Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Why This Chapter?: Aromatic Compounds
Why This Chapter?: Aromatic Compounds
Uploaded by
bebsybiswezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Why This Chapter?: Aromatic Compounds
Why This Chapter?: Aromatic Compounds
Uploaded by
bebsybiswezCopyright:
Available Formats
8/29/2015
John E. McMurry
Why this Chapter?
Aromatic rings are a common part of many
organic structures.
www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry
Chapter 5
Aromatic Compounds
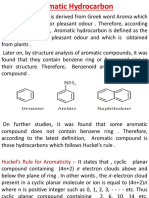
Aromatic Compounds
Aromatic was used to described some fragrant
compounds in early 19th century
Not correct: later they are grouped by chemical
behavior (unsaturated compounds that undergo
substitution rather than addition)
Aromatic compounds are particularly important
in nucleic acid chemistry and the chemistry of
several amino acids.
5.1 Structure of Benzene
Benzene reacts slowly with Br2 to give bromobenzene
(where Br replaces H)
This is substitution rather than the rapid addition
reaction common to compounds with C=C, suggesting
that, in benzene, there is a higher barrier
Current: distinguished from aliphatic compounds by
electronic configuration
Benzenes Unusual Structure
All its C-C bonds are the same length:
139 pm between
single (154 pm) and double (134 pm) bonds
Each C is sp2 and has a p orbital perpendicular to
the plane of the six-membered ring
Electron density in all six C-C bonds is identical
Structure is planar, hexagonal
CCC bond angles 120
8/29/2015
5.2 Naming Aromatic Compounds
Many common names
toluene = methylbenzene;
aniline = aminobenzene
Monosubstituted benzenes systematic names as
hydrocarbons with benzene
C6H5Br = bromobenzene
C6H5NO2 = nitrobenzene,
and C6H5CH2CH2CH3 is propylbenzene
methylbenzene
Common Names of Benzene
Derivatives
OH
CH3
phenol
H
C CH2
styrene
phenyl bromide
OCH3
aniline
O
CH3
benzaldehyde
When a benzene ring is a substituent, the term
phenyl is used (for C6H5)
You may also see Ph or f in place of C6H5
anisole
acetophenone
Br
The Phenyl Group
NH2
toluene
aminobenzene
Benzyl refers to C6H5CH2
OH
benzoic acid
CH2Br
benzyl bromide
Disubstituted Benzenes
Relative positions on a benzene ring
ortho- (o) on adjacent carbons (1,2)
meta- (m) separated by one carbon (1,3)
para- (p) separated by two carbons (1,4)
Describes reaction patterns (occurs at the para
position)
8/29/2015
Naming Benzenes with More Than Two
Substituents
Choose numbers to get lowest possible values
List substituents alphabetically with hyphenated
numbers
Common names, such as toluene can serve as
root name (as in TNT)
5.3 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
Reactions: Bromination
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
General Mechanism
Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated compound
with 6 electrons
Reactions of benzene lead to the retention of the
aromatic core
5.3 Electrophilic Aromatic
Substitution Reactions: Bromination
Benzenes electrons participate as a Lewis base in
reactions with Lewis acids
The product is formed by loss of a proton, which is
replaced by bromine
Formation of Product from Intermediate
The cationic addition intermediate transfers a
proton to FeBr4- (from Br- and FeBr3)
This restores aromaticity (in contrast with
addition in alkenes)
FeBr3 is added as a
catalyst to polarize the
bromine reagent
8/29/2015
5.4 Other Aromatic Substitutions
Chlorine and iodine (but not fluorine, which is too
reactive) can produce aromatic substitution with the
addition of other reagents to promote the reaction
Chlorination requires FeCl3
Aromatic Nitration
Iodine must be oxidized to form a more powerful I +
species (with Cu+ or peroxide)
Aromatic Sulfonation
Substitution of H by SO3H (sulfonation)
Reaction with a mixture of sulfuric acid and
SO3
The combination of nitric acid and sulfuric acid
produces NO2+ (nitronium ion)
The reaction with benzene produces nitrobenzene
5.5 The FriedelCrafts Alkylation and
Acylation Reactions
Alkylation among most useful electrophilic
aromatic subsitution reactions
Aromatic substitution of R+ for H+
Reactive species is sulfur trioxide or its conjugate acid
Aluminum chloride promotes the formation of
the carbocation
8/29/2015
Limitations of the Friedel-Crafts
Alkylation
Only alkyl halides can be used (F, Cl, I, Br)
Aryl halides and vinylic halides do not react (their
carbocations are too hard to form)
Will not work with rings containing an amino group
substituent or a strongly electron-withdrawing group
Acylation of Aromatic Rings
Reaction of an acid chloride (RCOCl) and an
aromatic ring in the presence of AlCl3 introduces
acyl group, COR
Benzene with acetyl chloride yields
acetophenone
5.8 Oxidation and Reduction of Aromatic
Compounds
Alkyl side chains can be oxidized to CO2H by
strong reagents such as KMnO4 and Na2Cr2O7 if they
have a CH next to the ring
Converts an alkylbenzene into a benzoic acid, ArR
ArCO2H
5.8 Oxidation and Reduction of Aromatic
Compounds
Just as aromatic rings are inert to oxidation, they are
also inert to reduction under typical alkene conditions
High temperatures and pressures are required in
order to reduce aromatic rings.
