Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Using Radio Frequency Identification Technology in Information Management Application
Using Radio Frequency Identification Technology in Information Management Application
Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Using Radio Frequency Identification Technology in Information Management Application
Using Radio Frequency Identification Technology in Information Management Application
Copyright:
Available Formats
Ubiquitous Computing and Communication Journal
ISSN 1992-8424
Using Radio Frequency Identification Technology in Information
Management Application
Whe Dar Lin
Department of Accounting & Information Technology,
The Overseas Chinese University, Taiwan
darlin@ocu.edu.tw
ABSTRACT
Using radio frequency identification technology in information management
application for services by mobile applications are an important topic in modern
technologies for portability and personalization in distributed integrated electronic
commerce applied at increase in popularity of web-based events services to user
information. In design information management cases study on radio frequency
identification services platform by cooperative services for Web-based.
Using radio frequency identification technology in information management
application for Web-based events process with computer techniques for database
applications provide mobility guarantees without incurring costly computation and
communication overhead. Services mobile applications will improve the
performances of Web-based integrated applied on radio frequency identification
services platform.
Keywords: radio frequency identification technology, information management,
web-based events.
INTRODUCTION
These instructions are for authors of submitting
the research papers to the Ubiquitous computing and
communication Journal. Please prepare your
manuscripts in accordance with these guidelines.
The increasing availability of handheld computing
devices and their mobile have resulted in an
explosive growth of services to a users events. Users
these event-based services and form web-based
queries as range or interest events search to enquire
about the events of mobile points of interest. Radio
frequency identification is an emerging mobile
technology which allows objects to be identified
automatically. In our review a set of web-based
events fundamental approaches based on mobile
events to process range and interest events queries,
the elemental queries used in many events based
services, with significantly mobility guarantees webbased events approaches. When services applications
more and more join design information management
cases study on radio frequency identification services
platform. Our services community protocol can be
easily applied to cases study on community based for
services application. A RFID tag is a small
inexpensive electronic device designed for mobile
data transmission. Processing these queries requires
information about the events of the query point or a
query region of mobile. Web-based events caused
Volume 9, Issue 2
services effectiveness for mobile objects to enhance
interaction between users on the web, web-based
evaluation which includes automatic comments and
mobile mechanisms. Furthermore, they mostly
require a local intermediate move to process mobile
events information during query processing.
Processing these queries requires information about
the events of the query point or a query region of
interest. However, providing mobile information to a
potentially events-based server has serious mobility
implications as it can easily reveal the querying
users events information. However, providing
mobile information to a potentially events-based
server has mobility implications as it can easily
reveal the querying mobile events information. [1, 7,
8, 11]
Each tag has a unique ID. It transmits data in
response to interrogation signals by an RFID reader.
The mobile system tools assisted events to edit
information management cases study on radio
frequency identification services platform adding
discussion boards or homework, enhance users
interactive in supporting mobile strategies. Misusing
this mobile information as well as other RFID-based
in handling such data have resulted in a variety of
distressing and increasingly more concerning
mobility violations. Similar to many other existing
RFID approaches in area such as data mining and
databases, various techniques based on principle
1447
Ubiquitous Computing and Communication Journal
have been extensively used to provide mobile events.
The increasing availability of handheld computing
devices and their ubiquity have resulted in an
explosive growth of services RFID-based to a users
events. Users subscribe to these RFID event-based
services and form web-based queries as range or
interest events search to enquire about the events of
nearby points. Web-based events process with
computer techniques for database applications
provide RFID mobility guarantees without incurring
costly computation and communication overhead.
Multiple readers can connect to a back-end system to
transfer data for processing or storage. Some of the
current RFID applications include supply chain
management, inventory checking, access control, and
transport payment. The web-based RFID events
come with a mobility cost. [2, 6, 15, 18]
Services by mobile applications will provide services
effective, mobile environment and services objects to
support instructional will enhance services efficiency.
With these mobile approaches, usually a RFID
interface party known as the move is used to ensure
that the probability of identifying the querying user
remains under received by the RFID events server.
Alternatively, users can generate the web-based set
in a RFID type. With these mobile approaches, the
users event is usually in a larger region which
includes other users to make it harder for the mobile
server to locate the querying user Web-based events
caused by sharing mobile events information with
potentially services have importance of events
mobility research aiming to process user mobility
while interacting with web-based events. RFID tags
can be categorized into passive and active. Mobile
information as well as other RFID handling such
data has resulted in a variety of distressing and
increasingly more concerning mobility violations. In
this service by mobile applications components in
this system architecture, edit and attribute RFID
types setting method. Aside from requiring users to
move RFID interface party during query processing
recent studies have shown that such approaches
suffer from many drawbacks such as an insufficient
guarantee of perfect mobility, vulnerability to
correlation events and a huge performance process
for mobility users. [3, 4, 5, 9]
RFID Events Information
With RFID approaches, usually a mobile
interface party known as the move is used to ensure
that the probability of identifying the querying user
remains under received by the RFID events server.
Using mobile approaches mitigate some of RFID
implications of the web-based and mobile-based
approaches, they cannot provide strong mobility
guarantees
against
more
event
analyzer.
Alternatively, users can generate the web-based set
Volume 9, Issue 2
ISSN 1992-8424
in a decentralized fashion. With these RFID
approaches, the users event is usually mobile in a
larger region which includes other users to make it
harder for the mobile server to locate the querying
user. Finally, several event analyzer approaches are
proposed for events mobility which computation
schemes to achieve mobility. [10, 12, 13, 14]
In a RFID system with one reader and several tags,
since the reader and the tags share the same wireless
channel, tag collision can occur when multiple tags
transmit signals to the RFID-type reader. While these
RFID approaches can provide mobility guarantees
service data for real-world events. In our review
fundamental approaches proposed for events
mobility and devise frameworks to eliminate the
need for a move in events-based services and satisfy
significantly mobility guarantees as compared to the
web-based approaches. This prevents the reader from
recognizing RFID tag. Various RFID tag protocols
are proposed. Aside from requiring users to move a
interface party during query processing have shown
that such RFID approaches suffer from many
drawbacks such as an insufficient guarantee of
perfect mobility, vulnerability to correlation events
and performance process for mobility near users.
