Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views4CCP1350 Assignment 1
4CCP1350 Assignment 1
Uploaded by
Mohamed Salhi1. A dust particle inside a Dyson vacuum cleaner rotating at 104,000 rpm experiences about 1.7 g of acceleration due to its high angular velocity and small size of 55 mm.
2. A 5 kg cube sitting on a 20 kg slab is pushed with a 90 N force. With no friction, the cube and slab will accelerate together. With friction, the cube will slip on the slab until static friction is overcome and they accelerate separately.
3. A particle's motion is described by equations showing it moves in circular trajectories, which is confirmed by a MATLAB simulation plotting its x and y positions over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- USAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Document311 pagesUSAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Science Olympiad Blog95% (19)
- Force AnalysisDocument152 pagesForce AnalysisWang Han Zhu100% (1)
- Drilling With Digital TwinsDocument18 pagesDrilling With Digital Twinsnicessg@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Pile Cap Design 1Document6 pagesPile Cap Design 1kjpatel2100% (2)
- WorksheetDocument3 pagesWorksheetdanielNo ratings yet
- Trabjo en Grupo Fisica MecanicaDocument14 pagesTrabjo en Grupo Fisica MecanicadilanNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet WPEDocument9 pagesPractice Sheet WPENaveen JaferNo ratings yet
- SHMDocument23 pagesSHMUnknownNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Regional Physics Olympiad 2022 1Document4 pagesIndonesian Regional Physics Olympiad 2022 1Marcus PoonNo ratings yet
- Tut Test 6 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 6 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document85 pagesCH 9tajveer1310No ratings yet
- Physics Porjectile QuestionsDocument3 pagesPhysics Porjectile QuestionskokoNo ratings yet
- Review Problems, Physics 111 Final ExamDocument13 pagesReview Problems, Physics 111 Final Examav742No ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document3 pagesWa0010.BxkxnzixbNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document85 pagesCH 9Ferdinand Yohannes Van LankhorstNo ratings yet
- Phys1101 Worksheeti 2014 EDocument6 pagesPhys1101 Worksheeti 2014 Ejhxnrx48f8No ratings yet
- Physics Rotational Dynamics PDFDocument11 pagesPhysics Rotational Dynamics PDFAshish RanjanNo ratings yet
- General Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityZiyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Electric FieldsDocument17 pagesChapter 15 Electric FieldsdrewNo ratings yet
- Irodov Friction and Tension QuesDocument60 pagesIrodov Friction and Tension QuesShaurya SokhandaNo ratings yet
- Physics I Quiz # 2 - 01/07/2022Document9 pagesPhysics I Quiz # 2 - 01/07/2022Nathaly SosaNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemDocument10 pagesProblem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemVongNo ratings yet
- EM - Model Questions - 2023Document8 pagesEM - Model Questions - 2023Aadi AhwanitNo ratings yet
- Part-1: Subjective Questions: KinematicsDocument27 pagesPart-1: Subjective Questions: KinematicsB AbhinavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ReviewDocument3 pagesChapter 2 ReviewFlora DongNo ratings yet
- Phys 1 Lab ManualDocument13 pagesPhys 1 Lab ManualemuphychemNo ratings yet
- Phys B 1st Semester LBQsDocument11 pagesPhys B 1st Semester LBQsCanjiNo ratings yet
- 2024spring General Physics (1) Problem Set 2 With SolutionsDocument31 pages2024spring General Physics (1) Problem Set 2 With SolutionspurevnaymbayarjargalNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Physics Sample PaperDocument3 pagesClass Xi Physics Sample Paperdhruvarora31No ratings yet
