Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 viewsGini Coefficient and Lorentz
Gini Coefficient and Lorentz
Uploaded by
0612001The document discusses the Gini coefficient and Lorenz curve. It explains that the Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion used to represent income inequality in a nation, with a value of 0 representing total equality and 1 representing maximal inequality. It also describes how the Lorenz curve graphically depicts wealth distribution compared to a hypothetical line of perfect equality, with the difference between the lines quantified by the Gini coefficient. As an example, it provides Bangladesh's 2010 Gini coefficients for urban, rural, and total populations as well as coefficients for the US and Sweden.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- More Than Money: How Economic Inequality Affects . . . EverythingFrom EverandMore Than Money: How Economic Inequality Affects . . . EverythingNo ratings yet
- Labor Economics: Chapter-07 The Wage StructureDocument28 pagesLabor Economics: Chapter-07 The Wage StructureIqbal ChyNo ratings yet
- GinicoefficientsDocument4 pagesGinicoefficientsapi-292484442No ratings yet
- The Declaration of IndependenceDocument2 pagesThe Declaration of Independence0612001100% (1)
- Gini CoefficientDocument10 pagesGini CoefficientstriiderNo ratings yet
- Gini Coefficient & Lorenz Curve: Assignment OnDocument3 pagesGini Coefficient & Lorenz Curve: Assignment On0612001No ratings yet
- Gini - and - Lorenz - Analysis & Terms of EconomistsDocument29 pagesGini - and - Lorenz - Analysis & Terms of EconomistspapanombaNo ratings yet
- Key Takeaways: Economic InequalityDocument4 pagesKey Takeaways: Economic InequalityVINITHANo ratings yet
- Development Theories and Policies (Course Code: MSPM 612)Document37 pagesDevelopment Theories and Policies (Course Code: MSPM 612)Meron AtilabachewNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Notes Econ-25Document9 pagesChap4 Notes Econ-25Erika May RamirezNo ratings yet
- Other Summary Measures of Poverty and InequalityDocument6 pagesOther Summary Measures of Poverty and InequalityNoor AliNo ratings yet
- CONADEV - Chapter 5Document16 pagesCONADEV - Chapter 5Lalaine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Poverty and Income InequalityDocument79 pagesChapter 5 - Poverty and Income InequalityKenzel lawasNo ratings yet
- Economic Inequality: Key TakeawaysDocument3 pagesEconomic Inequality: Key TakeawaysLoad7No ratings yet
- Proverty, Inequality, and Development: Group 5Document32 pagesProverty, Inequality, and Development: Group 5n. aisyahNo ratings yet
- Lorenz CurveDocument4 pagesLorenz CurveAayush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Itisastateor Situation in Which A Person or A Group of People Don't Have Enough Money or The Basic Things They Need To LiveDocument7 pagesItisastateor Situation in Which A Person or A Group of People Don't Have Enough Money or The Basic Things They Need To LiveDurjoy SarkerNo ratings yet
- SemHabiliDirect Entregable 7Document7 pagesSemHabiliDirect Entregable 7Michael BorjasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 DeveeconomicsDocument75 pagesChapter 5 DeveeconomicsErmias AtalayNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Income Inequality GrowthDocument35 pagesPakistan Income Inequality GrowthOsamaNo ratings yet
- DEVELOPMENT MODULE 3 MainDocument17 pagesDEVELOPMENT MODULE 3 Mainmrsynapse22No ratings yet
- Economic Development Ch.4.2023Document16 pagesEconomic Development Ch.4.2023Amgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document32 pagesCH 4Amgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4. Poverty and InequalityDocument7 pagesTopic 4. Poverty and InequalityAnita BoboNo ratings yet
- 6.1 - Measuring Inequality PDFDocument23 pages6.1 - Measuring Inequality PDFalabwalaNo ratings yet
- DE Ch3Document53 pagesDE Ch3kunuyakNo ratings yet
- Development Economics Assignment - 2: SUBMITTED BY-Shubham Gupta Roll No - 86 Semester - 5Document11 pagesDevelopment Economics Assignment - 2: SUBMITTED BY-Shubham Gupta Roll No - 86 Semester - 5Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Income Inequality in BangladeshDocument15 pagesIncome Inequality in Bangladeshফারুক হোসেন রিমন0% (1)