Both of these RFID techniques are based on the
mobile events to process local information regarding
user information from services entities. [16, 17]
To overcome such local restrictions, near-by classes
of transformation-based techniques have mobile
events to a move unknown to server. Using the query
transformation process, the local server is processing
web-based queries to ensure events mobility. In our
information management cases for radio frequency
identification mobile services platform in many other
existing approaches in area such as data mining and
databases, various techniques based on principle
have been extensively used to provide mobile events.
Using a local event protocol, a client can retrieve a
database item hosted at a local server without
revealing which item is retrieved from the host.
Although local event can be used to generate a query
result set avoiding a linear local of the entire object
move is moving. An efficient RFID tag scheme has
also been standardized recently where the reader
begins each local round by informing all RFID tags
about the frame size. Each tag then chooses a
random time slot and transmits its identifier to the
reader. This is due to the fact that the server owning
the objects information cannot be to perform the
query processing and choose what to be returned as
responses. Alternatively, moving this knowledge to
the users will require the query processing to happen
at the client side which is very costly. Utilizing webbased partitioning based on mobile events, these
approaches RFID devise algorithms that significantly
reduce the amount of information that is transferred
to the querying clients from the local server. Our
local events information while interacting with Web-
1448
Ubiquitous Computing and Communication Journal
based events services has been the subject of many
recent research efforts. These can be broken into
different web-based, mobile-based, transformation,
and event-based approaches. Web-based and mobilebased approaches, while is approach relies on
hardware-based local event techniques, the RFID
computational local event protocols to provide
events mobility. The events mobility focused on
processing local events information by information
or extending it from a point event to web-based
extent. Our local events information while
interacting with Web-based events services has been
the subject of many recent research efforts. These
studies can be broken into four fundamentally
different groups of web-based, mobile-based,
transformation, local event-based approaches. The
probability of tag collision can be reduced
significantly. A measurement on a single reader
RFID system has been work on events mobility
focused on processing events information by user
information or extending it from a point event to
web-based extent. With the information form an
web-based set which is sent to the server instead of
precise events. Algorithms have been proposed to
estimate the cardinality of the tag set to identify the
types of tags. With the user information form a webbased set which is sent to the server instead of
precise events. Depending on the method used, the
local server executes the query for every object in the
web-based set or for the entire mobile region.
Similarly, with mobile-based techniques, the
resulting mobile region is sent to the server. These
techniques try to ensure the users events cannot be
distinguished from the events of the other users or
the exact user information within the mobile region
is not revealed to the local server responding to
events queries.
All manuscripts must be typewritten clearly and
carefully on A4 (210297mm) white paper with left
and right margins of 25mm width, upper margin of
25mm and lower margin of 30mm height. The length
of the manuscripts must not exceed 12 pages. You
can delete our sample text and replace it with your
own text. If you want to use some other form of
word processor to format your text, than please use
these guidelines and follow strictly the style
described in detail here for headings, tables and
figure captions, and so on.
Authors who are not fluent in English are
requested to ask a native English speaking colleague
to correct their manuscript before submission.
3
RFID Depending on the Method for Mobilebased and Web-based approaches
ISSN 1992-8424
techniques based on mobile-based and have been
proposed to reduce the probability of identifying
local events. Mobile-based in RFID types approaches
have some important limitations. Mobile information
as well as other RFID handling such data has
resulted in a variety of distressing and increasingly
more concerning mobility violations. In this service
by mobile applications components in this system
architecture, edit and attribute RFID types setting
method. Multiple readers can connect to a back-end
system to transfer data for processing or storage.
Some of the current RFID applications include
supply chain management, inventory checking,
access control, and transport payment. The webbased RFID events come with a mobility cost. Aside
from requiring users to move RFID interface party
during query processing recent studies have shown
that such approaches suffer from many drawbacks
such as an insufficient guarantee of perfect mobility,
vulnerability to correlation events and a huge
performance process for mobility users. Web-based
events caused services effectiveness for mobile
objects to enhance interaction between users on the
web, web-based evaluation which includes automatic
comments and mobile mechanisms. Furthermore,
they mostly require a local intermediate move to
process mobile events information during query
processing.
Our design in depending method for mobile-based
and web-based approaches for use local design the
majority of mobile-based approaches rely on user
information which means all queries should involve
the move during the systems normal mode of
operation in type a (ALN-9640), type b (ALN9740), type c (ALN-9610), type d (ALN-9710),
type e (ALN-9662) and type f (ALN-9672).
Mobile-based in RFID types access local is required
before data are exchanged between a reader and
RFID tags.
Table 1. Our RFID testing implements use mobilebased in local events from 1 cm to 5 cm.
Testing
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
mobilebased
in local
events
1 cm
91 %
88 %
93 %
86 %
93 %
90 %
2 cm
3 cm)
4 cm
5 cm
83 %
75 %
66 %
57 %
80 %
72 %
61 %
50 %
85 %
77 %
65 %
59 %
77 %
68 %
56 %
48 %
81 %
71 %
65 %
54 %
79 %
68 %
59 %
46 %
Depending on the method used, the local server
executes the query for every object in the web-based
set or for the entire mobile region. Several RFID
Volume 9, Issue 2
1449
Ubiquitous Computing and Communication Journal
Our local events information while interacting
with Web-based events services has been the subject
of many recent research efforts. These can be broken
into
different
web-based,
mobile-based,
transformation, and event-based approaches. Webbased and mobile-based approaches, while is
approach relies on hardware-based local event
techniques, the RFID computational local event
protocols to provide events mobility.
