Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antifungals
Antifungals
Uploaded by
Brandon BarndtCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A - Level Project Work Insights & ReflectionsDocument3 pagesA - Level Project Work Insights & ReflectionsKou Uraki0% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Masturbation Free EbookDocument5 pagesMasturbation Free EbookVishal Pandey75% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- IEC 60950 Rev1Document3 pagesIEC 60950 Rev1Rip_BarNo ratings yet
- Proposal Majlis Berbuka PuasaDocument4 pagesProposal Majlis Berbuka PuasaheryizwanNo ratings yet
- Resistive Circuit PracticeDocument11 pagesResistive Circuit PracticeBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Project Report On RTS Juice PlantDocument7 pagesProject Report On RTS Juice PlantEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- LG 55ea9800Document102 pagesLG 55ea9800CadwillNo ratings yet
- Antivirals For HerpesDocument4 pagesAntivirals For HerpesBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- What Becomes What DevelopmentDocument10 pagesWhat Becomes What DevelopmentBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ChartDocument8 pagesEnzymes ChartBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and The TCA Cycle: Glycogen PathwaysDocument8 pagesGlycolysis and The TCA Cycle: Glycogen PathwaysBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction HandoutDocument14 pages01 Introduction HandoutBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Bio I Master Guide - Test 2Document20 pagesBio I Master Guide - Test 2Brandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Bio I Master GuideDocument44 pagesBio I Master GuideBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Price ListDocument28 pagesPrice ListBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument10 pagesEssayBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Soil Acidity and LimingDocument12 pagesSoil Acidity and LimingEloi Carlos GoveNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument79 pagesPreviewpdfcrisuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Questions WithoutSupersonicDocument5 pagesChapter4 Questions WithoutSupersonicsh1999No ratings yet
- OSH SeminarDocument2 pagesOSH SeminarSahar Ulu JeruasNo ratings yet
- Natural Rubber WikiDocument9 pagesNatural Rubber WikiMyra Wardati SNo ratings yet
- Trial Salary SlipDocument5 pagesTrial Salary SlipTvs12346No ratings yet
- Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, IncDocument4 pagesRamon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, IncPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- Case Study Booklet 2 PDFDocument43 pagesCase Study Booklet 2 PDFguddu yadavNo ratings yet
- STOC03 (Emissions)Document20 pagesSTOC03 (Emissions)tungluongNo ratings yet
- Covalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesCovalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionJuan Carlos Contreras CherresNo ratings yet
- Dec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech ReviewDocument58 pagesDec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech Reviewadyjoy antonioNo ratings yet
- Bio-Organic Chem LecturesDocument205 pagesBio-Organic Chem LecturesРаони Мессиас100% (2)
- IFU Acticor 439128-F EsDocument143 pagesIFU Acticor 439128-F EsMartin ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Sec3 Well Spud and Guide StructuresDocument15 pagesSec3 Well Spud and Guide StructuresDonald StraubNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lymph SystemDocument7 pagesPhysiology of Lymph SystemMwangi NyawiraNo ratings yet
- II 2015 4Document283 pagesII 2015 4tuni santeNo ratings yet
- BRAC Annual Report 2017 PDFDocument116 pagesBRAC Annual Report 2017 PDFShoaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- IdealStandard 120m-Frame R0094Document2 pagesIdealStandard 120m-Frame R0094nasser mhannaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets For Solutions AnalysisDocument2 pagesProblem Sets For Solutions AnalysisKamil Guillergan100% (1)
- Safe Practices For Welding InspectorsDocument39 pagesSafe Practices For Welding InspectorsAlejandro RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Material HPLCDocument19 pagesMaterial HPLCIsmil ImamaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Commissioning Checklist Non LeedDocument7 pagesElectrical Commissioning Checklist Non Leedcaleb isukuruNo ratings yet
- UO Mixing Liquid PhaseDocument2 pagesUO Mixing Liquid PhaseKumara Haekal Hafidz AmrullahNo ratings yet
- VBIED Attack July 31, 2007Document1 pageVBIED Attack July 31, 2007Rhonda NoldeNo ratings yet
Antifungals
Antifungals
Uploaded by
Brandon BarndtCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antifungals
Antifungals
Uploaded by
Brandon BarndtCopyright:
Available Formats
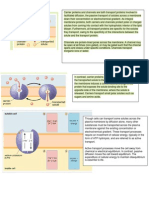
ANTIFUNGALS- ergosterol, beta 1,3-glucan, squalene blocker, mitosis, dna synthesis inhibitor
Drug
Mechanism
POLYENES
Amphotericin B
Nystatin
- binds ergosterol in cell
membrane (esp.
