Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Te2 Module 4
Te2 Module 4
Uploaded by
rmle100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views4 pagesThis document contains 11 soil mechanics problems related to compressibility and shear strength of soils. Problem 1 asks to compute the settlement of a clay layer under a landfill. Problem 2 gives borehole log data and asks about submerged unit weight, effective stress, and settlement of a clay layer. Problem 3 gives a soil profile and asks about settlement of a clay layer under a uniform load for different preconsolidation pressures.
Original Description:
soil mechanics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 11 soil mechanics problems related to compressibility and shear strength of soils. Problem 1 asks to compute the settlement of a clay layer under a landfill. Problem 2 gives borehole log data and asks about submerged unit weight, effective stress, and settlement of a clay layer. Problem 3 gives a soil profile and asks about settlement of a clay layer under a uniform load for different preconsolidation pressures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views4 pagesTe2 Module 4
Te2 Module 4
Uploaded by
rmleThis document contains 11 soil mechanics problems related to compressibility and shear strength of soils. Problem 1 asks to compute the settlement of a clay layer under a landfill. Problem 2 gives borehole log data and asks about submerged unit weight, effective stress, and settlement of a clay layer. Problem 3 gives a soil profile and asks about settlement of a clay layer under a uniform load for different preconsolidation pressures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
MODULE NO.
4 (HYDRO-GEO)
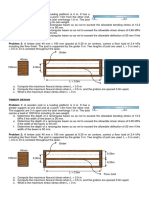
PROBLEM NO. 1 (TOPIC: COMPRESSIBILITY OF SOIL)
A 2-m clay layer (e=0.92, G=2.72, Cc=1/3) is overlain with 3 m thick of sand layer (e=0.5,
G=2.62, MC=0).
The water table is 1.5 m below the ground (sand) surface. If a 3-m thick
3
land fill (=17.3 KN/m ) is placed over the existing ground surface, compute the settlement of
the clay layer.
Ans: 106.7 mm
PROBLEM NO. 2 (TOPIC: COMPRESSIBILITY OF SOIL)
Given in the Figure is the borehole log in a project site. The proposed building will exert
a net stress of 12 Newton per square centimeter.
a.) Determine the submerged unit weight of the clay.
b.) Determine the effective vertical stress at the mid-height of the clay layer.
c.) Determine the average settlement of the normally consolidated clay layer. Use
compression index Cc=0.009(LL-10).
Ans: a.) 8.278 KN/m3; b.) 40 mm; c.) 152.8 mm
PROBLEM NO. 3 (TOPIC: COMPRESSIBILITY OF SOIL)
A soil is shown in the figure. A uniformly distributed load, P=50 Kpa, is applied at the
ground surface. Assume Cs=(1/5)Cc. Determine the settlement of the clay layer caused by
primary consolidation if:
1 (MODULE 4)
a.) The clay is normally consolidated.
b.) The preconsolidation pressure pc is 210 Kpa.
c.) The preconsolidation pressure pc is 150 Kpa.
Ans: a.) 200 mm; b.) 40 mm; c.) 152.8 mm
PROBLEM NO. 4 (TOPIC: COMPRESSIBILITY OF SOIL)
A normally consolidated clay layer, 3 m thick, has the following properties:
Initial void ratio, e=0.8
Compression index, Cc=0.25
Average effective pressure, p0=125 Kpa
Expected pressure increase, P=45 Kpa
Secondary compression index, C=0.02
Time for completion of primary settlement=1.5 years
What is the total settlement of the clay layer five years after the completion of primary
consolidation settlement?
Ans: 73.4 mm
2 (MODULE 4)
PROBLEM NO. 5 (TOPIC: COMPRESSIBILITY OF SOIL)
A rigid footing 1.2-m in diameter is constructed on unsaturated clay layer. The load on
the footing is 170 KN. Estimate the immediate settlement. Assume the clay has 6900 Kpa and
=0.2, let If=0.79.
Ans: 19.8 mm
PROBLEM NO. 6 (TOPIC: SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL)
A direct test is performed on a specimen of dry sand. The shear box is circular in cross
section with a diameter of 50 mm. The normal force imposed on the specimen is 250 N. The
shears when the shear force is 150 N. determine the angle of internal friction of this sand.
Ans: =30.96
PROBLEM NO. 7 (TOPIC: SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL)
A 7-m thick soil has water table 3m below the ground surface. The soil above the water
table has degree of saturation of 45%, void ratio of the soil is 0.4 and the solids have specific
gravity of 2.70. Tests show that the soil have angle of internal friction of 32 and cohesion of
14.6 kPa. What is the potential shear strength on a horizontal plane at a depth of 2 m below the
ground surface?
