Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Xi - Physics - Terminal Examination - II
Xi - Physics - Terminal Examination - II
Uploaded by
Sankar KumarasamyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Operating & Maintenance Procedure For Air Cooler Heat ExchangerDocument10 pagesOperating & Maintenance Procedure For Air Cooler Heat Exchangerrahim_33516285678% (9)
- Terms For Automatic Transaxle Repair Manual: Abbreviations Used in This ManualDocument155 pagesTerms For Automatic Transaxle Repair Manual: Abbreviations Used in This ManualFelipe Marques100% (1)
- Cat 140MDocument28 pagesCat 140MWicca GenesisNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Physics Annual Exam 2017 18Document3 pagesClass Xi Physics Annual Exam 2017 18Anupam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document2 pagesPhysics 2SHAIKH YUNUS ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Final TermDocument7 pagesClass Xi Final Termsuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Xi - Important Questions For Term-2 (2021-2022)Document2 pagesXi - Important Questions For Term-2 (2021-2022)SatendraNo ratings yet
- Xi PT Phy 2021 22Document3 pagesXi PT Phy 2021 22Joshua ZongteNo ratings yet
- 11-D-Physics Term-2Document3 pages11-D-Physics Term-2Himanshi TomerNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From and Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument3 pagesMaterial Downloaded From and Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksKunal RohitasNo ratings yet
- PHT (2e)Document2 pagesPHT (2e)krishNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics Hy NCSDocument2 pages11th Physics Hy NCSmohd yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Xi See Physics 2023-24Document6 pagesSample Paper Xi See Physics 2023-24jethvadevashyaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Document3 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Prajin MuruganNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics Set BDocument8 pagesClass Xii Physics Set Bvarshanair2005No ratings yet
- 1st PU Physics Model QP 2 PDFDocument6 pages1st PU Physics Model QP 2 PDFPrasad C M100% (2)
- Physics Class 11Document8 pagesPhysics Class 11sindhu1975nairNo ratings yet
- Class: XI Second Term Examination 2014-15 Subject: Physics Set B1 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70Document7 pagesClass: XI Second Term Examination 2014-15 Subject: Physics Set B1 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70Aryan SinghNo ratings yet
- 1st Assessment 2017-2019Document13 pages1st Assessment 2017-2019Uttalika NandaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa2 2014 2Document3 pagesCbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa2 2014 2sagarchidre114No ratings yet
- Ce2202 - Mechanics of FluidsDocument3 pagesCe2202 - Mechanics of FluidsPrashant GaradNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa2 2014 1Document3 pagesCbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa2 2014 1sagarchidre114No ratings yet
- Physics 17Document7 pagesPhysics 17UPAHAR SWAPNASHISNo ratings yet
- Xi Physics - Periodic Test - 2Document3 pagesXi Physics - Periodic Test - 2Aniket DasNo ratings yet
- Objective Worksheet For Final Term 2023Document18 pagesObjective Worksheet For Final Term 2023SnowYTNo ratings yet
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IIDocument16 pagesIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IISudharsananPRSNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheetwith Key-Term 2-2023Document7 pagesRevision Worksheetwith Key-Term 2-2023dhritidubaiNo ratings yet
- Physic Ss2 2019Document4 pagesPhysic Ss2 2019sulayajannyNo ratings yet
- List of DerivationsDocument7 pagesList of DerivationsJaruNo ratings yet
- 1st PU Physics November 2014 PDFDocument2 pages1st PU Physics November 2014 PDFPrasad C M100% (3)
- FULL PORTION TEST 2024Document8 pagesFULL PORTION TEST 2024sreyachandrasankarNo ratings yet
- A A PHYSICS MODEL EXAM 2011 Model TwoDocument9 pagesA A PHYSICS MODEL EXAM 2011 Model TwoKerod MohamedNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 10 (2019-20)Document29 pagesSample Paper 10 (2019-20)jain.radha.aggrNo ratings yet
