Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 viewsL3
L3
Uploaded by
r005w3ltThis document covers Lesson 3 of the Mechanics of Materials course MMME M1. The lesson topics include stress, strain, and Hooke's law. It discusses normal stresses and strains, Hooke's law, shear stress and strain. It provides examples of stress and strain, tensile tests, elasticity, plasticity and creep. It also discusses Poisson's ratio, shear stress, shear strain, and Hooke's law in shear. Homework is assigned from the textbook for Friday the 21st. Key concepts are stress, strain, Hooke's law, elasticity, plasticity, creep, Poisson's ratio, shear stress, and shear strain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Student'S Full Name: Licence No: ID No. / Passport No.: Examination Date: Student SignatureDocument2 pagesStudent'S Full Name: Licence No: ID No. / Passport No.: Examination Date: Student SignatureAdam MustafaNo ratings yet
- CE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement Composites - Lecture 9Document14 pagesCE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement Composites - Lecture 9Pranab BiswasNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 4Document19 pagesMme M1: Lesson 4r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 7Document23 pagesMme M1: Lesson 7r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 8Document17 pagesMme M1: Lesson 8r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 2Document24 pagesMme M1: Lesson 2r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 6Document17 pagesMme M1: Lesson 6r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanical MetallurgyDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Mechanical Metallurgyhsy5478No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document32 pagesUnit 1Swarina Arthur JamesNo ratings yet
- CE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement Composites - Lecture 6Document23 pagesCE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement Composites - Lecture 6Pranab Biswas100% (1)
- Module 2 PDFDocument25 pagesModule 2 PDFBhavana ANo ratings yet
- Module-1 Stresses and StrainsDocument33 pagesModule-1 Stresses and StrainsC.E.M JEFFREYSNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Stress and StrainDocument4 pagesUnit-I Stress and StrainBoopathi YoganathanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document45 pagesLecture 4SAIF ULLAHNo ratings yet
- TVKB GATE RCH SOM 03 Mech Behaviour MaterialsDocument33 pagesTVKB GATE RCH SOM 03 Mech Behaviour MaterialsSatish DhanyamrajuNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument14 pagesStress and StrainGetachew AbebeNo ratings yet
- The Annual Käs Lab X-Mas Bash 2013: When: December 14, 7pm Where: Feuerbachstr, 4, LeipzigDocument35 pagesThe Annual Käs Lab X-Mas Bash 2013: When: December 14, 7pm Where: Feuerbachstr, 4, LeipzigAlejandro LavradorNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Lecture NotesDocument272 pagesStrength of Materials Lecture NotesbookdigitNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialDocument6 pagesStrength of MaterialhaymanotNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Basics and Equations - Mechanics of Materials - Engineers EdgeDocument6 pagesStrength of Materials Basics and Equations - Mechanics of Materials - Engineers EdgeansarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 2to4Document44 pagesModule 1 Lecture 2to4alan roiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3mechanics 161231043743 PDFDocument17 pagesUnit 3mechanics 161231043743 PDFchincha chuNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain DiagramDocument4 pagesStress Strain DiagramMartine CastroNo ratings yet
- Sifat MekanikDocument16 pagesSifat MekanikMuhammad Reihan IskandarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3a Properties of Materials November 13 2023 BSEE 4 ContDocument70 pagesLesson 3a Properties of Materials November 13 2023 BSEE 4 ContenginearswebNo ratings yet
- Strain: It Is The Deformation of A Structural Member Per Unit LengthDocument25 pagesStrain: It Is The Deformation of A Structural Member Per Unit LengthSyed Hasnain BakhtNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter - 04. Macro Mechanics of A Lamina PDFDocument57 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter - 04. Macro Mechanics of A Lamina PDFPremsingh BanasiNo ratings yet