Ans: =39.82 kPa
PROBLEM NO. 8 (TOPIC: SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL)
In a triaxial test, a specimen of saturated (normally consolidated) clay was consolidated
under a chamber confining pressure of 90 kilopascals. The axial stress on the specimen was
then increased allowing the drainage from the specimen. The specimen fails when the deviator
stress is 60 kilopascals. The Pore water pressure (pw) at the time was 40 kilopascals. What the
consolidated drained friction angle (phi):
Ans: =22.024
3 (MODULE 4)
PROBLEM NO. 9 (TOPIC: SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL)
A triaxial test on a saturated soil has the following results:
Cell pressure
(kPa)
Deviator stress
(kPa)
200
119
400
143
600
178
a.) Determine the drained angle of internal friction of the soil.
b.) Determine the cohesion of the soil in drained condition.
Ans: a.) 8.737; b.) 42.22 kPa
Pore pressure
(kPa)
142.5
275.5
396
PROBLEM NO. 10 (TOPIC: SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL)
An unconfined compression test was carried out a saturated clay sample. The maximum
load the clay sustained was 127 N and the vertical displacement is 0.8 mm. The size of the
sample was 38 mm diameter x 76 mm long.
a.) Calculate the axial strain of the soil sample.
b.) Calculate the major principal stress at failure.
c.) Calculate the undrained shear strength of the soil sample.
Ans: a.) 0.010526 mm/mm b.) 110.814 kPa; c.) 55.4 kPa
PROBLEM NO. 11 (TOPIC: SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL)
The following data were obtained from a triaxial test on a cohesive soil:
Critical shearing stress=70 kPa
Angle of friction=28
Cohesion=30 kPa
a.) Determine the normal stress at failure plane.
b.) Determine the maximum normal stress (plunger stress) applied on the soil.
c.) Determine the minimum normal stress (confining pressure).
Ans: 75.23 kPa; b.) 191.73 kPa; c.) 33.17 kPa
4 (MODULE 4)
You might also like
- Lecture 5.0 - Spiral CurveDocument2 pagesLecture 5.0 - Spiral Curvermle50% (8)
- Pile Foundation (Part II-Group Piles)Document8 pagesPile Foundation (Part II-Group Piles)Francis Philippe Cruzana CariñoNo ratings yet
- Welded Simple Connection: Based On Block Shear Capacity ofDocument12 pagesWelded Simple Connection: Based On Block Shear Capacity ofhazelNo ratings yet
- Final Req. (Foundation Eng'g)Document6 pagesFinal Req. (Foundation Eng'g)ace fist100% (1)
- Quiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartDocument4 pagesQuiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartBenjamin Benicarlo Juanillo IIINo ratings yet
- Topic 8 - Load PatternDocument11 pagesTopic 8 - Load PatternKenny Cantila100% (1)
- Problem 1. Structural Design "CE Board Exam Nov. 1992Document2 pagesProblem 1. Structural Design "CE Board Exam Nov. 1992AlvinNo ratings yet
- Q1 - BasicDocument1 pageQ1 - BasicMac KYNo ratings yet
- Pulverized Used Ceramic Tiles As An Additive in Cement Mortar For PlasteringDocument10 pagesPulverized Used Ceramic Tiles As An Additive in Cement Mortar For PlasteringClairole Marie Quilantang100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Shallow FoundationsDocument29 pagesChapter 3 - Shallow FoundationsBuoyancyNo ratings yet
- FR-8x Editor Eng01 WDocument8 pagesFR-8x Editor Eng01 WRadulian Daniel100% (1)
- Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations Solution ManualDocument84 pagesNumerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations Solution ManualGui San100% (1)
- Consolidated Drained Tri AxialDocument15 pagesConsolidated Drained Tri AxialJemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- 620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Document4 pages620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Mona fabrigarNo ratings yet
- Retaining-WallDocument11 pagesRetaining-WallBosz' AceNo ratings yet
- CE Module 29 - StaticsDocument13 pagesCE Module 29 - StaticsAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Roblemsf Exercises: 3 ProblemDocument1 pageRoblemsf Exercises: 3 ProblemDesireine Louise JacintoNo ratings yet
- Soil MechanicsDocument2 pagesSoil MechanicsJonathan ArcillaNo ratings yet
- T-Beam: Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument12 pagesT-Beam: Reinforced Concrete DesignJulius RosasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document22 pagesChapter 3JommarVocalTagalog100% (1)
