- Program For Live Streaming NG Buwan NG Wika 2022Document2 pagesProgram For Live Streaming NG Buwan NG Wika 2022Timosa TeyobNo ratings yet
- Vendor Security Due Diligence ChecklistDocument9 pagesVendor Security Due Diligence ChecklistSukhveer SinghNo ratings yet
- STARS (SHE Tracking Analysis Reporting System) Plant ViewDocument18 pagesSTARS (SHE Tracking Analysis Reporting System) Plant ViewrajatNo ratings yet
- Guide To Supply Chain Management RemediationV2Document26 pagesGuide To Supply Chain Management RemediationV2Andrada-DianaFilipciucNo ratings yet
- Student Handout Carbon CycleDocument6 pagesStudent Handout Carbon CycleKaveen DNo ratings yet
- MFG Procedure ManualDocument46 pagesMFG Procedure ManualAdinanNo ratings yet
- De Thi Thu TN THPT 2024 Tieng Anh So GD Ha NoiDocument23 pagesDe Thi Thu TN THPT 2024 Tieng Anh So GD Ha NoiQuang Lê Hồ DuyNo ratings yet