- MSM Unit No.2 NotesDocument39 pagesMSM Unit No.2 NotesPratik SaindanePatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Mechanic of MaterialsDocument30 pagesChapter 3 - Mechanic of MaterialsMohd AjmainNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fibrous Structure (TM-3051) : Dr. M IrfanDocument45 pagesMechanics of Fibrous Structure (TM-3051) : Dr. M IrfanHussainNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fibrous Structure (TM-3051) : Dr. M IrfanDocument45 pagesMechanics of Fibrous Structure (TM-3051) : Dr. M IrfanHussainNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument162 pagesStainless SteelNavya AnilNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Institute of Technology: School of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Materials Science and EngineeringDocument40 pagesAddis Ababa Institute of Technology: School of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Materials Science and EngineeringColorgold BirlieNo ratings yet
- Session - 07 & 08Document38 pagesSession - 07 & 08Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Solid: MechanicsDocument106 pagesSolid: Mechanicssadiya mehzabinNo ratings yet
- 4 - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument28 pages4 - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsYusf ari jerjisNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PDFDocument39 pagesModule 1 PDFPrakhar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Strength of MweeaterialsDocument7 pagesStrength of MweeaterialsChristianNo ratings yet
- Basics of DesignDocument22 pagesBasics of Designgajendra yadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Stress and StrainDocument20 pagesLecture 2 Stress and Strainحسام النخلانيNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material CH-1 Ppt-1Document26 pagesStrength of Material CH-1 Ppt-1Nura Guyo67% (3)
- Stress StrainDocument25 pagesStress Strainphilippematthew000No ratings yet
- Module 6 Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument92 pagesModule 6 Mechanical Properties of MetalsJay LopezNo ratings yet
- Modulus of ElasticityDocument1 pageModulus of ElasticitydineshkeswaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument19 pagesMechanical Properties of Materialsth05691No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 StressStrainDocument10 pagesLecture 3 StressStrainMohammed ImranNo ratings yet
- TDS Lec 3Document78 pagesTDS Lec 3YAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNo ratings yet
- An Sys NotesDocument4 pagesAn Sys NotesbalabooksNo ratings yet
- 1594615385 II I Solid MechanicsDocument111 pages1594615385 II I Solid MechanicsFADHILI BENJAMINNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law - Poisson's RatioDocument2 pagesHooke's Law - Poisson's Ratiobinh.nsbcoNo ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodDocument86 pagesFinite Element MethodNavid NewazNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Materials OnlineDocument96 pagesIntroduction To Materials Onlinesh techNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Lecture NoteDocument22 pagesChapter-1 Lecture NoteeyobNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material NotesDocument32 pagesStrength of Material NotesAtul ManiNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanical Behavior of MaterialsDocument7 pages1 Mechanical Behavior of MaterialsMohammed Rashik B CNo ratings yet
- TDS Lec 3Document78 pagesTDS Lec 3YAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument24 pagesMechanical Properties of SolidsalayuNo ratings yet
- Machine Design - IntroductionDocument47 pagesMachine Design - IntroductionGanesh DongreNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingFrom EverandThe Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsFrom EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument22 pagesBlooms Taxonomyr005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Wheatstone's Bridge: Typical Applications: Strain Gauges (Stress Measurements), Temperature EtcDocument6 pagesWheatstone's Bridge: Typical Applications: Strain Gauges (Stress Measurements), Temperature Etcr005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Recap: - The Coulomb Force (Fundamental Force) - Voltage - Ohm's Law - Resistance - PowerDocument17 pagesRecap: - The Coulomb Force (Fundamental Force) - Voltage - Ohm's Law - Resistance - Powerr005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Transient Response RC Circuits ExamplesDocument10 pagesCapacitor Transient Response RC Circuits Examplesr005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Independent Voltage SourceDocument10 pagesIndependent Voltage Sourcer005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 8Document17 pagesMme M1: Lesson 8r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 7Document23 pagesMme M1: Lesson 7r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 6Document17 pagesMme M1: Lesson 6r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 4Document19 pagesMme M1: Lesson 4r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 2Document24 pagesMme M1: Lesson 2r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Assignment MME # 1 To Be Handed in Tuesday 11'th MarchDocument1 pageAssignment MME # 1 To Be Handed in Tuesday 11'th Marchr005w3ltNo ratings yet