- Rep 7 - 12 Phys 3311 StudentsDocument13 pagesRep 7 - 12 Phys 3311 StudentsCeleste SchepersNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Basic Dynamics NumericalsDocument7 pagesBasic Dynamics Numericalsashok royNo ratings yet
- Lista 3Document4 pagesLista 3Thales FreireNo ratings yet
- RotaionalDocument19 pagesRotaionalSujay BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Prob Set 5Document2 pagesProb Set 5Debolina DasNo ratings yet
- Block Prept1 g112324-1Document7 pagesBlock Prept1 g112324-1Alexxander Govinda KhevinNo ratings yet
- 2 (1) .Physics MechanicsDocument35 pages2 (1) .Physics MechanicsNo PainNo ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyDocument12 pagesRotational Dynamics: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyRoNNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Document5 pagesCentre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Kenny Ruiz0% (1)
- RefwfwefewwefwefewfwefDocument14 pagesRefwfwefewwefwefewfwefAidan Hager-BarlowNo ratings yet
- Rotational DynamicsDocument12 pagesRotational DynamicsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- PHY1505 Assignment 2 (9 May 2024)Document6 pagesPHY1505 Assignment 2 (9 May 2024)zakkiyah.i.essackNo ratings yet
- Draw A Picture!: You May Treat The Child As A Point ParticleDocument24 pagesDraw A Picture!: You May Treat The Child As A Point Particlebat.laughNo ratings yet
- Anna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important QuestionsDocument12 pagesAnna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important QuestionsPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Energi Momentum Dan Dinamika Rotasi Pelatihan Osn 2012Document7 pagesEnergi Momentum Dan Dinamika Rotasi Pelatihan Osn 2012Ivandito HerdayandityaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Example ProblemsDocument7 pagesDynamics Example ProblemsMuhayang Arifin KhalikNo ratings yet
- Physics Rotational DynamicsDocument11 pagesPhysics Rotational DynamicsSayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- ZadaniaDocument3 pagesZadaniatosia83No ratings yet
- 2018 June Test PrepquestionsDocument14 pages2018 June Test PrepquestionsSiinozuko MasentseNo ratings yet
- Tutoring QuestionsDocument7 pagesTutoring QuestionsJulieneNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir) PDFDocument5 pagesCentre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir) PDFkisan singhNo ratings yet
- SLP125 TutorialDocument3 pagesSLP125 Tutorialr4ww7cwbzcNo ratings yet
- Class-Xi Half Yearly ExaminationDocument3 pagesClass-Xi Half Yearly Examinationapi-328778920No ratings yet
- Example Problems On Newton's LawsDocument4 pagesExample Problems On Newton's LawshooriaroshanNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- JobDescriptionDocument7 pagesJobDescriptionMohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- 990-1-EI3848-CE - 20201118 B6 Parliamentary and Briefings Officer JDDocument9 pages990-1-EI3848-CE - 20201118 B6 Parliamentary and Briefings Officer JDMohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Beyond Prevent: A Real Alternative To Securitised PoliciesDocument51 pagesBeyond Prevent: A Real Alternative To Securitised PoliciesMohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Disabled Students Campaign Toolkit 2017Document18 pagesDisabled Students Campaign Toolkit 2017Mohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Termaxx KCLBC Catalogue - 2015Document18 pagesTermaxx KCLBC Catalogue - 2015Mohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Q1. Let Mxym Be The Mxy For Muscle and Mxyb Be The Mxy For Blood. A) Mxym M0 Exp ( - (21) /50) 0.6570 M0Document5 pagesQ1. Let Mxym Be The Mxy For Muscle and Mxyb Be The Mxy For Blood. A) Mxym M0 Exp ( - (21) /50) 0.6570 M0Mohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Chalmers - Panpsychism and Panprotopsychism (In Press)Document28 pagesChalmers - Panpsychism and Panprotopsychism (In Press)Andreu Ballús100% (3)
