Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Future Tenses
Future Tenses
Uploaded by
Cosmin LeonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- (Completed) Navigate Intermediate B1+ Coursebook (Teacher's Edition)Document241 pages(Completed) Navigate Intermediate B1+ Coursebook (Teacher's Edition)PabloVicari65% (26)
- FUTURE Tenses - PPTDocument37 pagesFUTURE Tenses - PPTi.diana100% (1)
- Swahili QuestionsDocument2 pagesSwahili Questionsquestnvr73No ratings yet
- Give You A Pay RiseDocument4 pagesGive You A Pay RiseAnca ȘtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Future Simple Perfect ContDocument1 pageFuture Simple Perfect ContOem So Sad SinaNo ratings yet
- Future Simple: Use 1: PromisesDocument6 pagesFuture Simple: Use 1: PromisesAlex TanasaNo ratings yet
- Future ContinuousDocument3 pagesFuture Continuousel mokhtar JalalNo ratings yet
- Test Romana EnglezaDocument97 pagesTest Romana EnglezaRaluca CiupeNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument4 pagesFuture FormsFruzsina FeketeNo ratings yet
- Will and Going To - 82762Document15 pagesWill and Going To - 82762freddy chacon guerreroNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Will and Going ToDocument3 pagesDifference Between Will and Going ToemilillaNo ratings yet
- Future Complete Ss ExcDocument3 pagesFuture Complete Ss ExcManuel Alejandro Restrepo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Be Going To BE GOING TO For IntentionsDocument5 pagesBe Going To BE GOING TO For IntentionsAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Microsoft WordDocument18 pagesEnglish Grammar Microsoft WordMarysia AndrunyszynNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument20 pagesFutureAli AteeqNo ratings yet
- U3 Future TensesDocument18 pagesU3 Future Tenses2257010141No ratings yet
- Future Tense - THEORYDocument7 pagesFuture Tense - THEORYRoxana Caia GheboianuNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument3 pagesFuture FormsRaso RasovicNo ratings yet
- Expect, Imagine and Expressions Be Sure, Be Afraid and The Adverbs Probably, Perhaps, CertainlyDocument2 pagesExpect, Imagine and Expressions Be Sure, Be Afraid and The Adverbs Probably, Perhaps, CertainlyMagdalenaNo ratings yet
- The Future Tenses: Subject + Auxiliary Verb + Main Verb (Present Part.)Document6 pagesThe Future Tenses: Subject + Auxiliary Verb + Main Verb (Present Part.)Чарли ЖутиNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument27 pagesFutureputri ayuniNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument7 pagesFutureAndreiAlexandruNo ratings yet
- Engleski (Future Forms)Document12 pagesEngleski (Future Forms)Kozmetika Amina-Mirnesa SubašićNo ratings yet
- El Futuro: Will / Won'T - Be Going To - Present Continuous - Present SimpleDocument12 pagesEl Futuro: Will / Won'T - Be Going To - Present Continuous - Present SimpleZayra GomezNo ratings yet
- PPT. Expressing The FutureDocument53 pagesPPT. Expressing The FutureHanizar Rachman100% (1)
- Future VerbsDocument6 pagesFuture VerbsElia Miranda CorralesNo ratings yet
- Referat Future Perfect: Universitatea Din BucureștiDocument8 pagesReferat Future Perfect: Universitatea Din BucureștiAlina PătruNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect: Grammar Encounter 25CDocument6 pagesFuture Perfect: Grammar Encounter 25CyisethNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect & ContinuousDocument7 pagesFuture Perfect & ContinuousAlejandro CarusoNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument52 pagesFuture TensesTấn Tài VõNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses: Shall I / We Will He / She / It / You / TheyDocument25 pagesFuture Tenses: Shall I / We Will He / She / It / You / TheyТетяна КовтунNo ratings yet
- Future Forms Form USE Examples: Will You Have Discussed This With Your Boss Before You GoDocument6 pagesFuture Forms Form USE Examples: Will You Have Discussed This With Your Boss Before You GoAgustina RealNo ratings yet
