Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CardioPulm Final Review
CardioPulm Final Review
Uploaded by
drng48Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Jansenkoh MRCP PacesDocument209 pagesJansenkoh MRCP PacesBob Yong83% (6)
- Pre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFDocument124 pagesPre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFdrng4850% (4)
- Índice Guild of American Lutherie BooksDocument283 pagesÍndice Guild of American Lutherie BooksDaniel AndradeNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal PainDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal Paindrng48100% (1)
- Med SurgDocument62 pagesMed SurgJean Soriano99% (67)
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3Document1 pagePages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3drng480% (1)
- MCQ Biomechanics of Hip JointDocument16 pagesMCQ Biomechanics of Hip Jointdrng48100% (10)
- Super Mario Galaxy 2 Prima Official Game GuideDocument273 pagesSuper Mario Galaxy 2 Prima Official Game GuideZachary RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsDocument125 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsAyeNo ratings yet
- R 5th Year OSCE - Part 2Document230 pagesR 5th Year OSCE - Part 2Leon RajanthiranNo ratings yet
- Synthesis: History Report SBAR Complete PA Know Your Patho!!! Don't Get Caught W/drawersDocument30 pagesSynthesis: History Report SBAR Complete PA Know Your Patho!!! Don't Get Caught W/drawersmmcgee002No ratings yet
- Clin Med For PAsDocument32 pagesClin Med For PAsMaryNguyen100% (2)
- Critical Care NursingDocument159 pagesCritical Care Nursinggretchen marie80% (5)
- IMA Nurse KKV SaifurDocument69 pagesIMA Nurse KKV Saifureva munartyNo ratings yet
- Mitral RegurgitationDocument43 pagesMitral Regurgitationraissasafitry100% (1)
- AV Nodal BlocksDocument13 pagesAV Nodal BlockslauraNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Diseases: Prof. Dr. Md. Nazrul IslamDocument23 pagesCongenital Heart Diseases: Prof. Dr. Md. Nazrul IslamprajwalNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cardiac SystemDocument51 pagesAssessment Cardiac Systemejarnmd100% (2)
- Cardiology QuizDocument3 pagesCardiology QuizHai TranNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NursingDocument159 pagesCritical Care NursingJoy Jarin50% (2)
- Lect9 CirculatoryDocument81 pagesLect9 CirculatoryTuTitNo ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument52 pagesCardiologyusmani_nida1No ratings yet
- Competency AppraisalDocument43 pagesCompetency AppraisalErica Ruvie AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- "Fifth Problem. The Painful Heartbeat": Emergency Medicine BlockDocument78 pages"Fifth Problem. The Painful Heartbeat": Emergency Medicine BlockFirdaus AldyNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Outline B - Joshua DiaoDocument17 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Outline B - Joshua DiaoLevi Rae CLerigo EstiponaNo ratings yet
- By: DR - Wesam AbdelazizDocument48 pagesBy: DR - Wesam AbdelazizTIRTH GANATRANo ratings yet
- Pericarditis - Morning ReportDocument51 pagesPericarditis - Morning ReportMaria DodonNo ratings yet
- Intern Survival Guide (UIC)Document51 pagesIntern Survival Guide (UIC)medstick100% (1)
- Medicine HO Guide Hosp AmpangDocument80 pagesMedicine HO Guide Hosp AmpangMohd Khairie100% (3)
- Cardio MTB 2:3 Notes DONEDocument10 pagesCardio MTB 2:3 Notes DONESumatt KaurNo ratings yet
- 5 - Cardio, RespiDocument287 pages5 - Cardio, RespiBeth CuntapayNo ratings yet
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument7 pagesAortic RegurgitationazaliavirsaNo ratings yet
- 3515 CompDocument28 pages3515 CompkaylasuleyNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-02-26 at 4.12.17 PM PDFDocument80 pagesScreenshot 2023-02-26 at 4.12.17 PM PDFAsyari HaxenNo ratings yet
- Icha Marissa Sofyan c11108318 UAPDocument24 pagesIcha Marissa Sofyan c11108318 UAPIcha Marissa SofyanNo ratings yet
- Cvs - 10 ConsolidatedDocument37 pagesCvs - 10 ConsolidatedezhilNo ratings yet