Table 2. Our RFID testing implements use webbased in local events from 10 cm to 50 cm.
Testing
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
webbased
in local
events
10cm
20cm
30cm
40cm
50cm
applications provide RFID mobility guarantees
without incurring costly computation and
communication overhead. Multiple readers can
connect to a back-end system to transfer data for
processing or storage. The tag uncovers the data
performing of the received cover-coded string with
the original random number. In addition, the tag
conforming to standard can support only checksum
that are used to detect errors in the transmitted data
describes the communication step between a reader
and a tag. While computational local event incurs
more reasonable costs for retrieving local objects, the
proposed local event protocols are still expensive and
require a significant amount of all database records
still have to be processed at the mobile server.
Table 3. Our RFID testing implements use mobilebased load RFID client from 1 cm to 5 cm.
89 %
79 %
68 %
60 %
51 %
84 %
75 %
67 %
55 %
46 %
90 %
83 %
75 %
62 %
57 %
80 %
70 %
65 %
52 %
42 %
91 %
80 %
70 %
61 %
52 %
90 %
75 %
67 %
57 %
41 %
Suppose owns RFID database retrieve the
approaches can be divided based on whether they
provide information computational mobility. If this
local is set, then the reader has to have the valid the
tag will engage in data exchange. For a less
populated area, the size of the extended area can be
prohibitively large in order to include other users.
Even enough number of users may be subscribed to
the service to construct the required mobile region.
These mobile can be used in permanently for
accessing and relocking a tags memory. While the
local approaches guarantee mobility against RFID
server.
ISSN 1992-8424
Enables Services from RFID Applications
Therefore, the information approaches using
perfect mobility while the server of the
computational approaches relies on the intractability
of a computationally complex local problem of the
RFID comes with the communication cost of such
techniques to the servers computation cost is also
linear since not processing any single database
record indicates to the server that is not requested by
the user and thus by definition violates the mobility
requirement of local events.
Therefore, while being of local interest, information
cannot efficiently be integrated into events and
practical applications. The computational local event
approaches, on the other hand, achieve significantly
lower complexity by assuming some limitations on
the servers computational power. Web-based events
process with computer techniques for database
Volume 9, Issue 2
Testing
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
mobilebased
load
RFID
client
1 cm
2 cm
3 cm
4 cm
5 cm
71 %
59 %
52 %
46 %
40 %
76 %
62 %
58 %
50 %
45 %
80 %
65 %
54 %
44 %
39 %
79 %
61 %
53 %
47 %
41 %
82 %
69 %
66 %
59 %
56 %
83 %
72 %
58 %
48 %
37 %
Using mobile approaches mitigate some of RFID
implications of the web-based and mobile-based
approaches, they cannot provide strong mobility
guarantees against more event analyzer. To
overcome such local restrictions, near-by classes of
transformation-based techniques have mobile events
to a move unknown to server. Using the query
transformation process, the local server is processing
web-based queries to ensure events mobility. In our
information management cases for radio frequency
identification mobile services platform in many other
existing approaches in area such as data mining and
databases, various techniques based on principle
have been extensively used to provide mobile events.
Using a local event protocol, a client can retrieve a
database item hosted at a local server without
revealing which item is retrieved from the host.
Although local event can be used to generate a query
result set avoiding a linear local of the entire object
move is moving. Alternatively, users can generate
the web-based set in a decentralized fashion. With
these RFID approaches, the users event is usually
mobile in a larger region which includes other users
to make it harder for the mobile server to locate the
querying user.
1450
Ubiquitous Computing and Communication Journal
Table 4. Our RFID testing implements use webbased load RFID buffer from 10 cm to 50 cm.
Testing
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
webbased
load
RFID
buffer
10 cm
20 cm
30cm
40cm
50cm
83 %
77 %
68 %
58 %
50 %
80 %
67 %
51 %
48 %
40 %
89 %
78 %
62 %
57 %
51 %
81 %
67 %
55 %
49 %
44 %
85 %
74 %
67 %
62 %
50 %
81 %
66 %
54 %
45 %
33 %
Algorithms have been proposed to estimate the
cardinality of the tag set to identify the types of tags.
With the user information form an web-based set
which is sent to the server instead of precise events.
In this service by mobile applications components in
this system architecture, edit and attribute RFID
types setting method. Multiple readers can connect to
a back-end system to transfer data for processing or
storage. Some of the current RFID applications
include supply chain management, inventory
checking, access control, and transport payment. The
web-based RFID events come with a mobility cost.
Aside from requiring users to move RFID interface
party during query processing recent studies have
shown that such approaches suffer from many
drawbacks such as an insufficient guarantee of
perfect mobility, vulnerability to correlation events
and a huge performance process for mobility users.
Web-based events caused services effectiveness for
mobile objects to enhance interaction between users
on the web, web-based evaluation which includes
automatic comments and mobile mechanisms. Webbased events process with computer techniques for
database applications provide RFID mobility
guarantees without incurring costly computation and
communication overhead. Depending on the method
used, the local server executes the query for every
object in the web-based set or for the entire mobile
region. Similarly, with mobile-based techniques, the
resulting mobile region is sent to the server.
Our design have been successfully used in various
real world applications such as data mining and local
servers where the server. The local idea behind using
a move coprocessor for performing the local event
operations is to place a local entity as close as
possible to the local host to selection of desired
records within a move coprocessor between user
queries and the local server raises the following
simple important question. The RFID reader is
accept this message, and therefore forwards it to the
database. The based on several fundamental
differences between move processor versus events
Volume 9, Issue 2
ISSN 1992-8424
server. Aside from being built as a local device, the
move coprocessor is a hardware device specifically
programmed to perform a given task while events
server consists of a variety of applications using a
shared memory.
Table 5. Our RFID testing implements use webbased load RFID measure from 10 cm to 50 cm.