- English For Business Ii: SESSION 02: Making DecisionsDocument16 pagesEnglish For Business Ii: SESSION 02: Making DecisionsMaribel Congona SalasNo ratings yet
- Simple Future TenseDocument11 pagesSimple Future TenseArifa NurhudayantiNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses in English: Key Words: I'm Sure, I Believe, I Expect, I Hope, IDocument5 pagesFuture Tenses in English: Key Words: I'm Sure, I Believe, I Expect, I Hope, IAdilaNo ratings yet
- Future - TeorieDocument3 pagesFuture - TeorieIonescu Cristina-LucianaNo ratings yet
- Future TimeDocument18 pagesFuture Timeapi-252190418No ratings yet
- Present Continuous FutureDocument26 pagesPresent Continuous Futuresandra razoNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses Basic Grammar 13th 1A FixedDocument31 pagesFuture Tenses Basic Grammar 13th 1A FixedungdoyieNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR REVISION Unit 4Document3 pagesGRAMMAR REVISION Unit 4Doung PichchanbosbaNo ratings yet
- Future SimpleDocument3 pagesFuture SimpleIonescu Cristina-LucianaNo ratings yet
- 10.2 GrammarDocument8 pages10.2 GrammarGeorgiana GiusepiNo ratings yet
- WILL Future: Sue Will Visit Her Grandparents Next WeekendDocument7 pagesWILL Future: Sue Will Visit Her Grandparents Next WeekendNikola.MNo ratings yet
- Future (Pt. 2)Document25 pagesFuture (Pt. 2)Mariana BlancoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For PracticeDocument8 pagesWorksheet For Practiceishika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument12 pagesFuture Tensesnemat.muhammadi786No ratings yet
- Means of Expressing FuturityDocument10 pagesMeans of Expressing FuturityPereteanu ElenaNo ratings yet
- I'll Have Finished This Book Soon. I'm Nearly at The EndDocument6 pagesI'll Have Finished This Book Soon. I'm Nearly at The EndValentin PatruNo ratings yet
- Future Continuous Future Perfect Alternative Ways Referring To FutureDocument8 pagesFuture Continuous Future Perfect Alternative Ways Referring To FutureEnrique Gomez OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Unit 11. The Future Simple TenseDocument6 pagesUnit 11. The Future Simple Tensegiangly2005spNo ratings yet
- The Future TenseDocument4 pagesThe Future Tensefanelemkhwanazi2No ratings yet
- B2 ExamDocument4 pagesB2 ExamKathy IsaNo ratings yet
- Future: Future: Will and ShallDocument1 pageFuture: Future: Will and Shallorion_scoNo ratings yet
- The Simple Future TenseDocument32 pagesThe Simple Future TenseBenydiktus DominggoNo ratings yet
- FUTURE TENSESDocument27 pagesFUTURE TENSESdaliaNo ratings yet
- Future EmlDocument5 pagesFuture EmlElvira MateoNo ratings yet
- Future PerfectDocument1 pageFuture Perfectmiss.yahiaoui.92No ratings yet
- Future Time 1Document16 pagesFuture Time 1taniaanglinawatiNo ratings yet
- WillDocument3 pagesWillThúy HằngNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument6 pagesFuture Tensesdragos.spinuNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument30 pagesFutureStefanDribler998No ratings yet
- Nouns, Subject and PredicateDocument27 pagesNouns, Subject and Predicatebaba dasNo ratings yet
- Antonyms and Synonyms: Sagatbek Zhansaya AI 20-3Document7 pagesAntonyms and Synonyms: Sagatbek Zhansaya AI 20-3Айсұлу АлтайбековаNo ratings yet
- (А Response То "Exploring Тне Nostra Tic Hypothesis")Document11 pages(А Response То "Exploring Тне Nostra Tic Hypothesis")twerkterNo ratings yet
- LAS #1 - Subject-Verb Agreement and Correct UsageDocument4 pagesLAS #1 - Subject-Verb Agreement and Correct UsageEldei ArchwingNo ratings yet
- Future Forms ExercisesDocument3 pagesFuture Forms ExercisesNatasa Beso.100% (1)
- TensesDocument28 pagesTensesDana ZamfirNo ratings yet
- Affirmative & Negative AgreementDocument19 pagesAffirmative & Negative AgreementIhsanGandentAprilioNo ratings yet