- StemiDocument39 pagesStemiFara OmarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approaches - DR Ahmed BakryDocument246 pagesClinical Approaches - DR Ahmed BakrydrthanallaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With A Heart MurmurDocument103 pagesApproach To The Patient With A Heart MurmurDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- The ElectrocardiogramDocument2 pagesThe ElectrocardiogramOh DehNo ratings yet
- Adult III Cardiac Study GuideDocument15 pagesAdult III Cardiac Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- Congenital Heart Disease-2Document57 pagesCongenital Heart Disease-2Deepika LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- STEMIDocument28 pagesSTEMIGP HMHNo ratings yet
- Medical AbbreviationsDocument4 pagesMedical AbbreviationsNelly PaniaguaNo ratings yet
- Achd Ug OriginalDocument43 pagesAchd Ug OriginalchristyNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease and Non Cardiac Surgery: Lakshmi P. YalavarthyDocument44 pagesValvular Heart Disease and Non Cardiac Surgery: Lakshmi P. YalavarthyLakshmi YalavarthyNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of Cardiovascular: DR - Ira Andaningsih SPJP Cardiovascular Block 2008Document89 pagesPhysical Examination of Cardiovascular: DR - Ira Andaningsih SPJP Cardiovascular Block 2008YeniNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiovascular System History & ExaminationDocument74 pagesPediatric Cardiovascular System History & Examinationعبدالله Abdullah INo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia: PalpitationDocument36 pagesArrhythmia: PalpitationHala BahaaNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument9 pagesCardioVirgilio Reyes ManuelNo ratings yet
- ED Study GuideDocument59 pagesED Study Guidemmmmz100% (1)
- Cardiology A. Woo PDFDocument52 pagesCardiology A. Woo PDFiuliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsDocument127 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Cardiac Problemssarah morleyNo ratings yet
- CVS Examination 3rd MBDocument30 pagesCVS Examination 3rd MBsnowlover boyNo ratings yet
- Mitral Stenosis: JONES Criteria - 2015 Modification Major CriteriaDocument13 pagesMitral Stenosis: JONES Criteria - 2015 Modification Major CriteriaBiswarup PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- Asthma:: Case Scenario: DDXDocument10 pagesAsthma:: Case Scenario: DDXFemale calmNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Torsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandTorsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeFrom EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeNo ratings yet
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National PhyDocument1 pagePages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phydrng48No ratings yet
- Neurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? AnswerDocument9 pagesNeurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? Answerdrng48No ratings yet
- توزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيDocument3 pagesتوزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيdrng48No ratings yet
- Assessment of Development and GrowthDocument21 pagesAssessment of Development and Growthdrng48No ratings yet
- MCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural MechanismsDocument3 pagesMCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural Mechanismsdrng48No ratings yet
- Stomacolostomy 161108133919Document3 pagesStomacolostomy 161108133919drng48100% (1)
- Infections: (2013 - 2017)Document1 pageInfections: (2013 - 2017)drng48No ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy MCQDocument2 pagesCerebral Palsy MCQdrng4882% (11)
- Shenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXDocument281 pagesShenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXJeronim H'gharNo ratings yet
- Name: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859Document12 pagesName: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859drng48No ratings yet
- Contraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania HospitalDocument20 pagesContraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania Hospitaldrng48No ratings yet
- Table: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest PainDocument2 pagesTable: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest Paindrng48No ratings yet
- Burn RehabilitationDocument5 pagesBurn Rehabilitationdrng48No ratings yet
