Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Light Propagation in Optical Fiber: Light Thought of As A Wave
Light Propagation in Optical Fiber: Light Thought of As A Wave
Uploaded by
Mona SayedCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PDFDocument36 pagesPDFayad60100% (2)
- OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsDocument36 pagesOPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsabidNo ratings yet
- OC Expt 6 PDFDocument5 pagesOC Expt 6 PDFPrasad RaneNo ratings yet
- 1.optical FibersDocument23 pages1.optical FibersYashNo ratings yet
- Sec1 OpticsDocument18 pagesSec1 Opticsaelsheikh834No ratings yet
- Lecture #1 Optical FibersDocument59 pagesLecture #1 Optical Fibersjeddo2005No ratings yet
- Fibre Optic Communication PDFDocument199 pagesFibre Optic Communication PDFBiswarup MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Lec.1 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsDocument45 pagesLec.1 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsMahmoud Sayed100% (1)
- Abramczy@mitr.p.lodz - PL WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/raman WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/evuDocument49 pagesAbramczy@mitr.p.lodz - PL WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/raman WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/evuChaitanya ShakyaNo ratings yet
- 3320 Fiber-Optic CommunicationDocument32 pages3320 Fiber-Optic CommunicationEdward FahmiNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication 123Document22 pagesOptical Communication 123prashanth_02No ratings yet
- Fiber Dispersion, Which Leads To Broadening of Individual OpticalDocument17 pagesFiber Dispersion, Which Leads To Broadening of Individual OpticalAnnas TunggalNo ratings yet
- OCN Unit I KeyDocument11 pagesOCN Unit I KeyChandra MathiNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument20 pagesOptical Fiber CommunicationSeenuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Optical FibersDocument60 pagesChapter 2 - Optical Fiberseyohamehari235No ratings yet
- Optical SensorsDocument17 pagesOptical SensorsHassanein Al-hadadNo ratings yet
- 01 1330682265 93458 PDFDocument32 pages01 1330682265 93458 PDFSanjay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Optical FibreDocument47 pagesOptical FibreThe Haneef ReyaziiNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Training GuideDocument17 pagesFiber Optic Training GuideIrfan IrshadNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Part IDocument46 pagesFiber Optics Part ImariahvahNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics1Document29 pagesFiber Optics1Biswajith MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics GeneralDocument29 pagesFiber Optics GeneralSurya6556No ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument64 pagesOptical CommunicationAmit Samrat MauryaNo ratings yet
- Lec.2 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsDocument17 pagesLec.2 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsMahmoud SayedNo ratings yet
- My Optic NotesDocument27 pagesMy Optic NotesRamesh MeherNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics (Unit - 3)Document28 pagesFiber Optics (Unit - 3)Rangu RohithNo ratings yet
- OFC Unit 1-ADocument22 pagesOFC Unit 1-AnaactitexcellenceNo ratings yet
- Sic 1605Document103 pagesSic 1605sanjaisanjai51110003No ratings yet
- Unit IintroductionDocument40 pagesUnit IintroductionkikiNo ratings yet
- Photonic Technologies For Millimeter - and Submillimeter TechnologiesDocument19 pagesPhotonic Technologies For Millimeter - and Submillimeter TechnologiesSenjuti KhanraNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication 2mark PDFDocument20 pagesOptical Communication 2mark PDFAnant ShankarNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication NetworksDocument8 pagesOptical Communication NetworksPonmalar Sivaraj100% (1)
- Part A University Questions2019 2020Document9 pagesPart A University Questions2019 2020thiruvengadam cNo ratings yet
- Ray ModelDocument11 pagesRay ModelV'nod Rathode BNo ratings yet
- Numerical With AnswerDocument19 pagesNumerical With AnswerRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cables Unit2Document84 pagesFiber Optic Cables Unit2Harish PandamaneniNo ratings yet