- Understanding The Gini CoefficientDocument9 pagesUnderstanding The Gini CoefficientaqsakhalilurrehmanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok 5 Ekonomi PembangunanDocument18 pagesTugas Kelompok 5 Ekonomi Pembangunann. aisyahNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Economic Growth On Poverty in Eastern Europe. Zarządzanie PubliczneDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Economic Growth On Poverty in Eastern Europe. Zarządzanie PubliczneSKNo ratings yet
- IPCWorking Paper 2Document29 pagesIPCWorking Paper 2Percy JacksonNo ratings yet
- Finals PPT Notes - Economic DevelopmentDocument6 pagesFinals PPT Notes - Economic DevelopmentGRACELINE JOY TOMENo ratings yet
- Economics Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 - 2023Document28 pagesEconomics Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 - 2023cyonela5No ratings yet
- The Gini Index and Measures of Inequality: Frank A. FarrisDocument14 pagesThe Gini Index and Measures of Inequality: Frank A. Farrisoscrend39No ratings yet
- Chapter Five Income Inequality, Poverty, and Development 123910Document24 pagesChapter Five Income Inequality, Poverty, and Development 123910Milkessa Dejene RobiNo ratings yet
- Putting The Gini Back in The Bottle?: Alex Cobham and Andy SumnerDocument30 pagesPutting The Gini Back in The Bottle?: Alex Cobham and Andy SumnerSammer BurgosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document15 pagesChapter 5Sheraz BajwaNo ratings yet
- Poverty, Inequality, and DevelopmentDocument58 pagesPoverty, Inequality, and DevelopmentAshib Uddin EmoNo ratings yet
- EC1103 Lecture 9 - Measuring Inequality - v2Document53 pagesEC1103 Lecture 9 - Measuring Inequality - v2kikiabrehamNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev Chapter 5Document6 pagesEcon Dev Chapter 5Feizhen Mae RodelasNo ratings yet
- Inequality MeasuresDocument11 pagesInequality MeasuresKatriKatariineNo ratings yet
- Milanovic (2013)Document33 pagesMilanovic (2013)Perez333No ratings yet
- Global Inequality and The Global Inequality Extraction RatioDocument29 pagesGlobal Inequality and The Global Inequality Extraction Ratiomody_escu1897No ratings yet
- Income Distribution - WikipediaDocument3 pagesIncome Distribution - WikipediaRajnikant BilungNo ratings yet
- Public AdministrationDocument10 pagesPublic AdministrationDurjoy SarkerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5Cyrus ArmamentoNo ratings yet
- Milanovic - Branko - GLOBAL INCOME and The Global InequalityDocument29 pagesMilanovic - Branko - GLOBAL INCOME and The Global InequalityRamón Rueda LópezNo ratings yet
- Work 654Document47 pagesWork 654NebilahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Inequality MeasuresDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 Inequality MeasuresJULDY SALAMANCANo ratings yet
- ааааааннDocument5 pagesааааааннsosamkerNo ratings yet
- Poverty and The Kuznets Hypothesis: A Cross Country AnalysisDocument6 pagesPoverty and The Kuznets Hypothesis: A Cross Country AnalysisJosephNo ratings yet
- What Is Income Inequality?Document4 pagesWhat Is Income Inequality?Ali ShanNo ratings yet
- Trade Openness and Income Inequality, GINIDocument3 pagesTrade Openness and Income Inequality, GINIAnonymous r2FQcl4jNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Lesson 3 - Distribution of IncomeDocument17 pagesUnit 11 - Lesson 3 - Distribution of Incomeapi-260512563No ratings yet
- Sheet 5 DevelopmentDocument4 pagesSheet 5 DevelopmentAly Emad MashhourNo ratings yet
- Measures of Development APHGDocument24 pagesMeasures of Development APHGhelmetlurchNo ratings yet
- Income Inequality in CyprusDocument14 pagesIncome Inequality in CyprusGiriNo ratings yet
- Sala I Martin2006Document47 pagesSala I Martin2006DjinNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 StudentDocument54 pagesTopic 3 Studentphamhuyen012005No ratings yet
- Climbing the ladder or falling off it: Essays on Economic Mobility in EuropeFrom EverandClimbing the ladder or falling off it: Essays on Economic Mobility in EuropeNo ratings yet
- Colorful 2017 CalendarDocument2 pagesColorful 2017 Calendar0612001No ratings yet
- Quali Survey FindingsDocument2 pagesQuali Survey Findings0612001No ratings yet