- 22-Year Clinical Evaluation of The Performance of Two Posterior Composites With Different Filler CharacteristicsDocument9 pages22-Year Clinical Evaluation of The Performance of Two Posterior Composites With Different Filler CharacteristicsAl-Kawthari As-SunniNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Distance MeasurementDocument16 pagesHorizontal Distance MeasurementAlfonso John AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Group # 3: 4cheaDocument16 pagesGroup # 3: 4cheaNishant ChughNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Optimal Design of DC Machine Unit-02/Lecture-01Document31 pagesUnit - 2 Optimal Design of DC Machine Unit-02/Lecture-01madeehaNo ratings yet
- B.S - Physics Semester SystemDocument47 pagesB.S - Physics Semester SystemIrfan NoorNo ratings yet
- CHP 15-3 Wave InteractionsDocument6 pagesCHP 15-3 Wave InteractionsDoyNo ratings yet
- OLD AUTOMATION Midterm-Exam SolutionDocument2 pagesOLD AUTOMATION Midterm-Exam SolutionsilverhandxNo ratings yet
- Mixtures ReviewDocument3 pagesMixtures Reviewapi-301425989No ratings yet
- IBO 2009 Theory AnswersDocument9 pagesIBO 2009 Theory AnswersPei JingNo ratings yet
- Table 2.1 Atmospheric Properties in ISA: Flight Dynamics-I Prof. E.G. Tulapurkara Chapter-2Document8 pagesTable 2.1 Atmospheric Properties in ISA: Flight Dynamics-I Prof. E.G. Tulapurkara Chapter-2Chegrani AhmedNo ratings yet
- B455Document3 pagesB455basha100% (1)
- Light Colour in The AtmosphereDocument1 pageLight Colour in The AtmosphereJordan ChizickNo ratings yet
- Engineering HydrologyDocument13 pagesEngineering Hydrologyapi-26150050100% (1)
- Three-Dimensional Analysis of Tokamaks and Stellarators: Paul R. GarabedianDocument4 pagesThree-Dimensional Analysis of Tokamaks and Stellarators: Paul R. GarabedianMustafa Umut SaracNo ratings yet
- Cement Process Engineering Vade Mecum: 2. StatisticsDocument15 pagesCement Process Engineering Vade Mecum: 2. StatisticsTamer FathyNo ratings yet
- Ase 301 - HW1Document3 pagesAse 301 - HW1isaac tsaiNo ratings yet
- MHTL G01 PDFDocument5 pagesMHTL G01 PDFalialavi2No ratings yet
- 1BDocument5 pages1BjhacademyhydNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Phase TransformationDocument26 pagesChapter 10 Phase TransformationEffendy AdipratamaNo ratings yet
- McFarland StandardDocument4 pagesMcFarland StandardHamid OkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ANSYS Mechanical: Workshop 6.1 Free Vibration AnalysisDocument11 pagesIntroduction To ANSYS Mechanical: Workshop 6.1 Free Vibration Analysisaslekha100% (1)
- Optimum Unbraced Length Ratios of Slender Steel Sections: Saleem M. Umair, Q. Hisham, and Zahid A. SiddiqiDocument5 pagesOptimum Unbraced Length Ratios of Slender Steel Sections: Saleem M. Umair, Q. Hisham, and Zahid A. SiddiqimargitorsiNo ratings yet
- Coagulant (Pac) and Flocculant (Pam)Document2 pagesCoagulant (Pac) and Flocculant (Pam)udit singhNo ratings yet
- Microstructure and Mechanical Characterization of Friction Stir Welded High Strength Low Alloy SteelsDocument8 pagesMicrostructure and Mechanical Characterization of Friction Stir Welded High Strength Low Alloy SteelsKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document37 pagesChapter 5TajTajNo ratings yet
- Quantum-Mechanical Aspects of The L. Pauling's Resonance Theory.Document4 pagesQuantum-Mechanical Aspects of The L. Pauling's Resonance Theory.Bezverkhniy VolodymyrNo ratings yet
4CCP1350 Assignment 1
4CCP1350 Assignment 1
Uploaded by
Mohamed Salhi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views5 pages1. A dust particle inside a Dyson vacuum cleaner rotating at 104,000 rpm experiences about 1.7 g of acceleration due to its high angular velocity and small size of 55 mm.