- 31 Da 7 CBB 2 eDocument2 pages31 Da 7 CBB 2 edrng48No ratings yet
- Epidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1Document3 pagesEpidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1drng48No ratings yet
- OTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingDocument16 pagesOTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingFrds123No ratings yet
- Task 1 - Pre Knowledge Quiz - CARRODocument15 pagesTask 1 - Pre Knowledge Quiz - CARROClaudia FilipoNo ratings yet
- CTEO Chapter II B Chemistry and 10 Clinker FactsDocument43 pagesCTEO Chapter II B Chemistry and 10 Clinker FactsFranciscoCorreaJara100% (2)
- 7th Heart Sounds and MurmursDocument6 pages7th Heart Sounds and MurmursbabibubeboNo ratings yet
- Countrys ClimateDocument20 pagesCountrys ClimateErika Jayne100% (1)
- Aquaculture Asia Jan 08Document60 pagesAquaculture Asia Jan 08Nilamdeen Mohamed ZamilNo ratings yet
- Fixed Asset RegisterDocument3 pagesFixed Asset Registerzuldvsb0% (1)
- Pro Tip Catalogue 4 07Document28 pagesPro Tip Catalogue 4 07notengofffNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan CLE-9Document5 pagesLearning Plan CLE-9Caren PondoyoNo ratings yet
- Ellipseregular 2Document4 pagesEllipseregular 2Nibha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Avionics 16 MarksDocument1 pageAvionics 16 MarksJessica CarterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Purpose of ArtDocument46 pagesLecture 3 - Purpose of ArtGrace LabayneNo ratings yet
- P1662/D8.0, March 2016 - IEEE Draft Recommended Practice For Design and Application of Power Electronics in Electrical Power SystemsDocument63 pagesP1662/D8.0, March 2016 - IEEE Draft Recommended Practice For Design and Application of Power Electronics in Electrical Power SystemsHgoglezNo ratings yet
- AbraDocument18 pagesAbraObed Andalis0% (1)
- Ac BDVDocument12 pagesAc BDVUhhoj JjxhkNo ratings yet
- All About Steamers - The Boilers and EnginesDocument7 pagesAll About Steamers - The Boilers and EnginesClyde SteamersNo ratings yet
- Index: High-Grade KeyboardDocument15 pagesIndex: High-Grade KeyboardDavid Emanuel Dauo0% (1)
- FFODocument12 pagesFFOzahab007No ratings yet
- X1D - USER GUIDE English PDFDocument157 pagesX1D - USER GUIDE English PDFSteveNo ratings yet
- Michigan Wing Encampment - 2008Document16 pagesMichigan Wing Encampment - 2008CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument18 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSreekanth PagadapalliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - MAT668 - Students HandoutDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - MAT668 - Students Handout2021826386No ratings yet
- Instron 3367 Frerichs GuideDocument9 pagesInstron 3367 Frerichs GuideNexhat QehajaNo ratings yet
- (8th) Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved AssignmentsDocument3 pages(8th) Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved AssignmentssushantNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsDocument50 pagesAtomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsACSVNo ratings yet
- Catalog-Basket ScreenDocument2 pagesCatalog-Basket ScreenBaskyNo ratings yet
- AKVA Group Cage Farming Aquaculture 2014 2015Document78 pagesAKVA Group Cage Farming Aquaculture 2014 2015norisnorisNo ratings yet
CardioPulm Final Review
CardioPulm Final Review
Uploaded by
drng48Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CardioPulm Final Review
CardioPulm Final Review
Uploaded by
drng48Copyright:
Available Formats
Cardiopulmonary Final Review
Cardiac Exam
Symptom descriptors angina, SoB, night dyspnea, orthopnea, link to exertion, palpitation, syncope/dizzy,
sweating
Dyspnea scale 1+ PT cant notice, 2+ PT notices, 3+ moderate but pt continues, 4+ pt cant
continue
Angina scale 1+ not noticeable, 2+ bothersome, 3+ very uncomfortable, 4+ worst pain ever
Observation
Posture, thoracic deformity, accessory muscles
Affect
Skin color, clubbing, edema, incisions, JVD
RR, breathing pattern, cough
Gait speed, rest requirements
Palpation
Pulses (0 absent, 1+ weak, 2+ norm, 3+ increased, 4+ bounding) & PMI
Skin temp & diaphoresis
Pitting edema grading 1+ barely, 2+ rebound <15sec, 3+ rebound 15-30sec, 4+ rebound >30sec