8/29/2015
5.7 An Explanation of Substituent Effects
O
Br
Fe
Br
-C
-C
Cl 3
Al
SO
H2
CH
3 Cl
AlCl
NO 3
2 SO
4
H-C
Cl
Deactivating groups withdraw electrons from the
ring, destabilizing the Wheland intermediate
Substituents can cause a compound to be (much)
more or (much) less reactive than benzene
Cl 3
Al
CH 3
H2
Activating groups donate electrons to the ring,
stabilizing the Wheland intermediate (carbocation)
CH 3
Summary Table: Effect of Substituents
in Aromatic Substitution
Substituents affect the orientation of the
reaction the positional relationship is
controlled
ortho- and para-directing activators,
ortho- and para-directing deactivators,
and meta-directing deactivators
(Table 16.1)
5.6 Substituent Effects in Electrophilic
Aromatic Substitution, Summary Graph
5.7 An Explanation of Substituent Effects
8/29/2015
SO
Br 3
Fe
B
r
Br
R
-C
Al - Cl
Cl
Fe
Br
Cl 3
Al
2 SO
4
H-C
Cl
CH
3 Cl
AlCl
CH 3
SO 4
H2 O3
N
H2
Synthesis as a Tool for Learning Organic
Chemistry
In order to propose a synthesis you must be familiar
with reactions
What they begin with
What they lead to
How they are accomplished
What the limitations are
3 Cl
CH
AlC
nO 4
KM O
H2
CH 3
A synthesis combines a series of proposed steps to
go from a defined set of reactants to a specified
product
Synthesizing a Substituted Aromatic
Compound
Synthesize p-bromobenzoic acid starting from benzene.
Questions related to synthesis can include partial
information about a reaction of series that the
student completes
Compare the target and the starting material
Consider reactions that efficiently produce the outcome.
Look at the product and think of what can lead to it
Synthesizing a Substituted Aromatic
Compound: Solution
Two workable routes are possible.
Strategy:
Work backward by first asking, What is an
immediate precursor of p-bromobenzoic acid?.
Continue this process until benzene is the starting
material.
Note: This is usually more than one synthetic route
possible.