- Foli Unit 1 - 2 Mark Question and AnswerDocument4 pagesFoli Unit 1 - 2 Mark Question and AnswerJayakumar ThangavelNo ratings yet
- Assignment-5: Galgotias College of Engineering& TechnologyDocument9 pagesAssignment-5: Galgotias College of Engineering& TechnologyAyushi GoelNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication Question BankDocument24 pagesOptical Communication Question BankdhivyakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Optical Full Units NOTESDocument98 pagesOptical Full Units NOTESkohilavaniapNo ratings yet
- Optic FiberDocument31 pagesOptic Fiberkeregi100% (1)
- Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 History of Fiber OpticsDocument8 pagesChapter 1. Introduction 1.1 History of Fiber OpticsTsy Less DahalNo ratings yet
- Dispersion in Optical FiberDocument36 pagesDispersion in Optical FiberSonakshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phy4 2Document16 pagesPhy4 2sakshamsharma7257No ratings yet
- OCN Unit 1,2Document23 pagesOCN Unit 1,2M Madhu MaliniNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication SystemDocument12 pagesOptical Fiber Communication Systemjamal123456No ratings yet
- Wave DM2Document45 pagesWave DM2Chandan HmNo ratings yet
- Turowicz 1Document62 pagesTurowicz 1Saurav KauraNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 and 2 OpticalDocument278 pagesUnit-1 and 2 OpticalGuru VelmathiNo ratings yet
- Ocn Two MarksDocument24 pagesOcn Two Marksmani kandanNo ratings yet
- BEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFDocument201 pagesBEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFMax DurendNo ratings yet
- Opto & Optical ComDocument222 pagesOpto & Optical ComRansford SackeyNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document27 pagesDay 2Abhiram SwarnaNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document52 pagesDay 1Abhiram SwarnaNo ratings yet
- EE493 - Second Set of Lecture Slides-Spring 2021Document78 pagesEE493 - Second Set of Lecture Slides-Spring 2021احمد الديريNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication 2017,2018,2020 and 2021 Past Questions and SolutionsDocument42 pagesOptical Communication 2017,2018,2020 and 2021 Past Questions and SolutionsMelsougly BryceNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Optical Communication SystemDocument18 pagesBlock Diagram of Optical Communication SystemSuhana Sharma100% (4)
- PhotodetectorsDocument46 pagesPhotodetectorsShivam AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Laser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsFrom EverandLaser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- Noise in Nanoscale Semiconductor DevicesFrom EverandNoise in Nanoscale Semiconductor DevicesTibor GrasserNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines : Year / Semester: 3 /2Document13 pagesElectrical Machines : Year / Semester: 3 /2Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- EEDP Lect 09 Logic FamiliesDocument34 pagesEEDP Lect 09 Logic Familiessiddu smartNo ratings yet
- 28 - BenchmarkingDocument14 pages28 - BenchmarkingMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Lean As A Universal Model of Excellence: It Is Not Just A Manufacturing Tool!Document8 pagesLean As A Universal Model of Excellence: It Is Not Just A Manufacturing Tool!Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- 24 - The Fit OrganizationDocument5 pages24 - The Fit OrganizationMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines : Three-Phase Induction MotorsDocument18 pagesElectrical Machines : Three-Phase Induction MotorsMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines : Torque of Induction MotorDocument12 pagesElectrical Machines : Torque of Induction MotorMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Electrical Machines .PPT (Compatibility Mode) - 1Document6 pagesLecture 1 - Electrical Machines .PPT (Compatibility Mode) - 1Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines (3206) Induction Motors: Year / Semester: 3 / 2Document10 pagesElectrical Machines (3206) Induction Motors: Year / Semester: 3 / 2Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Electrical Machines .PPT (Compatibility Mode) - 1Document17 pagesLecture 2 - Electrical Machines .PPT (Compatibility Mode) - 1Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Resistance: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument48 pagesChapter 3 - Resistance: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Voltage and Current: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument44 pagesChapter 2 - Voltage and Current: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Sequential Logic CircuitsDocument18 pagesSequential Logic CircuitsMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Ch2.Fourier Theory and Communication SignalsDocument20 pagesCh2.Fourier Theory and Communication SignalsMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Discrete-Time ConvolutionDocument14 pagesDiscrete-Time ConvolutionMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Continuous-Time Signals (C-T Signals)Document21 pagesSignals and Systems Continuous-Time Signals (C-T Signals)Mona SayedNo ratings yet
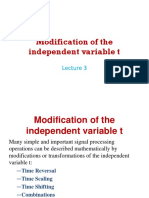
- Modification of The Independent Variable TDocument15 pagesModification of The Independent Variable TMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Ch1.Background and PreviewDocument9 pagesCh1.Background and PreviewMona SayedNo ratings yet
- 08s Week06 2 Lab ManetDocument5 pages08s Week06 2 Lab ManetMona SayedNo ratings yet
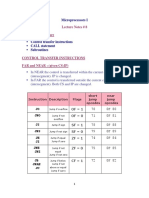
- Lecture Notes # 8 Outline of The Lecture: Control Transfer Instructions CALL Statement SubroutinesDocument7 pagesLecture Notes # 8 Outline of The Lecture: Control Transfer Instructions CALL Statement SubroutinesMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Boyle StadDocument50 pagesBoyle StadRodel MarananNo ratings yet
- 7 Segment DisplayDocument6 pages7 Segment DisplayTwesigomwe Gilbert GabrielNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1Gaurav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Datasheet OptoDocument12 pagesDatasheet OptoAdrian RgFlNo ratings yet
- Gate Characteristics Design Thyristor Ratings Requirements of The Gate CircuitDocument9 pagesGate Characteristics Design Thyristor Ratings Requirements of The Gate CircuitAayu JainNo ratings yet
- Solar and InvertersDocument7 pagesSolar and InverterskashafNo ratings yet
- Iteco Esdbook - 2004 - Eng PDFDocument32 pagesIteco Esdbook - 2004 - Eng PDFAnonymous FZs3yBHh7No ratings yet
- Power Electronics MnualDocument16 pagesPower Electronics MnualRitika JainNo ratings yet
- CAD Lab Manual KEC 653B (4mail)Document38 pagesCAD Lab Manual KEC 653B (4mail)Piyush0% (1)
- LifiDocument21 pagesLifiAnonymous QIuAGIadXmNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument3 pagesDatasheetselocaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument24 pagesChemistryJimmy OrajayNo ratings yet
- Inst Control and Elec Tech Ice (2178) - 1Document13 pagesInst Control and Elec Tech Ice (2178) - 1balajirajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Cyclic Convolution Based On FNTDocument6 pagesImplementation of Cyclic Convolution Based On FNTInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 7SG14 Duobias M Catalogue Sheet PDFDocument20 pages7SG14 Duobias M Catalogue Sheet PDFanuj100% (1)
- Generator Overfluxing PDFDocument6 pagesGenerator Overfluxing PDFName Is100% (3)
- CRT Television Repair CourseDocument131 pagesCRT Television Repair Coursejakovpekovic100% (2)
- Manual Ogt100 enDocument5 pagesManual Ogt100 enJavier Alcubilla ArribasNo ratings yet
- Full-Color Micro-LED Display With CsPbBr3 Perovskite and CdSe Quantum Dots As Color Conversion LayersDocument6 pagesFull-Color Micro-LED Display With CsPbBr3 Perovskite and CdSe Quantum Dots As Color Conversion Layers18maxwell61No ratings yet
- Surface Engineering of Nanomaterials: Lecture 12: Physical Vapour Deposition (PVD)Document19 pagesSurface Engineering of Nanomaterials: Lecture 12: Physical Vapour Deposition (PVD)hrana287No ratings yet
- Solid State Pressure Sensor: FeaturesDocument2 pagesSolid State Pressure Sensor: FeaturesCarlosDíazPeñaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Common Emitter I-V Characteristics of A NPN Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument3 pagesLab 6 Common Emitter I-V Characteristics of A NPN Bipolar Junction TransistorMohamad AyoubNo ratings yet