- Qvî FWZ© - 2017 Wkÿvel©: 1G KöwyDocument10 pagesQvî FWZ© - 2017 Wkÿvel©: 1G Köwy0612001No ratings yet
- Market Models PDFDocument14 pagesMarket Models PDF0612001No ratings yet
- Business Development Officer NeededDocument1 pageBusiness Development Officer Needed0612001No ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument3 pagesReflection Paper061200150% (2)
- Colours One, Two Buckle My ShoeDocument1 pageColours One, Two Buckle My Shoe0612001No ratings yet
- Dissatisfaction Create To Quit JobDocument11 pagesDissatisfaction Create To Quit Job0612001No ratings yet
- A Study On Detergent PowderDocument64 pagesA Study On Detergent Powder0612001No ratings yet
- Gini Coefficient & Lorenz Curve: Assignment OnDocument3 pagesGini Coefficient & Lorenz Curve: Assignment On0612001No ratings yet
- What Is 'Organizational Behavior - OB'Document3 pagesWhat Is 'Organizational Behavior - OB'0612001No ratings yet
- World Fair Trade OrganizationDocument6 pagesWorld Fair Trade Organization0612001No ratings yet
- STD 4. Ch-11Document7 pagesSTD 4. Ch-110612001No ratings yet
- Glossary of Shipbuilding Terms-PrintDocument17 pagesGlossary of Shipbuilding Terms-Print0612001No ratings yet
- Depreciation 140513051242 Phpapp02Document22 pagesDepreciation 140513051242 Phpapp020612001No ratings yet
- Banglalink Internet ServicesDocument2 pagesBanglalink Internet Services0612001No ratings yet
- Test Tactics and Sectional Strategies For The GREDocument4 pagesTest Tactics and Sectional Strategies For The GRE0612001No ratings yet
- Gini Coefficient and Lorenz Curve ReportDocument47 pagesGini Coefficient and Lorenz Curve ReportĐào Bích DiệpNo ratings yet
- Jenkins (2008)Document88 pagesJenkins (2008)Juan PalominoNo ratings yet
- Inequality Measurement: Development Issues No. 2Document2 pagesInequality Measurement: Development Issues No. 2SimeonNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariationDocument26 pagesMeasures of VariationSifat MahmudNo ratings yet
- Todaro N Smith - CH 5Document13 pagesTodaro N Smith - CH 5Shrishti AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and Its Impact On Poverty and Inequality Case Study of Lower Middle Income CountriesDocument11 pagesGlobalisation and Its Impact On Poverty and Inequality Case Study of Lower Middle Income CountriesEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Poverty in India: Concepts, Measurement and TrendsDocument8 pagesPoverty in India: Concepts, Measurement and TrendsSadaf KushNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Development EconomicsDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Development EconomicsKhant Zaw ThantNo ratings yet
- Assefa Final ThesisDocument73 pagesAssefa Final ThesisKemal TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Final The MacroeconomyDocument82 pagesFinal The MacroeconomySiddhant JhawarNo ratings yet
- Competitive Balance in Football: Trends and Effects: September 2004Document51 pagesCompetitive Balance in Football: Trends and Effects: September 2004usmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Edited Inequality, Poverty and DevelopmentDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Edited Inequality, Poverty and DevelopmentkasuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document36 pagesChapter 18hussein harbNo ratings yet
- 3.measures of DispersionDocument10 pages3.measures of DispersionNchumthung JamiNo ratings yet
- Todaro (Report)Document18 pagesTodaro (Report)Dara LazadaNo ratings yet
- Lorenz Curve and QQ PlotDocument14 pagesLorenz Curve and QQ PlotTanmay MaityNo ratings yet
- Mathematicaleconomics PDFDocument84 pagesMathematicaleconomics PDFSayyid JifriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MemoDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 MemoHappinessNo ratings yet
- Economics Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 - 2023Document28 pagesEconomics Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 - 2023cyonela5No ratings yet
- Rural Development Chapter 3 PDFDocument22 pagesRural Development Chapter 3 PDFsomiNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Notes Econ-25Document9 pagesChap4 Notes Econ-25Erika May RamirezNo ratings yet
- Lorenz CurveDocument5 pagesLorenz CurveAsif ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Lorenz CurveDocument5 pagesLorenz CurveApollon PheboNo ratings yet
