Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answers To Assignment #10: (B) L Mol CM
Answers To Assignment #10: (B) L Mol CM
Uploaded by
Sunil KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers To Assignment #10: (B) L Mol CM
Answers To Assignment #10: (B) L Mol CM
Uploaded by
Sunil KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers to Assignment #10
1.
According to the Beer-Lambert law,
A=lc
where A = absorbance (no units)
= molar absorptivity (?)
l = path length (cm), typically 1cm cells are used.
c = concentration (moles per litre)
The units of are
(a) cm.mol.L-1
2.
(b) L.mol-1.cm-1
(c) no units
(d) none of the above
It is common to report spectroscopic properties of a compound using the expression max
(). Using the spectrum in Figure 1, how would you report the peak labelled Y?
(a) 600 (2)
(b) 2.5 x 10-3 (600)
(c) 600 (2.5 x 10-3)
(d) 600 (800)
Figure 1: UV-Vis for questions 2, 1013.
3.
What does tell you about your molecule?
(i) not a lot
(ii) how likely a particular transition is going to occur
(iii) if you are going to get a big peak
(a) i
(b) ii
(c) iii
(d) ii + iii
4.
Which answer best represents the boundary between the uv region and the visible region?
(a) 200 nm
(b) 350 nm (c) 500 nm
(d) 650 nm
(e) 800 nm
5.
Which wavelength represents the highest energy transition?
(a) 200 nm (b) 350 nm
(c) 500 nm
(d) 650 nm
(e) 800 nm
6.
In a spectrum, the position of a peak is described by max. This is the wavelength at which
the peak has maximum height. If the spectrum of a compound is recorded at different
concentrations, what will change?
(a) absorbance
(b) max
(c) (d) absorbance & max
(e) max &
7.
If the concentration is not given, the absorbance scale is not very useful. The size of the
peak may then be measured in units of log . If a peak measures 3.1 on the log scale,
what is the value of ? Round your answer to one significant figure and choose the best
answer.
(a) 1
(b) 100
(c) 1000
8.
Ligand to metal charge transfer transitions cause the solution to be intensely coloured.
Which of the three answers best represents the typical value of that you might expect?
(a) 1
(b) 100
(c) 1000
9.
n 6 * transitions typically have a value of closest to which answer?
(a) 50
(b) 500
(c) 5000
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------True or false?
Figure 1 is the spectrum of a pure compound dissolved in the only solvent in which it is soluble.
If this solution is prepared again at a different concentration, describe the following statements
as true (T) or false (F):
10.
Peak X will always be smaller than peak Y, regardless of the concentration. True
11.
The ratio of the (peak height of X) : (peak height Y) will always remain the same, for
every concentration checked. True
12.
In more concentrated solutions, max for peak X will move towards max for peak Y. False
13.
In weaker solutions, max for peak Y will move towards max for peak X. False
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
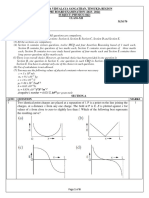
The spectrum in Figure 2 was found in the UVVis spectrometer. There was a labeled flask
containing the remains of a solution.
Unfortunately, the label had three different
concentrations written on it. Please answer the
following questions 14 - 17:
Figure 2: UV-Vis spectrum for questions 14-17
14.
If the contents of the flask are colourless, what value is W likely to take?
(a) W = 100 (b) W = 250 (c) W = 400 (d) W = 550
15.
If the concentration on the label is read as 2.6 x 10-2 M and W is 300 nm, which transition
do you think is responsible for the peak?
(a) n 6 *
(b) 6 *
(c) d 6 d
(d) L 6 M charge transfer.
16.
If the concentration on the label is read as 5 x 10-2 M and W is 605 nm, which transition
do you think is responsible for the peak?
(a) n 6 *
(b) 6 *
(c) d 6 d
(d) L 6 M charge transfer.
17.
What colour is the solution in question 16? Green-blue
---------------------------------------------------------------------18.
Fact: Transition metal complexes are coloured.
Fact: Organic compounds are typically colourless.
Fact: tetraphenylporphyrin (at right) is a beautiful
purple colour.
Why?
Extensive conjugation
19.
If the concentration of the solution in Figure 3 is
known to be 1.8 x 10-3 M, would you say that the
spectrum is caused by
(i) n 6 * (ii) 6 * (iii) L 6 M
(iv) d 6 d (v) 6 * (vi) n 6 *
Tetraphenylporphyrin
Choose one of the following answers:
(a) i + ii (b) iii + v (c) ii + iv
(d) v + vi (e) iv + vi
20.