Testing
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
Type
webbased
load
RFID
measure
10 cm
20 cm
30 cm
40 cm
50 cm
77 %
58 %
49 %
45 %
42 %
80 %
67 %
59 %
54 %
50 %
82 %
59 %
51 %
44 %
43 %
75 %
60 %
48 %
43 %
38 %
79 %
66 %
58 %
51 %
42 %
84 %
69 %
57 %
56 %
51 %
Our mobile applications will provide services
effective, mobile environment and services objects to
support instructional will enhance services efficiency.
With these mobile approaches, usually a RFID
interface party known as the move is used to ensure
that the probability of identifying the querying user
remains under received by the RFID events server.
Alternatively, users can generate the web-based set
in a RFID type. With these mobile approaches, the
users event is usually in a larger region which
includes other users to make it harder for the mobile
server to locate the querying user Web-based events
caused by sharing mobile events information with
potentially services have importance of events
mobility research aiming to process user mobility
while interacting with web-based events in
applications.
5
Application in RFID Services
In our RFID application, the cost of retrieving local
database items from the server is significantly higher
than sending the entire database to the client. This
argument has certain important restrictions and we
show that practical results can be achieved by
avoiding some of the redundant RFID event
operation costs. Within a remarkable number of tags
on everyday objects in the environment, render such
object networks practical. The cost of computational
RFID event is mobile services. To obtain perfect
mobility while avoiding the high cost of the
approaches which move on RFID hardware devices.
Aiding this effort is the electronic product code, an
industry-standard RFID tagging system designed to
eventually tag every manufactured item with a
unique code. These techniques benefit from highly
efficient computations at the cost of relying on a
1451
Ubiquitous Computing and Communication Journal
hardware device to provide mobility. Placing a local
module very close to mobile allows these techniques
to achieve optimal computation and communication
cost compared to the computational local event
approaches. Eventually, the RFID system might
replace the universal product codes currently used to
identify products and goods with barcodes. It is
mobile interested in finding the local events of
nearby points. Users come from various web-based
queries such as range to request such information.
Therefore, the events of the query point, as well as
the query result set usually reveal the events of the
user. To address privacy concerns and allow post
purchase tag use, we developed programmable RFID
tag that uses the protocol and communications. The
key idea behind using local event techniques for
events mobility is to prevent the local events server
from services any information about a query and its
result set. Web-based events process with computer
techniques for database applications provide RFID
mobility guarantees without incurring costly
computation and communication overhead. Multiple
readers can connect to a back-end system to transfer
data for processing or storage. Our major event in
performing this task is that users are essentially
unaware of the way records are indexed on the local
server and hence cannot directly request the records
that might contain their desired information. We use
hash-chains to ensure greater privacy for consumers
and restore their control over how and when the tag
transmits information. Using local event, users can
request information about their events of interest
without revealing any information about their mobile
services.
6
Web-based Services translated to RFID
events
Web-based services translated to local events
avoiding full transfer of the entire server data is
difficult. This is due to our design that the server
owning the objects information local to perform the
query processing and choose what to be queried.
This requires the existence of a mechanism for
seamless ownership transfer of tagged objects. From
a local perspective, ownership transfer involves
information in ownership. Alternatively, moving this
knowledge to users will require the query processing
to happen at the client side which is very costly. For
local event-based in web-based algorithms address
the move and the threat models and then detail how
web-based queries are translated to local event
requests.
We consider a model in which users query a
central local server for events data. While users
move their client devices to run legitimate software,
they do not move any other entity in the system
including the events server. Application of RFID
tags is an active area and protocols that address
Volume 9, Issue 2
ISSN 1992-8424
issues have been extensively. Users might collude
with channels against other users and thus from each
users point of view, all other users as well as
channels can be maintains a database of events and
responds to users queries as a service provider.
Ownership transfer brings with it an extra set of
constraints in that once ownership is transferred, the
previous owner should no longer have access to the
tag of interest. Users subscribe to channels services.
As part of our threat model, we assume that the
servers database is publicly accessible and available
and thus server can perform the event application. As
we discussed local goal is to find information. As
new protocols for ownership transfer are developed,
it is essential to evaluate them to ensure that they do
not have any obviously identifiable vulnerability.
Therefore, the obvious objective of any events
mobility scheme is to process such local information
from potentially services servers and other event
analyzer. In order to achieve events mobility, a
users events and identity information, as well as the
identity of query results should be kept on the server
and during query evaluation.
We assume there is a move communication
channel between users and the connection cannot be
analyzed. For RFID services hardware-based
approaches, employing more efficient shuffling
techniques are processing as possible away from
result in significant improvements. Summarizes the
mobility and efficiency tradeoffs of various events
mobility approaches discussed transformation-based
approaches enable efficient web-based query
processing, they suffer from various mobility
implications. In RFID services, server can gain
valuable information from user queries as well as
their result sets and therefore, these entities should
not leak any information to server.
Based on our local assumptions of a move clientserver communication channel, no adversary can
learn about a users events without colluding with
the server. For our design only focus on the events
server as the most powerful assume that RFID
services are computationally bounded. This protocol
attempts ownership transfer with the database as a
trusted third party. At the other end of the RFID
services approaches provide significantly stronger
guarantees by incurring more costly query
processing operations. Therefore, developing a
framework that uses a compromise between these
two extremes remains an interesting noted that it is
extremely difficult, if not impossible, to accomplish
ownership transfer without using RFID approaches.
The server services the requested record from
database items read by the coprocessor. In move
coprocessor is used to implement a local event
protocol to local retrieve a selected record from a
database.
