Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EPS 2 Tut1
EPS 2 Tut1
Uploaded by
Deep ShethOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EPS 2 Tut1
EPS 2 Tut1
Uploaded by
Deep ShethCopyright:
Available Formats
List of practical EPS II - 2016
Electrical Power systems II
TERM WORK 2016
Practical 1
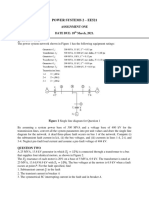
1. Write a note on short transmission line with phasor diagram for Resistive, Capacitive and
Inductive loads, and also derive the formulae for voltage regulation for each case.
(Rest of the questions were already discussed during Laboratory hours. Students are
expected to solve numerical and also attach MATLAB/SiLAB code for the same.)
Practical 2
1. Using the nominal - method, find the sending-end voltage and voltage regulation of a
250 km, three-phase 50 Hz, transmission line delivering 25 MVA at 0.8 lagging power
factor to a balanced load at 132 kV. The line conductors are spaced equilaterally 3 m
apart. The conductor resistance is 0.11 /km and its effective diameter is 1.6 cm. Neglect
leakage reactance. (Eg. 5.4 Nagrath Kothari)
2. A three phase, 60 Hz, completely transposed 345 kV, 200 km line has z= 0.032+ j0.35
/km and y= j4.2 x 10-6 S/km. Full load at the receiving end is 700 MW at 0.99 p.f.
leading and at 95% of rated voltage. Assuming a medium length line, determine the
following: ABCD parameters of the nominal circuit, sending end voltage and current
and real power delivered by sending end. (nov 2013)
3. A 3-phase overhead transmission line delivers a load of 80 MW at 0.8 pf lagging and 220
kV between the lines. Its total series impedance per phase and shunt admittance per phase
is 200 80 ohms and 0.0013 90 mhos per phase respectively. Using nominal T
method determine (i) A,B,C,D constants of the line (ii) Sending end voltage (iii) Sending
end current (iv) Sending end power factor (v) Transmission efficiency of the line. (June
2014)
Practical 3
1. A 275 kV transmission line has the following line constants: A = 0.85 50, 20 75 (i)
Determine the power at unity power factor that can be received, if the voltage profile at
each end is to be maintained at 275 kV (b) What type of compensation equipment would
be required if the load is 150 MW at unity pf with the same voltage profile as in part
(summer 2014)
2.
List of practical EPS II - 2016
3.
(solve part (d) and rest of the solution
using MATLAB)
4.
NOTE: problem number 1 , 2 and 3 are solved
from Hadi sadat and Nagrath Kothari.
problems
Answer for problem 4 is 47.56 MVAR lagging
Practical 4
To simulate transient in series R-L circuit with special attention to change in DC offset
current for application of excitation at different instant.
Write the equation of current during transient conditions
Plot steady state, transient components and total current separately (using subgraph)
for different values of alpha.
Use MATLAB/SIMULINK to verify the results.
Comment on how value of alpha changes results.
Practical 5
Dynamic simulation of three phase fault on terminal of unloaded synchronous generator. The
simulation should show the waveforms of all three line current for fault at different instant on
voltage wave of phase A.
List of practical EPS II - 2016
Write the equation of current during transient conditions
Plot steady state, transient, sub-transient components and total current separately
(using subgraph) for different values of alpha.
Comment on how value of alpha changes results.
Practical 6
To write a computer program for obtaining symmetrical components for a given set of
unbalanced phasors.
1. Derive the equation of three phase power in terms of symmetrical components of voltages
and currents.
2. The currents in three phase unbalanced system are IR = (12 + j6) A, IY = (12 - j12) A, IB
= (-15 + j10) A. The phase sequence is RYB. Calculate, positive, negative and zero
sequence components of currents (winter 2014)
3. Nagrath Kothari : - unsolved 10.5
4. Given Va 553, V 7164, V 7105, find the symmetrical
components.
5. Given V0 = 3.5 122 V1 = 5.0 10 and V2 = 1.9 92, find the phase
sequence components.
(You are supposed to solve these problems and verify answer using
that they have developed. Also each solution must contain proper
for both balanced and unbalanced condition e.g. shown in figure)
MATLAB code
phasor diagram
Practical 7
To plot sending end power circle diagram and receiving end power circle diagram of a
transmission line on a graph paper with some suitable scale.