- QB FMDocument1 pageQB FMAnil ChauvanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument21 pagesPHYSICSdishugirdhar08100% (1)
- CBSE Model QP Class XIDocument4 pagesCBSE Model QP Class XIroythomascNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper Class 12Document6 pagesPhysics Paper Class 12animeshkumar.cityparkNo ratings yet
- Class11 - Physics - Subjective QPDocument3 pagesClass11 - Physics - Subjective QPAkshat VasudevaNo ratings yet
- Dungtse ClusterDocument17 pagesDungtse ClusterRigzean Thinley Lhendrup100% (1)
- MCQ (Pure) (Sp2)Document8 pagesMCQ (Pure) (Sp2)Huiming OngNo ratings yet
- Physics 12THDocument10 pagesPhysics 12THparikshitrakhecha512No ratings yet
- V V) VV VV.: VX (Sii) S'V:X:Ii - Iix /is Ii Ii V - Iivv - Ii Ii Vii Ii) Ii/1 U U U) U) UDocument2 pagesV V) VV VV.: VX (Sii) S'V:X:Ii - Iix /is Ii Ii V - Iivv - Ii Ii Vii Ii) Ii/1 U U U) U) U754097No ratings yet
- Physics2015 16Document6 pagesPhysics2015 16tranquil_452889939No ratings yet
- Physics Second Terminal ExaminationDocument21 pagesPhysics Second Terminal ExaminationAbdul Rasaq MukailaNo ratings yet
- 1st PU Physics Model QP 1 PDFDocument14 pages1st PU Physics Model QP 1 PDFPrasad C M71% (7)
- 12 Science HHWDocument26 pages12 Science HHWOmkar VikalNo ratings yet
- MCQ (Pure) (Sp1)Document8 pagesMCQ (Pure) (Sp1)Huiming OngNo ratings yet
- Term End Examination-Physics (2020-2021, PHYSICS)Document2 pagesTerm End Examination-Physics (2020-2021, PHYSICS)Venkat BalajiNo ratings yet
- Second Terminal Examination, 2017: PhysicsDocument3 pagesSecond Terminal Examination, 2017: PhysicsTechy RodanNo ratings yet
- QDB 35Document4 pagesQDB 35ਤਨ੍ਹਾ ਰਾਜੀਵ ਮਾਯੂਸNo ratings yet
- p1 FinalDocument9 pagesp1 FinalDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- FLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsDocument4 pagesFLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsChetanNo ratings yet
- SPM 4531 2006 Physics p1 BerjawapanDocument12 pagesSPM 4531 2006 Physics p1 Berjawapanpss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- 7 Models-I PU PhysicsDocument40 pages7 Models-I PU PhysicsMir RayyanNo ratings yet
- DPS Phy - Set - ADocument3 pagesDPS Phy - Set - AscNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper-I For 2020-21: (According To Reduced Syllabus) I Puc PhysicsDocument5 pagesModel Question Paper-I For 2020-21: (According To Reduced Syllabus) I Puc PhysicsSyed Sha100% (1)
- 11 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1Document10 pages11 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1guptadeepka168No ratings yet
- ............Document5 pages............Dax ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersFrom EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics in Channel, Pipe and Aerodynamic Design Geometries 2From EverandFluid Mechanics in Channel, Pipe and Aerodynamic Design Geometries 2No ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 1 (P, C, B) - 30.07.2017Document15 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 1 (P, C, B) - 30.07.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 6 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Document19 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 6 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 2 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Document20 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 2 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 4 (P, C, B) - 23.07.2017Document21 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 4 (P, C, B) - 23.07.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 3 (P, C, B) - 16.07.2017Document19 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 3 (P, C, B) - 16.07.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 5 (P, C, B) - 30.07.2017Document18 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 5 (P, C, B) - 30.07.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Biology Test - 2 - 11.11.2016Document1 pageClass Xii - Biology Test - 2 - 11.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 1 (P, C, B) - 06.04.2017Document22 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 1 (P, C, B) - 06.04.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Neet Physics: 1B/1, TVS Street, Rasipuram - 637408. Namakkal (DT.) Mob: 9444331869, EmailDocument3 pagesClass Xii - Neet Physics: 1B/1, TVS Street, Rasipuram - 637408. Namakkal (DT.) Mob: 9444331869, EmailSankar Kumarasamy100% (1)