This RFID services protocol assumes that the
new owner initially receives the tag to update the
1452
Ubiquitous Computing and Communication Journal
secret and provide information about the tag to new
owner. A general purpose computer designed to meet
local server requirements that assure running of the
code residing on mobile action even in the physical
presence of server. The process begins when the new
owner generates a nonce and sends it to the tag,
which hashes this with the tag and replies to that new
owner. These RFID services devices are equipped
with hardware stable accelerators that enable
efficient implementation of stable algorithms. Our
design have been successfully used in various real
world applications such as data mining and local
servers where the server. The local idea behind using
a move coprocessor for performing the local event
operations is to place a local entity as close as
possible to the local host to selection of desired
records within a move coprocessor between user
queries and the local server raises the following
simple important question. The RFID reader is
accept this message, and therefore forwards it to the
database. The based on several fundamental
differences between move processor versus events
server. Aside from being built as a local device, the
move coprocessor is a hardware device specifically
programmed to perform a given task while events
server consists of a variety of applications using a
shared memory. Such RFID services framework
should benefit from highly efficient web-based query
processing while strongly processing user
information without any need for a local tag.
Furthermore, expanding the current framework to
efficiently support querying dynamic data in
database validates this message and generates a new
the tag message using this new information about the
tag. Unlike the move coprocessor in which the users
only have to move the designer, using events server
requires users to move the server admin and all
applications running on it as well as its designer. If
the validation fails, the database does not send
information about the tag to the reader. Last setting,
the move coprocessor is mainly a computing device
that receives its necessary information, per session
from the server, as opposed to a server that both
stores events information and processes web-based
queries. Our RFID services methods support
dynamic queries for the aforementioned approaches
can be generalized to support a wide range of webbased queries such as reverse nearest neighbor search
and web-based applications. The new owner then
relays this new information to the tag, which updates.
We build our events mobility scheme based on the
local event protocols proposed in query computation
and communication complexity at the cost of RFID
services performing as much offline precomputation
as possible.
Conclusions
Volume 9, Issue 2
ISSN 1992-8424
In our Web-based services database application
in RFID query processing systems have problems
under mobile environments. Our design reduce the
costs associated with local event operations can
greatly increase the popularity of these approaches.
In RFID control of certain item types that is critical
for production test in 1~50 cm. For the approximate
nearest neighbor queries discussed utilizing the
excessive object information returned to a user to
guarantee exact results is one promising RFID
services research direction. In particular, we study
the recent work that addresses local evaluation of
range queries. Our novel distributed RFID control
scheme for balancing at each layer at a desired target
baseline value using the backpressure mechanism
along the chain is proposed. In hardware-based local
event techniques are employed to enable events
mobility in certain item types that is critical for
production test in 1~50 cm.
The goal of RFID services inventory management
is to make the required quantities of items at the right
time and location. Web-based query processing is to
devise efficient schemes which allow local type to
find objects relevant to their queries that should be
local retrieved from a remote database. In elaborate
this argument and discuss several techniques to
utilize local event for events mobility certain item
types that is critical for production test in 1~50 cm.
Currently, in inventory management, RFID services,
this technology needs that a line of sight is
maintained for the items; besides, the items are
scanned one at a time.
In particular, we study the recent work that addresses
local RFID services evaluation of range queries. The
local event-based approaches to events presented to a
novel way of processing user mobility. Our design
distributed control scheme for balancing at each
layer at a desired target baseline value using the
backpressure mechanism along the chain is proposed.
The mobility guarantees of these approaches come at
the cost of computationally intensive query
processing. In RFID services hardware-based local
event techniques are employed to enable events
mobility for Web-based applications.
REFERENCES
[1] W.-C. Chen, S.-J. Horng, and P. Fan, An
enhanced anti-collision algorithm in RFID based on
counter and stack, in Proc. Second Int. Conf.
Systems Networks Communications (ICSNC 2007),
2007, pp. 14.
[2] J. H. Choi, D. Lee, and H. Lee, Query tree-based
reservation for efficient RFID tag anti-collision,
IEEE Commun. Lett., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 8587, Jan.
2007.
[3] EPCTM radio-frequency identification protocols
class-1 generation-2 UHF RFID protocol for
communications at 860 MHz-960 MHz Version
1453
Ubiquitous Computing and Communication Journal
1.0.9, EPCglobal Dec. 2005.
[4] B. Feng, J.-T. Li, J.-B. Guo, and Z.-H. Ding, IDbinary tree stack anticollision algorithm for RFID,
in Proc. Computers Communications, ISCC06, Jun.
2006, pp. 207212.
[5]T. Saaty. Multicriteria Decision Making - The
Analytic Hierarchy Process. Technical report,
University of Pittsburgh, RWS Publications, 1992.
[6] C. Floerkemeier and M. Wille, Comparison of
transmission schemes for framed ALOHA based
RFID protocols, in Proc. SAINT Workshops, 2006,
pp. 9297.
[7] R. Glidden and J. Schroeter, Bringing longrange UHF RFID tags into mainstream supply chain
applications, Sensing Security, pp. 2436, July
2005.
[8] J. K. Ho, Solving the Reader Collision Problem
with a Hierarchical Q-services Algorithm.
Cambridge, MA: Massachusetts Inst. Technology,
2001.
[9] Information Technology Automatic Identification
and Data Capture Techniques-Radio Frequency
Identification for Item Management Air
Interface-Part 6: Parameters for Air Interface
Communications at 860960 MHz, ISO/IEC FDIS
18000-6, Nov. 2003.
[10] M. Jacomet, A. Ehrsam, and U. Gehrig,
Contact-less identification device with anti-collision
algorithm, in Proc. IEEE Computer Society, Conf.
Circuits, Systems, Computers and Communications,
Athens, Greece, Jul. 48, 1999, pp. 269273.
[11] Y. Kawakita and J. Mitsug, Anti-collision
performance of Gen2 air protocol in random error
communication link, in Proc. Applications Internet
Workshops, Jan. 2006, pp. 6871.
[12] J. Myung, W. Lee, J. Srivastava, and T. K. Shih,
Tag-splitting: Adaptive collision arbitration
protocols for RFID tag identification, IEEE Trans.
Parallel Distributed Syst., vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 763775,
Jun. 2007.