- Lorenz Curve and Gini Concentration RatioDocument2 pagesLorenz Curve and Gini Concentration RatioSai ShreeNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Explore and Discuss 1Document3 pagesExercises: Explore and Discuss 1luka zaridzeNo ratings yet
- RausDocument2 pagesRausSourav KaranthNo ratings yet
- Churn AssignmentDocument11 pagesChurn AssignmentSanjeet BeheraNo ratings yet
- The Pareto Principle: Rosie Dunford, Quanrong Su, Ekraj Tamang and Abigail WintourDocument9 pagesThe Pareto Principle: Rosie Dunford, Quanrong Su, Ekraj Tamang and Abigail Wintourසම්පත් චන්ද්රරත්නNo ratings yet
Gini Coefficient and Lorentz
Gini Coefficient and Lorentz
Uploaded by
06120010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views3 pagesThe document discusses the Gini coefficient and Lorenz curve. It explains that the Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion used to represent income inequality in a nation, with a value of 0 representing total equality and 1 representing maximal inequality. It also describes how the Lorenz curve graphically depicts wealth distribution compared to a hypothetical line of perfect equality, with the difference between the lines quantified by the Gini coefficient. As an example, it provides Bangladesh's 2010 Gini coefficients for urban, rural, and total populations as well as coefficients for the US and Sweden.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the Gini coefficient and Lorenz curve. It explains that the Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion used to represent income inequality in a nation, with a value of 0 representing total equality and 1 representing maximal inequality. It also describes how the Lorenz curve graphically depicts wealth distribution compared to a hypothetical line of perfect equality, with the difference between the lines quantified by the Gini coefficient. As an example, it provides Bangladesh's 2010 Gini coefficients for urban, rural, and total populations as well as coefficients for the US and Sweden.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views3 pagesGini Coefficient and Lorentz
Gini Coefficient and Lorentz
Uploaded by
0612001The document discusses the Gini coefficient and Lorenz curve. It explains that the Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion used to represent income inequality in a nation, with a value of 0 representing total equality and 1 representing maximal inequality. It also describes how the Lorenz curve graphically depicts wealth distribution compared to a hypothetical line of perfect equality, with the difference between the lines quantified by the Gini coefficient. As an example, it provides Bangladesh's 2010 Gini coefficients for urban, rural, and total populations as well as coefficients for the US and Sweden.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Assignment #
GINI COEFFICIENT & LORENZ CURVE
Prepared for:
Professor Dr. Muhammad Ziaulhaq Mamun
Course Instructor: Managing Operations (P 501)
Prepared by:
Navid Ahmed Mamun
MBA, 53D
Roll: ZR-48
Institute of Business Administration
University of Dhaka
April 25, 2016
Gini Coefficient: The Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion intended to
represent the income distribution of a nation's residents, and is the most commonly used
measure of inequality. Italian statistician Corrado Gini invented the Gini Coefficient. The
United Nations (UN) uses this coefficient in their annual ranking of nations.
The Gini coefficient measures the inequality among values of a frequency distribution (for
example, levels of income). A Gini coefficient of zero expresses perfect equality, where all
values are the same, for example, where everyone has the same income. A Gini coefficient of
one or 100% expresses maximal inequality among values e.g., for a large number of people,
where only one person has all the income or consumption, and all others have none, the Gini
coefficient will be very nearly one. However a value greater than one may occur if some
persons represent negative contribution to the total. For example, by having a negative
income or wealth. For larger groups, values close to or above 1 are very unlikely in practice.