- Xii - Combined Test - 1 (Neet) - 11.06.2017Document23 pagesXii - Combined Test - 1 (Neet) - 11.06.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- NEET 2017 Vectors - 03.04.2017Document4 pagesNEET 2017 Vectors - 03.04.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- 1 1+cot 1 1+tan: Test-9Document1 page1 1+cot 1 1+tan: Test-9Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Assignment - 1 (Subj) # Magnetic Effects of Current - 18.11.2016Document2 pagesClass Xii - Assignment - 1 (Subj) # Magnetic Effects of Current - 18.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument6 pagesMeasurementSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- RM Sol ProbDocument26 pagesRM Sol ProbSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Work SheetDocument15 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Work SheetSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Assignment - 2 (Subj) # Electromagnetic Induction - 26.11.2016Document3 pagesClass Xii - Assignment - 2 (Subj) # Electromagnetic Induction - 26.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- NEET - Physics # DPP (Motion in 1D) - 05.04.2017Document7 pagesNEET - Physics # DPP (Motion in 1D) - 05.04.2017Sankar Kumarasamy100% (1)
- DPP 1Document2 pagesDPP 1Sankar Kumarasamy100% (2)
- Class Xii - Assignment - 1 (Obj) # Moving Charges and Magnetism - 18.11.2016Document8 pagesClass Xii - Assignment - 1 (Obj) # Moving Charges and Magnetism - 18.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Complete Rotational System Manual ME 8950A PDFDocument49 pagesComplete Rotational System Manual ME 8950A PDFSindi DayanaNo ratings yet
- TOCA NGTC Technical Partner TenderDocument16 pagesTOCA NGTC Technical Partner Tenderranjitv10No ratings yet
- The Drawworks and The CompoundDocument135 pagesThe Drawworks and The CompoundIbrahim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Power Drive: Gesellschaft Fuer Wissenschaftlichen Apparatebau Gesellschaft Fuer Wissenschaftlichen ApparatebauDocument2 pagesPower Drive: Gesellschaft Fuer Wissenschaftlichen Apparatebau Gesellschaft Fuer Wissenschaftlichen ApparatebauGomez, Francisco (AJR)No ratings yet
- ECT and A/T Indicator (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV), Engine Control (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV)Document33 pagesECT and A/T Indicator (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV), Engine Control (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV)Erick Lizana Neyra100% (4)
- RT ProcedureDocument43 pagesRT ProcedureJeganeswaranNo ratings yet
- ThermodynaDocument14 pagesThermodynaMostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- Lube Oil Console Functional Test ProcedureDocument10 pagesLube Oil Console Functional Test Proceduremohamedsaib438No ratings yet
- Brochure L60H L70H L90H EN 21 20044815 A 2014.12 PDFDocument28 pagesBrochure L60H L70H L90H EN 21 20044815 A 2014.12 PDFvolvotadNo ratings yet
- Modern American LATHE PRACTICEDocument438 pagesModern American LATHE PRACTICEJollygreen21100% (1)
- ICE Plant Schedule of LoadsDocument6 pagesICE Plant Schedule of LoadsClifford GatonNo ratings yet
- Alpha Lubricator System Operation Manual MC EnginesDocument4 pagesAlpha Lubricator System Operation Manual MC EnginesshashishekharsinghNo ratings yet
- Centrifuge Digtor22CDocument9 pagesCentrifuge Digtor22Cbilal khan0% (1)
- Gas Compression Dresser Rand PDFDocument28 pagesGas Compression Dresser Rand PDFAnonymous 1XHScfCINo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Practice ProblemsCody WaltonNo ratings yet
- Abma Guide 2013-14 WebDocument64 pagesAbma Guide 2013-14 WebAdolfo Perez MonteroNo ratings yet
- LIFT OFF ModuleDocument28 pagesLIFT OFF Modulericardo100% (1)
