Professional Documents
Culture Documents
O o o O: English Tenses
O o o O: English Tenses
Uploaded by
amaro.sandra3996Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
O o o O: English Tenses
O o o O: English Tenses
Uploaded by
amaro.sandra3996Copyright:
Available Formats
ENGLISH TENSES
OBJECTIVES
Present tenses
o Present simple: I work
o Present continuous: I am working
o Present perfect: I have worked
o Present perfect continuous: I have been working
Past tenses
o Past simple: I worked
o Past continuous: I was working
o Past perfect: I had worked
o Past perfect continuous: I had been working
Conditional
o If you go to the exhibition, you will enjoy it.
o If you went to the exhibition, you would enjoy it.
o If you had gone to the exhibition, you would have enjoyed it.
Modal Verbs
o May I come in?
o I must go home now.
Future Tenses
o Simple Future They will go
o Going to Im going to buy
Future Perfect
o Ex.: I shall have finished the report in three hours. (Eu terei terminado)
Imperative
o Ex.: Go ahead! (Vai em frente!)
1 de 6
PRESENT SIMPLE: I WORK
PRESENT CONTINUOUS: I AM WORKING
Ao habitual ou repetida
I go to work on foot.
Situaes imutveis ou permanentes
The sun moves round the earth
Planos futuros relativos a viagens,
espetculos e horrios
When does the show begin?
The show begins at 12.30
Em ligao a certas expresses de tempo:
frequently
often
generally
sometimes
usually
everyday
rarely
once a week
always
several times
Aes que acontecem no momento em que
se fala
o The telephone is ringing.
Situaes temporrias de mudana
o I am working in a factory for the time
being.
o It is getting colder.
Projetos pessoais num futuro prximo
o She is arriving in Lisbon next
Saturday.
Em ligao com certas expresses de tempo
o now at present at this moment
Usa-se o Present Simple e no o Present Continuous, com os seguintes verbos:
Verbs of
thinking
think
believe
agree
understand
know
remember
forget
Verbs of feeling
want
wish
like
love
hate
Verbs of
perception
Verbs of
possession
see
hear
notice
have
own
belong
Reporting verbs
Other verbs
say
ask
tell
answer
cost
weigh
seem
appear
need
Com os verbos acima citados empregue sempre o Present Simple e nunca o Present Continuous.
Ex.:
I remember his face. (Im remembering his face.)
I know his name. (Im knowing his name.)
I believe you. (Im believing you.)
I like this film. (Im liking this film.)
Use o Present Continuous e nunca o Present Simple para falar de planos e combinaes pessoais.
What time do you meet me?
What time are you meeting me?
PRESENT PERFECT: I HAVE WORKED
PAST SIMPLE: I WORKED
2 de 6
Ao que decorre num tempo indefinido
Ive seen her.
Ao que comea no passado e continua at
ao presente
Ive worked in England for three
years.
Ao que acontece num passado muito
recente
Ive seen her this morning.
Usa-se com just
Ive just written the email.
Usa-se com os seguintes advrbios e
expresses adverbiais:
recently
ever
lately
never
up to now
already
its the first time
yet (interrogative
this morning
and negative)
Usa-se com as soon as, until, when, quando
equivalente a after
Come and see me when (=after) you
have had your dinner.
Ao que decorre num momento bem
definido do passado
I saw her yesterday.
Ao completamente passada sem nenhuma
relao com o presente
I worked in England four years ago.
Usa-se com as seguintes expresses
adverbiais
yesterday
the day before yesterday
last Saturday
last week
a few minutes ago
long ago
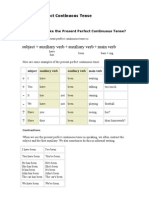
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS: I HAVE BEEN WORKING
Equivale ao Present Perfect; usa-se no mesmo sentido e nas mesmas condies
Exprime, alm disso, reforo de continuidade de ao
Usa-se com adevbios precedidos de all
All the morning
All day
Usa-se (de preferncia ao Present Perfect) com verbos que exprimem uma ao que dura e prolonga
no tempo
expect
learn
lie
live
sit
sleep
stand
stay
study
rest
work
Em vez de dizer I have worked pode dizer I have been working
PAST CONTINUOUS: I WAS WORKING
Equivale ao Present Continuous
3 de 6
Usa-se para exprimir aes simultneas no passado
I was having dinner when the telephone rang.
No se usa com verbos como know, want, ect. (ver Present Simple).
PAST PERFECT: I HAD WORKED
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS: I HAD BEEN
WORKING
Ao anterior a outra no passado
When I arrived, the train had started.
Equivale ao Past Perfect; usa-se no mesmo
sentido
Exprime reforo de durao e continuidade
Usa-se com certos verbos que exprimem uma
ao que dura e se prolonga no tempo
Expect, learn, lie, etc. (ver Present
Perfect Continuous)
IF CLAUSES
As oraes condicionais so normalmente classificadas em trs grupos.