- PerfektDocument18 pagesPerfektGovind MilaniNo ratings yet
- Boeckx 2000 Quirky AgrDocument27 pagesBoeckx 2000 Quirky Agrka6kaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Form 5 Unit 1Document15 pagesGrammar Form 5 Unit 1Adibah AnuarNo ratings yet
- اختبار لغة انجليزية ثالث متوسط الفصل الأول أ. نوريه الغامديDocument5 pagesاختبار لغة انجليزية ثالث متوسط الفصل الأول أ. نوريه الغامديRokia MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Presentation of SFL by Hira Haroon To DR - Hafiz QasimDocument22 pagesPresentation of SFL by Hira Haroon To DR - Hafiz QasimÎqřą ÑãvèéđNo ratings yet
- Word FormationDocument2 pagesWord FormationViktorija SmilkovaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument48 pagesParts of SpeechAmna ShoukatNo ratings yet
- 10day Exam1Document2 pages10day Exam1yomnahelmyNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument5 pagesFuture TensesDiego TaveraNo ratings yet
- Part 5 - Day 5 - Realtive ClausesDocument17 pagesPart 5 - Day 5 - Realtive ClausesKhánh VyNo ratings yet
- English 10D 2ND ExamDocument3 pagesEnglish 10D 2ND ExamGlenda Ortillano LeeNo ratings yet
- Adjectives As NounsDocument2 pagesAdjectives As NounsLeila NadjafovaNo ratings yet
- Differences in American and British English Grammar - ArticleDocument14 pagesDifferences in American and British English Grammar - ArticleDraku DakpaeNo ratings yet
- Listening Activities With Verb TensesDocument3 pagesListening Activities With Verb Tenses663No ratings yet
- Iprimary English Year 3Document5 pagesIprimary English Year 3NI NI AYENo ratings yet
- Report Text: Dinda Lana Estetika 2201417023Document7 pagesReport Text: Dinda Lana Estetika 2201417023Dinda LanaNo ratings yet
- Common and Proper NounsDocument16 pagesCommon and Proper Nounsdaien quequeNo ratings yet
- T LF 2549688 Personal Pronouns Powerpoint - Ver - 3Document11 pagesT LF 2549688 Personal Pronouns Powerpoint - Ver - 3Htet Htet NaingNo ratings yet
- Standards 2 Grade Writing 1 2 3 4 Text Types and PurposesDocument3 pagesStandards 2 Grade Writing 1 2 3 4 Text Types and Purposesapi-310408496No ratings yet
- Curso 6 CHAPTER 8 Calusac Level 6Document70 pagesCurso 6 CHAPTER 8 Calusac Level 6dessireechuy199310No ratings yet
- PräpositionenDocument8 pagesPräpositionenfperezbrNo ratings yet
Future Tenses
Future Tenses
Uploaded by
Cosmin LeonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Future Tenses
Future Tenses
Uploaded by
Cosmin LeonCopyright:
Available Formats
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
Future Simple: We use the future simple (will + bare infinitive) for:
Decisions made at the moment of speaking. It is cold. I will close the
window.
Predictions about the future, based on what we think, belive or imagine,
using the verbs
think, belive, expect etc the expressions be sure, be afraid, etc and the
adverbs
probably, certainly, perhaps etc. He will probably tell you later.
Promises, threats, warnings, requests, hopes and offers
Actions, events, situations which will definitely happen in the future and
which we cannot
control. Bob will be thirty years old in May.
Be going to:
We use be going to :
For plans, intentions or ambitions for the future. He is going to be a lawyer
when he
finishes university.
Actions we have already decided to do in the near future. Steve is going to
spend his
holidays in Spain.
Predictions based on what we can see or what we know, especially when
there is
evidence that something will happen. Look at the dark clouds. It is going to
rain.
The time expressions we use the future simple and going to are: tomorrow,
the day after
tomorrow, tonight, soon, next week, in a week, etc.
Future Continuous:
we use the future continuous (will be + verbing):
For actions which will be in progress at a stated future time. This time next
year, I will be
lying on the beach.