- U2270B TEMICSemiconductorsDocument13 pagesU2270B TEMICSemiconductorsВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Datasheet CI PS229Document11 pagesDatasheet CI PS229tumaistuNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller-Based Single-Phase Automatic Voltage RegulatorDocument5 pagesMicrocontroller-Based Single-Phase Automatic Voltage RegulatorFuh ValleryNo ratings yet
- SM-XXXPC8 Series: 205 285watt Photovoltaic ModuleDocument2 pagesSM-XXXPC8 Series: 205 285watt Photovoltaic ModuleSeptimiu BotaNo ratings yet
- FM DocumentationDocument23 pagesFM DocumentationJohnMatthewBancilNo ratings yet
- Mobile Jammer Circuit: Inventory ListDocument2 pagesMobile Jammer Circuit: Inventory ListCarlo Piere DayaoNo ratings yet
Light Propagation in Optical Fiber: Light Thought of As A Wave
Light Propagation in Optical Fiber: Light Thought of As A Wave
Uploaded by
Mona SayedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Light Propagation in Optical Fiber: Light Thought of As A Wave
Light Propagation in Optical Fiber: Light Thought of As A Wave
Uploaded by
Mona SayedCopyright:
Available Formats
Light propagation in optical fiber
Introduction
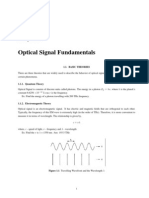
Light thought of as a wave
Electric field component (E) can be expressed mathematically as
E=E 0 cos ( wtkx +)
Where
E0
= amplitude of electric field (V/m)
=2 f =
angular frequency (rad/s)
F= optical frequency (Hz)
t = time (s)
k=
x=
= wavenumber or propagation constant (rad/m)
distance (m)
= optical wavelength (m)
= phase constant (rad)
Light thought of as a wave
Velocity of propagation
C
V =f = 0
n
Where
C0 =3 108 m/s
velocity of the light in free space
n= refractive index of the medium in which light is propagating
Basic principles of light propagation
Ray Theory (Geometrical Optics)
1
Law of reflection
I =r
Law of refraction (Snells law)
n1 sin 1=n2 sin 2
Where
n1 and n2 are refractive index of two materials
1 and
2 the angle of incident and refraction respectively
Critical angles
If
n1 >n2
, then we can have
When the angle of refraction
is 90o, the refracted ray emerges parallel to the
interface between the media.
Critical angle of incidence
Total Reflection
At angles of incidence
> c, the light is totally reflected back into the
incidence higher refractive index medium. This is known as total internal reflection
(T. I. R)
Optical fiber
3
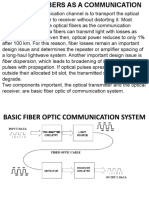
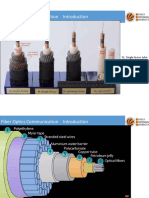
An optical fiber is a dielectric waveguide that operates at optical frequencies.
Typical structure of an optical fiber is shown in figure
The cylinder in the middle of the fiber id known as core. The core is
n2
surrounded by a solid dielectric cladding. The refractive index
of the
cladding is less than the refractive index
n1
of the core. Most fibers are
encapsulated in an elastic, abrasion-resistant plastic material in order to add
strength to the fiber itself.
Different type of optical fiber
Monmode step-index fiber
The core diameter is almost equal to the equal to the wave length of the emitted
light so that it propagates along a single path
Multimode step-index fiber
Core and Cladding material has uniform but different refractive index.
Multimode graded-index fiber
Core and Cladding material has uniform but different refractive index
Fiber Optics Transmission
Low Attenuation
Very High Bandwidth (THz)
Small Size and Low Weight
No Electromagnetic Interference
Low Security Risk
Elements of Optical Transmission
Elements of Optical Transmission
Electrical-to-optical Transducers
Optical Media
Optical-to-electrical Transducers
Digital Signal Processing, repeaters and clock recovery
Transducers
Electrical-to-Optical Transducers
LED - Light Emitting Diode is inexpensive, reliable but can support only lower
bandwidth.
LD Laser Diode provides high bandwidth and narrow spectrum
Optical-to-Electrical Transducers
PIN Diode - Silicone or InGaAs based p-i-n Diode operates well at low
bandwidth.
Avalanche Diode Silicone or InGaAs Diode with internal gain can work with
high data rate.
