Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk Priority Impact v0.1
Risk Priority Impact v0.1
Uploaded by
anthonymqCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ServiceNow Master The Change Management ProcessDocument17 pagesServiceNow Master The Change Management ProcessDalipKumar100% (1)
- Change Management PolicyDocument8 pagesChange Management PolicyKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Change Enablement in ITIL 4Document7 pagesChange Enablement in ITIL 4Daniel ErgichoNo ratings yet
- Change Management PolicyDocument9 pagesChange Management PolicySecret SecretNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 4Document4 pagesAssignment No 4heemishaNo ratings yet
- Document: Change Control Plan Owner: CIO Services Project OfficeDocument4 pagesDocument: Change Control Plan Owner: CIO Services Project OfficePhil WolfeNo ratings yet
- NFPA Document Information Pages (List of NFPA Codes & Standards)Document9 pagesNFPA Document Information Pages (List of NFPA Codes & Standards)Sitole S SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice Safe Work at HeightDocument71 pagesCode of Practice Safe Work at Heightgalaxy25No ratings yet
- VUITChange ProcessDocument22 pagesVUITChange Processkalyan thallapaneniNo ratings yet
- Change Management Process TrainingDocument37 pagesChange Management Process TrainingFlavio ManriqueNo ratings yet
- Change Management PolicyDocument6 pagesChange Management PolicyJulius SoqNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Change ManagementDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Change ManagementAleksandarNo ratings yet
- Change and Release Management - V1Document14 pagesChange and Release Management - V1SULOCHNA KUJURNo ratings yet
- ITIL ProcessDocument3 pagesITIL ProcessAllison RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Change Management PolicyDocument7 pagesChange Management PolicyErvin PregNo ratings yet
- PinkSCAN Change MGMTDocument8 pagesPinkSCAN Change MGMTMartin LeckNo ratings yet
- Coordinator Training v2Document26 pagesCoordinator Training v2MichellPamela PMNo ratings yet
- CAB Change Advisory & Management ProcessDocument3 pagesCAB Change Advisory & Management ProcessMahaboob PeerNo ratings yet
- Technology Vendor Transition StrategyDocument7 pagesTechnology Vendor Transition StrategyasadnawazNo ratings yet
- Change ManagementDocument3 pagesChange ManagementArif ArifNo ratings yet
- Change Management Standard and Procedures v2.0 Revised August 2019Document16 pagesChange Management Standard and Procedures v2.0 Revised August 2019asmaa hassanNo ratings yet
- Incident Management: What Makes A Standard Change Standard?Document5 pagesIncident Management: What Makes A Standard Change Standard?beignaNo ratings yet
- Change Management Process Guide - FinalDocument16 pagesChange Management Process Guide - FinalWelvya TingaNo ratings yet
- Six Steps To Implementing Change Management That WorksDocument19 pagesSix Steps To Implementing Change Management That WorksOgnjen SimisicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Change ProcessesDocument45 pagesChapter 7 - Change Processeshackerchess84No ratings yet
- KU IT Change Request TypesDocument3 pagesKU IT Change Request Typesmakumba1972No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4Sherlene Antenor SolisNo ratings yet
- IT Change Management PolicyDocument9 pagesIT Change Management Policymusaab elameenNo ratings yet
- SEMMChange Control Plan Preparation GuidelinesDocument10 pagesSEMMChange Control Plan Preparation GuidelinesRudy MontignyNo ratings yet
- 8 Requirements ManagementDocument36 pages8 Requirements ManagementSana Bilal 063No ratings yet
- Prioritize Your Cost Optimization Efforts: A Decision Framework ForDocument5 pagesPrioritize Your Cost Optimization Efforts: A Decision Framework FornikNo ratings yet