- Variable Speed Unit VARIMOT DF16: Sew-Eurodrive, IncDocument2 pagesVariable Speed Unit VARIMOT DF16: Sew-Eurodrive, Inccarlos aguileraNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Maintenance ChartsDocument2 pagesYamaha Maintenance ChartsJeff KendallNo ratings yet
- CER133.1 - Modulus of Rupture Concepts (Manuscript) - Jimenez&OrdejanDocument8 pagesCER133.1 - Modulus of Rupture Concepts (Manuscript) - Jimenez&OrdejanShara Rose OrdejanNo ratings yet
- DHLDocument20 pagesDHLMohammad Faraz AkhterNo ratings yet
- Renault PistonesDocument44 pagesRenault PistonesnicolasNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 QP 42Document4 pages9709 w16 QP 42Yadvi ChoolunNo ratings yet
- Medium Range MotorsDocument38 pagesMedium Range MotorsSamNo ratings yet
- Isolated Footing Design Guidelines: Specifications For Design of Footings As Per IS 456: 2000Document6 pagesIsolated Footing Design Guidelines: Specifications For Design of Footings As Per IS 456: 2000Gani AnosaNo ratings yet
- Genset 550 Kva CatalogueDocument4 pagesGenset 550 Kva CatalogueFirdasu CahyanaNo ratings yet
- SAE 1010 SAE J 403 - BBN STEEL STORES (Mechanical Properties)Document4 pagesSAE 1010 SAE J 403 - BBN STEEL STORES (Mechanical Properties)roberto.alvarezNo ratings yet
Xi - Physics - Terminal Examination - II
Xi - Physics - Terminal Examination - II
Uploaded by
Sankar KumarasamyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Xi - Physics - Terminal Examination - II
Xi - Physics - Terminal Examination - II
Uploaded by
Sankar KumarasamyCopyright:
Available Formats
V
ACADEMIC YEAR 2015 16
TERMINAL EXAMINATION - II
Subject : PHYSICS
Grade
: XI
Marks : 70
Time : 3 hrs
Date :
21.03.2016
General Instructions :
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
g)
h)
All the questions are compulsory.
There are 26 questions in total.
Questions 1 to 5 are very short answer type questions and carry one mark each.
Questions 6 to 10 carry two marks each.
Questions 11 to 22 carry three marks each.
Questions 23 is value based question carrying four marks.
Questions 24 to 26 carry five marks each.
Use of calculators is not permitted. However, you may use log tables if necessary.
SECTION - A
1.
Write down the dimensions of Viscosity coefficient.
ur
ur
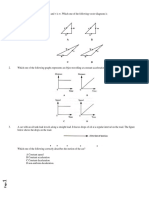
A i 2 j 3k and B 2i j
2.
Prove that
are perpendicular to each other.
3.
What is Elastic fatigue?
4.
State Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics.
5.
A physical quantity P is related to four variables a, b, c and d as follows ;
d
2 3
P = ab / c
the percentage errors in a, b, c and d are 2%, 4%, 3% and 2%
respectively. What is the % error in P?
SECTION - B
6.
Draw the position time graph for following cases when :
(i) object is moving with positive acceleration
(ii) An object in under free fall.
7.
In a refrigerator, heat from inside at 277K is transferred to a room at 300K. How many
joules of heat shall be delivered to the room for each joule of electrical energy consumed
ideally?
1
8.
Discuss the variation of acceleration due to gravity with altitude. How does the
expression modify when h << R?
9.
A projectile is fired in air making an angle with horizontal. Show that its path is
parabolic in nature.
10.
It is easier to pull a lawn roller than to push it. Explain using the resolution of forces.
SECTION C
11.
Explain why should the beams used in the construction of bridges have large depth and
small breadth.
12.
Derive equations of motion by Calculus method.
13.
Derive an expression for the potential energy of an elastic stretched spring.
14.
A liquid drop of diameter D breaks up into 27 tiny drops. Find the resulting change in
energy. Take surface tension of the liquid as T.
15.
Four sphere of diameter 2a and mass M each are placed with their centre on the four
corners of a square of side b. Calculate the moment of inertia of the system about one
side of the square taken as its axis.
16.
What is meant by coefficient of linear expansion and coefficient of cubical expansion?
Derive relationship between them.
17.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 20m/s from the top of a building, the
height of point from where the ball is thrown is 25m from the ground.
(i) How high the ball will rise?
(ii) How long will it be before the ball hits the ground?
18.