Given the normalization of both the cumulative population and the cumulative share of
income used to calculate the Gini coefficient, the measure is not overly sensitive to the
specifics of the income distribution, but rather only on how incomes vary relative to the other
members of a population. The exception to this is in the redistribution of wealth resulting in a
minimum income for all people. When the population is sorted, if their income distribution
were to approximate a well known function, then some representative values could be
calculated.
It is a way of comparing how distribution of income in a society compares with a similar
society in which everyone earned exactly the same amount. Inequality on the Gini scale is
measured between 0, where everybody is equal, and 1, where all the country's income is
earned by a single person.
Gini developed his coefficient in 1912, building on the work of American economist Max
Lorenz, who published a hypothetical way to depict total equality - a straight diagonal line on
a graph - in 1905. The difference between this hypothetical line and the actual line produced
of people's incomes is the Gini ratio.
According to Antonio Cabrales, a professor of economics at University College London,
The Gini coefficient provides an index to measure inequality.
"The Gini has been around for a very long time, and it's very technically sound if you want to
measure income inequality across the whole population," explains Andy Sumner, director of
the International Development Institute at Kings College, London. "But one might say the
Gini is oversensitive to changes in the middle, and under sensitive at the extremes."
The coefficient doesn't capture very explicitly changes in the top 10% - which has become
the focus of much inequality research in the past 10 years - or the bottom 40%, where most
poverty lies.
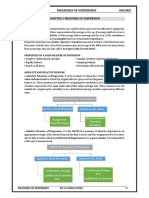
Lorenz Curve:
The Lorenz curve is the graphical representation of wealth distribution developed by
American economist Max Lorenz in 1905. On the graph, a straight diagonal line represents
perfect equality of wealth distribution; the Lorenz curve lies beneath it, showing the reality of
wealth distribution. The difference between the straight line and the curved line is the amount
of inequality of wealth distribution, a figure described by the Gini coefficient.
Lorenz Curve for Bangladesh (2010)
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
Figure: Lorenz Curve for Bangladesh (2010)
Gini Coefficient for Bangladesh, USA, and Denmark:
Table: Gini Coefficient for Bangladesh, USA, and Sweden.
Country
Bangladesh
USA
Sweden
Year
2010
Gini Coefficient
Urban
0.452
2015
2013
Rural
0.431
0.8056
0.249
Total
0.458
Reference:
1. Monitor, BBC Magazine. Who, What, Why: What is the Gini coefficient? [Online] 2015. [Cited:
April 24, 2016.] http://www.bbc.com/news/blogs-magazine-monitor-31847943.
2. Report of the Household Income & Expenditure Survey. Statistics, Bangladesh Bureau of. 2010,
p. 30.