- Cisco Change ManagementDocument24 pagesCisco Change ManagementRaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Change Management PolicyDocument5 pagesChange Management PolicyOluwatobi Edith Ojo100% (1)
- Based On The Points Put Forth by The Group, We Have Found The FollowingDocument1 pageBased On The Points Put Forth by The Group, We Have Found The FollowingAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Change ManagmentDocument78 pagesChange ManagmentAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Business Continuity PlanDocument3 pagesA Business Continuity PlanMaajith Marzook100% (1)
- SLADocument4 pagesSLADevaraj Ghatualo100% (1)
- B02-008 - Predictive and Preventive MaintenanceDocument18 pagesB02-008 - Predictive and Preventive MaintenanceRBC TDNo ratings yet
- Itil Change Management A Beginners GuideDocument17 pagesItil Change Management A Beginners Guidedesi1992No ratings yet
- ITIL Change Management XXXDocument10 pagesITIL Change Management XXXdev007No ratings yet
- Change Approval Board TemplateDocument9 pagesChange Approval Board TemplateJonathan Kwame Kwesi100% (2)
- ITKnowledgeDocument ProgramChangeDocument6 pagesITKnowledgeDocument ProgramChangeJoel Colquepisco EspinozaNo ratings yet
- MoC 1715507371Document34 pagesMoC 1715507371tekcellentNo ratings yet
- Educause - IT Change Management - A Practical Approach For Higher EducationDocument21 pagesEducause - IT Change Management - A Practical Approach For Higher EducationSuresh Rajamani100% (1)
- Cherwell - RFC Categories and Requirements v2 PDFDocument12 pagesCherwell - RFC Categories and Requirements v2 PDFAnonymous yQxGL0pENo ratings yet
- Professionaldiploma in Project Management: Lesson 5: Change Control & Risk ManagementDocument41 pagesProfessionaldiploma in Project Management: Lesson 5: Change Control & Risk Managementjethro_012No ratings yet
- Change Manager ClassificationtableDocument1 pageChange Manager Classificationtablelashanj2No ratings yet
- GTAG 02 Global Technology Audit GuideDocument14 pagesGTAG 02 Global Technology Audit GuideLuis Robles100% (1)
- Topic 08Document24 pagesTopic 08Anket SinghNo ratings yet
- Predictive and Preventive MaintenanceDocument18 pagesPredictive and Preventive MaintenanceWynn ChoNo ratings yet
- Change Management: Process & ImplementationDocument5 pagesChange Management: Process & ImplementationAnantNo ratings yet
- Cisco Change Management Best PracticesDocument14 pagesCisco Change Management Best Practicessmuliaw100% (1)
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 NotesImran GureNo ratings yet
- Integrated Change Control in Manu PDFDocument16 pagesIntegrated Change Control in Manu PDFasd123412No ratings yet
- 13-06-13 Managment of Change ProcedureDocument17 pages13-06-13 Managment of Change Procedurekelvin OsemeNo ratings yet
- Verteda Support Handbook Do 110919cxDocument8 pagesVerteda Support Handbook Do 110919cxEmma UnderwoodNo ratings yet
- Change Management: - A Change Is "An Event That Results in A New Status of One or MoreDocument13 pagesChange Management: - A Change Is "An Event That Results in A New Status of One or MoreRoomman ArifNo ratings yet
- Aroosha OSS: Change ManagementDocument55 pagesAroosha OSS: Change Managementsemko2No ratings yet
- SM India Sub Region Back To Basics Incident Management HPIM Process PDFDocument33 pagesSM India Sub Region Back To Basics Incident Management HPIM Process PDFJEEVAN PRAMODNo ratings yet
- 01 - Change Management ProcessDocument44 pages01 - Change Management ProcessAnonymous zWUrYoc2VNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Maintenance FundamentalsDocument55 pagesInstrumentation Maintenance FundamentalsJanna Mariz MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ketop c100 t2 1384364 72700 0648630 Panel Operatorski Keba ManualDocument151 pagesKetop c100 t2 1384364 72700 0648630 Panel Operatorski Keba ManualJavier Del Pozo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Crisis GuideDocument249 pagesCrisis GuideDaniel Checchia100% (1)