State the laws of limiting friction. The coefficient of static friction between block A and the
table is 0.2. What would be the maximum mass of block B so that the two blocks do not
move. The string and the pulley are assumed to be smooth and massless. [g = 10m/s2]
19.
Show that in head on collision between two balls of equal masses moving along a
straight line, the balls simply exchange their velocities.
20.
Derive an expression for moment of inertia of a thin circular ring about an axis passing
through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring.
21.
State Stokes law for the viscous drag experienced by the spherical body falling through
a viscous liquid. Why does a spherical body attain terminal speed. On what factors does
the terminal speed depend.
22.
The stress-strain graph for a metal wire is shown in figure. Up to the point E, the wire
returns to its original state O along the curve EPO when it is gradually unloaded. Point B
corresponds to the fracture of the wire.
(a) Up to which point on the curve is Hookes law obeyed? This point is sometimes
called proportionality limit
(b) Which point on the curve corresponds to elastic limit and yield point of the wire?
(c) Describe what happens when the wire is loaded upto a stress corresponding to the
point A on the graph, and then unloaded gradually. In particular, explain the dotted
curve.
SECTION - D
23.
Sonia and Mahima are good friends and living in a city near the equator.
Sonia went to a
country located near the north pole of the earth with her parents. Her friend
Mahima requested her to bring a gold necklace as gold was cheaper in that
country. Sonia purchased the necklace weighting 20 gm wt. and handed it
over to Mahima. When Mahima got necklace weighted from the local gold
Smith, its weight was less than 20 gm weight Mahima told Sonia that she was
cheating her. However, Sonia explained that weight of a body at equator is
less that at poles. Sonia asked Mahima to return the necklace to her because
she was not interested to spoil her friendship with Mahima.
(i)
Why the weight of necklace is less at equator than at poles?
(ii)
Comment on the attitude of Mahima.
(iii)
What values are shown by Sonia?
SECTION - E
24.
Derive an expression for the rise of liquid in a capillary tube and show that
the height of liquid column supported is inversely proportional to the
curvature of the tube.
OR
Water stands at depth H in a tank whose side walls are
vertical. A hole is made on one of the walls at a depth
h below the water surface.
(i) Calculate the velocity of efflux?
(ii) At what distance R from the foot of the wall does the
emerging stream of the water strike the floor?
(iii) For what value of h this range is maximum?
25.
What is an isothermal process? State two essential conditions for such a
process to take
place. Show analytically that work done by one mole of an ideal gas during
V2
V1
volume expansion from V1 to V2 at temperature T is given by W = RT loge
OR
(i) State first law of thermodynamics?
(ii) Define molar specific heat at constant volume and at constant pressure.
Derive
the
relation between them.
26.
Derive expression for maximum safe velocity with which a vehicle can travel
on banked road. Derive minimum angle of banking to travel without wear and
tear?
OR
A bob of mass m is suspended by a light string of length L. It is imparted a horizontal
velocity vo at the lowest point A such that it complete a semicircular trajectory in the
vertical plane with the string becoming slack only on reaching the top most point C.