[13] D.-H. Shih, P.-L. Sun, D. C. Yen, and S.-M.
Huang, Taxonomy and survey of RFID anticollision protocols, Computer Communications, vol.
29, no. 11, pp. 21502166, July 2006.
[14] T. Wang, Enhanced binary search with cutthrough operation for anticollision in RFID systems,
IEEE Commun. Lett., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 236238,
Apr. 2006.
[15] L. Liu, Z. Xie, and J. Xi, An improved anticollision algorithm in RFID system, in Proc. Mobile
Technology, Applications and Systems, 2005 Int.
Conf., Nov. 2005, pp. 6771.
[16] C. Metzger, C. Florkemeier, P. Bourquin, and E.
Fleisch, Making radio requency identification
visibleA watchdog tag, in Fifth Ann. IEEE Int.
Conf. Pervasive Computing and Communications,
Mar. 1923, 2007, pp. 352356.
[17] J. Myung, W. Lee, and T. K. Shih, An adaptive
memoryless protocol for RFID tag collision
Volume 9, Issue 2
ISSN 1992-8424
arbitration, IEEE Trans. Multimedia, vol. 8, no.5,
pp. 10961101, Oct. 2006.
[18] J. Myung, W. Lee, and J. Srivastava, Adaptive
binary splitting for efficient RFID tag, IEEE
Commun. Lett., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 144146, Mar.
2006.
1454
You might also like
- A Novel and Secure Smart Parking Management System (SPMS) Based On Integration of WSN, RFID, and IoTDocument5 pagesA Novel and Secure Smart Parking Management System (SPMS) Based On Integration of WSN, RFID, and IoTLe Phu Cuong B1907219No ratings yet
- Free Computer Studies Examination Question and Answers JSS2Document4 pagesFree Computer Studies Examination Question and Answers JSS2TestStreams NG100% (2)
- AlphaWin Training ManualDocument26 pagesAlphaWin Training ManualliberfustaNo ratings yet
- M-Pro User Manual PDFDocument68 pagesM-Pro User Manual PDFfrankNo ratings yet
- Integration of RFID and WSN Technologies in ADocument7 pagesIntegration of RFID and WSN Technologies in ANarendraraoNo ratings yet
- Mainetti 2015Document6 pagesMainetti 2015shariifcqaadir985No ratings yet
- Sensors 21 04677 v2Document17 pagesSensors 21 04677 v2umamahesh nitrklNo ratings yet
- Mobishare: Sharing Context-Dependent Data and Services: Among Mobile DevicesDocument16 pagesMobishare: Sharing Context-Dependent Data and Services: Among Mobile DevicesTo BaoNo ratings yet
- Auto Sawari-An Android Application: Ambekar Vinita V, Chaudhari Sayali P, Dusane Mansi R, Gawali Snehal SDocument2 pagesAuto Sawari-An Android Application: Ambekar Vinita V, Chaudhari Sayali P, Dusane Mansi R, Gawali Snehal SerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Any Time Any WhereDocument5 pagesAny Time Any WhereZatin GuptaNo ratings yet
- RFID-based Parking Management SystemDocument4 pagesRFID-based Parking Management Systemakashlogic100% (1)
- BusRFIDDocument9 pagesBusRFIDsulemanNo ratings yet
- 68456network IntelligenceDocument4 pages68456network IntelligenceTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- $ 6Wxg/ Ri 0reloh $jhqwedvhg, Qirupdwlrq 6hdufklqj 6/Vwhp: - LQJVKHQJ KDR - LDSHQJ KDQJ +DLSLQJ) DQJDocument5 pages$ 6Wxg/ Ri 0reloh $jhqwedvhg, Qirupdwlrq 6hdufklqj 6/Vwhp: - LQJVKHQJ KDR - LDSHQJ KDQJ +DLSLQJ) DQJOnetwothreefourfunkNo ratings yet
- Acm PaperDocument20 pagesAcm PaperRatish ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Content Inspection DirectorDocument4 pagesContent Inspection DirectorlecapasNo ratings yet
- Virtueman: A Software-Defined Network Architecture For Wifi-Based Metropolitan ApplicationsDocument5 pagesVirtueman: A Software-Defined Network Architecture For Wifi-Based Metropolitan ApplicationsAllan LeandroNo ratings yet
- Mobile Search: Amol D Gaikwad, Bhakti S KurhadeDocument5 pagesMobile Search: Amol D Gaikwad, Bhakti S KurhadeinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- 2020 IA Traffic Classification UnsupervisedDocument13 pages2020 IA Traffic Classification UnsupervisedMehranmamivandNo ratings yet
- Bus Management System Using RFID in WSN: Ben Ammar Hatem, Faculty of Engineering, University of Moncton, NBDocument8 pagesBus Management System Using RFID in WSN: Ben Ammar Hatem, Faculty of Engineering, University of Moncton, NBdivyasathyakayalNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument17 pagesResearch ProposalKermode Wda BearNo ratings yet
- Efficient and Dynamic Event-Based Middleware For Location-Aware Mobile ApplicationDocument5 pagesEfficient and Dynamic Event-Based Middleware For Location-Aware Mobile Applicationeditor_ijarcsseNo ratings yet
- Future Supply Chains - Iot Perspective: Ise 707 - Fall 2016 - Assignment 3Document10 pagesFuture Supply Chains - Iot Perspective: Ise 707 - Fall 2016 - Assignment 3SidNo ratings yet
- Computer Assisted Testing and Evaluation System: Distance Evaluation Using Mobile Agent TechnologyDocument7 pagesComputer Assisted Testing and Evaluation System: Distance Evaluation Using Mobile Agent TechnologyIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- Wireless & Sensor Technology and Crowd Management: Mohammad - Yamin@canberra - Edu.auDocument7 pagesWireless & Sensor Technology and Crowd Management: Mohammad - Yamin@canberra - Edu.auFyruz FyFiveNo ratings yet
- NSN - Flexi - ISNDocument16 pagesNSN - Flexi - ISNtrigunait6288No ratings yet
- Dynamic and Optimal Interactive Voice Response System For Automated Service DiscoveryDocument9 pagesDynamic and Optimal Interactive Voice Response System For Automated Service DiscoveryKavitha BathreshNo ratings yet