Transmission Limitations
5
Transmission over fiber is limited by the attenuation and dispersion
Multimode fibers may experience
Multimode dispersion: The delayed rays cause pulse spreading
Chromatic dispersion: Individual wavelengths may travel at different
speeds
Dispersion creates an inherent operational limit defined as a bandwidthdistance product (BDP)
You might also like
- PDFDocument36 pagesPDFayad60100% (2)
- OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsDocument36 pagesOPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsabidNo ratings yet
- OC Expt 6 PDFDocument5 pagesOC Expt 6 PDFPrasad RaneNo ratings yet
- 1.optical FibersDocument23 pages1.optical FibersYashNo ratings yet
- Sec1 OpticsDocument18 pagesSec1 Opticsaelsheikh834No ratings yet
- Lecture #1 Optical FibersDocument59 pagesLecture #1 Optical Fibersjeddo2005No ratings yet
- Fibre Optic Communication PDFDocument199 pagesFibre Optic Communication PDFBiswarup MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Lec.1 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsDocument45 pagesLec.1 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsMahmoud Sayed100% (1)
- Abramczy@mitr.p.lodz - PL WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/raman WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/evuDocument49 pagesAbramczy@mitr.p.lodz - PL WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/raman WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/evuChaitanya ShakyaNo ratings yet
- 3320 Fiber-Optic CommunicationDocument32 pages3320 Fiber-Optic CommunicationEdward FahmiNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication 123Document22 pagesOptical Communication 123prashanth_02No ratings yet
- Fiber Dispersion, Which Leads To Broadening of Individual OpticalDocument17 pagesFiber Dispersion, Which Leads To Broadening of Individual OpticalAnnas TunggalNo ratings yet
- OCN Unit I KeyDocument11 pagesOCN Unit I KeyChandra MathiNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument20 pagesOptical Fiber CommunicationSeenuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Optical FibersDocument60 pagesChapter 2 - Optical Fiberseyohamehari235No ratings yet
- Optical SensorsDocument17 pagesOptical SensorsHassanein Al-hadadNo ratings yet
- 01 1330682265 93458 PDFDocument32 pages01 1330682265 93458 PDFSanjay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Optical FibreDocument47 pagesOptical FibreThe Haneef ReyaziiNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Training GuideDocument17 pagesFiber Optic Training GuideIrfan IrshadNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Part IDocument46 pagesFiber Optics Part ImariahvahNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics1Document29 pagesFiber Optics1Biswajith MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics GeneralDocument29 pagesFiber Optics GeneralSurya6556No ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument64 pagesOptical CommunicationAmit Samrat MauryaNo ratings yet
- Lec.2 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsDocument17 pagesLec.2 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsMahmoud SayedNo ratings yet
- My Optic NotesDocument27 pagesMy Optic NotesRamesh MeherNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics (Unit - 3)Document28 pagesFiber Optics (Unit - 3)Rangu RohithNo ratings yet
- OFC Unit 1-ADocument22 pagesOFC Unit 1-AnaactitexcellenceNo ratings yet
- Sic 1605Document103 pagesSic 1605sanjaisanjai51110003No ratings yet
- Unit IintroductionDocument40 pagesUnit IintroductionkikiNo ratings yet
- Photonic Technologies For Millimeter - and Submillimeter TechnologiesDocument19 pagesPhotonic Technologies For Millimeter - and Submillimeter TechnologiesSenjuti KhanraNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication 2mark PDFDocument20 pagesOptical Communication 2mark PDFAnant ShankarNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication NetworksDocument8 pagesOptical Communication NetworksPonmalar Sivaraj100% (1)
- Part A University Questions2019 2020Document9 pagesPart A University Questions2019 2020thiruvengadam cNo ratings yet
- Ray ModelDocument11 pagesRay ModelV'nod Rathode BNo ratings yet
- Numerical With AnswerDocument19 pagesNumerical With AnswerRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cables Unit2Document84 pagesFiber Optic Cables Unit2Harish PandamaneniNo ratings yet
- Foli Unit 1 - 2 Mark Question and AnswerDocument4 pagesFoli Unit 1 - 2 Mark Question and AnswerJayakumar ThangavelNo ratings yet