Sternal points (sternal, aortic, pulmonic, Rvent, Lvent, epigastric)
Vitals temp, HR (60-100 norm), RR(~12-16 norm), BP(< 120/80 norm, 140-159/90-99 HTN I), pain
Auscultation
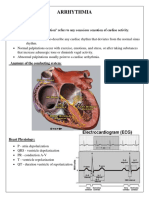
Heart sounds
Aortic R 2nd space Pulmonary L 2nd space
Tricuspid L 4th space Mitral at PMI point
S4 (late diastole, HTN / cardiomyopathy), S 1 (lub, AV valve close at start of systole), S2 (dub,
semilunar valve close at end of systole), S 3 (early diastole, vent fail / tachy, MR)
Adventitious murmur, click, snap
Differentiate CP and associated symptoms
Cardiac symptoms Central cyanosis, night dyspnea, palpitation, UE / jaw pain, unusual sweating, syncope
Pulmonary symptoms Peripheral cyanosis, stridor, wheezing, activity limitation
Worse: deep breath, trunk / pleural stretch
Better: quadruped, lean forward, hold breath
Bi-system symptoms dyspnea/orthopnea, cough, chest pain,
peripheral edema
Anginas
Chronic, stable known onset / level of demand nitroglycerin
Stable set level of activity nitroglycerin, rest, no stress
Unstable at rest or differ from prior onset nitroglycerin
Prinzmetal early morning, no exertion link, 2o vasospasm
MI last 30+min, not relieved by nitroglycerin, sense of doom
GI pain worse after eating, supine, acid-food
Acute Lecture
Pulmonary artery cathether / Swan Ganz
Internal jugular subclavian R atrium
Pulm A pressure, wedge pressure (LVEDvol), LVEDP
** if LVEDP >12 no supine, move & percuss carefully
R heart catheter (Swan Ganz is 1 type)
Continuous venous O2 sat monitor (normal = 60-80%, but arterial normal = 95-98%)
Arterial line
Radial artery or femoral artery
Systemic BP
** DONT disconnect!!!, no hip >60o if femoral, infection, check manually if weird reading
Central venous line
Subclavian vein, internal jugular vein or femoral vein
Cardiopulmonary Final Review
R atrial pressure
** Move carefully
Intravenous line
Superficial vein
Immediate blood input of fluids, electrolytes, medication, nutrition
** Must be changed every 3-4days
Percutaneous intra-cardiac catheter (PICC)
Forearm vein R atrium
Prevent multi-sticking
** no submersion, watch for bleeds, phlebitis, infection, blocking, clotting, arrhythmia
Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP)
Femoral artery descending aorta (just below subclavian)
Inflate / deflate timed to cardiac cycle perfusion
** usually not PT Tx, no hip , check radial pulses
Extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
**bleeding, clotting, infection
ABG measures
pO2 (87.5) / pCO2 (40) / HCO3- (24) / pH (7.4) / SaO2 (97)
I & O affecters fluid retention, oral/IV intake fluid shift, sweat, wound drain, diarrhea/vomit,
hemorrhage, urine
Pacemakers
Placement coding
1st letter chamber placed in (O none, A atrium, V ventricle, D dual)
2nd letter chamber sensed (O none, A atrium, V ventricle, D dual)
3rd letter pacemaker response to sensed activity (O none, I inhibit, T trigger, D dual)
4th & 5th letters - programmability
Demand pacemaker kicks in when HR too low can HR when SA no cant (chronotropic incompetence)
Pacemaker precautions
Re-eval every 3-6mo check function, batter lasts 5-8yr
Avoid full contact sport
Avoid electromagnetic interference cell phone, MRI, TENS, therapeutic radiation, subway brakes
**Airport carry ID cardOK to go through security, but dont stand in scanner long
Pacemaker indications
Usually for brady, sinus node dysfunction (sinus arrest, SSS, chronotropic incompetence), block,
CHF
SSS sinus brady, tachy, or alternating
Pacemaker for brady, meds/ablation for tachy
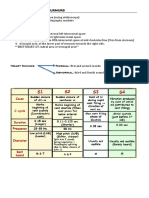
1st Degree block Good Pwave, 1P:1QRS, consistent long PRinterval
2nd Degree block I PRinterval until QRS dropped
2nd Degree block II 2+P:1QRS, regular PRinterval when QRS does happen
3rd Degree block atrial rate & ventricular rate independent
Linked signs/Sx syncope, dizzy, energy, fatigue, exercise intolerance, SoB, palpitation, confusion
Know the medication chart
Exercise Tests and VO2
Ventilation pathologies COPD, pneumonia, asthma, CF, ARDS, neuromuscular Dz, restrictive Dz
Heart pathologies CAD, CHF, dysrhythmia, mycarditis, cardiomyopathy
Vascular pathologies PVD, DVT, DMII
Muscle / endurance pathologies immobilization, CHF, MD, nutritional Dz, myositis, DMII