5.9 Other Aromatic Compounds
Aromatic compounds can have rings that share a set of
carbon atoms (fused rings)
Compounds from fused benzene or aromatic heterocycle
rings are themselves aromatic
8/29/2015
Naphthalene Orbitals
Three resonance forms and delocalized electrons
5.9 Other Aromatic Compounds
heterocyclic aromatic compounds contain elements
other than carbon in a ring, such as N,S,O,P
Cyclic compounds that contain only carbon are called
carbocycles (not homocycles)
Nomenclature is specialized
Pyridine
A six-membered heterocycle with a nitrogen atom in
its ring
electron structure resembles benzene (6 electrons)
The nitrogen lone pair electrons are not part of the
aromatic system (perpendicular orbital)
Pyridine is a relatively weak base compared to
normal amines but protonation does not affect
aromaticity
Pyrrole
A five-membered heterocycle with one nitrogen
electron system similar to that of cyclopentadienyl
anion
Four sp2-hybridized carbons with 4 p orbitals
perpendicular to the ring and 4 p electrons
Nitrogen atom is sp2-hybridized, and lone pair of
electrons occupies a p orbital (6 electrons)
Since lone pair electrons are in the aromatic ring,
protonation destroys aromaticity, making pyrrole a
very weak base
You might also like
- Saturated HydrocarbonDocument60 pagesSaturated HydrocarbonMarvin K. Candor100% (1)
- Chapter 2.5 Aromatic CompoundDocument38 pagesChapter 2.5 Aromatic Compound0JTINGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Aromatic CompoundsDocument41 pagesChapter 6 Aromatic Compoundsnur izzaidahNo ratings yet
- Lects. 15,16 (OH) Alkenes & Aromaticity +answersDocument48 pagesLects. 15,16 (OH) Alkenes & Aromaticity +answersvintu pvNo ratings yet
- Materi 03Document38 pagesMateri 03Syukri DaimonNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry LecDocument75 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Lecبن آجروم50% (2)
- 5.aromatic Compounds WholeDocument71 pages5.aromatic Compounds WholeNura Adila100% (2)
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument56 pagesAromatic CompoundsSeth Andrew Salih100% (2)
- Aromatic Compounds: © 2006 Thomson Higher EducationDocument103 pagesAromatic Compounds: © 2006 Thomson Higher Educationbrigittanwp putriNo ratings yet
- WEEK 10 Aromatic HydrocarbonDocument26 pagesWEEK 10 Aromatic HydrocarbonChris Angelo De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Benzene MilanaDocument61 pagesBenzene MilanaMilana WalujoNo ratings yet
- Section 12a-HydrocarbonsDocument77 pagesSection 12a-HydrocarbonsMonique AldanaNo ratings yet
- 4 Aromatic CompoundsDocument25 pages4 Aromatic CompoundsÉL FikryNo ratings yet
- Benzene and Derivatives Members GroupDocument57 pagesBenzene and Derivatives Members GroupHaris KhanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem 2 by HaftomDocument285 pagesOrganic Chem 2 by Haftomdereje dawitNo ratings yet
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument50 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonsEdan Balao-asNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds: By: Group 1Document41 pagesAromatic Compounds: By: Group 1Kyle PalacioNo ratings yet
- Edited 2022 - Aromatic CompoundsDocument73 pagesEdited 2022 - Aromatic CompoundsedinapetermugaduiNo ratings yet
- C2 Benzene & AromaticityDocument74 pagesC2 Benzene & AromaticityMimi Sharina HassanNo ratings yet
- Benzene and Aromaticity (2nd Year Ndaweni)Document54 pagesBenzene and Aromaticity (2nd Year Ndaweni)Mbali MazongweNo ratings yet
- Corrected Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryDocument71 pagesCorrected Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryDAM2120No ratings yet
- AromaticsDocument53 pagesAromaticsIbsaNo ratings yet
- Benzene and Its DerivativesDocument36 pagesBenzene and Its DerivativesMoh. AliNo ratings yet
- CY 1001: Organic Chemistry: Aromaticity: (4 Classes + 1 Tutorial)Document80 pagesCY 1001: Organic Chemistry: Aromaticity: (4 Classes + 1 Tutorial)Sai naveenNo ratings yet
- 4 Benzene PDFDocument90 pages4 Benzene PDFCrishen VinzonNo ratings yet
- Electrophillic Aromatci SubstitutionDocument114 pagesElectrophillic Aromatci SubstitutionAbe KobNo ratings yet
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument37 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonsMae Rose PicaranaNo ratings yet
- Mod1 1. Structure and FormulaeDocument50 pagesMod1 1. Structure and FormulaeAntonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity CompleteDocument104 pagesAromaticity Completewahidalwahdi100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry CHEM107Document41 pagesOrganic Chemistry CHEM107AhmedAdelIbrahimNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12 Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 12 Unsaturated HydrocarbonsShania ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument55 pagesAromatic CompoundsNadine Bacalangco100% (1)