- Assignment-5: Galgotias College of Engineering& TechnologyDocument9 pagesAssignment-5: Galgotias College of Engineering& TechnologyAyushi GoelNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication Question BankDocument24 pagesOptical Communication Question BankdhivyakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Optical Full Units NOTESDocument98 pagesOptical Full Units NOTESkohilavaniapNo ratings yet
- Optic FiberDocument31 pagesOptic Fiberkeregi100% (1)
- Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 History of Fiber OpticsDocument8 pagesChapter 1. Introduction 1.1 History of Fiber OpticsTsy Less DahalNo ratings yet
- Dispersion in Optical FiberDocument36 pagesDispersion in Optical FiberSonakshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phy4 2Document16 pagesPhy4 2sakshamsharma7257No ratings yet
- OCN Unit 1,2Document23 pagesOCN Unit 1,2M Madhu MaliniNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication SystemDocument12 pagesOptical Fiber Communication Systemjamal123456No ratings yet
- Wave DM2Document45 pagesWave DM2Chandan HmNo ratings yet
- Turowicz 1Document62 pagesTurowicz 1Saurav KauraNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 and 2 OpticalDocument278 pagesUnit-1 and 2 OpticalGuru VelmathiNo ratings yet
- Ocn Two MarksDocument24 pagesOcn Two Marksmani kandanNo ratings yet
- BEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFDocument201 pagesBEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFMax DurendNo ratings yet
- Opto & Optical ComDocument222 pagesOpto & Optical ComRansford SackeyNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document27 pagesDay 2Abhiram SwarnaNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document52 pagesDay 1Abhiram SwarnaNo ratings yet
- EE493 - Second Set of Lecture Slides-Spring 2021Document78 pagesEE493 - Second Set of Lecture Slides-Spring 2021احمد الديريNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication 2017,2018,2020 and 2021 Past Questions and SolutionsDocument42 pagesOptical Communication 2017,2018,2020 and 2021 Past Questions and SolutionsMelsougly BryceNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Optical Communication SystemDocument18 pagesBlock Diagram of Optical Communication SystemSuhana Sharma100% (4)
- PhotodetectorsDocument46 pagesPhotodetectorsShivam AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Laser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsFrom EverandLaser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- Noise in Nanoscale Semiconductor DevicesFrom EverandNoise in Nanoscale Semiconductor DevicesTibor GrasserNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines : Year / Semester: 3 /2Document13 pagesElectrical Machines : Year / Semester: 3 /2Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- EEDP Lect 09 Logic FamiliesDocument34 pagesEEDP Lect 09 Logic Familiessiddu smartNo ratings yet
- 28 - BenchmarkingDocument14 pages28 - BenchmarkingMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Lean As A Universal Model of Excellence: It Is Not Just A Manufacturing Tool!Document8 pagesLean As A Universal Model of Excellence: It Is Not Just A Manufacturing Tool!Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- 24 - The Fit OrganizationDocument5 pages24 - The Fit OrganizationMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines : Three-Phase Induction MotorsDocument18 pagesElectrical Machines : Three-Phase Induction MotorsMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines : Torque of Induction MotorDocument12 pagesElectrical Machines : Torque of Induction MotorMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Electrical Machines .PPT (Compatibility Mode) - 1Document6 pagesLecture 1 - Electrical Machines .PPT (Compatibility Mode) - 1Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines (3206) Induction Motors: Year / Semester: 3 / 2Document10 pagesElectrical Machines (3206) Induction Motors: Year / Semester: 3 / 2Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Electrical Machines .PPT (Compatibility Mode) - 1Document17 pagesLecture 2 - Electrical Machines .PPT (Compatibility Mode) - 1Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Resistance: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument48 pagesChapter 3 - Resistance: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Voltage and Current: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument44 pagesChapter 2 - Voltage and Current: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Sequential