1. Discuss steps to draw circle diagram. Also demonstrate how receiving and sending
end circle diagram for a short transmission line would look like.
2. Solve tutorial 3, problem no. 4 using circle diagrams and verify your answer.
3. Nagrath Kothari solved 5.11
3
List of practical EPS II - 2016
Practical 8
To write a computer program for animation of travelling waves of a long transmission line
with different operating conditions.
Practical 9
To analyse L-G fault of a small system (containing generator, transformer and lines) using
interconnection of sequence networks.
1. Nagrath Kothari unsolved 10.8
List of practical EPS II - 2016
2. Nagrath Kothari Solved 11.7 ( You are supposed to solve this numerical by both
connection of sequence network and by Zbus method and verify your answers)
3. Considering system shown in fig. 2 at no load, find out the line current Ia at fault
point when A-G fault occurs at the terminals of the motor. Let zero sequence
5
List of practical EPS II - 2016
reactance of generator and motor is 50 % each. Zero sequence reactance of
transformers is 25 % each and zero sequence reactance of line is 20 %. 1 ohm each is
connected in the neutral circuit of both the synchronous machines. (summer 2015)
Fig. 2
Practical 10
To analyse L- L-G and L- L fault of a small system (containing generators, transformers and
lines) using interconnection of sequence network.
1. A synchronous generator is rated at 25 MVA, 11 kV. It is star connected with neutral
point solidly grounded. The generator is operating on no-load at rated voltage. Its
reactances are X=X2 = 0.2 pu and X0 = 0.08 pu. Calculate the symmetrical
subtransient currents for (i)LG fault (ii) LL fault (iii) LLG fault (iv) LLL fault. After
calculating the values of fault currents do you find something surprising in the values
of fault currents for LG and LLL faults? Why? (summer 2014)
2. Considering system shown in fig. 2 at no load, find out the line current Ia at fault
point when B-C-G fault occurs at the terminals of the motor. Let zero sequence
reactance of generator and motor is 50 % each. Zero sequence reactance of
transformers is 25 % each and zero sequence reactance of line is 20 %. 1 ohm each is
connected in the neutral circuit of both the synchronous machines. (summer 2015)
Practical 11
Calculation of fault current for a three phase fault in a small power system.
1. A synchronous generator and a synchronous motor each rated 25 MVA, 11 kV having
15% sub-transient reactance are connected through transformer and a line as shown in
Fig. 2. The transformers are rated 25 MVA, 11/66 kV and 66/11 kV with leakage
reactance of 10% each. The line has a reactance of 10% on a base of 25 MVA, 66 kV.
The motor is drawing 15 MW at 0.8 power factor leading and a terminal voltage of
10.6 kV when a symmetrical three-phase fault occurs at the motor terminals. Find the
sub-transient current in the motor, generator and fault. (Winter 2015)
2. Consider the three bus system shown in fig. The generators are 100 MVA, with a
transient reactance of 10% each. Both the transformers are 100 MVA with a leakage
reactance of 5%. The reactance of each of the lines to a base of 100 MVA, 110 kV is
10%. Obtain the value of fault current for a three phase solid short circuit on bus 3.