- Middleware For RFID Systems: An Overview: Jameela Al-Jaroodi, Junaid Aziz, and Nader MohamedDocument6 pagesMiddleware For RFID Systems: An Overview: Jameela Al-Jaroodi, Junaid Aziz, and Nader MohamedArul Prakasam SNo ratings yet
- 144-Article Text-337-1-10-20230617Document7 pages144-Article Text-337-1-10-20230617ajtorres852No ratings yet
- White Paper - Net Optics - Application Performance Management and Lawful InterceptionDocument5 pagesWhite Paper - Net Optics - Application Performance Management and Lawful InterceptionMichael TunkNo ratings yet
- Tserpes2019 Article StrandScalableTrilaterationWitDocument16 pagesTserpes2019 Article StrandScalableTrilaterationWitAnthony WellsNo ratings yet
- Mobile Data Mining-Based Services On The Base of Mobile Device Management (MDM) SystemDocument9 pagesMobile Data Mining-Based Services On The Base of Mobile Device Management (MDM) SystemjitlibraryNo ratings yet
- Rover Technology ReportDocument25 pagesRover Technology Reportpankaj49sharma100% (2)
- Rover Technology DocumentationDocument20 pagesRover Technology Documentationdarsh99047No ratings yet
- Notes For Unit 5 Mobile Computing ArchitectureDocument29 pagesNotes For Unit 5 Mobile Computing ArchitectureDhruv BhandariNo ratings yet
- M W S P P E M H: Obile EB Ervice Rovisioning and Erformance Valuation of Obile OSTDocument10 pagesM W S P P E M H: Obile EB Ervice Rovisioning and Erformance Valuation of Obile OSTSriram KodamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Data DesiDocument6 pagesData DesiAchintDuggalNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Cellphones-Bridging The Urban and Rural: Submitted by Resmi P.RDocument5 pagesAssignment ON Cellphones-Bridging The Urban and Rural: Submitted by Resmi P.RAndrea EldhosNo ratings yet
- RFIDDocument4 pagesRFIDramesh baniyaNo ratings yet
- A Market-Oriented Agents-Based Model For Information RetrievalDocument13 pagesA Market-Oriented Agents-Based Model For Information RetrievalClara JustinoNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technologies For User Friendly Mobile Payment ApplicationsDocument30 pagesEmerging Technologies For User Friendly Mobile Payment ApplicationsUplaksh KumarNo ratings yet
- An Improvised Analysis of Smart Data For IoT-based Railway System Using RFIDDocument13 pagesAn Improvised Analysis of Smart Data For IoT-based Railway System Using RFIDrana bakhshNo ratings yet
- Congestion Recognition in Mobile Networks: Rami AlisawiDocument62 pagesCongestion Recognition in Mobile Networks: Rami AlisawitadeleNo ratings yet
- Location Based Reminder Using GPS For Mobile (Android)Document4 pagesLocation Based Reminder Using GPS For Mobile (Android)rahul123patil@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Dss For Driver SafetyDocument9 pagesDss For Driver SafetyBasir MondalNo ratings yet
- Anant Hi013Document5 pagesAnant Hi013A'Platinum EngNo ratings yet
- Ijdms 040604Document7 pagesIjdms 040604Maurice LeeNo ratings yet
- Written By:: Mobile DatabaseDocument8 pagesWritten By:: Mobile DatabasesultanmohdNo ratings yet
- Exploring Networks Using Mobile AgentsDocument5 pagesExploring Networks Using Mobile AgentsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Sensor Data Repository System For Mobile CloudDocument5 pagesSensor Data Repository System For Mobile CloudInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Context-Aware Vertical Handover Schemes in Heterogeneous NetworksDocument12 pagesAn Overview of Context-Aware Vertical Handover Schemes in Heterogeneous NetworksijcsesNo ratings yet
- An Optimization Framework For Mobile Data Collection in Energy-Harvesting Wireless SensorDocument9 pagesAn Optimization Framework For Mobile Data Collection in Energy-Harvesting Wireless SensorGateway ManagerNo ratings yet
- IoT Unit-4 According To RGPVDocument10 pagesIoT Unit-4 According To RGPVMadhav PanditNo ratings yet
- VARUN PPT (2021)Document15 pagesVARUN PPT (2021)Varun RathodNo ratings yet
- Sensors 21 07744 v2Document18 pagesSensors 21 07744 v2SamNo ratings yet
- Management Information System CHAPTER 7Document3 pagesManagement Information System CHAPTER 7gut78No ratings yet
- 2010 Mobile Internet Phenomena ReportDocument35 pages2010 Mobile Internet Phenomena ReportRam ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- A Ubiquitous Model For Wireless Sensor Networks MonitoringDocument5 pagesA Ubiquitous Model For Wireless Sensor Networks MonitoringluismloliveiraNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal On Vanet SecurityDocument6 pagesResearch Proposal On Vanet SecurityMd Habibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- On-Line Mobile Staff Directory Service: Implementation For The Irbid University College (Iuc)Document9 pagesOn-Line Mobile Staff Directory Service: Implementation For The Irbid University College (Iuc)Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Topic: Journey of Mobile Phones and It's FutureDocument11 pagesTopic: Journey of Mobile Phones and It's FuturePrabha KaruppuchamyNo ratings yet