- On A/C All: Reference DesignationDocument3 pagesOn A/C All: Reference DesignationbillyNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Aircraft Anti Hijack OperationsDocument6 pagesIntroduction of Aircraft Anti Hijack OperationsHasitha KolambageNo ratings yet
- C G e e C H C R A F T ®: Pilot'S Operating Handbook and Faa Approved Airplane Flight Man U AlDocument9 pagesC G e e C H C R A F T ®: Pilot'S Operating Handbook and Faa Approved Airplane Flight Man U Almickstads0% (1)
- Bombardier-Challenger 01-Air Cond and PressDocument23 pagesBombardier-Challenger 01-Air Cond and PressEmanøel AlvesNo ratings yet
- PHYS 2048 Test 1Document11 pagesPHYS 2048 Test 1Vince Rabin CandidatoNo ratings yet
- Formulas AerorreactorDocument18 pagesFormulas AerorreactorJaf JimenezNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document58 pagesModule 6Zbor ZborNo ratings yet
- ZG InterfaceControlDoc RevA2Document24 pagesZG InterfaceControlDoc RevA2LoveNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of The Guidance Systems ParametersDocument6 pagesAnalytical Modeling of The Guidance Systems ParametersthesijNo ratings yet
- Lab Thermo 4Document15 pagesLab Thermo 4Fajobi AbeebNo ratings yet
- 010 - Air Law - QuestionsDocument36 pages010 - Air Law - QuestionsEASA ATPL Question Bank67% (3)
- Javascript Sample: Precipitation (MM) Per YearDocument3 pagesJavascript Sample: Precipitation (MM) Per YearAndriciMugurelTeodorNo ratings yet
- F-22 Park Jet (Parts Templates Scaled 120 Non-Tiled) PDFDocument1 pageF-22 Park Jet (Parts Templates Scaled 120 Non-Tiled) PDFVikram DamleNo ratings yet
- EspdicDocument875 pagesEspdicBrian CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Recreational Airpark Design: Standard Specification ForDocument6 pagesRecreational Airpark Design: Standard Specification ForAhmad Zubair RasulyNo ratings yet
- Spin Stability at Indy 1619812067Document6 pagesSpin Stability at Indy 1619812067Pierre LalsingNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Vented Interstage in A Typical Launch Vehicle IJERTV4IS080369Document5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Vented Interstage in A Typical Launch Vehicle IJERTV4IS080369Jav butNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Rocket Motor Casing by Using Fem TechniqueDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Rocket Motor Casing by Using Fem TechniqueRudra Sai SandeepNo ratings yet
- Hawt Vawt PDFDocument4 pagesHawt Vawt PDFDilipraja KolliNo ratings yet
- 2012 04 Rotor Runnin Flexrotor Phase VideoDocument2 pages2012 04 Rotor Runnin Flexrotor Phase VideocodrinatcNo ratings yet
- Form 667Document3 pagesForm 667Le ThangNo ratings yet
- M13 HelicopterDocument4 pagesM13 HelicopterJuan NightstandNo ratings yet
- EASA Form 4 - Details of Nominated Personnel - Aircraft Maintenance OrganisationsDocument2 pagesEASA Form 4 - Details of Nominated Personnel - Aircraft Maintenance OrganisationssebastienNo ratings yet
- RunwayDocument22 pagesRunwaysajid9363% (8)
- Haelok Katalog q1 2016sDocument36 pagesHaelok Katalog q1 2016sDuzzysNo ratings yet
- EndeDocument8 pagesEndeandyNo ratings yet
- A320 CBT Air Conditioning: Table of ContentDocument12 pagesA320 CBT Air Conditioning: Table of ContentRom CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (PART A) 17Document116 pagesChapter 2 (PART A) 17Waleed PaliNo ratings yet
L3
L3
Uploaded by
r005w3lt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views22 pagesThis document covers Lesson 3 of the Mechanics of Materials course MMME M1. The lesson topics include stress, strain, and Hooke's law. It discusses normal stresses and strains, Hooke's law, shear stress and strain. It provides examples of stress and strain, tensile tests, elasticity, plasticity and creep. It also discusses Poisson's ratio, shear stress, shear strain, and Hooke's law in shear. Homework is assigned from the textbook for Friday the 21st. Key concepts are stress, strain, Hooke's law, elasticity, plasticity, creep, Poisson's ratio, shear stress, and shear strain.