VO2 factors age, gender ( 15-30% less), heredity, body composition, endurance training, O 2 transport Dz
NO exercise testing
Significant EKG change
Acute PE / infarct
Cardiopulmonary Final Review
Unstable angina
Acute myocarditis / pericarditis
Uncontrolled dysrhythmia
Dissecting aneurysm
Symptomatic severe AS
Systemic infection
Uncontrolled CHF
Careful exercise testing
L main artery disease
Atrioventricular block
Moderate valve stenosis
Ventricular aneurysm
Abnormal electrolytes
Uncontrolled metabolic disease
Severe HTN at rest (>200/110)
Chronic infections
Tachy or brady
Mental / physical impairments
Dz exacerbated by exercise
Walking tests
3m or 10m walk test community ambulation requires 0.5-1.22m/sec
6min (or 12min or 2min) walk test self-pacednot very great motivationally
10m walk shuttle or 20m run shuttle externally pacedmore motivational
1mi walk test
Step tests external pacing (metronome)
Stop testing a healthy adult if
Angina
Failure of normal HR
systolic BP by 10+mmHg
Rhythm change
Excessive BP (>250/115)
Complaint of fatigue
SoB, wheezing, cramps, claudication
Equipment failure
Cyanosis
You might also like
- Jansenkoh MRCP PacesDocument209 pagesJansenkoh MRCP PacesBob Yong83% (6)
- Pre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFDocument124 pagesPre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFdrng4850% (4)
- Índice Guild of American Lutherie BooksDocument283 pagesÍndice Guild of American Lutherie BooksDaniel AndradeNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal PainDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal Paindrng48100% (1)
- Med SurgDocument62 pagesMed SurgJean Soriano99% (67)
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3Document1 pagePages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3drng480% (1)
- MCQ Biomechanics of Hip JointDocument16 pagesMCQ Biomechanics of Hip Jointdrng48100% (10)
- Super Mario Galaxy 2 Prima Official Game GuideDocument273 pagesSuper Mario Galaxy 2 Prima Official Game GuideZachary RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsDocument125 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsAyeNo ratings yet
- R 5th Year OSCE - Part 2Document230 pagesR 5th Year OSCE - Part 2Leon RajanthiranNo ratings yet
- Synthesis: History Report SBAR Complete PA Know Your Patho!!! Don't Get Caught W/drawersDocument30 pagesSynthesis: History Report SBAR Complete PA Know Your Patho!!! Don't Get Caught W/drawersmmcgee002No ratings yet
- Clin Med For PAsDocument32 pagesClin Med For PAsMaryNguyen100% (2)
- Critical Care NursingDocument159 pagesCritical Care Nursinggretchen marie80% (5)
- IMA Nurse KKV SaifurDocument69 pagesIMA Nurse KKV Saifureva munartyNo ratings yet
- Mitral RegurgitationDocument43 pagesMitral Regurgitationraissasafitry100% (1)
- AV Nodal BlocksDocument13 pagesAV Nodal BlockslauraNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Diseases: Prof. Dr. Md. Nazrul IslamDocument23 pagesCongenital Heart Diseases: Prof. Dr. Md. Nazrul IslamprajwalNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cardiac SystemDocument51 pagesAssessment Cardiac Systemejarnmd100% (2)
- Cardiology QuizDocument3 pagesCardiology QuizHai TranNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NursingDocument159 pagesCritical Care NursingJoy Jarin50% (2)
- Lect9 CirculatoryDocument81 pagesLect9 CirculatoryTuTitNo ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument52 pagesCardiologyusmani_nida1No ratings yet
- Competency AppraisalDocument43 pagesCompetency AppraisalErica Ruvie AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- "Fifth Problem. The Painful Heartbeat": Emergency Medicine BlockDocument78 pages"Fifth Problem. The Painful Heartbeat": Emergency Medicine BlockFirdaus AldyNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Outline B - Joshua DiaoDocument17 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Outline B - Joshua DiaoLevi Rae CLerigo EstiponaNo ratings yet
- By: DR - Wesam AbdelazizDocument48 pagesBy: DR - Wesam AbdelazizTIRTH GANATRANo ratings yet
- Pericarditis - Morning ReportDocument51 pagesPericarditis - Morning ReportMaria DodonNo ratings yet
- Intern Survival Guide (UIC)Document51 pagesIntern Survival Guide (UIC)medstick100% (1)