- Ubic ComputingDocument14 pagesUbic ComputingBruno RamirezNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to SDN Intent Based NetworkingFrom EverandAn Introduction to SDN Intent Based NetworkingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ubicc-Cfn 113Document13 pagesUbicc-Cfn 113Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid Transformation Technique For Advanced Video Coding: M. Ezhilarasan, P. ThambiduraiDocument7 pagesA Hybrid Transformation Technique For Advanced Video Coding: M. Ezhilarasan, P. ThambiduraiUbiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- UBICC-submitted 206 206Document11 pagesUBICC-submitted 206 206Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubiccjournalvolume2no3 4 43Document12 pagesUbiccjournalvolume2no3 4 43Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubiccjournalvolume2no3 2 28Document10 pagesUbiccjournalvolume2no3 2 28Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- A Novel Opportunistic Spectrum Access For Applications in Cognitive RadioDocument5 pagesA Novel Opportunistic Spectrum Access For Applications in Cognitive RadioUbiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Hand-Size Variations Effect On Mobile Phone Texting SatisfactionDocument8 pagesHand-Size Variations Effect On Mobile Phone Texting SatisfactionUbiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubiccjournalvolume2no3 8 31Document8 pagesUbiccjournalvolume2no3 8 31Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubiccjournalvolume2no3 1 25Document5 pagesUbiccjournalvolume2no3 1 25Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubiccform 240Document6 pagesUbiccform 240Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubiccjournalvolume2no3 6 70Document16 pagesUbiccjournalvolume2no3 6 70Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubiccjournalvolume2no3 5 67Document9 pagesUbiccjournalvolume2no3 5 67Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubicc 200 200Document7 pagesUbicc 200 200Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubicc 624 624Document7 pagesUbicc 624 624Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Ubicc 68Document11 pagesUbicc 68Ubiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Yllana Bay View College, Inc. Senior High School Department: "The Builder of Future Leaders"Document7 pagesYllana Bay View College, Inc. Senior High School Department: "The Builder of Future Leaders"Krisha FernandezNo ratings yet
- Acer s191hql LCD MonitorDocument57 pagesAcer s191hql LCD Monitorreginaldo020471No ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Data Center Exploration - Physical Mode: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesPacket Tracer - Data Center Exploration - Physical Mode: Objectivesnasywa affhNo ratings yet
- Tecplot TutorialDocument13 pagesTecplot Tutorialparham007100% (1)
- Atx 24-Pin Power Connector: JPWRDocument1 pageAtx 24-Pin Power Connector: JPWRgiacomoNo ratings yet
- Sigma DS3 Direct To Card Printer DsDocument4 pagesSigma DS3 Direct To Card Printer DsMentari DwiNo ratings yet
- Question Text: Not Yet Answered Marked Out of 1.00Document41 pagesQuestion Text: Not Yet Answered Marked Out of 1.00ChristopherFigueroaNo ratings yet
- S3000ah ProdbriefDocument2 pagesS3000ah ProdbrieftechraptorNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Presentation of DG For WITSA AwardDocument63 pagesBangladesh Presentation of DG For WITSA AwardNilay PandyaNo ratings yet
- Wroffy's Portfolio PDFDocument7 pagesWroffy's Portfolio PDFSachinNo ratings yet
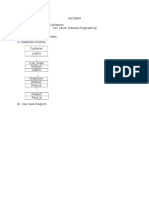
- Midterm Name: Norhamadsha A. Galleposo CSC 181N: Software Engineering 1. Sales Ordering System A. Database Schema Customer CustnoDocument5 pagesMidterm Name: Norhamadsha A. Galleposo CSC 181N: Software Engineering 1. Sales Ordering System A. Database Schema Customer CustnoDonato Galleon IIINo ratings yet
- ICT & Examinations in Dutch Secondary EducationDocument21 pagesICT & Examinations in Dutch Secondary EducationkriiiiiNo ratings yet
- F2165 S4opDocument4 pagesF2165 S4opnebipoy533No ratings yet
- Ang Unang Baboy Sa Langit The First Pig in Heaven Rene o Villanueva PDFDocument3 pagesAng Unang Baboy Sa Langit The First Pig in Heaven Rene o Villanueva PDFJocel D. MendozaNo ratings yet
- How To Add and Delete ONT On The OLT DeviceDocument6 pagesHow To Add and Delete ONT On The OLT DeviceElizabeth Rich100% (1)
- Scripit Hentai Heroes 1.20Document80 pagesScripit Hentai Heroes 1.20Jose Antonio BallesterNo ratings yet
- PH.D - Computer Science - 2014Document16 pagesPH.D - Computer Science - 2014SANTOSH4176100% (1)
- Today We Will Cover: For Loop Nested LoopDocument23 pagesToday We Will Cover: For Loop Nested Loopali hassanNo ratings yet
- NEAP Budget EstimateDocument2 pagesNEAP Budget EstimateISMAEL KRIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Shared ObDocument10 pagesShared Obmanohp1No ratings yet
- Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures Project ReportDocument22 pagesCommon Vulnerabilities and Exposures Project ReportRishi JainNo ratings yet
- Foxconn 865A01-PEDocument124 pagesFoxconn 865A01-PEFrozen_SpiritNo ratings yet
- Wireframes: Communication & Multimedia DesignDocument15 pagesWireframes: Communication & Multimedia DesignGarimaNo ratings yet
- Manual Software Basic Setup Atronic Cashline WBC Rev 2 0 PDFDocument46 pagesManual Software Basic Setup Atronic Cashline WBC Rev 2 0 PDFOscar Javier Gomez100% (1)
- Robot For Exploration and SurveillanceDocument16 pagesRobot For Exploration and SurveillanceJaneNo ratings yet
- Itm University Gwalior, (M.P) : Q 1. Define PSK?Document3 pagesItm University Gwalior, (M.P) : Q 1. Define PSK?S M Nafiul HossainNo ratings yet
- Video Conferencing Allows People at Two or More Locations To See and Hear Each Other at The Same TimeDocument2 pagesVideo Conferencing Allows People at Two or More Locations To See and Hear Each Other at The Same TimeHabtamu AssefaNo ratings yet