- Earthquake Contingency Plan For Dhaka City CorporationDocument50 pagesEarthquake Contingency Plan For Dhaka City CorporationCDMP Bangladesh100% (3)
- Practice Teaching On "Disaster Nursing"Document10 pagesPractice Teaching On "Disaster Nursing"Rumela Ganguly ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Floods in Mumbai (Matter)Document8 pagesFloods in Mumbai (Matter)366- Rachel D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Municipal Ordinance No. 25-2021 DRRM-HDocument5 pagesMunicipal Ordinance No. 25-2021 DRRM-HJason Lape0% (1)
- (Download PDF) Introduction To Emergency Management 7Th Edition George D Haddow Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Introduction To Emergency Management 7Th Edition George D Haddow Online Ebook All Chapter PDFmarguerite.sansotta786100% (8)
- University of Washington Police Crime Prevention Unit Workplace Security PlanDocument12 pagesUniversity of Washington Police Crime Prevention Unit Workplace Security Plan08102676064No ratings yet
- Key Control & All Types of KeysDocument8 pagesKey Control & All Types of KeysrudraNo ratings yet
- Bus DriverDocument3 pagesBus Drivermmsb67No ratings yet
- WI-HSE-04-00 Fire Safety PDFDocument5 pagesWI-HSE-04-00 Fire Safety PDFSandi ImantakahNo ratings yet
- Mca Doctors Manual LinksDocument276 pagesMca Doctors Manual LinksStudent_tangerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Events ManagementDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Events Management_hola-chico_No ratings yet
- 18CEO307T DMM Unit-I Lecture Notes V1.1Document16 pages18CEO307T DMM Unit-I Lecture Notes V1.1pratham sainiNo ratings yet
- Competency Dictionary-PAO-PRCSDDocument2 pagesCompetency Dictionary-PAO-PRCSDJaymark L. AgmataNo ratings yet
- Public Health Preparedness - A Systems - Level ApproachDocument5 pagesPublic Health Preparedness - A Systems - Level ApproachViorentina YofianiNo ratings yet
- Active Shooter How To RespondDocument13 pagesActive Shooter How To RespondgabrielMeuNomeAquiNo ratings yet
- Responding To EmergenciesDocument45 pagesResponding To EmergenciesFakhrur ZainudinNo ratings yet
- PDF School Disaster Management Contingency Plan - CompressDocument23 pagesPDF School Disaster Management Contingency Plan - CompressArnel B. PrestoNo ratings yet
- Improving Paramedic Preparedness To Mass Casualty Incidents: An Implementation Study Using PARIHS FrameworkDocument4 pagesImproving Paramedic Preparedness To Mass Casualty Incidents: An Implementation Study Using PARIHS FrameworkMaheshPVNo ratings yet
- Training ModulesDocument33 pagesTraining Modulesslamet suryantoNo ratings yet
- 5 - Primary and Secondary SurveyDocument28 pages5 - Primary and Secondary SurveyZakiah Zahrin100% (1)
- Mobile Crisis Response Team (MCRT) : What To Expect After You CallDocument2 pagesMobile Crisis Response Team (MCRT) : What To Expect After You CallGrant TomeyNo ratings yet
- Emergency Planning and Crisis ManagementDocument111 pagesEmergency Planning and Crisis ManagementFrancis Rey Gayanilo100% (1)
- GG Ifa CL Af CB FV v5 4-1-GFS Protected enDocument117 pagesGG Ifa CL Af CB FV v5 4-1-GFS Protected enbrahim citruNo ratings yet
- Armed ConflictsDocument22 pagesArmed ConflictsJappy JapelaNo ratings yet
- UNDAC HandbookDocument418 pagesUNDAC HandbookShane Briggs100% (2)
- CRISIS MANAGEMENT Lecture PDFDocument35 pagesCRISIS MANAGEMENT Lecture PDFPrincess Juliana AgustinNo ratings yet
Risk Priority Impact v0.1
Risk Priority Impact v0.1
Uploaded by
anthonymqOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk Priority Impact v0.1
Risk Priority Impact v0.1
Uploaded by
anthonymqCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk
A change analyst performs Risk Analysis to identify and assess factors that may jeopardize an existing
service/system during and after implementation by identifying countermeasures to successfully deal with constraints if
developed and avert possible negative effects on the existing services.