Obtain an expression for
(i) vo
(ii) speed at point B & C
(iii) Ratio of KE (KB / KC) at B & C
All the Best
You might also like
- Operating & Maintenance Procedure For Air Cooler Heat ExchangerDocument10 pagesOperating & Maintenance Procedure For Air Cooler Heat Exchangerrahim_33516285678% (9)
- Terms For Automatic Transaxle Repair Manual: Abbreviations Used in This ManualDocument155 pagesTerms For Automatic Transaxle Repair Manual: Abbreviations Used in This ManualFelipe Marques100% (1)
- Cat 140MDocument28 pagesCat 140MWicca GenesisNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Physics Annual Exam 2017 18Document3 pagesClass Xi Physics Annual Exam 2017 18Anupam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document2 pagesPhysics 2SHAIKH YUNUS ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Final TermDocument7 pagesClass Xi Final Termsuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Xi - Important Questions For Term-2 (2021-2022)Document2 pagesXi - Important Questions For Term-2 (2021-2022)SatendraNo ratings yet
- Xi PT Phy 2021 22Document3 pagesXi PT Phy 2021 22Joshua ZongteNo ratings yet
- 11-D-Physics Term-2Document3 pages11-D-Physics Term-2Himanshi TomerNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From and Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument3 pagesMaterial Downloaded From and Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksKunal RohitasNo ratings yet
- PHT (2e)Document2 pagesPHT (2e)krishNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics Hy NCSDocument2 pages11th Physics Hy NCSmohd yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Xi See Physics 2023-24Document6 pagesSample Paper Xi See Physics 2023-24jethvadevashyaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Document3 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Prajin MuruganNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics Set BDocument8 pagesClass Xii Physics Set Bvarshanair2005No ratings yet
- 1st PU Physics Model QP 2 PDFDocument6 pages1st PU Physics Model QP 2 PDFPrasad C M100% (2)
- Physics Class 11Document8 pagesPhysics Class 11sindhu1975nairNo ratings yet
- Class: XI Second Term Examination 2014-15 Subject: Physics Set B1 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70Document7 pagesClass: XI Second Term Examination 2014-15 Subject: Physics Set B1 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70Aryan SinghNo ratings yet
- 1st Assessment 2017-2019Document13 pages1st Assessment 2017-2019Uttalika NandaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa2 2014 2Document3 pagesCbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa2 2014 2sagarchidre114No ratings yet
- Ce2202 - Mechanics of FluidsDocument3 pagesCe2202 - Mechanics of FluidsPrashant GaradNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa2 2014 1Document3 pagesCbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa2 2014 1sagarchidre114No ratings yet
- Physics 17Document7 pagesPhysics 17UPAHAR SWAPNASHISNo ratings yet
- Xi Physics - Periodic Test - 2Document3 pagesXi Physics - Periodic Test - 2Aniket DasNo ratings yet
- Objective Worksheet For Final Term 2023Document18 pagesObjective Worksheet For Final Term 2023SnowYTNo ratings yet
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IIDocument16 pagesIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IISudharsananPRSNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheetwith Key-Term 2-2023Document7 pagesRevision Worksheetwith Key-Term 2-2023dhritidubaiNo ratings yet
- Physic Ss2 2019Document4 pagesPhysic Ss2 2019sulayajannyNo ratings yet
- List of DerivationsDocument7 pagesList of DerivationsJaruNo ratings yet
- 1st PU Physics November 2014 PDFDocument2 pages1st PU Physics November 2014 PDFPrasad C M100% (3)
- FULL PORTION TEST 2024Document8 pagesFULL PORTION TEST 2024sreyachandrasankarNo ratings yet
- A A PHYSICS MODEL EXAM 2011 Model TwoDocument9 pagesA A PHYSICS MODEL EXAM 2011 Model TwoKerod MohamedNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 10 (2019-20)Document29 pagesSample Paper 10 (2019-20)jain.radha.aggrNo ratings yet
- QB FMDocument1 pageQB FMAnil ChauvanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument21 pagesPHYSICSdishugirdhar08100% (1)
- CBSE Model QP Class XIDocument4 pagesCBSE Model QP Class XIroythomascNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper Class 12Document6 pagesPhysics Paper Class 12animeshkumar.cityparkNo ratings yet
- Class11 - Physics - Subjective QPDocument3 pagesClass11 - Physics - Subjective QPAkshat VasudevaNo ratings yet