- Sebatian AromatikDocument100 pagesSebatian AromatikGanthimathi SugumaranNo ratings yet
- Dienes & Aromatic Compounds, FNDocument60 pagesDienes & Aromatic Compounds, FNMuzahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Benzena Dan AromatisanDocument34 pagesBenzena Dan AromatisanShelly Trissa RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AromaticDocument76 pagesChapter 5 AromaticMELVINDO JACOBNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Pertemuan KeduapptDocument60 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Pertemuan Keduapptnadhilah shabrinaNo ratings yet
- Addition ReactionDocument34 pagesAddition Reactionmichot feleguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document38 pagesChapter 4iB13eNo ratings yet
- OCR Chemistry NotesDocument10 pagesOCR Chemistry NotesJack WoodNo ratings yet
- 307 Aromatic CompoundDocument42 pages307 Aromatic CompoundFAHEEM UD DINNo ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument14 pagesAttachmentaberaendale334No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFAzadnikov94% (16)
- Section B Lecture Notes With AnnotationsDocument111 pagesSection B Lecture Notes With AnnotationsLeevan BarrattNo ratings yet
- Aromatics 2Document28 pagesAromatics 2swagataNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution + The Chemistry of BenzeneDocument28 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution + The Chemistry of BenzeneTrescia Mae EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Lecture Chapter 15Document48 pagesLecture Chapter 15Aldren RebaLdeNo ratings yet
- Aromatic HydrocarbonDocument45 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonPrashantNo ratings yet
- Lecture Nine Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesLecture Nine Organic Chemistryabdihakimhasssan344No ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxDocument96 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxEgbebessemenow oben ashuNo ratings yet
- Chem 120.1 - Experiment No. 9aDocument20 pagesChem 120.1 - Experiment No. 9aSharmaine DoronNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document9 pagesChapter 4luckshimiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 14 - : Aromatic CompoundsDocument28 pagesOrganic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 14 - : Aromatic CompoundsLurthu PushparajNo ratings yet
- Alkenes Lecture 2Document33 pagesAlkenes Lecture 2Дана ЧилибаеваNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: K. Atkins IB Chemistry Pensacola High SchoolDocument31 pagesHydrocarbons: K. Atkins IB Chemistry Pensacola High Schoollianchen251110No ratings yet
- AromaticsDocument70 pagesAromaticsEceDiril100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document51 pagesChapter 4Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- 1 Hydrocarbons, 2022Document96 pages1 Hydrocarbons, 2022primalgroup71No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For USTH Students Benzene and Aromatic SystemsDocument69 pagesOrganic Chemistry For USTH Students Benzene and Aromatic SystemsHoàng Hiệp100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Mcmurry Foc7e Ch03Document12 pagesMcmurry Foc7e Ch03bebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Selection Criteria: 1. Availability of Raw MaterialsDocument4 pagesSelection Criteria: 1. Availability of Raw MaterialsbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- CHME324-B-Lab Manual Fall 2016 (Ahmed Elkhatat)Document99 pagesCHME324-B-Lab Manual Fall 2016 (Ahmed Elkhatat)bebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Dibutyl PhthalateDocument1 pageDibutyl PhthalatebebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial # 1 - KineticsDocument7 pagesTutorial # 1 - KineticsbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Template - PHYS 194-3Document9 pagesLab Report Template - PHYS 194-3bebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- CH (8) L209 PDFDocument6 pagesCH (8) L209 PDFbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Gas To Liquids (GTL) Is A Refinery Process To ConvertDocument3 pagesGas To Liquids (GTL) Is A Refinery Process To ConvertbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- What Historical Events Shaped The Formation of QatarDocument4 pagesWhat Historical Events Shaped The Formation of QatarbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- GENG 