A risk is an event that “may” occur. The probability of it occurring can range from just above 0% to just below 100%
by its very nature; a risk has a negative impact. However, the size of the impact varies in terms of cost and impact on
the CTC brand or some other critical factor. The table below provides a Risk Assessment considering an Impact V/s
its Probability of Occurrence.
Probabilit Impact
Mediu
y Low High Major Severe
m
Almost
Medium High High Emergency Emergency
Certain
Most Likely Medium Medium Medium High Emergency
Possible Low Medium Medium High Emergency
Unlikely Low Medium Medium Medium High
Rare Low Low Medium Medium High
Impact
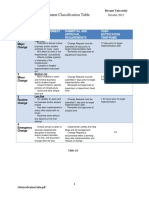
Impact is a measure of business criticality during and after implementing a change. Impact is generally
differentiated by the scope and the overall effect on the business. Impact can be determined in
consultation with the SME’s and reviewing the formalized Service Level Agreements. Typically the extent
of services, systems and/or the number of users that could be affected defines the scope of an Impact.
The following matrix provides an idea on how to categorize and impact.
Code Definition
Severe • Business critical system and/or service would are affected
• Extensive revenue impact across the customer base.
• Regulatory/Strategic non planned impact which cannot be
deferred till next change schedule.
High • Business critical systems and/or services are severely degraded or
partial loss of mission critical features / functionality.
• Impacting upon a large number of users (non critical services).
• Revenue impact that cannot be deferred but absorbed for a
limited period.
• To be given highest priority for change building, testing, and
implementation resources.
Medium • A change is justified and necessary, but can wait until the next
scheduled release or upgrade.
• No Financial impact.
• Minimal impact to business systems and services.
Low • A change is justified and necessary, but can wait until the next
scheduled release or upgrade.
It is recommended that all High, Medium and Low categorized Impact result from PLANNED activities. Unplanned
requests should be accepted subjected to approval by Senior Management with appropriate justification.
Priority
Change Priority levels can be defined using a variety of variables. As part of the Change Management
process, being able to establish a change priority is part of the change evaluation.
Change Priority levels are typically set at levels such as High, Medium, Low and Urgent or Emergency.
These levels are determined by understanding the combined impact and urgency of the change being
considered. The impact of a change describes the degree of 'disturbance' that a change may have on the
infrastructure or what impact on the business not performing the change may have on the organization.
The urgency of a change is a way of expressing the level of resources that should be applied to the
change being considered. Resources can be in the form of people, infrastructure, costs, etc.
The following chart provides a graphical representation of Priority based on comparing Impact and Urgency.
Urgent
Priority = High Priority = Emergency
CAB approval required E/CAB Approval required
High
URGENCY
Medium
Priority = Low Priority = Medium
Since impact is “Low/Medium” Change
CAB approval required, since impact is
can be approved by CM. (These can
High
comprise of standard change as well)
Low
Low Medium High Major
IMPACT
Code Definition
Emergency • Users require expedited restoration of service as soon as possible.
• Resolving an issue causing high revenue impact.
• Providing solution to a high delegated user.
• Implement a non-planned solution for highly regulatory/strategic
service/system.(needs additional approval)
• Generally users are unable to work and no work around is
available. Resources may need to be immediately allocated to deploy such
authorized changes.
Urgent • When action is required before the weekly board meeting.
• Need to respond in a timely manner to resolve issues since lack of
change will result in degradation of services or poor data integrity.
• Unplanned but tested change of high business importance.
High • Users require expedited restoration of service, but can bear
Code Definition
minimal delays.
• Issue causing financial impact across a limited range.
• Having high level dependencies.
Medium • No severe impact identified, but rectification of an incident cannot
be deferred until the next scheduled upgrade.
• Revenue impact that cannot be deferred but absorbed for a
limited period.
Low • Customers may be inconvenienced but a delay in resolution is
considered acceptable
Note :-
In case of an emergency the submitted change shall immediately follow the specified fast-track for
authorization by the EC/CAB. If the change fails to recover and requires additional changes to restore service, the
implementer should inform relevant managers for approval.