Original Description:
mmm l3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document covers Lesson 3 of the Mechanics of Materials course MMME M1. The lesson topics include stress, strain, and Hooke's law. It discusses normal stresses and strains, Hooke's law, shear stress and strain. It provides examples of stress and strain, tensile tests, elasticity, plasticity and creep. It also discusses Poisson's ratio, shear stress, shear strain, and Hooke's law in shear. Homework is assigned from the textbook for Friday the 21st. Key concepts are stress, strain, Hooke's law, elasticity, plasticity, creep, Poisson's ratio, shear stress, and shear strain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views22 pagesL3
L3
Uploaded by
r005w3ltThis document covers Lesson 3 of the Mechanics of Materials course MMME M1. The lesson topics include stress, strain, and Hooke's law. It discusses normal stresses and strains, Hooke's law, shear stress and strain. It provides examples of stress and strain, tensile tests, elasticity, plasticity and creep. It also discusses Poisson's ratio, shear stress, shear strain, and Hooke's law in shear. Homework is assigned from the textbook for Friday the 21st. Key concepts are stress, strain, Hooke's law, elasticity, plasticity, creep, Poisson's ratio, shear stress, and shear strain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 22
Lesson 3
MMME M1
Mechanics of Materials
Topics : Stress Strain and Hookes Law
Homework (12.5-6)
Normal Stresses and strains
Hookes Law
Shear Stress and shear strain
Homework to Tuesday 18th Feb
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Stress
(Tensile and Compression)
Unit: Pascal,Mega Pascal or Giga Pascal
Limitations:
Load uniformly distributed
-> Force acts on centroid. (no bending)
Observing at the uniform part
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
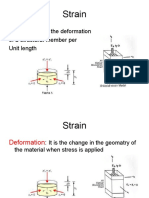
Strain (Epsilon)
( Dimensionless )
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Tensile Test
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Elasticity ,Plasticity and Creep
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Reloading of a material
By stretching material such as steel or aluminium into the inelastic or plastic
range, the properties of the material are changed. The linearly elastic region
is increased and the elastic limit is raised.
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Creep and Relaxation
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Linear Elasticity , Hookes law and Poissons Ratio
In the linear, elastic area
Some E values ( App H) :
Steel:
Alu:
Plastics
210 Gpa
73 Gpa
1-14 GPa
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Poissons Ratio:
For most materials Poissons ration is assumed to be the same in
both tension and compression
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Shear Stress
(Average Bearing Stress )
Average Shear Stress
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Equality of shear stresses on perp planes
Shear stresses on opposite and parallel faces of an element are equal
In magnitude and opposite in direction
Shear stresses on adjacent and perpendicular faces of an element
are equal in magnitude and have directions such that both stresses
Point towards , or point away, from the line of intersections of the faces
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Shear Strain
Sign Convention:
A shear stress acting on a positive face of an element is
positive if it acts in the positive direction of one of the
coordinate axis.
A shear stress acting on a negative face of an element is
Positive, if it acts in the negative direction of an axis.
Shear Strain in an element is positive, when the angle
between the two positive is reduced.