Assume prefault voltages to be 1.0 p.u. and prefualt currents to be zero. (summer
2014)
List of practical EPS II - 2016
You might also like
- Original PDF Design of Water Resource Recovery Facilities Manual of Practice No 8 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Design of Water Resource Recovery Facilities Manual of Practice No 8 6th Edition PDFcynthia.stewart295100% (37)
- UACDC (2010) - Low Impact Development ManualDocument117 pagesUACDC (2010) - Low Impact Development ManualSalomão Amorim100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan JaundiceDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan Jaundicegandhialpit76% (29)
- Power System AnalysisDocument23 pagesPower System AnalysisSaeed Al BlooshiNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument5 pagesAssignment IPrasenjit DeyNo ratings yet
- (SLD) One Line DiagramDocument8 pages(SLD) One Line DiagramIbrahim AkaliNo ratings yet
- Holmes-Poirot DocumentDocument2 pagesHolmes-Poirot Documentapi-242851904No ratings yet
- Power System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperDocument2 pagesPower System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperKeyur PatelNo ratings yet
- PSADocument25 pagesPSAramyadspNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWDocument13 pagesPower System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis ImportantDocument8 pagesPower System Analysis Importantsparkle courageNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-IDocument8 pagesPower Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-ISoniya GJNo ratings yet
- ELEC4612-11 Exp 1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesELEC4612-11 Exp 1 IntroductionJoseph MouNo ratings yet
- EE6501-Question BankDocument16 pagesEE6501-Question BankBelayneh TadesseNo ratings yet
- IGEE 402 - Power System Analysis Final Examination - Sample Fall 2004Document28 pagesIGEE 402 - Power System Analysis Final Examination - Sample Fall 2004Akinbode Sunday OluwagbengaNo ratings yet
- Ee2351 Psa Im 2013Document11 pagesEe2351 Psa Im 2013ZARGHAM KHAN100% (1)
- CAPS Lab ManualDocument18 pagesCAPS Lab ManualAyush NemaNo ratings yet
- Tight Tight TyteDocument3 pagesTight Tight TyteShubhang TadasNo ratings yet
- Psa (21ee53) - Iat3 QBDocument3 pagesPsa (21ee53) - Iat3 QBShubhang TadasNo ratings yet
- Eee-Vi-Power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - AssignmentDocument22 pagesEee-Vi-Power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - Assignmentsandoval.sherwynneNo ratings yet
- Additional Questions - Unit 1Document6 pagesAdditional Questions - Unit 1manvenderNo ratings yet
- PSASghhggdvDocument6 pagesPSASghhggdvDarshan GowdaNo ratings yet
- Eee Iii Year 2017-2018Document48 pagesEee Iii Year 2017-2018J JulietNo ratings yet
- Ee521 Assignment 1 2021Document3 pagesEe521 Assignment 1 2021Khondwani BandaNo ratings yet
- Ee1351 PsaDocument16 pagesEe1351 PsaStephen Kenth La GuerreNo ratings yet
- Model 1Document2 pagesModel 1ponselvanvNo ratings yet
- Unit4questions 100415042439 Phpapp01Document4 pagesUnit4questions 100415042439 Phpapp01Mohamad HishamNo ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument3 pagesPower SystemMogaka LucasNo ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument4 pagesPower Systemj settyNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Introduction Part - A (2 Marks)Document14 pagesUnit I - Introduction Part - A (2 Marks)Ragul RamNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Nithiya MaharajanNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis-IiDocument115 pagesPower System Analysis-IiSrinivasReddy100% (2)
- Computer Methods in Power SystemsDocument7 pagesComputer Methods in Power SystemssuhrudkumarNo ratings yet
- PSA SolutionDocument5 pagesPSA SolutionviswaNo ratings yet
- QueBank - Unit 3 - Unsymmetrical Fault AnalysisDocument3 pagesQueBank - Unit 3 - Unsymmetrical Fault AnalysisBelayneh TadesseNo ratings yet
- Psa ModelDocument2 pagesPsa ModelSyed MeerNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument10 pagesPower System AnalysisAlluri Appa RaoNo ratings yet
- Problems Chapter 5 1Document7 pagesProblems Chapter 5 1Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- Psa Imp QuestDocument11 pagesPsa Imp Questdrmsrmurty9473No ratings yet
- Power System Reactance Diagram Questions PDFDocument22 pagesPower System Reactance Diagram Questions PDFHota bNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet-2Document5 pagesTutorial Sheet-2Rishabh Kalia100% (1)