Urgency can be determined as the time within which resolution is required or an extent to which the
business or user can bear delay in reaching a resolution. VIP status may also influence the Urgency status. Potential
financial Impact of a service downtime on the business may also influence the Urgency. If a service is simply
degraded or there is an alternate solution, the degree of Urgency will generally be less than for a service that is
completely unavailable with no known workaround or solution. For urgent changes the requestor must procure
approval from their SVP or VP in order to schedule the change, the change should fall within a normal maintenance
window if possible.
You might also like
- ServiceNow Master The Change Management ProcessDocument17 pagesServiceNow Master The Change Management ProcessDalipKumar100% (1)
- Change Management PolicyDocument8 pagesChange Management PolicyKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Change Enablement in ITIL 4Document7 pagesChange Enablement in ITIL 4Daniel ErgichoNo ratings yet
- Change Management PolicyDocument9 pagesChange Management PolicySecret SecretNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 4Document4 pagesAssignment No 4heemishaNo ratings yet
- Document: Change Control Plan Owner: CIO Services Project OfficeDocument4 pagesDocument: Change Control Plan Owner: CIO Services Project OfficePhil WolfeNo ratings yet
- NFPA Document Information Pages (List of NFPA Codes & Standards)Document9 pagesNFPA Document Information Pages (List of NFPA Codes & Standards)Sitole S SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice Safe Work at HeightDocument71 pagesCode of Practice Safe Work at Heightgalaxy25No ratings yet
- VUITChange ProcessDocument22 pagesVUITChange Processkalyan thallapaneniNo ratings yet
- Change Management Process TrainingDocument37 pagesChange Management Process TrainingFlavio ManriqueNo ratings yet
- Change Management PolicyDocument6 pagesChange Management PolicyJulius SoqNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Change ManagementDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Change ManagementAleksandarNo ratings yet
- Change and Release Management - V1Document14 pagesChange and Release Management - V1SULOCHNA KUJURNo ratings yet
- ITIL ProcessDocument3 pagesITIL ProcessAllison RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Change Management PolicyDocument7 pagesChange Management PolicyErvin PregNo ratings yet
- PinkSCAN Change MGMTDocument8 pagesPinkSCAN Change MGMTMartin LeckNo ratings yet
- Coordinator Training v2Document26 pagesCoordinator Training v2MichellPamela PMNo ratings yet
- CAB Change Advisory & Management ProcessDocument3 pagesCAB Change Advisory & Management ProcessMahaboob PeerNo ratings yet
- Technology Vendor Transition StrategyDocument7 pagesTechnology Vendor Transition StrategyasadnawazNo ratings yet
- Change ManagementDocument3 pagesChange ManagementArif ArifNo ratings yet
- Change Management Standard and Procedures v2.0 Revised August 2019Document16 pagesChange Management Standard and Procedures v2.0 Revised August 2019asmaa hassanNo ratings yet
- Incident Management: What Makes A Standard Change Standard?Document5 pagesIncident Management: What Makes A Standard Change Standard?beignaNo ratings yet
- Change Management Process Guide - FinalDocument16 pagesChange Management Process Guide - FinalWelvya TingaNo ratings yet
- Six Steps To Implementing Change Management That WorksDocument19 pagesSix Steps To Implementing Change Management That WorksOgnjen SimisicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Change ProcessesDocument45 pagesChapter 7 - Change Processeshackerchess84No ratings yet
- KU IT Change Request TypesDocument3 pagesKU IT Change Request Typesmakumba1972No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4Sherlene Antenor SolisNo ratings yet
- IT Change Management PolicyDocument9 pagesIT Change Management Policymusaab elameenNo ratings yet