3 The World Bank. GINI Index (World Bank Estimate)
http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI
You might also like
- More Than Money: How Economic Inequality Affects . . . EverythingFrom EverandMore Than Money: How Economic Inequality Affects . . . EverythingNo ratings yet
- Labor Economics: Chapter-07 The Wage StructureDocument28 pagesLabor Economics: Chapter-07 The Wage StructureIqbal ChyNo ratings yet
- GinicoefficientsDocument4 pagesGinicoefficientsapi-292484442No ratings yet
- The Declaration of IndependenceDocument2 pagesThe Declaration of Independence0612001100% (1)
- Gini CoefficientDocument10 pagesGini CoefficientstriiderNo ratings yet
- Gini Coefficient & Lorenz Curve: Assignment OnDocument3 pagesGini Coefficient & Lorenz Curve: Assignment On0612001No ratings yet
- Gini - and - Lorenz - Analysis & Terms of EconomistsDocument29 pagesGini - and - Lorenz - Analysis & Terms of EconomistspapanombaNo ratings yet
- Key Takeaways: Economic InequalityDocument4 pagesKey Takeaways: Economic InequalityVINITHANo ratings yet
- Development Theories and Policies (Course Code: MSPM 612)Document37 pagesDevelopment Theories and Policies (Course Code: MSPM 612)Meron AtilabachewNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Notes Econ-25Document9 pagesChap4 Notes Econ-25Erika May RamirezNo ratings yet
- Other Summary Measures of Poverty and InequalityDocument6 pagesOther Summary Measures of Poverty and InequalityNoor AliNo ratings yet
- CONADEV - Chapter 5Document16 pagesCONADEV - Chapter 5Lalaine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Poverty and Income InequalityDocument79 pagesChapter 5 - Poverty and Income InequalityKenzel lawasNo ratings yet
- Economic Inequality: Key TakeawaysDocument3 pagesEconomic Inequality: Key TakeawaysLoad7No ratings yet
- Proverty, Inequality, and Development: Group 5Document32 pagesProverty, Inequality, and Development: Group 5n. aisyahNo ratings yet
- Lorenz CurveDocument4 pagesLorenz CurveAayush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Itisastateor Situation in Which A Person or A Group of People Don't Have Enough Money or The Basic Things They Need To LiveDocument7 pagesItisastateor Situation in Which A Person or A Group of People Don't Have Enough Money or The Basic Things They Need To LiveDurjoy SarkerNo ratings yet
- SemHabiliDirect Entregable 7Document7 pagesSemHabiliDirect Entregable 7Michael BorjasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 DeveeconomicsDocument75 pagesChapter 5 DeveeconomicsErmias AtalayNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Income Inequality GrowthDocument35 pagesPakistan Income Inequality GrowthOsamaNo ratings yet
- DEVELOPMENT MODULE 3 MainDocument17 pagesDEVELOPMENT MODULE 3 Mainmrsynapse22No ratings yet
- Economic Development Ch.4.2023Document16 pagesEconomic Development Ch.4.2023Amgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document32 pagesCH 4Amgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4. Poverty and InequalityDocument7 pagesTopic 4. Poverty and InequalityAnita BoboNo ratings yet
- 6.1 - Measuring Inequality PDFDocument23 pages6.1 - Measuring Inequality PDFalabwalaNo ratings yet
- DE Ch3Document53 pagesDE Ch3kunuyakNo ratings yet
- Development Economics Assignment - 2: SUBMITTED BY-Shubham Gupta Roll No - 86 Semester - 5Document11 pagesDevelopment Economics Assignment - 2: SUBMITTED BY-Shubham Gupta Roll No - 86 Semester - 5Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Income Inequality in BangladeshDocument15 pagesIncome Inequality in Bangladeshফারুক হোসেন রিমন0% (1)
- Understanding The Gini CoefficientDocument9 pagesUnderstanding The Gini CoefficientaqsakhalilurrehmanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok 5 Ekonomi PembangunanDocument18 pagesTugas Kelompok 5 Ekonomi Pembangunann. aisyahNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Economic Growth On Poverty in Eastern Europe. Zarządzanie PubliczneDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Economic Growth On Poverty in Eastern Europe. Zarządzanie PubliczneSKNo ratings yet
- IPCWorking Paper 2Document29 pagesIPCWorking Paper 2Percy JacksonNo ratings yet
- Finals PPT Notes - Economic DevelopmentDocument6 pagesFinals PPT Notes - Economic DevelopmentGRACELINE JOY TOMENo ratings yet