ergosterol), leading to cell
death
ECHINOCANDINS
(FUNGINS)
AZOLES- General
Inhibit beta-1,3-glucan
synthase, decreasing beta1,3-glucan production
- Inhibit fungal cytochrome
P450, decreasing
ergosterol formation
Absorption/
Kinetics
Concentration
dependent
-concentration
dependent
- not
eliminated
renally
- all have
some hepatic
metabolism
- fluconazole
excreted
renally
- time
dependent
Itraconazole
Posaconazole
OthersKetoconazole
- IV
- topical
- oral: GI
fungi (topical)
- wellabsorbed,
hepatically
metabolized
- non-linear
- SBECD of IV
form is renally
eliminated
Uses
Adverse Effects
broadest spectrum antifungal
- Candidas
- Cryptococcus neoformans
- Nephrotoxicity (renal
elimination)
- Electrolyte Wasting
- Infusion-related reactions
IV Only
Strong in vitro activity against Candida
Active against Aspergillus
Ineffective for Cryptococcus
- hepatotoxicity
- infusion-related reactions
- phlebitis
Use a cane for your HIP
(hepatotox, infusion, phlebitis)
IV
Tablets
Oral
Candidiasis
Cryptoccocus
Febrile Neutropenia- (voriconazole)
Aspergillosis(vori, itra)
Onynchomycosis- (Itraconazole)
Prophylaxis (posiconazole)
- Hepatotoxicity (p450) (all)
- Rash (ketokonazole)
- drug interaction (all)
- visual (vori)
IV
Tablets
Oral
Fluconazole
Voriconazole
Admin.
IV
Capsule
Oral Solution
IV
Capsules
Oral
Candidiasis
Cryptococcal meningitis
NOT ASPERGILLUS/NON-ALBICANS
Invasive aspergillosis
Febrile neutropenia
Yeasts- candida and Cryptococcus
VISUAL
-Visual Effects
-Visual Halluinations
Candidiasis
Cryptococcus
Aspergillosis
candidiasis
Onychomycosis
Prophylaxis of fungal infections
Mold infections
Yeast- candida, cryptococcus
Dermatologic
5- Flucytosine (5FC)
- Antimetabolite
- Deaminated within fungal
DNA inhibitor
Terbinafine
- allylamine
antifungal
- inhibits fungal squalene
metabolism ( squalene
toxic), ergosterol
Griseofulvin
- inhibits fungal mitosis
via interaction with
microtubules
-Widely
distributed,
including CNS
-Renally
excreted
40%
bioavailable
(1st pass)
-metabolized
in liver,
metabolites
excreted
renally
-non-linear
elimination
Some activity vs. aspergillus
Combination therapy for cryptococcal meningitis
Rarely used for candidiasis (non-albicans)
- topical
- oral
(terbinafine)
Clinical activity mainly for dermatophytes(EMTs)
Active against Candida, Aspergillus
Onychomycosis
Orally
Active against dermatophytes
Tx for onchomycosis (last line)
All azoles: new emergence of resistant strains in AIDS patients; resistance is otherwise fairly rare.