- Medicine HO Guide Hosp AmpangDocument80 pagesMedicine HO Guide Hosp AmpangMohd Khairie100% (3)
- Cardio MTB 2:3 Notes DONEDocument10 pagesCardio MTB 2:3 Notes DONESumatt KaurNo ratings yet
- 5 - Cardio, RespiDocument287 pages5 - Cardio, RespiBeth CuntapayNo ratings yet
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument7 pagesAortic RegurgitationazaliavirsaNo ratings yet
- 3515 CompDocument28 pages3515 CompkaylasuleyNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-02-26 at 4.12.17 PM PDFDocument80 pagesScreenshot 2023-02-26 at 4.12.17 PM PDFAsyari HaxenNo ratings yet
- Icha Marissa Sofyan c11108318 UAPDocument24 pagesIcha Marissa Sofyan c11108318 UAPIcha Marissa SofyanNo ratings yet
- Cvs - 10 ConsolidatedDocument37 pagesCvs - 10 ConsolidatedezhilNo ratings yet
- StemiDocument39 pagesStemiFara OmarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approaches - DR Ahmed BakryDocument246 pagesClinical Approaches - DR Ahmed BakrydrthanallaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With A Heart MurmurDocument103 pagesApproach To The Patient With A Heart MurmurDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- The ElectrocardiogramDocument2 pagesThe ElectrocardiogramOh DehNo ratings yet
- Adult III Cardiac Study GuideDocument15 pagesAdult III Cardiac Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- Congenital Heart Disease-2Document57 pagesCongenital Heart Disease-2Deepika LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- STEMIDocument28 pagesSTEMIGP HMHNo ratings yet
- Medical AbbreviationsDocument4 pagesMedical AbbreviationsNelly PaniaguaNo ratings yet
- Achd Ug OriginalDocument43 pagesAchd Ug OriginalchristyNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease and Non Cardiac Surgery: Lakshmi P. YalavarthyDocument44 pagesValvular Heart Disease and Non Cardiac Surgery: Lakshmi P. YalavarthyLakshmi YalavarthyNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of Cardiovascular: DR - Ira Andaningsih SPJP Cardiovascular Block 2008Document89 pagesPhysical Examination of Cardiovascular: DR - Ira Andaningsih SPJP Cardiovascular Block 2008YeniNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiovascular System History & ExaminationDocument74 pagesPediatric Cardiovascular System History & Examinationعبدالله Abdullah INo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia: PalpitationDocument36 pagesArrhythmia: PalpitationHala BahaaNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument9 pagesCardioVirgilio Reyes ManuelNo ratings yet
- ED Study GuideDocument59 pagesED Study Guidemmmmz100% (1)
- Cardiology A. Woo PDFDocument52 pagesCardiology A. Woo PDFiuliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsDocument127 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Cardiac Problemssarah morleyNo ratings yet
- CVS Examination 3rd MBDocument30 pagesCVS Examination 3rd MBsnowlover boyNo ratings yet
- Mitral Stenosis: JONES Criteria - 2015 Modification Major CriteriaDocument13 pagesMitral Stenosis: JONES Criteria - 2015 Modification Major CriteriaBiswarup PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- Asthma:: Case Scenario: DDXDocument10 pagesAsthma:: Case Scenario: DDXFemale calmNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Torsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandTorsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeFrom EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeNo ratings yet
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National PhyDocument1 pagePages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phydrng48No ratings yet
- Neurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? AnswerDocument9 pagesNeurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? Answerdrng48No ratings yet
- توزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيDocument3 pagesتوزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيdrng48No ratings yet
- Assessment of Development and GrowthDocument21 pagesAssessment of Development and Growthdrng48No ratings yet
- MCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural MechanismsDocument3 pagesMCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural Mechanismsdrng48No ratings yet
- Stomacolostomy 161108133919Document3 pagesStomacolostomy 161108133919drng48100% (1)