- Economics Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 - 2023Document28 pagesEconomics Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 - 2023cyonela5No ratings yet
- The Gini Index and Measures of Inequality: Frank A. FarrisDocument14 pagesThe Gini Index and Measures of Inequality: Frank A. Farrisoscrend39No ratings yet
- Chapter Five Income Inequality, Poverty, and Development 123910Document24 pagesChapter Five Income Inequality, Poverty, and Development 123910Milkessa Dejene RobiNo ratings yet
- Putting The Gini Back in The Bottle?: Alex Cobham and Andy SumnerDocument30 pagesPutting The Gini Back in The Bottle?: Alex Cobham and Andy SumnerSammer BurgosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document15 pagesChapter 5Sheraz BajwaNo ratings yet
- Poverty, Inequality, and DevelopmentDocument58 pagesPoverty, Inequality, and DevelopmentAshib Uddin EmoNo ratings yet
- EC1103 Lecture 9 - Measuring Inequality - v2Document53 pagesEC1103 Lecture 9 - Measuring Inequality - v2kikiabrehamNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev Chapter 5Document6 pagesEcon Dev Chapter 5Feizhen Mae RodelasNo ratings yet
- Inequality MeasuresDocument11 pagesInequality MeasuresKatriKatariineNo ratings yet
- Milanovic (2013)Document33 pagesMilanovic (2013)Perez333No ratings yet
- Global Inequality and The Global Inequality Extraction RatioDocument29 pagesGlobal Inequality and The Global Inequality Extraction Ratiomody_escu1897No ratings yet
- Income Distribution - WikipediaDocument3 pagesIncome Distribution - WikipediaRajnikant BilungNo ratings yet
- Public AdministrationDocument10 pagesPublic AdministrationDurjoy SarkerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5Cyrus ArmamentoNo ratings yet
- Milanovic - Branko - GLOBAL INCOME and The Global InequalityDocument29 pagesMilanovic - Branko - GLOBAL INCOME and The Global InequalityRamón Rueda LópezNo ratings yet
- Work 654Document47 pagesWork 654NebilahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Inequality MeasuresDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 Inequality MeasuresJULDY SALAMANCANo ratings yet
- ааааааннDocument5 pagesааааааннsosamkerNo ratings yet
- Poverty and The Kuznets Hypothesis: A Cross Country AnalysisDocument6 pagesPoverty and The Kuznets Hypothesis: A Cross Country AnalysisJosephNo ratings yet
- What Is Income Inequality?Document4 pagesWhat Is Income Inequality?Ali ShanNo ratings yet
- Trade Openness and Income Inequality, GINIDocument3 pagesTrade Openness and Income Inequality, GINIAnonymous r2FQcl4jNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Lesson 3 - Distribution of IncomeDocument17 pagesUnit 11 - Lesson 3 - Distribution of Incomeapi-260512563No ratings yet
- Sheet 5 DevelopmentDocument4 pagesSheet 5 DevelopmentAly Emad MashhourNo ratings yet
- Measures of Development APHGDocument24 pagesMeasures of Development APHGhelmetlurchNo ratings yet
- Income Inequality in CyprusDocument14 pagesIncome Inequality in CyprusGiriNo ratings yet
- Sala I Martin2006Document47 pagesSala I Martin2006DjinNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 StudentDocument54 pagesTopic 3 Studentphamhuyen012005No ratings yet
- Climbing the ladder or falling off it: Essays on Economic Mobility in EuropeFrom EverandClimbing the ladder or falling off it: Essays on Economic Mobility in EuropeNo ratings yet
- Colorful 2017 CalendarDocument2 pagesColorful 2017 Calendar0612001No ratings yet
- Quali Survey FindingsDocument2 pagesQuali Survey Findings0612001No ratings yet
- Qvî FWZ© - 2017 Wkÿvel©: 1G KöwyDocument10 pagesQvî FWZ© - 2017 Wkÿvel©: 1G Köwy0612001No ratings yet
- Market Models PDFDocument14 pagesMarket Models PDF0612001No ratings yet
- Business Development Officer NeededDocument1 pageBusiness Development Officer Needed0612001No ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument3 pagesReflection Paper061200150% (2)
- Colours One, Two Buckle My ShoeDocument1 pageColours One, Two Buckle My Shoe0612001No ratings yet
- Dissatisfaction Create To Quit JobDocument11 pagesDissatisfaction Create To Quit Job0612001No ratings yet
- A Study On Detergent PowderDocument64 pagesA Study On Detergent Powder0612001No ratings yet