- SEMMChange Control Plan Preparation GuidelinesDocument10 pagesSEMMChange Control Plan Preparation GuidelinesRudy MontignyNo ratings yet
- 8 Requirements ManagementDocument36 pages8 Requirements ManagementSana Bilal 063No ratings yet
- Prioritize Your Cost Optimization Efforts: A Decision Framework ForDocument5 pagesPrioritize Your Cost Optimization Efforts: A Decision Framework FornikNo ratings yet
- Cisco Change ManagementDocument24 pagesCisco Change ManagementRaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Change Management PolicyDocument5 pagesChange Management PolicyOluwatobi Edith Ojo100% (1)
- Based On The Points Put Forth by The Group, We Have Found The FollowingDocument1 pageBased On The Points Put Forth by The Group, We Have Found The FollowingAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Change ManagmentDocument78 pagesChange ManagmentAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Business Continuity PlanDocument3 pagesA Business Continuity PlanMaajith Marzook100% (1)
- SLADocument4 pagesSLADevaraj Ghatualo100% (1)
- B02-008 - Predictive and Preventive MaintenanceDocument18 pagesB02-008 - Predictive and Preventive MaintenanceRBC TDNo ratings yet
- Itil Change Management A Beginners GuideDocument17 pagesItil Change Management A Beginners Guidedesi1992No ratings yet
- ITIL Change Management XXXDocument10 pagesITIL Change Management XXXdev007No ratings yet
- Change Approval Board TemplateDocument9 pagesChange Approval Board TemplateJonathan Kwame Kwesi100% (2)
- ITKnowledgeDocument ProgramChangeDocument6 pagesITKnowledgeDocument ProgramChangeJoel Colquepisco EspinozaNo ratings yet
- MoC 1715507371Document34 pagesMoC 1715507371tekcellentNo ratings yet
- Educause - IT Change Management - A Practical Approach For Higher EducationDocument21 pagesEducause - IT Change Management - A Practical Approach For Higher EducationSuresh Rajamani100% (1)
- Cherwell - RFC Categories and Requirements v2 PDFDocument12 pagesCherwell - RFC Categories and Requirements v2 PDFAnonymous yQxGL0pENo ratings yet
- Professionaldiploma in Project Management: Lesson 5: Change Control & Risk ManagementDocument41 pagesProfessionaldiploma in Project Management: Lesson 5: Change Control & Risk Managementjethro_012No ratings yet
- Change Manager ClassificationtableDocument1 pageChange Manager Classificationtablelashanj2No ratings yet
- GTAG 02 Global Technology Audit GuideDocument14 pagesGTAG 02 Global Technology Audit GuideLuis Robles100% (1)
- Topic 08Document24 pagesTopic 08Anket SinghNo ratings yet
- Predictive and Preventive MaintenanceDocument18 pagesPredictive and Preventive MaintenanceWynn ChoNo ratings yet
- Change Management: Process & ImplementationDocument5 pagesChange Management: Process & ImplementationAnantNo ratings yet
- Cisco Change Management Best PracticesDocument14 pagesCisco Change Management Best Practicessmuliaw100% (1)
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 NotesImran GureNo ratings yet
- Integrated Change Control in Manu PDFDocument16 pagesIntegrated Change Control in Manu PDFasd123412No ratings yet
- 13-06-13 Managment of Change ProcedureDocument17 pages13-06-13 Managment of Change Procedurekelvin OsemeNo ratings yet
- Verteda Support Handbook Do 110919cxDocument8 pagesVerteda Support Handbook Do 110919cxEmma UnderwoodNo ratings yet
- Change Management: - A Change Is "An Event That Results in A New Status of One or MoreDocument13 pagesChange Management: - A Change Is "An Event That Results in A New Status of One or MoreRoomman ArifNo ratings yet
- Aroosha OSS: Change ManagementDocument55 pagesAroosha OSS: Change Managementsemko2No ratings yet
- SM India Sub Region Back To Basics Incident Management HPIM Process PDFDocument33 pagesSM India Sub Region Back To Basics Incident Management HPIM Process PDFJEEVAN PRAMODNo ratings yet