2. A 5 kg cube sitting on a 20 kg slab is pushed with a 90 N force. With no friction, the cube and slab will accelerate together. With friction, the cube will slip on the slab until static friction is overcome and they accelerate separately.
3. A particle's motion is described by equations showing it moves in circular trajectories, which is confirmed by a MATLAB simulation plotting its x and y positions over time.
Original Description:
fdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. A dust particle inside a Dyson vacuum cleaner rotating at 104,000 rpm experiences about 1.7 g of acceleration due to its high angular velocity and small size of 55 mm.
2. A 5 kg cube sitting on a 20 kg slab is pushed with a 90 N force. With no friction, the cube and slab will accelerate together. With friction, the cube will slip on the slab until static friction is overcome and they accelerate separately.
3. A particle's motion is described by equations showing it moves in circular trajectories, which is confirmed by a MATLAB simulation plotting its x and y positions over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views5 pages4CCP1350 Assignment 1
4CCP1350 Assignment 1
Uploaded by
Mohamed Salhi1. A dust particle inside a Dyson vacuum cleaner rotating at 104,000 rpm experiences about 1.7 g of acceleration due to its high angular velocity and small size of 55 mm.
2. A 5 kg cube sitting on a 20 kg slab is pushed with a 90 N force. With no friction, the cube and slab will accelerate together. With friction, the cube will slip on the slab until static friction is overcome and they accelerate separately.
3. A particle's motion is described by equations showing it moves in circular trajectories, which is confirmed by a MATLAB simulation plotting its x and y positions over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
4CCP1350 Mathematics and Mechanics
for Physics I
Assignment 1
1 Calculate how many g of acceleration are experienced by a dust particle
rotating inside a Dyson DC31 vacuum cleaner, said to be the fastest on Earth,
with an angular velocity of 104000 rpm, and a size of 55,0 mm.
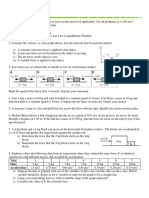
2 A cube of mass M1 5 kg lays on a large slab of mass M2 20 kg placed
over a plane. A constant force FE 90 N is applied to the cube. The
cube and the slab are rough, such that their interaction can be described
by a static friction coecient S 1 0.60 and a dynamic friction coecient
D 1 0.60. Determine the motion of the cube and the slab for the two
cases:
2.1 for no friction between the slab and the plane.
2.2 the friction between the plane and the slab is described by the two
coecient S 2 0.15 and D 2 0.10.
3 Describe the motion of a particle whose equation of motion is
3.1
xptq r cospt2 q
xptq r sinpt2 q
3.2
xptq rt cospt2 q
xptq rt sinpt2 q
3.3 Confirm your results with a simple script as for example the following
Matlab script:
t=0.01*(1:1000); % time axis
x = t.*cos(t.2); % x ais
y = t.*sin(t.2); % y axis
plot(x,y)
xlabel('Position in the x axis [A.U.]','FontSize',18)
ylabel('Position in the y axis [A.U.]','FontSize',18)
title('Trajectory','FontSize',18)
4 A spring-loaded toy gun is used to shoot a ball of mass M straight up in the
air. The ball is not attached to the spring. The ball is pushed down onto the
spring so that the spring is compressed a distance S below its unstretched
point. After release, the ball reaches a maximum height 3S, measured from
the unstretched position of the spring (see diagram).
4.1 Find the spring constant of the spring.
4.2 Find the equilibrium point of the ball when it is sitting on the spring with
no forces other than gravity and the spring acting on it. Clearly indicate the
point you are using as the origin of your coordinate system and what direction
is positive.
4.3 Now, the ball is glued onto the spring so that it oscillates up and down
rather than flying o the spring. The spring is again compressed the same
distance S below its unstretched point. Write an equation for the position of
the ball as a function of time after it is released.
5 A clock is build out of a light particle of mass m which bounces elastically
back and forth between two very heavy mirrors like in the figure, a unit of
time is defined as the round-trip time of the bouncing mass. The distance
between the two mirrors is L and the velocity of the bouncing ball is v0 .