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Hookes Law in Shear
G is called Shear Modulus or Modulus of
rigidity
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Homework Friday 21th
source: Hibbeler 3rd ed., P7-69, p. 355
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Homework Friday 21th
Source Hippeler)
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
Friday 21th Readings
Kim Rask Petersen, MME M1 Spring 2014
You might also like
- Student'S Full Name: Licence No: ID No. / Passport No.: Examination Date: Student SignatureDocument2 pagesStudent'S Full Name: Licence No: ID No. / Passport No.: Examination Date: Student SignatureAdam MustafaNo ratings yet
- CE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement Composites - Lecture 9Document14 pagesCE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement Composites - Lecture 9Pranab BiswasNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 4Document19 pagesMme M1: Lesson 4r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 7Document23 pagesMme M1: Lesson 7r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 8Document17 pagesMme M1: Lesson 8r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 2Document24 pagesMme M1: Lesson 2r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 6Document17 pagesMme M1: Lesson 6r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanical MetallurgyDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Mechanical Metallurgyhsy5478No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document32 pagesUnit 1Swarina Arthur JamesNo ratings yet
- CE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement Composites - Lecture 6Document23 pagesCE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement Composites - Lecture 6Pranab Biswas100% (1)
- Module 2 PDFDocument25 pagesModule 2 PDFBhavana ANo ratings yet
- Module-1 Stresses and StrainsDocument33 pagesModule-1 Stresses and StrainsC.E.M JEFFREYSNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Stress and StrainDocument4 pagesUnit-I Stress and StrainBoopathi YoganathanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document45 pagesLecture 4SAIF ULLAHNo ratings yet
- TVKB GATE RCH SOM 03 Mech Behaviour MaterialsDocument33 pagesTVKB GATE RCH SOM 03 Mech Behaviour MaterialsSatish DhanyamrajuNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument14 pagesStress and StrainGetachew AbebeNo ratings yet
- The Annual Käs Lab X-Mas Bash 2013: When: December 14, 7pm Where: Feuerbachstr, 4, LeipzigDocument35 pagesThe Annual Käs Lab X-Mas Bash 2013: When: December 14, 7pm Where: Feuerbachstr, 4, LeipzigAlejandro LavradorNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Lecture NotesDocument272 pagesStrength of Materials Lecture NotesbookdigitNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialDocument6 pagesStrength of MaterialhaymanotNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Basics and Equations - Mechanics of Materials - Engineers EdgeDocument6 pagesStrength of Materials Basics and Equations - Mechanics of Materials - Engineers EdgeansarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 2to4Document44 pagesModule 1 Lecture 2to4alan roiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3mechanics 161231043743 PDFDocument17 pagesUnit 3mechanics 161231043743 PDFchincha chuNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain DiagramDocument4 pagesStress Strain DiagramMartine CastroNo ratings yet
- Sifat MekanikDocument16 pagesSifat MekanikMuhammad Reihan IskandarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3a Properties of Materials November 13 2023 BSEE 4 ContDocument70 pagesLesson 3a Properties of Materials November 13 2023 BSEE 4 ContenginearswebNo ratings yet
- Strain: It Is The Deformation of A Structural Member Per Unit LengthDocument25 pagesStrain: It Is The Deformation of A Structural Member Per Unit LengthSyed Hasnain BakhtNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter - 04. Macro Mechanics of A Lamina PDFDocument57 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter - 04. Macro Mechanics of A Lamina PDFPremsingh BanasiNo ratings yet