- Stresses in SoilDocument52 pagesStresses in SoilAndrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- Palma Bsce-2a Assignment2 Pce2Document4 pagesPalma Bsce-2a Assignment2 Pce2CHRISTIAN NATHANIEL PALMANo ratings yet
- Glanfill Module 1 - Part 2Document57 pagesGlanfill Module 1 - Part 2LeiVasAllanigueVillanueva100% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: 1 (MODULE 2)Document4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: 1 (MODULE 2)Poppy MooreNo ratings yet
- Hge - Geotech 3Document19 pagesHge - Geotech 3Pat SisonNo ratings yet
- CE Board Exam PDFDocument17 pagesCE Board Exam PDFDarwin BasNo ratings yet
- Steel Design 5 Nov 2020Document2 pagesSteel Design 5 Nov 2020Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Wallfooting Sample Design (A Brief Approach)Document11 pagesWallfooting Sample Design (A Brief Approach)Samuel Espartero100% (1)
- Struct Nov2019Document4 pagesStruct Nov2019ryanmikeNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering and Hydraulics Final Coaching Nov 2018Document87 pagesGeotechnical Engineering and Hydraulics Final Coaching Nov 2018Jeremy Mark SorianoNo ratings yet
- Problem 1 Structural Design Ce Board Exam Nov 1992 PDF FreeDocument2 pagesProblem 1 Structural Design Ce Board Exam Nov 1992 PDF FreeRachel Delosreyes0% (1)
- Set BDocument12 pagesSet BDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Design of Square Footing (With or Without Moment)Document13 pagesDesign of Square Footing (With or Without Moment)Ella Clent moralesNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics 2Document3 pagesSoil Mechanics 2MarvinPatricioNarcaNo ratings yet
- Plate 4 Effective Stresses in SoilDocument14 pagesPlate 4 Effective Stresses in SoilSofia Isabelle GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lateral Loads On Building Frames: Seismic Analysis Design Base ShearDocument3 pagesLateral Loads On Building Frames: Seismic Analysis Design Base ShearAngel CristobalNo ratings yet
- Review Module: Steel Design - Plastic Analysis and The Collapse MechanismDocument3 pagesReview Module: Steel Design - Plastic Analysis and The Collapse MechanismDJ GRNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING PDFowaisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document25 pagesChapter 6anon_749279665No ratings yet
- Module1 IntroductionDocument13 pagesModule1 Introductionmarlo ignacioNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerBebit FerolinoNo ratings yet
- 10 Relative EquilibriumDocument35 pages10 Relative EquilibriumTrixia DuazoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument36 pagesFluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingFrancis Philippe CariñoNo ratings yet
- 4 BuoyancyDocument5 pages4 BuoyancyDaniel Vasquez0% (1)
- Title: Properties of Steel Self Learning Assessment (Problem Set)Document14 pagesTitle: Properties of Steel Self Learning Assessment (Problem Set)Migaea AndresNo ratings yet
- Friction ProblemsDocument4 pagesFriction ProblemsDaniel PerezNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 With AnsDocument4 pagesProblem Set 1 With AnsRaine ZaficoNo ratings yet
- PREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set ADocument2 pagesPREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set AEngr. HLDCNo ratings yet
- Plate No.5 - Autor, Joy - STEELDocument10 pagesPlate No.5 - Autor, Joy - STEELJoy lauria100% (1)
- Design Nov 2013Document12 pagesDesign Nov 2013Cath100% (1)
- Module 1Document23 pagesModule 1Edbert TulipasNo ratings yet
- M05 - SEC 5 Solution (131331) For FB PostingDocument11 pagesM05 - SEC 5 Solution (131331) For FB PostingRimar LiguanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 12Document6 pagesQuiz 12John Taylor BernasNo ratings yet
- Problems - Timber & Construction: Situation: Problem 1 To 3 (May 2000)Document23 pagesProblems - Timber & Construction: Situation: Problem 1 To 3 (May 2000)Caro Kan Lopez100% (1)
- HAU Teaching DemoDocument15 pagesHAU Teaching DemoRonwell De LeonNo ratings yet
- Lec 18Document10 pagesLec 18Brian chunguliNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- CE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Document21 pagesCE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Irmak ÜnalNo ratings yet
- Assnmt 11Document2 pagesAssnmt 11RK MEHTANo ratings yet
- Soil 2-2022-45minDocument13 pagesSoil 2-2022-45minJames chideraNo ratings yet