The clock is mounted on a ship that move with velocity v and magnitude |v|
smaller than |v0 |. Treat the clock as an isolated system to which no external
forces are acting.
v0
v
v0
v
v
5.1 Calculate the value of a time unit for an observer on the ship and for
one on ground.
5.2 Replace the mass m with a photon, which is a particle of no mass and
fixed velocity |v0 | c. Calculate the value of a time unit for an observer on
the ship and for one on ground.
6 A children toy is composed of a point mass of value m 1 kg and an ideal
(no mass, inextensible) rope of length r 20 cm. The rope has a breaking
tension of Tmax 30 N after which it breaks. By spinning the toy on Earth,
the children can achieve instantaneously an angular velocity of 10 rad/s.
6.1 Will the toy rotate or will the rope break?
6.2 Calculate the tension of the rope as a function of the rotation angle .
6.3 At time t 0 the children decrease the angular rotation speed from
10 rad/s to 1 rad/s. Will the toy still rotate?
You might also like
- USAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Document311 pagesUSAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Science Olympiad Blog95% (19)
- Force AnalysisDocument152 pagesForce AnalysisWang Han Zhu100% (1)
- Drilling With Digital TwinsDocument18 pagesDrilling With Digital Twinsnicessg@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Pile Cap Design 1Document6 pagesPile Cap Design 1kjpatel2100% (2)
- WorksheetDocument3 pagesWorksheetdanielNo ratings yet
- Trabjo en Grupo Fisica MecanicaDocument14 pagesTrabjo en Grupo Fisica MecanicadilanNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet WPEDocument9 pagesPractice Sheet WPENaveen JaferNo ratings yet
- SHMDocument23 pagesSHMUnknownNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Regional Physics Olympiad 2022 1Document4 pagesIndonesian Regional Physics Olympiad 2022 1Marcus PoonNo ratings yet
- Tut Test 6 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 6 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document85 pagesCH 9tajveer1310No ratings yet
- Physics Porjectile QuestionsDocument3 pagesPhysics Porjectile QuestionskokoNo ratings yet
- Review Problems, Physics 111 Final ExamDocument13 pagesReview Problems, Physics 111 Final Examav742No ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document3 pagesWa0010.BxkxnzixbNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document85 pagesCH 9Ferdinand Yohannes Van LankhorstNo ratings yet
- Phys1101 Worksheeti 2014 EDocument6 pagesPhys1101 Worksheeti 2014 Ejhxnrx48f8No ratings yet
- Physics Rotational Dynamics PDFDocument11 pagesPhysics Rotational Dynamics PDFAshish RanjanNo ratings yet
- General Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityZiyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Electric FieldsDocument17 pagesChapter 15 Electric FieldsdrewNo ratings yet
- Irodov Friction and Tension QuesDocument60 pagesIrodov Friction and Tension QuesShaurya SokhandaNo ratings yet
- Physics I Quiz # 2 - 01/07/2022Document9 pagesPhysics I Quiz # 2 - 01/07/2022Nathaly SosaNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemDocument10 pagesProblem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemVongNo ratings yet
- EM - Model Questions - 2023Document8 pagesEM - Model Questions - 2023Aadi AhwanitNo ratings yet
- Part-1: Subjective Questions: KinematicsDocument27 pagesPart-1: Subjective Questions: KinematicsB AbhinavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ReviewDocument3 pagesChapter 2 ReviewFlora DongNo ratings yet
- Phys 1 Lab ManualDocument13 pagesPhys 1 Lab ManualemuphychemNo ratings yet
- Phys B 1st Semester LBQsDocument11 pagesPhys B 1st Semester LBQsCanjiNo ratings yet