For actions which will definitely happen in the future as the result of a
routine or
arrangement. We will be visiting the Smiths at the weekend.
25/01/2016 my div
2/2
40
When we ask politely about someone s plans for the near future. Will you
be finishing
the report soon ?
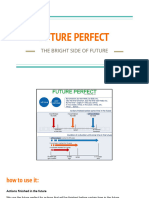
Future Perfect:
We use the future perfect (will have + past particle) for actions that will
have finished
10
15
20
25
before a stated time in the future. We will have moved house by the end of
June.
The time expressions we use with the future perfect are: before, by, then,
by the time, until / till,
(only in negative sentences).
Future Perfect Continuous:
We use the future perfect continuous ( will have been + verbing)
to emphasise the
duration of an action up to a certain time in the future. The future perfect
continuous is used
with: by ... for.
By the end of May, John will have been working here for ten years.
Time clauses when talking about the future :
When weuse words and expressions such as while, before, after, as,
when, once, as
soon as, as long as, by the time etc to introduce time clauses, we use the
present
simple or present perfect Not future forms .
We also use the present simple and present perfect, Not future forms, after
words and
expressions such as unless, if, suppose / supposing, in case etc.
We use future forms with:
When, when it is used as a question word. When will you be going skiing ?
If / whether after
expressions which show uncertaintly / ignorance etc, such as I don t
know, I doubt, I wonder, I'm not sure etc.
You might also like
- (Completed) Navigate Intermediate B1+ Coursebook (Teacher's Edition)Document241 pages(Completed) Navigate Intermediate B1+ Coursebook (Teacher's Edition)PabloVicari65% (26)
- FUTURE Tenses - PPTDocument37 pagesFUTURE Tenses - PPTi.diana100% (1)
- Swahili QuestionsDocument2 pagesSwahili Questionsquestnvr73No ratings yet
- Give You A Pay RiseDocument4 pagesGive You A Pay RiseAnca ȘtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Future Simple Perfect ContDocument1 pageFuture Simple Perfect ContOem So Sad SinaNo ratings yet
- Future Simple: Use 1: PromisesDocument6 pagesFuture Simple: Use 1: PromisesAlex TanasaNo ratings yet
- Future ContinuousDocument3 pagesFuture Continuousel mokhtar JalalNo ratings yet
- Test Romana EnglezaDocument97 pagesTest Romana EnglezaRaluca CiupeNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument4 pagesFuture FormsFruzsina FeketeNo ratings yet
- Will and Going To - 82762Document15 pagesWill and Going To - 82762freddy chacon guerreroNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Will and Going ToDocument3 pagesDifference Between Will and Going ToemilillaNo ratings yet
- Future Complete Ss ExcDocument3 pagesFuture Complete Ss ExcManuel Alejandro Restrepo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Be Going To BE GOING TO For IntentionsDocument5 pagesBe Going To BE GOING TO For IntentionsAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Microsoft WordDocument18 pagesEnglish Grammar Microsoft WordMarysia AndrunyszynNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument20 pagesFutureAli AteeqNo ratings yet
- U3 Future TensesDocument18 pagesU3 Future Tenses2257010141No ratings yet
- Future Tense - THEORYDocument7 pagesFuture Tense - THEORYRoxana Caia GheboianuNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument3 pagesFuture FormsRaso RasovicNo ratings yet
- Expect, Imagine and Expressions Be Sure, Be Afraid and The Adverbs Probably, Perhaps, CertainlyDocument2 pagesExpect, Imagine and Expressions Be Sure, Be Afraid and The Adverbs Probably, Perhaps, CertainlyMagdalenaNo ratings yet