- Examination Papers On Introductory GeotechnicsDocument53 pagesExamination Papers On Introductory GeotechnicsTakchandra JaikeshanNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Scientific Definition: The Basic UnitDocument6 pagesEcosystem Scientific Definition: The Basic UnitrmleNo ratings yet
- Policy ReviewDocument18 pagesPolicy ReviewrmleNo ratings yet
- Algebra Refresher Module Set 1Document3 pagesAlgebra Refresher Module Set 1Rizpah0% (1)
- The Comprehensive Land Use PlanDocument4 pagesThe Comprehensive Land Use PlanrmleNo ratings yet
- Third ReportDocument22 pagesThird ReportrmleNo ratings yet
- StaadDocument2 pagesStaadrmleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.0b - Unsymmetrical Parabolic CurvesDocument1 pageLecture 4.0b - Unsymmetrical Parabolic Curvesrmle17% (6)
- Friction ProblemsDocument13 pagesFriction ProblemsrmleNo ratings yet
- Tangents External InternalDocument1 pageTangents External InternalrmleNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Leadership Three Classical Models and CasesDocument123 pagesPhilosophy and Leadership Three Classical Models and Casesliona efrinaunajaNo ratings yet
- (Denise Eileen McCoskey, Emily Zakin) Bound by TheDocument356 pages(Denise Eileen McCoskey, Emily Zakin) Bound by TheZenia YébenesNo ratings yet
- Ce6012 - QB 3 - BY Civildatas - Blogspot.inDocument5 pagesCe6012 - QB 3 - BY Civildatas - Blogspot.invivek murthyNo ratings yet
- Mae 5310: Combustion Fundamentals: Laminar Premixed Flames Example, Applications and CommentsDocument22 pagesMae 5310: Combustion Fundamentals: Laminar Premixed Flames Example, Applications and CommentsAlex KeaneNo ratings yet
- Leadershipdevelopment BR DdiDocument12 pagesLeadershipdevelopment BR DdihrahmayadiNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Technical Change: Toward A Taxonomy and A TheoryDocument31 pagesPatterns of Technical Change: Toward A Taxonomy and A TheoryRobson GuedesNo ratings yet
- Final Design Review ChecklistDocument3 pagesFinal Design Review ChecklisttnchsgNo ratings yet
- Making Sense Out of Life: The Joy of EconomicsDocument322 pagesMaking Sense Out of Life: The Joy of EconomicsSEVERA KULENKAMPNo ratings yet
- IntroduccionDocument7 pagesIntroduccionValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Problem Statement: Fluid CepDocument6 pagesProblem Statement: Fluid CepMuneer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Digital Self Service Kiosks and The Customer ExperienceDocument9 pagesDigital Self Service Kiosks and The Customer Experiencelatha loganathanNo ratings yet
- Schindler 1000 Elevator inDocument16 pagesSchindler 1000 Elevator inSiddhartha JanaNo ratings yet
- Daifuku MIT BrochureDocument5 pagesDaifuku MIT BrochureZiqi LinNo ratings yet
- TDS - Thioseal PSDocument4 pagesTDS - Thioseal PSCristal Haze VictoriaNo ratings yet
- A Report On Self Defence Workshop For Women and GirlsDocument7 pagesA Report On Self Defence Workshop For Women and GirlsANJALI GHANSHANINo ratings yet
- Fs 1-Episode 1Document9 pagesFs 1-Episode 1Louween Mendoza50% (2)
- Anna University EDDocument48 pagesAnna University EDSivaji SivaNo ratings yet
- Surveying For Beginners by J. B. Davis (1909) PDFDocument202 pagesSurveying For Beginners by J. B. Davis (1909) PDFSandy Star BrandaNo ratings yet
- Analysis - Bio - NEET 2023Document5 pagesAnalysis - Bio - NEET 2023oniichanNo ratings yet
- Al 9351 Tractor and Farm EquipmentsDocument2 pagesAl 9351 Tractor and Farm EquipmentsDhivya PNo ratings yet
- Learning and Teaching Styles in Engineering EducationDocument11 pagesLearning and Teaching Styles in Engineering EducationAndy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Products Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)Document31 pagesProducts Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)osama raufNo ratings yet
- BIOLS340. Chapter 16 SummaryDocument10 pagesBIOLS340. Chapter 16 SummaryNawaf Al.RiffaiNo ratings yet
- Multimodal Assignment Sheet 1900-28Document3 pagesMultimodal Assignment Sheet 1900-28api-446885679No ratings yet
- Your Boss May Need Motivating, TooDocument3 pagesYour Boss May Need Motivating, TooegahmuliaNo ratings yet
- James Clerk Maxwell BiographyDocument3 pagesJames Clerk Maxwell BiographypseudonimNo ratings yet
- Question Text Question Type Option 1: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesQuestion Text Question Type Option 1: Multiple Choicemohamed elgammlNo ratings yet
- AGFA DX-M BrochureDocument8 pagesAGFA DX-M BrochureEmmanuel HeliesNo ratings yet