107 Engineering Skills and Ethics - Lecture - Chapter 1 - Preparing To Be An EngineerDocument28 pagesGENG 107 Engineering Skills and Ethics - Lecture - Chapter 1 - Preparing To Be An EngineerbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- GENG 107 Engineering Skills and Ethics - Lecture - Chapter 2 - The EngineerDocument46 pagesGENG 107 Engineering Skills and Ethics - Lecture - Chapter 2 - The EngineerbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Types of ProcessingDocument1 pageTypes of ProcessingbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Factsheet 1Document3 pagesFactsheet 1bebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.3Document4 pagesUnit 1.3Husen Ibn IsmailNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Database MsDocument10 pages1.6 Database MsbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress AnalysisDocument11 pagesThermal Stress AnalysisFahad KhanNo ratings yet
- Uninyvin: Certified CompanyDocument4 pagesUninyvin: Certified CompanyDEEPAKNo ratings yet
- 2014 Guidelines Rockfall RemediationDocument9 pages2014 Guidelines Rockfall RemediationVashdevNo ratings yet
- Tata Institute of Fundamental Research TIFRDocument5 pagesTata Institute of Fundamental Research TIFRGangadhar BituNo ratings yet
- PIPE by Capote - TermsDocument109 pagesPIPE by Capote - TermsRochelle May CatbaganNo ratings yet
- Design Connection AISCDocument49 pagesDesign Connection AISCAmey Gudigar100% (1)
- Trim Stability BasicDocument64 pagesTrim Stability Basicdakidofdaboom80% (5)
- U1 Test Version ADocument4 pagesU1 Test Version AFarhan HabibzaiNo ratings yet
- CH1018E-Ch1. - U1-The Structure of Atoms-Lectuer NotesDocument55 pagesCH1018E-Ch1. - U1-The Structure of Atoms-Lectuer NotesHà ChiNo ratings yet
- A Statistical Model For Urban Radio PropagationDocument8 pagesA Statistical Model For Urban Radio PropagationBoblaw LawbobNo ratings yet
- Powder Filling MachineDocument9 pagesPowder Filling MachineCao Ngoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Review On Study of Jaw Crusher PDFDocument4 pagesReview On Study of Jaw Crusher PDFRagab AbulmagdNo ratings yet
- TG Lube Oil FlushingDocument3 pagesTG Lube Oil FlushingS V NAGESHNo ratings yet
- Unsymmetrical BendingDocument29 pagesUnsymmetrical Bendingdevansh SriNo ratings yet
- 1.PTSP SyllabusDocument2 pages1.PTSP SyllabusSaivenkat BingiNo ratings yet
- BC10 Examstudy U2Document91 pagesBC10 Examstudy U2Bryant Villarin BaldivicioNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of U-Shaped Ribbon Blender With Screw ConveyorDocument9 pagesDesign and Analysis of U-Shaped Ribbon Blender With Screw ConveyorAasawari MahagaonkarNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. (Fourth Semester) Mechanical Engineering Me-202 E Production TechnologyDocument8 pagesB.Tech. (Fourth Semester) Mechanical Engineering Me-202 E Production TechnologyMohit PunaniNo ratings yet
- Fracture MechanicsDocument31 pagesFracture MechanicsDhany SSat100% (2)
- Radix Sort AlgorithmDocument10 pagesRadix Sort AlgorithmNithin ChandyNo ratings yet
- 07-01-2024 - SR - Super60 - Elite, Target & LIIT-BTs - Jee-Main-GTM-09 - KEY & Sol'SDocument21 pages07-01-2024 - SR - Super60 - Elite, Target & LIIT-BTs - Jee-Main-GTM-09 - KEY & Sol'SSaketh UchihaNo ratings yet
- Ics Notes by Polarao SirDocument184 pagesIcs Notes by Polarao Sirsanyasirao1100% (1)
- Steam Powered Absorption Chiller Installation and Operation Manual TTDocument44 pagesSteam Powered Absorption Chiller Installation and Operation Manual TTromi_hamdani0% (1)
- Example Problems With SolutionsDocument20 pagesExample Problems With SolutionsAnonymous KlBhyI75% (4)
- JEE 2024-50 PYQs in 100 MinsDocument135 pagesJEE 2024-50 PYQs in 100 MinsVedu VedanthNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec V Art 6 Ed 2004Document10 pagesAsme Sec V Art 6 Ed 2004Anonymous fnVTzv9XlNo ratings yet
- (CALIL Et Al., 2006) Comparison of the Biodegradation of Poly (Ε-caprolactone), Cellulose Acetate and Their Blends by the Sturm Test and Selected Cultured FungiDocument8 pages(CALIL Et Al., 2006) Comparison of the Biodegradation of Poly (Ε-caprolactone), Cellulose Acetate and Their Blends by the Sturm Test and Selected Cultured FungiLeonardo LopesNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines: DR Tuan Mohammad Yusoff ShahDocument31 pagesMechanics of Machines: DR Tuan Mohammad Yusoff ShahSuthan Muthu KrisnanNo ratings yet
- Application of Chitosan Shells Meti Batissa ViolacDocument12 pagesApplication of Chitosan Shells Meti Batissa Violacnia herianiNo ratings yet
- DM302 Om PDFDocument12 pagesDM302 Om PDFDaniel BolivarNo ratings yet