A molecule shows an electronic spectrum. Put a check mark (T) next to the following
compounds which might be responsible for this output (you can choose more than one
answer):
(g) phenolphthalein T
(a) an alkane
(d) aromatic T
(b) an alkene T
(e) a transition metal complex T
(c) a conjugated alkene T (f) sodium chloride
Answer multiple choice questions 21-33, using choices:
wavelengths, (nm): a) <200
b) 210-280
c) 290-380
d) 450-550
e) 550-700
molar absorbtivity, (Lmol-1cm-1): a) <1
b) 1-50
c) 100-900
d) >1000
shifts: a) bathochromic
b) hypsochromic
c) hyperchromic
d) hypochromic
transitions:
a) n6*
b) 6*
c) n6*
d) d-d
e) charge transfer
ORGANIC
contains
lone pairs
(ie: N, O, P, S, X)
contains
-bonds
- *
allowed
> 1000
= 190 nm + 30 each
unit of conjugation
n - *
forbidden
< 50
= 280 nm + 30 each
unit of conjugation
INORGANIC
strong colours
Charge Transfer
allowed
> 1000
: use the
colour wheel
weak colours
d-d
forbidden
< 50
: use the
colour wheel
Yellow
550 nm
Green
500 nm
Orange
600 nm
Blue
450 nm
Red
670 nm
Violet
400 nm
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
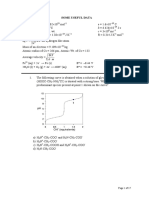
Where would you expect to find the n63*
for H2C=CH-CH=CH-CH=CH-OH?
C
max = 280 + 30 + 30 = 340 nm
What would be the value for this transition?
B
Forbidden, < 50 Lmol-1cm-1
Where would you expect to find the 63* for H2C=CH-CH=CH-CH=CH-OH?
B
max = 190 + 30 + 30 = 250 nm
What would be the value for this transition?
D
Allowed, > 10,000 Lmol-1cm-1
What transition is responsible for the strong band that is observed below 200 nm when
the vacuum UV of H2C=CH-CH=CH-CH=CH-OH is recorded?
C
vacuum UV below 200 nm, n6*
If NaOH was added to H2C=CH-CH=CH-CH=CH-OH how would you expect the max to
shift?
A
Deprotonation of an alcohol extends the conjugation and the max increases,
bathochromic shift.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
If NaOH was added to H2C=CH-CH=CH-CH=CH-OH how would you expect the to
shift?
C
Deprotonation of an alcohol extends the conjugation and the increases,
hyperchromic shift.
If a glass of tomato juice appears red, what wavelength would it absorb if you recorded
its UV-Vis spectrum?
D
Absorbs green at 500 nm.
If a laser pointer appears red, what wavelength does it emit?
E
Emits red at 670 nm.
What transition is responsible for the intense red color of Mo(CO)4(phenanthroline)?
E
Intense colors are due to charge transfer transitions.
What would be the value for this transition?
D
CT are allowed, > 10,000 Lmol-1cm-1
What transition is responsible for the pale red color of Mn3+ in solution?
D
Pale colors are due to d-d transitions.
What would be the value for this transition?
B
d-d are forbidden, < 50 Lmol-1cm-1
You might also like
- NF Monographs Benzalkonium Chloride SolutionDocument3 pagesNF Monographs Benzalkonium Chloride Solutionsergio910113No ratings yet
- Kağıt Terimleri Sözlüğü İngilizce-İngilizceDocument145 pagesKağıt Terimleri Sözlüğü İngilizce-İngilizceMünir KarıncaoğluNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper (Physics)Document10 pagesSample Question Paper (Physics)Milanjyoti BorahNo ratings yet
- IES CONV Electronic Comm. 1998Document9 pagesIES CONV Electronic Comm. 1998gateandiesNo ratings yet
- GS2011 QP ChemistryDocument17 pagesGS2011 QP ChemistryAkash AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Jad Dcio CBRT 08032020 An - 1Document17 pagesJad Dcio CBRT 08032020 An - 1AdityaNo ratings yet
- Appsc DL 2012 Physics Question PaperDocument18 pagesAppsc DL 2012 Physics Question Papertvsagar8387% (15)
- IES Conventional Electronics 2013Document32 pagesIES Conventional Electronics 2013Debi Prasad DashNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications MCQDocument20 pagesWireless Communications MCQRenisha BennoNo ratings yet
- 8.physics - Class XII - CPBE 2023Document11 pages8.physics - Class XII - CPBE 2023EMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- VSAT Droppers JEE Sample Questions PDFDocument5 pagesVSAT Droppers JEE Sample Questions PDFHarsha vardhanNo ratings yet
- AIPMT 2007 Mains QuestionPaper-With-solDocument26 pagesAIPMT 2007 Mains QuestionPaper-With-solAshish PaswanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Useful ConstantsDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure: Useful ConstantsSrinjoy BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper Higher Secondary - Second Year - PhysicsDocument6 pagesModel Question Paper Higher Secondary - Second Year - Physicsbindum_9No ratings yet
- Student Guidance Cell-NITC Chemistry QuestionsDocument5 pagesStudent Guidance Cell-NITC Chemistry QuestionsVedurupaka Venkata SaiNo ratings yet