- Dungtse ClusterDocument17 pagesDungtse ClusterRigzean Thinley Lhendrup100% (1)
- MCQ (Pure) (Sp2)Document8 pagesMCQ (Pure) (Sp2)Huiming OngNo ratings yet
- Physics 12THDocument10 pagesPhysics 12THparikshitrakhecha512No ratings yet
- V V) VV VV.: VX (Sii) S'V:X:Ii - Iix /is Ii Ii V - Iivv - Ii Ii Vii Ii) Ii/1 U U U) U) UDocument2 pagesV V) VV VV.: VX (Sii) S'V:X:Ii - Iix /is Ii Ii V - Iivv - Ii Ii Vii Ii) Ii/1 U U U) U) U754097No ratings yet
- Physics2015 16Document6 pagesPhysics2015 16tranquil_452889939No ratings yet
- Physics Second Terminal ExaminationDocument21 pagesPhysics Second Terminal ExaminationAbdul Rasaq MukailaNo ratings yet
- 1st PU Physics Model QP 1 PDFDocument14 pages1st PU Physics Model QP 1 PDFPrasad C M71% (7)
- 12 Science HHWDocument26 pages12 Science HHWOmkar VikalNo ratings yet
- MCQ (Pure) (Sp1)Document8 pagesMCQ (Pure) (Sp1)Huiming OngNo ratings yet
- Term End Examination-Physics (2020-2021, PHYSICS)Document2 pagesTerm End Examination-Physics (2020-2021, PHYSICS)Venkat BalajiNo ratings yet
- Second Terminal Examination, 2017: PhysicsDocument3 pagesSecond Terminal Examination, 2017: PhysicsTechy RodanNo ratings yet
- QDB 35Document4 pagesQDB 35ਤਨ੍ਹਾ ਰਾਜੀਵ ਮਾਯੂਸNo ratings yet
- p1 FinalDocument9 pagesp1 FinalDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- FLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsDocument4 pagesFLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsChetanNo ratings yet
- SPM 4531 2006 Physics p1 BerjawapanDocument12 pagesSPM 4531 2006 Physics p1 Berjawapanpss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- 7 Models-I PU PhysicsDocument40 pages7 Models-I PU PhysicsMir RayyanNo ratings yet
- DPS Phy - Set - ADocument3 pagesDPS Phy - Set - AscNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper-I For 2020-21: (According To Reduced Syllabus) I Puc PhysicsDocument5 pagesModel Question Paper-I For 2020-21: (According To Reduced Syllabus) I Puc PhysicsSyed Sha100% (1)
- 11 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1Document10 pages11 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1guptadeepka168No ratings yet
- ............Document5 pages............Dax ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersFrom EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics in Channel, Pipe and Aerodynamic Design Geometries 2From EverandFluid Mechanics in Channel, Pipe and Aerodynamic Design Geometries 2No ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 1 (P, C, B) - 30.07.2017Document15 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 1 (P, C, B) - 30.07.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 6 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Document19 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 6 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 2 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Document20 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 2 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 4 (P, C, B) - 23.07.2017Document21 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 4 (P, C, B) - 23.07.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 3 (P, C, B) - 16.07.2017Document19 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 3 (P, C, B) - 16.07.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 5 (P, C, B) - 30.07.2017Document18 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 5 (P, C, B) - 30.07.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Biology Test - 2 - 11.11.2016Document1 pageClass Xii - Biology Test - 2 - 11.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Neet - Combined Test - 1 (P, C, B) - 06.04.2017Document22 pagesNeet - Combined Test - 1 (P, C, B) - 06.04.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Neet Physics: 1B/1, TVS Street, Rasipuram - 637408. Namakkal (DT.) Mob: 9444331869, EmailDocument3 pagesClass Xii - Neet Physics: 1B/1, TVS Street, Rasipuram - 637408. Namakkal (DT.) Mob: 9444331869, EmailSankar Kumarasamy100% (1)