- MSM Unit No.2 NotesDocument39 pagesMSM Unit No.2 NotesPratik SaindanePatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Mechanic of MaterialsDocument30 pagesChapter 3 - Mechanic of MaterialsMohd AjmainNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fibrous Structure (TM-3051) : Dr. M IrfanDocument45 pagesMechanics of Fibrous Structure (TM-3051) : Dr. M IrfanHussainNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fibrous Structure (TM-3051) : Dr. M IrfanDocument45 pagesMechanics of Fibrous Structure (TM-3051) : Dr. M IrfanHussainNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument162 pagesStainless SteelNavya AnilNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Institute of Technology: School of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Materials Science and EngineeringDocument40 pagesAddis Ababa Institute of Technology: School of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Materials Science and EngineeringColorgold BirlieNo ratings yet
- Session - 07 & 08Document38 pagesSession - 07 & 08Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Solid: MechanicsDocument106 pagesSolid: Mechanicssadiya mehzabinNo ratings yet
- 4 - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument28 pages4 - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsYusf ari jerjisNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PDFDocument39 pagesModule 1 PDFPrakhar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Strength of MweeaterialsDocument7 pagesStrength of MweeaterialsChristianNo ratings yet
- Basics of DesignDocument22 pagesBasics of Designgajendra yadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Stress and StrainDocument20 pagesLecture 2 Stress and Strainحسام النخلانيNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material CH-1 Ppt-1Document26 pagesStrength of Material CH-1 Ppt-1Nura Guyo67% (3)
- Stress StrainDocument25 pagesStress Strainphilippematthew000No ratings yet
- Module 6 Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument92 pagesModule 6 Mechanical Properties of MetalsJay LopezNo ratings yet
- Modulus of ElasticityDocument1 pageModulus of ElasticitydineshkeswaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument19 pagesMechanical Properties of Materialsth05691No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 StressStrainDocument10 pagesLecture 3 StressStrainMohammed ImranNo ratings yet
- TDS Lec 3Document78 pagesTDS Lec 3YAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNo ratings yet
- An Sys NotesDocument4 pagesAn Sys NotesbalabooksNo ratings yet
- 1594615385 II I Solid MechanicsDocument111 pages1594615385 II I Solid MechanicsFADHILI BENJAMINNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law - Poisson's RatioDocument2 pagesHooke's Law - Poisson's Ratiobinh.nsbcoNo ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodDocument86 pagesFinite Element MethodNavid NewazNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Materials OnlineDocument96 pagesIntroduction To Materials Onlinesh techNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Lecture NoteDocument22 pagesChapter-1 Lecture NoteeyobNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material NotesDocument32 pagesStrength of Material NotesAtul ManiNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanical Behavior of MaterialsDocument7 pages1 Mechanical Behavior of MaterialsMohammed Rashik B CNo ratings yet
- TDS Lec 3Document78 pagesTDS Lec 3YAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument24 pagesMechanical Properties of SolidsalayuNo ratings yet
- Machine Design - IntroductionDocument47 pagesMachine Design - IntroductionGanesh DongreNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingFrom EverandThe Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsFrom EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument22 pagesBlooms Taxonomyr005w3ltNo ratings yet
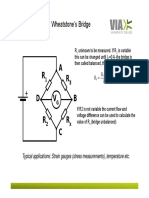