Logic CircuitsDocument18 pagesSequential Logic CircuitsMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Ch2.Fourier Theory and Communication SignalsDocument20 pagesCh2.Fourier Theory and Communication SignalsMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Discrete-Time ConvolutionDocument14 pagesDiscrete-Time ConvolutionMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Continuous-Time Signals (C-T Signals)Document21 pagesSignals and Systems Continuous-Time Signals (C-T Signals)Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- Modification of The Independent Variable TDocument15 pagesModification of The Independent Variable TMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Ch1.Background and PreviewDocument9 pagesCh1.Background and PreviewMona SayedNo ratings yet
- 08s Week06 2 Lab ManetDocument5 pages08s Week06 2 Lab ManetMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes # 8 Outline of The Lecture: Control Transfer Instructions CALL Statement SubroutinesDocument7 pagesLecture Notes # 8 Outline of The Lecture: Control Transfer Instructions CALL Statement SubroutinesMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Boyle StadDocument50 pagesBoyle StadRodel MarananNo ratings yet
- 7 Segment DisplayDocument6 pages7 Segment DisplayTwesigomwe Gilbert GabrielNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1Gaurav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Datasheet OptoDocument12 pagesDatasheet OptoAdrian RgFlNo ratings yet
- Gate Characteristics Design Thyristor Ratings Requirements of The Gate CircuitDocument9 pagesGate Characteristics Design Thyristor Ratings Requirements of The Gate CircuitAayu JainNo ratings yet
- Solar and InvertersDocument7 pagesSolar and InverterskashafNo ratings yet
- Iteco Esdbook - 2004 - Eng PDFDocument32 pagesIteco Esdbook - 2004 - Eng PDFAnonymous FZs3yBHh7No ratings yet
- Power Electronics MnualDocument16 pagesPower Electronics MnualRitika JainNo ratings yet
- CAD Lab Manual KEC 653B (4mail)Document38 pagesCAD Lab Manual KEC 653B (4mail)Piyush0% (1)
- LifiDocument21 pagesLifiAnonymous QIuAGIadXmNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument3 pagesDatasheetselocaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument24 pagesChemistryJimmy OrajayNo ratings yet
- Inst Control and Elec Tech Ice (2178) - 1Document13 pagesInst Control and Elec Tech Ice (2178) - 1balajirajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Cyclic Convolution Based On FNTDocument6 pagesImplementation of Cyclic Convolution Based On FNTInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 7SG14 Duobias M Catalogue Sheet PDFDocument20 pages7SG14 Duobias M Catalogue Sheet PDFanuj100% (1)
- Generator Overfluxing PDFDocument6 pagesGenerator Overfluxing PDFName Is100% (3)
- CRT Television Repair CourseDocument131 pagesCRT Television Repair Coursejakovpekovic100% (2)
- Manual Ogt100 enDocument5 pagesManual Ogt100 enJavier Alcubilla ArribasNo ratings yet
- Full-Color Micro-LED Display With CsPbBr3 Perovskite and CdSe Quantum Dots As Color Conversion LayersDocument6 pagesFull-Color Micro-LED Display With CsPbBr3 Perovskite and CdSe Quantum Dots As Color Conversion Layers18maxwell61No ratings yet
- Surface Engineering of Nanomaterials: Lecture 12: Physical Vapour Deposition (PVD)Document19 pagesSurface Engineering of Nanomaterials: Lecture 12: Physical Vapour Deposition (PVD)hrana287No ratings yet
- Solid State Pressure Sensor: FeaturesDocument2 pagesSolid State Pressure Sensor: FeaturesCarlosDíazPeñaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Common Emitter I-V Characteristics of A NPN Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument3 pagesLab 6 Common Emitter I-V Characteristics of A NPN Bipolar Junction TransistorMohamad AyoubNo ratings yet
- U2270B TEMICSemiconductorsDocument13 pagesU2270B TEMICSemiconductorsВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Datasheet CI PS229Document11 pagesDatasheet CI PS229tumaistuNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller-Based Single-Phase Automatic Voltage RegulatorDocument5 pagesMicrocontroller-Based Single-Phase Automatic Voltage RegulatorFuh ValleryNo ratings yet
- SM-XXXPC8 Series: 205 285watt Photovoltaic ModuleDocument2 pagesSM-XXXPC8 Series: 205 285watt Photovoltaic ModuleSeptimiu BotaNo ratings yet
- FM DocumentationDocument23 pagesFM DocumentationJohnMatthewBancilNo ratings yet
- Mobile Jammer Circuit: Inventory ListDocument2 pagesMobile Jammer Circuit: Inventory ListCarlo Piere DayaoNo ratings yet