- Xii - Combined Test - 1 (Neet) - 11.06.2017Document23 pagesXii - Combined Test - 1 (Neet) - 11.06.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- NEET 2017 Vectors - 03.04.2017Document4 pagesNEET 2017 Vectors - 03.04.2017Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- 1 1+cot 1 1+tan: Test-9Document1 page1 1+cot 1 1+tan: Test-9Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Assignment - 1 (Subj) # Magnetic Effects of Current - 18.11.2016Document2 pagesClass Xii - Assignment - 1 (Subj) # Magnetic Effects of Current - 18.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument6 pagesMeasurementSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- RM Sol ProbDocument26 pagesRM Sol ProbSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Work SheetDocument15 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Work SheetSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Assignment - 2 (Subj) # Electromagnetic Induction - 26.11.2016Document3 pagesClass Xii - Assignment - 2 (Subj) # Electromagnetic Induction - 26.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- NEET - Physics # DPP (Motion in 1D) - 05.04.2017Document7 pagesNEET - Physics # DPP (Motion in 1D) - 05.04.2017Sankar Kumarasamy100% (1)
- DPP 1Document2 pagesDPP 1Sankar Kumarasamy100% (2)
- Class Xii - Assignment - 1 (Obj) # Moving Charges and Magnetism - 18.11.2016Document8 pagesClass Xii - Assignment - 1 (Obj) # Moving Charges and Magnetism - 18.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Complete Rotational System Manual ME 8950A PDFDocument49 pagesComplete Rotational System Manual ME 8950A PDFSindi DayanaNo ratings yet
- TOCA NGTC Technical Partner TenderDocument16 pagesTOCA NGTC Technical Partner Tenderranjitv10No ratings yet
- The Drawworks and The CompoundDocument135 pagesThe Drawworks and The CompoundIbrahim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Power Drive: Gesellschaft Fuer Wissenschaftlichen Apparatebau Gesellschaft Fuer Wissenschaftlichen ApparatebauDocument2 pagesPower Drive: Gesellschaft Fuer Wissenschaftlichen Apparatebau Gesellschaft Fuer Wissenschaftlichen ApparatebauGomez, Francisco (AJR)No ratings yet
- ECT and A/T Indicator (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV), Engine Control (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV)Document33 pagesECT and A/T Indicator (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV), Engine Control (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV)Erick Lizana Neyra100% (4)
- RT ProcedureDocument43 pagesRT ProcedureJeganeswaranNo ratings yet
- ThermodynaDocument14 pagesThermodynaMostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- Lube Oil Console Functional Test ProcedureDocument10 pagesLube Oil Console Functional Test Proceduremohamedsaib438No ratings yet
- Brochure L60H L70H L90H EN 21 20044815 A 2014.12 PDFDocument28 pagesBrochure L60H L70H L90H EN 21 20044815 A 2014.12 PDFvolvotadNo ratings yet
- Modern American LATHE PRACTICEDocument438 pagesModern American LATHE PRACTICEJollygreen21100% (1)
- ICE Plant Schedule of LoadsDocument6 pagesICE Plant Schedule of LoadsClifford GatonNo ratings yet
- Alpha Lubricator System Operation Manual MC EnginesDocument4 pagesAlpha Lubricator System Operation Manual MC EnginesshashishekharsinghNo ratings yet
- Centrifuge Digtor22CDocument9 pagesCentrifuge Digtor22Cbilal khan0% (1)
- Gas Compression Dresser Rand PDFDocument28 pagesGas Compression Dresser Rand PDFAnonymous 1XHScfCINo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Practice ProblemsCody WaltonNo ratings yet
- Abma Guide 2013-14 WebDocument64 pagesAbma Guide 2013-14 WebAdolfo Perez MonteroNo ratings yet
- LIFT OFF ModuleDocument28 pagesLIFT OFF Modulericardo100% (1)
- Variable Speed Unit VARIMOT DF16: Sew-Eurodrive, IncDocument2 pagesVariable Speed Unit VARIMOT DF16: Sew-Eurodrive, Inccarlos aguileraNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Maintenance ChartsDocument2 pagesYamaha Maintenance ChartsJeff KendallNo ratings yet
- CER133.1 - Modulus of Rupture Concepts (Manuscript) - Jimenez&OrdejanDocument8 pagesCER133.1 - Modulus of Rupture Concepts (Manuscript) - Jimenez&OrdejanShara Rose OrdejanNo ratings yet
- DHLDocument20 pagesDHLMohammad Faraz AkhterNo ratings yet
- Renault PistonesDocument44 pagesRenault PistonesnicolasNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 QP 42Document4 pages9709 w16 QP 42Yadvi ChoolunNo ratings yet
- Medium Range MotorsDocument38 pagesMedium Range MotorsSamNo ratings yet
- Isolated Footing Design Guidelines: Specifications For Design of Footings As Per IS 456: 2000Document6 pagesIsolated Footing Design Guidelines: Specifications For Design of Footings As Per IS 456: 2000Gani AnosaNo ratings yet
- Genset 550 Kva CatalogueDocument4 pagesGenset 550 Kva CatalogueFirdasu CahyanaNo ratings yet
- SAE 1010 SAE J 403 - BBN STEEL STORES (Mechanical Properties)Document4 pagesSAE 1010 SAE J 403 - BBN STEEL STORES (Mechanical Properties)roberto.alvarezNo ratings yet