Bone marrow suppression
GI intolerance, rash,
hepatotoxicity
-Hepatotoxicity
-Neutropenia
-Steven-Johnson syndrome
CNS- headache
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A - Level Project Work Insights & ReflectionsDocument3 pagesA - Level Project Work Insights & ReflectionsKou Uraki0% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Masturbation Free EbookDocument5 pagesMasturbation Free EbookVishal Pandey75% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- IEC 60950 Rev1Document3 pagesIEC 60950 Rev1Rip_BarNo ratings yet
- Proposal Majlis Berbuka PuasaDocument4 pagesProposal Majlis Berbuka PuasaheryizwanNo ratings yet
- Resistive Circuit PracticeDocument11 pagesResistive Circuit PracticeBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Project Report On RTS Juice PlantDocument7 pagesProject Report On RTS Juice PlantEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- LG 55ea9800Document102 pagesLG 55ea9800CadwillNo ratings yet
- Antivirals For HerpesDocument4 pagesAntivirals For HerpesBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- What Becomes What DevelopmentDocument10 pagesWhat Becomes What DevelopmentBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ChartDocument8 pagesEnzymes ChartBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and The TCA Cycle: Glycogen PathwaysDocument8 pagesGlycolysis and The TCA Cycle: Glycogen PathwaysBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction HandoutDocument14 pages01 Introduction HandoutBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Bio I Master Guide - Test 2Document20 pagesBio I Master Guide - Test 2Brandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Bio I Master GuideDocument44 pagesBio I Master GuideBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Price ListDocument28 pagesPrice ListBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument10 pagesEssayBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Soil Acidity and LimingDocument12 pagesSoil Acidity and LimingEloi Carlos GoveNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument79 pagesPreviewpdfcrisuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Questions WithoutSupersonicDocument5 pagesChapter4 Questions WithoutSupersonicsh1999No ratings yet
- OSH SeminarDocument2 pagesOSH SeminarSahar Ulu JeruasNo ratings yet
- Natural Rubber WikiDocument9 pagesNatural Rubber WikiMyra Wardati SNo ratings yet
- Trial Salary SlipDocument5 pagesTrial Salary SlipTvs12346No ratings yet
- Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, IncDocument4 pagesRamon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, IncPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- Case Study Booklet 2 PDFDocument43 pagesCase Study Booklet 2 PDFguddu yadavNo ratings yet
- STOC03 (Emissions)Document20 pagesSTOC03 (Emissions)tungluongNo ratings yet
- Covalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesCovalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionJuan Carlos Contreras CherresNo ratings yet
- Dec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech ReviewDocument58 pagesDec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech Reviewadyjoy antonioNo ratings yet
- Bio-Organic Chem LecturesDocument205 pagesBio-Organic Chem LecturesРаони Мессиас100% (2)
- IFU Acticor 439128-F EsDocument143 pagesIFU Acticor 439128-F EsMartin ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Sec3 Well Spud and Guide StructuresDocument15 pagesSec3 Well Spud and Guide StructuresDonald StraubNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lymph SystemDocument7 pagesPhysiology of Lymph SystemMwangi NyawiraNo ratings yet
- II 2015 4Document283 pagesII 2015 4tuni santeNo ratings yet
- BRAC Annual Report 2017 PDFDocument116 pagesBRAC Annual Report 2017 PDFShoaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- IdealStandard 120m-Frame R0094Document2 pagesIdealStandard 120m-Frame R0094nasser mhannaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets For Solutions AnalysisDocument2 pagesProblem Sets For Solutions AnalysisKamil Guillergan100% (1)
- Safe Practices For Welding InspectorsDocument39 pagesSafe Practices For Welding InspectorsAlejandro RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Material HPLCDocument19 pagesMaterial HPLCIsmil ImamaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Commissioning Checklist Non LeedDocument7 pagesElectrical Commissioning Checklist Non Leedcaleb isukuruNo ratings yet
- UO Mixing Liquid PhaseDocument2 pagesUO Mixing Liquid PhaseKumara Haekal Hafidz AmrullahNo ratings yet
- VBIED Attack July 31, 2007Document1 pageVBIED Attack July 31, 2007Rhonda NoldeNo ratings yet