- C24 BTTS-03 - Physics (Jee Mains)Document19 pagesC24 BTTS-03 - Physics (Jee Mains)Gajab HeisterNo ratings yet
- All India JEE Mock Test - Entrance Test 2 For JEE Eklavya 2023Document38 pagesAll India JEE Mock Test - Entrance Test 2 For JEE Eklavya 2023purple youNo ratings yet
- Physics: (Mock Test-1) 1Document6 pagesPhysics: (Mock Test-1) 1ManishKumarNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument14 pagesMCQشمس صبيح عبد الرحيم100% (1)
- A, A, A B) A, A, A C) A, A, A D) A, A, ADocument18 pagesA, A, A B) A, A, A C) A, A, A D) A, A, Avenki786No ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - GATE ECE Solved Paper - 2003Document20 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - GATE ECE Solved Paper - 2003Nandha KumarNo ratings yet
- Iit Jam Cy 2008Document10 pagesIit Jam Cy 2008Moksh GroverNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Physics PB I 2023-24Document6 pagesQuestion Paper Physics PB I 2023-24rishirajkaran2006No ratings yet
- CY101-Inorganic Quiz-Questions-FinalDocument8 pagesCY101-Inorganic Quiz-Questions-FinalPravat Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Cbse PMT - 2007 Mains: PhysicsDocument26 pagesCbse PMT - 2007 Mains: Physicsapi-19826463No ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya JEE-Main - Shift-02 - 04-04-2024 - Question PaperDocument10 pagesSri Chaitanya JEE-Main - Shift-02 - 04-04-2024 - Question PaperNick SinghNo ratings yet
- 03 - Physics - March 2007Document6 pages03 - Physics - March 2007Bernardo Gonzalez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Question BankDocument20 pagesMultiple Choice Question BankNithya sree100% (1)
- Physics PapersDocument61 pagesPhysics PapersDanial Amjad ChohanNo ratings yet
- Physics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionDocument25 pagesPhysics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionA KNo ratings yet
- Berklee Hw4 SolutionsDocument8 pagesBerklee Hw4 SolutionsSnakefistx100% (1)
- Sample Papers SolvedDocument185 pagesSample Papers Solvedjovanbhaskaran10No ratings yet
- KV Sample Paper With SolutionDocument17 pagesKV Sample Paper With Solutionrohan gk gamingNo ratings yet
- 1asp MergedDocument73 pages1asp MergedHarrison BennettNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 10Document10 pagesPhysics Set 10bijayakumal819No ratings yet
- Paper 1Document5 pagesPaper 1Nitin JadhavNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument22 pages4 PDFjavacobNo ratings yet
- Uv MCQDocument1 pageUv MCQmohammedabubakrNo ratings yet
- JEE MAINS Solved Paper 2013Document24 pagesJEE MAINS Solved Paper 2013chithrasajeev67% (3)
- Ce Gate 2012Document17 pagesCe Gate 2012Mukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Btech Model QuestionsDocument22 pagesBtech Model QuestionsAkshayKannanNo ratings yet
- QP12PHY02PB23Document8 pagesQP12PHY02PB23Ayush TomarNo ratings yet
- Cbse PMT - 2007 Mains: PhysicsDocument26 pagesCbse PMT - 2007 Mains: PhysicsanuvikaNo ratings yet
- Aipmt 2007 Exam Paper MainsDocument26 pagesAipmt 2007 Exam Paper MainsBring them DownNo ratings yet
- ModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Document1 pageModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Maulik KarasaliyaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Properties of Material QuestionsDocument6 pagesElectronic Properties of Material Questionsaryan mike minzNo ratings yet
- ECE795 Math Practice Solns PDFDocument40 pagesECE795 Math Practice Solns PDFadiazNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii Phy March 2020 QPDocument8 pagesHsslive Xii Phy March 2020 QPalbedo16163No ratings yet
- IES-CONV-Electrical Engineering 1994 PDFDocument9 pagesIES-CONV-Electrical Engineering 1994 PDFvineethkbNo ratings yet
- ch31 PDFDocument26 pagesch31 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- Dec 2019Document81 pagesDec 2019sridharR hahahaNo ratings yet
- 3rd SemDocument13 pages3rd SemKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics PapersDocument61 pagesPhysics PapersDanial Amjad ChohanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 1 Mark QuestionsDocument5 pagesCircuit Theory 1 Mark QuestionsSridhar Kuty100% (3)
- JEE MAINS Solved Paper 2012Document30 pagesJEE MAINS Solved Paper 2012chithrasajeev100% (1)
- G12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsDocument25 pagesG12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsSreshta ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question PaperDocument4 pagesChemistry Question PaperRiya Maria SijuNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryFrom EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNo ratings yet