- The Future Tenses: Subject + Auxiliary Verb + Main Verb (Present Part.)Document6 pagesThe Future Tenses: Subject + Auxiliary Verb + Main Verb (Present Part.)Чарли ЖутиNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument27 pagesFutureputri ayuniNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument7 pagesFutureAndreiAlexandruNo ratings yet
- Engleski (Future Forms)Document12 pagesEngleski (Future Forms)Kozmetika Amina-Mirnesa SubašićNo ratings yet
- El Futuro: Will / Won'T - Be Going To - Present Continuous - Present SimpleDocument12 pagesEl Futuro: Will / Won'T - Be Going To - Present Continuous - Present SimpleZayra GomezNo ratings yet
- PPT. Expressing The FutureDocument53 pagesPPT. Expressing The FutureHanizar Rachman100% (1)
- Future VerbsDocument6 pagesFuture VerbsElia Miranda CorralesNo ratings yet
- Referat Future Perfect: Universitatea Din BucureștiDocument8 pagesReferat Future Perfect: Universitatea Din BucureștiAlina PătruNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect: Grammar Encounter 25CDocument6 pagesFuture Perfect: Grammar Encounter 25CyisethNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect & ContinuousDocument7 pagesFuture Perfect & ContinuousAlejandro CarusoNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument52 pagesFuture TensesTấn Tài VõNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses: Shall I / We Will He / She / It / You / TheyDocument25 pagesFuture Tenses: Shall I / We Will He / She / It / You / TheyТетяна КовтунNo ratings yet
- Future Forms Form USE Examples: Will You Have Discussed This With Your Boss Before You GoDocument6 pagesFuture Forms Form USE Examples: Will You Have Discussed This With Your Boss Before You GoAgustina RealNo ratings yet
- English For Business Ii: SESSION 02: Making DecisionsDocument16 pagesEnglish For Business Ii: SESSION 02: Making DecisionsMaribel Congona SalasNo ratings yet
- Simple Future TenseDocument11 pagesSimple Future TenseArifa NurhudayantiNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses in English: Key Words: I'm Sure, I Believe, I Expect, I Hope, IDocument5 pagesFuture Tenses in English: Key Words: I'm Sure, I Believe, I Expect, I Hope, IAdilaNo ratings yet
- Future - TeorieDocument3 pagesFuture - TeorieIonescu Cristina-LucianaNo ratings yet
- Future TimeDocument18 pagesFuture Timeapi-252190418No ratings yet
- Present Continuous FutureDocument26 pagesPresent Continuous Futuresandra razoNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses Basic Grammar 13th 1A FixedDocument31 pagesFuture Tenses Basic Grammar 13th 1A FixedungdoyieNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR REVISION Unit 4Document3 pagesGRAMMAR REVISION Unit 4Doung PichchanbosbaNo ratings yet
- Future SimpleDocument3 pagesFuture SimpleIonescu Cristina-LucianaNo ratings yet
- 10.2 GrammarDocument8 pages10.2 GrammarGeorgiana GiusepiNo ratings yet
- WILL Future: Sue Will Visit Her Grandparents Next WeekendDocument7 pagesWILL Future: Sue Will Visit Her Grandparents Next WeekendNikola.MNo ratings yet
- Future (Pt. 2)Document25 pagesFuture (Pt. 2)Mariana BlancoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For PracticeDocument8 pagesWorksheet For Practiceishika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument12 pagesFuture Tensesnemat.muhammadi786No ratings yet
- Means of Expressing FuturityDocument10 pagesMeans of Expressing FuturityPereteanu ElenaNo ratings yet
- I'll Have Finished This Book Soon. I'm Nearly at The EndDocument6 pagesI'll Have Finished This Book Soon. I'm Nearly at The EndValentin PatruNo ratings yet
- Future Continuous Future Perfect Alternative Ways Referring To FutureDocument8 pagesFuture Continuous Future Perfect Alternative Ways Referring To FutureEnrique Gomez OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Unit 11. The Future Simple TenseDocument6 pagesUnit 11. The Future Simple Tensegiangly2005spNo ratings yet
- The Future TenseDocument4 pagesThe Future Tensefanelemkhwanazi2No ratings yet