- 2024spring General Physics (1) Problem Set 2 With SolutionsDocument31 pages2024spring General Physics (1) Problem Set 2 With SolutionspurevnaymbayarjargalNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Physics Sample PaperDocument3 pagesClass Xi Physics Sample Paperdhruvarora31No ratings yet
- Rep 7 - 12 Phys 3311 StudentsDocument13 pagesRep 7 - 12 Phys 3311 StudentsCeleste SchepersNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Basic Dynamics NumericalsDocument7 pagesBasic Dynamics Numericalsashok royNo ratings yet
- Lista 3Document4 pagesLista 3Thales FreireNo ratings yet
- RotaionalDocument19 pagesRotaionalSujay BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Prob Set 5Document2 pagesProb Set 5Debolina DasNo ratings yet
- Block Prept1 g112324-1Document7 pagesBlock Prept1 g112324-1Alexxander Govinda KhevinNo ratings yet
- 2 (1) .Physics MechanicsDocument35 pages2 (1) .Physics MechanicsNo PainNo ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyDocument12 pagesRotational Dynamics: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyRoNNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Document5 pagesCentre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Kenny Ruiz0% (1)
- RefwfwefewwefwefewfwefDocument14 pagesRefwfwefewwefwefewfwefAidan Hager-BarlowNo ratings yet
- Rotational DynamicsDocument12 pagesRotational DynamicsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- PHY1505 Assignment 2 (9 May 2024)Document6 pagesPHY1505 Assignment 2 (9 May 2024)zakkiyah.i.essackNo ratings yet
- Draw A Picture!: You May Treat The Child As A Point ParticleDocument24 pagesDraw A Picture!: You May Treat The Child As A Point Particlebat.laughNo ratings yet
- Anna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important QuestionsDocument12 pagesAnna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important QuestionsPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Energi Momentum Dan Dinamika Rotasi Pelatihan Osn 2012Document7 pagesEnergi Momentum Dan Dinamika Rotasi Pelatihan Osn 2012Ivandito HerdayandityaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Example ProblemsDocument7 pagesDynamics Example ProblemsMuhayang Arifin KhalikNo ratings yet
- Physics Rotational DynamicsDocument11 pagesPhysics Rotational DynamicsSayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- ZadaniaDocument3 pagesZadaniatosia83No ratings yet
- 2018 June Test PrepquestionsDocument14 pages2018 June Test PrepquestionsSiinozuko MasentseNo ratings yet
- Tutoring QuestionsDocument7 pagesTutoring QuestionsJulieneNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir) PDFDocument5 pagesCentre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir) PDFkisan singhNo ratings yet
- SLP125 TutorialDocument3 pagesSLP125 Tutorialr4ww7cwbzcNo ratings yet
- Class-Xi Half Yearly ExaminationDocument3 pagesClass-Xi Half Yearly Examinationapi-328778920No ratings yet
- Example Problems On Newton's LawsDocument4 pagesExample Problems On Newton's LawshooriaroshanNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- JobDescriptionDocument7 pagesJobDescriptionMohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- 990-1-EI3848-CE - 20201118 B6 Parliamentary and Briefings Officer JDDocument9 pages990-1-EI3848-CE - 20201118 B6 Parliamentary and Briefings Officer JDMohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Beyond Prevent: A Real Alternative To Securitised PoliciesDocument51 pagesBeyond Prevent: A Real Alternative To Securitised PoliciesMohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Disabled Students Campaign Toolkit 2017Document18 pagesDisabled Students Campaign Toolkit 2017Mohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Termaxx KCLBC Catalogue - 2015Document18 pagesTermaxx KCLBC Catalogue - 2015Mohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Q1. Let Mxym Be The Mxy For Muscle and Mxyb Be The Mxy For Blood. A) Mxym M0 Exp ( - (21) /50) 0.6570 M0Document5 pagesQ1. Let Mxym Be The Mxy For Muscle and Mxyb Be The Mxy For Blood. A) Mxym M0 Exp ( - (21) /50) 0.6570 M0Mohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Chalmers - Panpsychism and Panprotopsychism (In Press)Document28 pagesChalmers - Panpsychism and Panprotopsychism (In Press)Andreu Ballús100% (3)