- Gini Coefficient & Lorenz Curve: Assignment OnDocument3 pagesGini Coefficient & Lorenz Curve: Assignment On0612001No ratings yet
- What Is 'Organizational Behavior - OB'Document3 pagesWhat Is 'Organizational Behavior - OB'0612001No ratings yet
- World Fair Trade OrganizationDocument6 pagesWorld Fair Trade Organization0612001No ratings yet
- STD 4. Ch-11Document7 pagesSTD 4. Ch-110612001No ratings yet
- Glossary of Shipbuilding Terms-PrintDocument17 pagesGlossary of Shipbuilding Terms-Print0612001No ratings yet
- Depreciation 140513051242 Phpapp02Document22 pagesDepreciation 140513051242 Phpapp020612001No ratings yet
- Banglalink Internet ServicesDocument2 pagesBanglalink Internet Services0612001No ratings yet
- Test Tactics and Sectional Strategies For The GREDocument4 pagesTest Tactics and Sectional Strategies For The GRE0612001No ratings yet
- Gini Coefficient and Lorenz Curve ReportDocument47 pagesGini Coefficient and Lorenz Curve ReportĐào Bích DiệpNo ratings yet
- Jenkins (2008)Document88 pagesJenkins (2008)Juan PalominoNo ratings yet
- Inequality Measurement: Development Issues No. 2Document2 pagesInequality Measurement: Development Issues No. 2SimeonNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariationDocument26 pagesMeasures of VariationSifat MahmudNo ratings yet
- Todaro N Smith - CH 5Document13 pagesTodaro N Smith - CH 5Shrishti AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and Its Impact On Poverty and Inequality Case Study of Lower Middle Income CountriesDocument11 pagesGlobalisation and Its Impact On Poverty and Inequality Case Study of Lower Middle Income CountriesEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Poverty in India: Concepts, Measurement and TrendsDocument8 pagesPoverty in India: Concepts, Measurement and TrendsSadaf KushNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Development EconomicsDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Development EconomicsKhant Zaw ThantNo ratings yet
- Assefa Final ThesisDocument73 pagesAssefa Final ThesisKemal TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Final The MacroeconomyDocument82 pagesFinal The MacroeconomySiddhant JhawarNo ratings yet
- Competitive Balance in Football: Trends and Effects: September 2004Document51 pagesCompetitive Balance in Football: Trends and Effects: September 2004usmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Edited Inequality, Poverty and DevelopmentDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Edited Inequality, Poverty and DevelopmentkasuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document36 pagesChapter 18hussein harbNo ratings yet
- 3.measures of DispersionDocument10 pages3.measures of DispersionNchumthung JamiNo ratings yet
- Todaro (Report)Document18 pagesTodaro (Report)Dara LazadaNo ratings yet
- Lorenz Curve and QQ PlotDocument14 pagesLorenz Curve and QQ PlotTanmay MaityNo ratings yet
- Mathematicaleconomics PDFDocument84 pagesMathematicaleconomics PDFSayyid JifriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MemoDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 MemoHappinessNo ratings yet
- Economics Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 - 2023Document28 pagesEconomics Grade 11 Revision Terms 3 and 4 - 2023cyonela5No ratings yet
- Rural Development Chapter 3 PDFDocument22 pagesRural Development Chapter 3 PDFsomiNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Notes Econ-25Document9 pagesChap4 Notes Econ-25Erika May RamirezNo ratings yet
- Lorenz CurveDocument5 pagesLorenz CurveAsif ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Lorenz CurveDocument5 pagesLorenz CurveApollon PheboNo ratings yet
- Lorenz Curve and Gini Concentration RatioDocument2 pagesLorenz Curve and Gini Concentration RatioSai ShreeNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Explore and Discuss 1Document3 pagesExercises: Explore and Discuss 1luka zaridzeNo ratings yet
- RausDocument2 pagesRausSourav KaranthNo ratings yet
- Churn AssignmentDocument11 pagesChurn AssignmentSanjeet BeheraNo ratings yet
- The Pareto Principle: Rosie Dunford, Quanrong Su, Ekraj Tamang and Abigail WintourDocument9 pagesThe Pareto Principle: Rosie Dunford, Quanrong Su, Ekraj Tamang and Abigail Wintourසම්පත් චන්ද්රරත්නNo ratings yet