- 01 - Change Management ProcessDocument44 pages01 - Change Management ProcessAnonymous zWUrYoc2VNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Maintenance FundamentalsDocument55 pagesInstrumentation Maintenance FundamentalsJanna Mariz MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ketop c100 t2 1384364 72700 0648630 Panel Operatorski Keba ManualDocument151 pagesKetop c100 t2 1384364 72700 0648630 Panel Operatorski Keba ManualJavier Del Pozo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Crisis GuideDocument249 pagesCrisis GuideDaniel Checchia100% (1)
- Earthquake Contingency Plan For Dhaka City CorporationDocument50 pagesEarthquake Contingency Plan For Dhaka City CorporationCDMP Bangladesh100% (3)
- Practice Teaching On "Disaster Nursing"Document10 pagesPractice Teaching On "Disaster Nursing"Rumela Ganguly ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Floods in Mumbai (Matter)Document8 pagesFloods in Mumbai (Matter)366- Rachel D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Municipal Ordinance No. 25-2021 DRRM-HDocument5 pagesMunicipal Ordinance No. 25-2021 DRRM-HJason Lape0% (1)
- (Download PDF) Introduction To Emergency Management 7Th Edition George D Haddow Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Introduction To Emergency Management 7Th Edition George D Haddow Online Ebook All Chapter PDFmarguerite.sansotta786100% (8)
- University of Washington Police Crime Prevention Unit Workplace Security PlanDocument12 pagesUniversity of Washington Police Crime Prevention Unit Workplace Security Plan08102676064No ratings yet
- Key Control & All Types of KeysDocument8 pagesKey Control & All Types of KeysrudraNo ratings yet
- Bus DriverDocument3 pagesBus Drivermmsb67No ratings yet
- WI-HSE-04-00 Fire Safety PDFDocument5 pagesWI-HSE-04-00 Fire Safety PDFSandi ImantakahNo ratings yet
- Mca Doctors Manual LinksDocument276 pagesMca Doctors Manual LinksStudent_tangerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Events ManagementDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Events Management_hola-chico_No ratings yet
- 18CEO307T DMM Unit-I Lecture Notes V1.1Document16 pages18CEO307T DMM Unit-I Lecture Notes V1.1pratham sainiNo ratings yet
- Competency Dictionary-PAO-PRCSDDocument2 pagesCompetency Dictionary-PAO-PRCSDJaymark L. AgmataNo ratings yet
- Public Health Preparedness - A Systems - Level ApproachDocument5 pagesPublic Health Preparedness - A Systems - Level ApproachViorentina YofianiNo ratings yet
- Active Shooter How To RespondDocument13 pagesActive Shooter How To RespondgabrielMeuNomeAquiNo ratings yet
- Responding To EmergenciesDocument45 pagesResponding To EmergenciesFakhrur ZainudinNo ratings yet
- PDF School Disaster Management Contingency Plan - CompressDocument23 pagesPDF School Disaster Management Contingency Plan - CompressArnel B. PrestoNo ratings yet
- Improving Paramedic Preparedness To Mass Casualty Incidents: An Implementation Study Using PARIHS FrameworkDocument4 pagesImproving Paramedic Preparedness To Mass Casualty Incidents: An Implementation Study Using PARIHS FrameworkMaheshPVNo ratings yet
- Training ModulesDocument33 pagesTraining Modulesslamet suryantoNo ratings yet
- 5 - Primary and Secondary SurveyDocument28 pages5 - Primary and Secondary SurveyZakiah Zahrin100% (1)
- Mobile Crisis Response Team (MCRT) : What To Expect After You CallDocument2 pagesMobile Crisis Response Team (MCRT) : What To Expect After You CallGrant TomeyNo ratings yet
- Emergency Planning and Crisis ManagementDocument111 pagesEmergency Planning and Crisis ManagementFrancis Rey Gayanilo100% (1)
- GG Ifa CL Af CB FV v5 4-1-GFS Protected enDocument117 pagesGG Ifa CL Af CB FV v5 4-1-GFS Protected enbrahim citruNo ratings yet
- Armed ConflictsDocument22 pagesArmed ConflictsJappy JapelaNo ratings yet
- UNDAC HandbookDocument418 pagesUNDAC HandbookShane Briggs100% (2)
- CRISIS MANAGEMENT Lecture PDFDocument35 pagesCRISIS MANAGEMENT Lecture PDFPrincess Juliana AgustinNo ratings yet