- Kuppam Engineering College, KuppamDocument1 pageKuppam Engineering College, KuppamManohar_3020No ratings yet
- Part - B (2 X 15 30 Marks) Answer All QuestionsDocument2 pagesPart - B (2 X 15 30 Marks) Answer All QuestionsGokul ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- PSA QB 15-16 With AnswerDocument75 pagesPSA QB 15-16 With Answerkmohanadasse100% (1)
- Ee306 ADocument3 pagesEe306 AAparna JoseNo ratings yet
- 18-05 Power System Analysis (EL)Document2 pages18-05 Power System Analysis (EL)keerthanavijayaNo ratings yet
- Ee 1351 Power System AnalysisDocument31 pagesEe 1351 Power System AnalysisStephen Kenth La GuerreNo ratings yet
- Psa QB 2016-2017 Questions OnlyDocument25 pagesPsa QB 2016-2017 Questions OnlykmohanadasseNo ratings yet
- Psa Question Bank 2Document9 pagesPsa Question Bank 2Krishnakumar IesNo ratings yet
- Ps 2 NewDocument7 pagesPs 2 NewAditya PatilNo ratings yet
- BE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Document5 pagesBE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Adesh Bhortakke100% (1)
- Chapter 3-Power Flow Solution-Gauss Seidel 2Document32 pagesChapter 3-Power Flow Solution-Gauss Seidel 2Avianda Sinyo100% (1)
- Figure For Question No. 1Document4 pagesFigure For Question No. 1noybit mondalNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis (Jan-2014)Document10 pagesPower System Analysis (Jan-2014)Likhitha YerraNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Advanced Multilevel Converters and Applications in Grid IntegrationFrom EverandAdvanced Multilevel Converters and Applications in Grid IntegrationAli Iftekhar MaswoodNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Usmc Vector 21Document64 pagesUsmc Vector 21David PerrinNo ratings yet
- Drums and Hardware: General CatalogDocument39 pagesDrums and Hardware: General CatalogmiquNo ratings yet
- Enrichment Exercise No. 3 Problem Solving Exercise. Now That You Have Learned The Nature, Scope, FunctionsDocument2 pagesEnrichment Exercise No. 3 Problem Solving Exercise. Now That You Have Learned The Nature, Scope, FunctionsQueenVictoriaAshleyPrietoNo ratings yet
- Coe 2Document8 pagesCoe 2Jean Lindley JosonNo ratings yet
- Oleh: Riris Retno Wulan, Mochammad MustamDocument20 pagesOleh: Riris Retno Wulan, Mochammad MustamMario100% (1)
- Articulo Sordo CegueraDocument11 pagesArticulo Sordo CegueraIsidoraBelénRojasTorresNo ratings yet
- Sat Sankalp EnglishDocument2 pagesSat Sankalp Englishrohan100% (1)
- Miscible Blend & ImMisible BlendDocument18 pagesMiscible Blend & ImMisible BlendHamzahSardarNo ratings yet
- Sds Limestone-F-PulverizedDocument6 pagesSds Limestone-F-PulverizedAzuan MABKNo ratings yet
- Double Take Chinese Optics and Their Media in Postglobal PDFDocument47 pagesDouble Take Chinese Optics and Their Media in Postglobal PDFparker03No ratings yet
- The Rebel: by D.J.EnrightDocument20 pagesThe Rebel: by D.J.EnrightNandini kNo ratings yet
- GD - or MPW 84918 1 300 GD - OR..editedDocument2 pagesGD - or MPW 84918 1 300 GD - OR..editediolcdhnlNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Hospital Information SystemsDocument8 pagesLiterature Review On Hospital Information Systemsc5mr3mxfNo ratings yet
- Mini Manifesting GuideDocument13 pagesMini Manifesting Guidesabweed100% (4)
- Emotions LectureDocument12 pagesEmotions LecturePalwasha SheikhNo ratings yet
- Protections Study SDP1-1: Sur Desalination - Oman (SDP1-1)Document27 pagesProtections Study SDP1-1: Sur Desalination - Oman (SDP1-1)Ayoub CherkaouiNo ratings yet
- VMX User ManualDocument94 pagesVMX User ManualRoger M OlsonNo ratings yet
- Pan African University: Institute For Basic Sciences, Technology and InnovationDocument9 pagesPan African University: Institute For Basic Sciences, Technology and InnovationMarc MarinNo ratings yet
- Critikon Dinamap Compact - Service Manual 2Document78 pagesCritikon Dinamap Compact - Service Manual 2Ayaovi JorlauNo ratings yet
- Class 9 GrammarDocument32 pagesClass 9 GrammarPerajothi PalanirajaNo ratings yet
- Analogy - Verbal Reasoning Questions and Answers Page 4Document2 pagesAnalogy - Verbal Reasoning Questions and Answers Page 4Palak JioNo ratings yet
- 9 CH 1 2024-25Document12 pages9 CH 1 2024-25Muhammad Abdullah ToufiqueNo ratings yet
- 55-5-1 PhysicsDocument19 pages55-5-1 Physicsvikas aggarwalNo ratings yet
- LPG Sensor TechnologyDocument20 pagesLPG Sensor Technologyeddie eddNo ratings yet
- Barto Thesis 2020Document34 pagesBarto Thesis 2020Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument89 pagesWater Soluble Vitaminsahmedatef100% (1)