- Wheatstone's Bridge: Typical Applications: Strain Gauges (Stress Measurements), Temperature EtcDocument6 pagesWheatstone's Bridge: Typical Applications: Strain Gauges (Stress Measurements), Temperature Etcr005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Recap: - The Coulomb Force (Fundamental Force) - Voltage - Ohm's Law - Resistance - PowerDocument17 pagesRecap: - The Coulomb Force (Fundamental Force) - Voltage - Ohm's Law - Resistance - Powerr005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Transient Response RC Circuits ExamplesDocument10 pagesCapacitor Transient Response RC Circuits Examplesr005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Independent Voltage SourceDocument10 pagesIndependent Voltage Sourcer005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 8Document17 pagesMme M1: Lesson 8r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 7Document23 pagesMme M1: Lesson 7r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 6Document17 pagesMme M1: Lesson 6r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 4Document19 pagesMme M1: Lesson 4r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Mme M1: Lesson 2Document24 pagesMme M1: Lesson 2r005w3ltNo ratings yet
- Assignment MME # 1 To Be Handed in Tuesday 11'th MarchDocument1 pageAssignment MME # 1 To Be Handed in Tuesday 11'th Marchr005w3ltNo ratings yet
- On A/C All: Reference DesignationDocument3 pagesOn A/C All: Reference DesignationbillyNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Aircraft Anti Hijack OperationsDocument6 pagesIntroduction of Aircraft Anti Hijack OperationsHasitha KolambageNo ratings yet
- C G e e C H C R A F T ®: Pilot'S Operating Handbook and Faa Approved Airplane Flight Man U AlDocument9 pagesC G e e C H C R A F T ®: Pilot'S Operating Handbook and Faa Approved Airplane Flight Man U Almickstads0% (1)
- Bombardier-Challenger 01-Air Cond and PressDocument23 pagesBombardier-Challenger 01-Air Cond and PressEmanøel AlvesNo ratings yet
- PHYS 2048 Test 1Document11 pagesPHYS 2048 Test 1Vince Rabin CandidatoNo ratings yet
- Formulas AerorreactorDocument18 pagesFormulas AerorreactorJaf JimenezNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document58 pagesModule 6Zbor ZborNo ratings yet
- ZG InterfaceControlDoc RevA2Document24 pagesZG InterfaceControlDoc RevA2LoveNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of The Guidance Systems ParametersDocument6 pagesAnalytical Modeling of The Guidance Systems ParametersthesijNo ratings yet
- Lab Thermo 4Document15 pagesLab Thermo 4Fajobi AbeebNo ratings yet
- 010 - Air Law - QuestionsDocument36 pages010 - Air Law - QuestionsEASA ATPL Question Bank67% (3)
- Javascript Sample: Precipitation (MM) Per YearDocument3 pagesJavascript Sample: Precipitation (MM) Per YearAndriciMugurelTeodorNo ratings yet
- F-22 Park Jet (Parts Templates Scaled 120 Non-Tiled) PDFDocument1 pageF-22 Park Jet (Parts Templates Scaled 120 Non-Tiled) PDFVikram DamleNo ratings yet
- EspdicDocument875 pagesEspdicBrian CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Recreational Airpark Design: Standard Specification ForDocument6 pagesRecreational Airpark Design: Standard Specification ForAhmad Zubair RasulyNo ratings yet
- Spin Stability at Indy 1619812067Document6 pagesSpin Stability at Indy 1619812067Pierre LalsingNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Vented Interstage in A Typical Launch Vehicle IJERTV4IS080369Document5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Vented Interstage in A Typical Launch Vehicle IJERTV4IS080369Jav butNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Rocket Motor Casing by Using Fem TechniqueDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Rocket Motor Casing by Using Fem TechniqueRudra Sai SandeepNo ratings yet
- Hawt Vawt PDFDocument4 pagesHawt Vawt PDFDilipraja KolliNo ratings yet
- 2012 04 Rotor Runnin Flexrotor Phase VideoDocument2 pages2012 04 Rotor Runnin Flexrotor Phase VideocodrinatcNo ratings yet
- Form 667Document3 pagesForm 667Le ThangNo ratings yet
- M13 HelicopterDocument4 pagesM13 HelicopterJuan NightstandNo ratings yet
- EASA Form 4 - Details of Nominated Personnel - Aircraft Maintenance OrganisationsDocument2 pagesEASA Form 4 - Details of Nominated Personnel - Aircraft Maintenance OrganisationssebastienNo ratings yet
- RunwayDocument22 pagesRunwaysajid9363% (8)
- Haelok Katalog q1 2016sDocument36 pagesHaelok Katalog q1 2016sDuzzysNo ratings yet
- EndeDocument8 pagesEndeandyNo ratings yet
- A320 CBT Air Conditioning: Table of ContentDocument12 pagesA320 CBT Air Conditioning: Table of ContentRom CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (PART A) 17Document116 pagesChapter 2 (PART A) 17Waleed PaliNo ratings yet