- Infections: (2013 - 2017)Document1 pageInfections: (2013 - 2017)drng48No ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy MCQDocument2 pagesCerebral Palsy MCQdrng4882% (11)
- Shenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXDocument281 pagesShenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXJeronim H'gharNo ratings yet
- Name: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859Document12 pagesName: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859drng48No ratings yet
- Contraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania HospitalDocument20 pagesContraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania Hospitaldrng48No ratings yet
- Table: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest PainDocument2 pagesTable: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest Paindrng48No ratings yet
- Burn RehabilitationDocument5 pagesBurn Rehabilitationdrng48No ratings yet
- 31 Da 7 CBB 2 eDocument2 pages31 Da 7 CBB 2 edrng48No ratings yet
- Epidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1Document3 pagesEpidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1drng48No ratings yet
- OTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingDocument16 pagesOTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingFrds123No ratings yet
- Task 1 - Pre Knowledge Quiz - CARRODocument15 pagesTask 1 - Pre Knowledge Quiz - CARROClaudia FilipoNo ratings yet
- CTEO Chapter II B Chemistry and 10 Clinker FactsDocument43 pagesCTEO Chapter II B Chemistry and 10 Clinker FactsFranciscoCorreaJara100% (2)
- 7th Heart Sounds and MurmursDocument6 pages7th Heart Sounds and MurmursbabibubeboNo ratings yet
- Countrys ClimateDocument20 pagesCountrys ClimateErika Jayne100% (1)
- Aquaculture Asia Jan 08Document60 pagesAquaculture Asia Jan 08Nilamdeen Mohamed ZamilNo ratings yet
- Fixed Asset RegisterDocument3 pagesFixed Asset Registerzuldvsb0% (1)
- Pro Tip Catalogue 4 07Document28 pagesPro Tip Catalogue 4 07notengofffNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan CLE-9Document5 pagesLearning Plan CLE-9Caren PondoyoNo ratings yet
- Ellipseregular 2Document4 pagesEllipseregular 2Nibha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Avionics 16 MarksDocument1 pageAvionics 16 MarksJessica CarterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Purpose of ArtDocument46 pagesLecture 3 - Purpose of ArtGrace LabayneNo ratings yet
- P1662/D8.0, March 2016 - IEEE Draft Recommended Practice For Design and Application of Power Electronics in Electrical Power SystemsDocument63 pagesP1662/D8.0, March 2016 - IEEE Draft Recommended Practice For Design and Application of Power Electronics in Electrical Power SystemsHgoglezNo ratings yet
- AbraDocument18 pagesAbraObed Andalis0% (1)
- Ac BDVDocument12 pagesAc BDVUhhoj JjxhkNo ratings yet
- All About Steamers - The Boilers and EnginesDocument7 pagesAll About Steamers - The Boilers and EnginesClyde SteamersNo ratings yet
- Index: High-Grade KeyboardDocument15 pagesIndex: High-Grade KeyboardDavid Emanuel Dauo0% (1)
- FFODocument12 pagesFFOzahab007No ratings yet
- X1D - USER GUIDE English PDFDocument157 pagesX1D - USER GUIDE English PDFSteveNo ratings yet
- Michigan Wing Encampment - 2008Document16 pagesMichigan Wing Encampment - 2008CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument18 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSreekanth PagadapalliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - MAT668 - Students HandoutDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - MAT668 - Students Handout2021826386No ratings yet
- Instron 3367 Frerichs GuideDocument9 pagesInstron 3367 Frerichs GuideNexhat QehajaNo ratings yet
- (8th) Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved AssignmentsDocument3 pages(8th) Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved AssignmentssushantNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsDocument50 pagesAtomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsACSVNo ratings yet
- Catalog-Basket ScreenDocument2 pagesCatalog-Basket ScreenBaskyNo ratings yet
- AKVA Group Cage Farming Aquaculture 2014 2015Document78 pagesAKVA Group Cage Farming Aquaculture 2014 2015norisnorisNo ratings yet