- B2 ExamDocument4 pagesB2 ExamKathy IsaNo ratings yet
- Future: Future: Will and ShallDocument1 pageFuture: Future: Will and Shallorion_scoNo ratings yet
- The Simple Future TenseDocument32 pagesThe Simple Future TenseBenydiktus DominggoNo ratings yet
- FUTURE TENSESDocument27 pagesFUTURE TENSESdaliaNo ratings yet
- Future EmlDocument5 pagesFuture EmlElvira MateoNo ratings yet
- Future PerfectDocument1 pageFuture Perfectmiss.yahiaoui.92No ratings yet
- Future Time 1Document16 pagesFuture Time 1taniaanglinawatiNo ratings yet
- WillDocument3 pagesWillThúy HằngNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument6 pagesFuture Tensesdragos.spinuNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument30 pagesFutureStefanDribler998No ratings yet
- Nouns, Subject and PredicateDocument27 pagesNouns, Subject and Predicatebaba dasNo ratings yet
- Antonyms and Synonyms: Sagatbek Zhansaya AI 20-3Document7 pagesAntonyms and Synonyms: Sagatbek Zhansaya AI 20-3Айсұлу АлтайбековаNo ratings yet
- (А Response То "Exploring Тне Nostra Tic Hypothesis")Document11 pages(А Response То "Exploring Тне Nostra Tic Hypothesis")twerkterNo ratings yet
- LAS #1 - Subject-Verb Agreement and Correct UsageDocument4 pagesLAS #1 - Subject-Verb Agreement and Correct UsageEldei ArchwingNo ratings yet
- Future Forms ExercisesDocument3 pagesFuture Forms ExercisesNatasa Beso.100% (1)
- TensesDocument28 pagesTensesDana ZamfirNo ratings yet
- Affirmative & Negative AgreementDocument19 pagesAffirmative & Negative AgreementIhsanGandentAprilioNo ratings yet
- PerfektDocument18 pagesPerfektGovind MilaniNo ratings yet
- Boeckx 2000 Quirky AgrDocument27 pagesBoeckx 2000 Quirky Agrka6kaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Form 5 Unit 1Document15 pagesGrammar Form 5 Unit 1Adibah AnuarNo ratings yet
- اختبار لغة انجليزية ثالث متوسط الفصل الأول أ. نوريه الغامديDocument5 pagesاختبار لغة انجليزية ثالث متوسط الفصل الأول أ. نوريه الغامديRokia MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Presentation of SFL by Hira Haroon To DR - Hafiz QasimDocument22 pagesPresentation of SFL by Hira Haroon To DR - Hafiz QasimÎqřą ÑãvèéđNo ratings yet
- Word FormationDocument2 pagesWord FormationViktorija SmilkovaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument48 pagesParts of SpeechAmna ShoukatNo ratings yet
- 10day Exam1Document2 pages10day Exam1yomnahelmyNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument5 pagesFuture TensesDiego TaveraNo ratings yet
- Part 5 - Day 5 - Realtive ClausesDocument17 pagesPart 5 - Day 5 - Realtive ClausesKhánh VyNo ratings yet
- English 10D 2ND ExamDocument3 pagesEnglish 10D 2ND ExamGlenda Ortillano LeeNo ratings yet
- Adjectives As NounsDocument2 pagesAdjectives As NounsLeila NadjafovaNo ratings yet
- Differences in American and British English Grammar - ArticleDocument14 pagesDifferences in American and British English Grammar - ArticleDraku DakpaeNo ratings yet
- Listening Activities With Verb TensesDocument3 pagesListening Activities With Verb Tenses663No ratings yet
- Iprimary English Year 3Document5 pagesIprimary English Year 3NI NI AYENo ratings yet
- Report Text: Dinda Lana Estetika 2201417023Document7 pagesReport Text: Dinda Lana Estetika 2201417023Dinda LanaNo ratings yet
- Common and Proper NounsDocument16 pagesCommon and Proper Nounsdaien quequeNo ratings yet
- T LF 2549688 Personal Pronouns Powerpoint - Ver - 3Document11 pagesT LF 2549688 Personal Pronouns Powerpoint - Ver - 3Htet Htet NaingNo ratings yet
- Standards 2 Grade Writing 1 2 3 4 Text Types and PurposesDocument3 pagesStandards 2 Grade Writing 1 2 3 4 Text Types and Purposesapi-310408496No ratings yet
- Curso 6 CHAPTER 8 Calusac Level 6Document70 pagesCurso 6 CHAPTER 8 Calusac Level 6dessireechuy199310No ratings yet
- PräpositionenDocument8 pagesPräpositionenfperezbrNo ratings yet