- 22-Year Clinical Evaluation of The Performance of Two Posterior Composites With Different Filler CharacteristicsDocument9 pages22-Year Clinical Evaluation of The Performance of Two Posterior Composites With Different Filler CharacteristicsAl-Kawthari As-SunniNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Distance MeasurementDocument16 pagesHorizontal Distance MeasurementAlfonso John AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Group # 3: 4cheaDocument16 pagesGroup # 3: 4cheaNishant ChughNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Optimal Design of DC Machine Unit-02/Lecture-01Document31 pagesUnit - 2 Optimal Design of DC Machine Unit-02/Lecture-01madeehaNo ratings yet
- B.S - Physics Semester SystemDocument47 pagesB.S - Physics Semester SystemIrfan NoorNo ratings yet
- CHP 15-3 Wave InteractionsDocument6 pagesCHP 15-3 Wave InteractionsDoyNo ratings yet
- OLD AUTOMATION Midterm-Exam SolutionDocument2 pagesOLD AUTOMATION Midterm-Exam SolutionsilverhandxNo ratings yet
- Mixtures ReviewDocument3 pagesMixtures Reviewapi-301425989No ratings yet
- IBO 2009 Theory AnswersDocument9 pagesIBO 2009 Theory AnswersPei JingNo ratings yet
- Table 2.1 Atmospheric Properties in ISA: Flight Dynamics-I Prof. E.G. Tulapurkara Chapter-2Document8 pagesTable 2.1 Atmospheric Properties in ISA: Flight Dynamics-I Prof. E.G. Tulapurkara Chapter-2Chegrani AhmedNo ratings yet
- B455Document3 pagesB455basha100% (1)
- Light Colour in The AtmosphereDocument1 pageLight Colour in The AtmosphereJordan ChizickNo ratings yet
- Engineering HydrologyDocument13 pagesEngineering Hydrologyapi-26150050100% (1)
- Three-Dimensional Analysis of Tokamaks and Stellarators: Paul R. GarabedianDocument4 pagesThree-Dimensional Analysis of Tokamaks and Stellarators: Paul R. GarabedianMustafa Umut SaracNo ratings yet
- Cement Process Engineering Vade Mecum: 2. StatisticsDocument15 pagesCement Process Engineering Vade Mecum: 2. StatisticsTamer FathyNo ratings yet
- Ase 301 - HW1Document3 pagesAse 301 - HW1isaac tsaiNo ratings yet
- MHTL G01 PDFDocument5 pagesMHTL G01 PDFalialavi2No ratings yet
- 1BDocument5 pages1BjhacademyhydNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Phase TransformationDocument26 pagesChapter 10 Phase TransformationEffendy AdipratamaNo ratings yet
- McFarland StandardDocument4 pagesMcFarland StandardHamid OkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ANSYS Mechanical: Workshop 6.1 Free Vibration AnalysisDocument11 pagesIntroduction To ANSYS Mechanical: Workshop 6.1 Free Vibration Analysisaslekha100% (1)
- Optimum Unbraced Length Ratios of Slender Steel Sections: Saleem M. Umair, Q. Hisham, and Zahid A. SiddiqiDocument5 pagesOptimum Unbraced Length Ratios of Slender Steel Sections: Saleem M. Umair, Q. Hisham, and Zahid A. SiddiqimargitorsiNo ratings yet
- Coagulant (Pac) and Flocculant (Pam)Document2 pagesCoagulant (Pac) and Flocculant (Pam)udit singhNo ratings yet
- Microstructure and Mechanical Characterization of Friction Stir Welded High Strength Low Alloy SteelsDocument8 pagesMicrostructure and Mechanical Characterization of Friction Stir Welded High Strength Low Alloy SteelsKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document37 pagesChapter 5TajTajNo ratings yet
- Quantum-Mechanical Aspects of The L. Pauling's Resonance Theory.Document4 pagesQuantum-Mechanical Aspects of The L. Pauling's Resonance Theory.Bezverkhniy VolodymyrNo ratings yet