- Electrogravimetry and CoulometryDocument53 pagesElectrogravimetry and CoulometrySunil Kumar100% (3)
- Raman SpectraDocument40 pagesRaman SpectraSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Euroncap Fiat Grande Punto 2005 5stars PDFDocument1 pageEuroncap Fiat Grande Punto 2005 5stars PDFSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- UV-VIS SpectrosDocument19 pagesUV-VIS SpectrosSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MSCDocument46 pagesChemistry MSCSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- B Pharm PDFDocument93 pagesB Pharm PDFSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2012Document2 pagesChemistry 2012Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Unfiled Notes Page 1: 29 March 2010 10:52 PMDocument4 pagesUnfiled Notes Page 1: 29 March 2010 10:52 PMSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Time Table 2011Document5 pagesTime Table 2011Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Tad ADocument2 pagesTad ASunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Hair Straightening CompositionDocument13 pagesHair Straightening Compositionzorro21072107No ratings yet
- Komparasi Inergen, FM-200, Dan Novec 1230Document4 pagesKomparasi Inergen, FM-200, Dan Novec 1230Bagus PrambudiNo ratings yet
- LED Color ChartDocument1 pageLED Color ChartskycrazeeNo ratings yet
- Food Aroma - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument10 pagesFood Aroma - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsSaba KhanNo ratings yet
- 6251 Desinfección Por Productos - Haloaceticos Acidos y Tricloro FenolDocument12 pages6251 Desinfección Por Productos - Haloaceticos Acidos y Tricloro FenolCecilia AvilaNo ratings yet
- POGGIO - 2016 - Modelling The Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Organic Waste - SubstrateDocument15 pagesPOGGIO - 2016 - Modelling The Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Organic Waste - SubstrateThobiasNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Corrosion KKDocument65 pagesModule 3 Corrosion KKAastha MandaliaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Novel Polymeric NanoparticlesDocument10 pagesSynthesis, Characterization, and Application of Novel Polymeric NanoparticlesRawan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Acid, Base, and SaltDocument12 pagesAcid, Base, and SaltTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Testing Module 1Document6 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing Module 1Weld Bro SandeepNo ratings yet
- Co Ordinationcompounds Exercise 1Document17 pagesCo Ordinationcompounds Exercise 1HafserhNo ratings yet
- Phenol From Toulene Oxidation RouteDocument18 pagesPhenol From Toulene Oxidation RouteSwapneelThombareNo ratings yet
- Science 10 FourthDocument3 pagesScience 10 FourthEDGAR DELGADONo ratings yet
- Final Poster PPT of ERWDocument1 pageFinal Poster PPT of ERWMaksudur Rahman SumonNo ratings yet
- Molecules 23 00511 v2Document38 pagesMolecules 23 00511 v2Amierson TilendoNo ratings yet
- Date: Experiment No 9 Determination of K A by Sulphite Oxidation MethodDocument4 pagesDate: Experiment No 9 Determination of K A by Sulphite Oxidation Methodanon_64239065No ratings yet
- Bioenergetics: Mahpara Gondal Pharm D Ms Pharmaceutical Chemistry Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument30 pagesBioenergetics: Mahpara Gondal Pharm D Ms Pharmaceutical Chemistry Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Elastomeric Impression MaterialsDocument3 pagesElastomeric Impression MaterialsDuong LeNo ratings yet
- Tujan ProjDocument4 pagesTujan ProjMayson BaliNo ratings yet
- OligomerDocument3 pagesOligomerRommelBaldagoNo ratings yet
- Buffer and Buffer PreparationDocument18 pagesBuffer and Buffer PreparationOluwaseyi OsipitanNo ratings yet
- Nano Dap3Document11 pagesNano Dap3Rohit GarnayakNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory Report: I. Data and ResultsDocument4 pagesInorganic Chemistry Laboratory Report: I. Data and Resultskim allysaNo ratings yet
- Module 17 Calculating The Empirical FormulaeDocument2 pagesModule 17 Calculating The Empirical Formulaerudi_zNo ratings yet
- Schoeller and Powell-The Analysis of Minerals and Ores of The Rarer Elements 1919Document258 pagesSchoeller and Powell-The Analysis of Minerals and Ores of The Rarer Elements 1919RonLayton100% (1)
- Inorganic PolymerDocument19 pagesInorganic PolymerAhmed AtefNo ratings yet
- Potato Plastic Lab ModuleDocument4 pagesPotato Plastic Lab ModuleAnoif Naputo AidnamNo ratings yet
- Skims Paper Pattern SyllabusDocument4 pagesSkims Paper Pattern SyllabusWani ZahoorNo ratings yet