Em cada um deles, as formas seguidamente apresentadas so as mais importantes e as mais comuns.
TIPO 1 EXPRIME UMA CONDIO PROVVEL:
IF
PRESENT
FUTURE OR IMPERATIVE
If
you go to the exhibition,
you will enjoy it.
If
you go to the exhibition,
advise me.
If
she doesnt take care,
shell be hurt.
If
he doesnt train hard,
he wont gain any prize.
TIPO 2 EXPRIME UMA CONDIO IMPROVVEL:
IF
PAST
CONDITIONAL
If
you went to the exhibition,
you would enjoy it.
If
she didnt take care,
she would be hurt.
If
he didnt train hard,
he wouldnt gain any prize.
A forma do conjuntivo do verbo ser (fosse) were em todas as pessoas: If I were, if you were; if he were, etc.
Esta forma usada em ingls nas frases condicionais.
Na linguagem falada, porm, pode usar-se a forma do conjuntivo were ou a forma do indicativo was.
Contudo, a expresso if I were you mantm-se mesmo na lngua falada.
TIPO 3 EXPRIME UMA CONDIO IMPOSSVEL:
4 de 6
IF
PAST PERFECT
PERFECT CONDITIONAL
If
you had gone to the exhibition,
you would have enjoyed it.
If
she hadnt taken care,
she would have been hurt.
If
he hadnt trained hard,
he wouldnt have gained any prize.
MODAL VERBS
CAN / COULD
MUST
SHALL / SHOULD
NEED
MAY / MIGHT
OUGHT TO
WILL / WOULD
DARE
Os chamados Modal Verbs so usados como verbos auxiliares, exprimindo sentidos e funes especficas em ligao com o
verbo principal.
CAN / COULD = to be able to (ser capaz de)
MAY / MIGHT = to be allowed to (ser permitido)
MUST = to have to (ter de / precisar)
SHOULD / OUGHT TO (dever)
SHALL / SHOULD
WILL / WOULD
NEED (precisar)
DARE (ousar / atrver-se)
FUTURE TENSES
Simple Future They will go
Going to Im going to buy
Podemos falar de futuro em ingls usando shall / will (Simple Future) e a forma going to.
SIMPLE FUTURE
I
We
You
shall go
He, she, it
will go
They
A forma will hoje em dia usada para todas as pessoas, exceto na interrogativa. (Nunca pode dizer: Will I open the
window?)
GOING TO FUTURE
Ex.:
Im going to buy a new house.
Is he going to take you to the Zoo?
They are not going to pay me.
5 de 6
Os advrbios ou expresses adverbiais ligadas ao futuro so as seguintes:
soon
tonight
next week
in a few minutes
by next week
shorty
tomorrow
next month
in a few weeks
by two oclock
next year
SHALL /WILL EMPREGA-SE PARA EXPRIMIR:
previses;
Ex.:
promessas e oferecimentos;
Ex.:
Itll soon be midnight. Ill feel better tomorrow.
Ill help you. Ill carry it for you.
pedidos declinados e formais.
Ex.: Will you fetch my cardigan, please?
GOING TO EMPREGA-SE PARA EXPRIMIR:
intenes e decises pessoais previamente tomadas; por isso mais usada com pessoas do que com coisas;
Ex.: Hes going to pick me up at 5. Shes going to sell her house. (Estava previamente combinado e
decidido.)
situaes futuras (futuro prximo), que so consequncia de situaes presentes.
Ex.: Hes eaten too much. He is going to get sick.
FUTURE PERFECT
Esta forma de futuro significa que uma determinada ao ir ficar completada num determinado momento do futuro.
Ex.: I shall have finished the report in three hours. (Eu terei terminado)
IMPERATIVE
O imperative emprega-se para exprimir:
Ordens, advertncias e instrues.
Ex.:
Go ahead! (Vai em frente!)
Dont do that!
Lets + infinitive (envolve o sujeito que fala)
Lets = let us
Ex.:
Lets go ahead! (Vamos em frente!)
6 de 6
You might also like
- 2nd Restatement of ContractsDocument30 pages2nd Restatement of Contractsgeorge100% (1)
- Articles 1Document3 pagesArticles 1nico ryNo ratings yet
- Grammar Glossary PDFDocument11 pagesGrammar Glossary PDFPecky27No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan AssignmentDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Assignmentapi-267195310No ratings yet
- Examples of English TensesDocument17 pagesExamples of English TensesKeerthi VasanNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect ContinuousFelipe R CruzNo ratings yet
- Prepositions: Kinds of Prepositions - Simple PrepositionsDocument2 pagesPrepositions: Kinds of Prepositions - Simple PrepositionsasadrazaNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative Form Uses: Conditional SimpleDocument5 pagesAffirmative Negative Interrogative Form Uses: Conditional SimplePrinces Aliesa Bulanadi0% (1)
- English Verb Tense ReviewDocument46 pagesEnglish Verb Tense ReviewKashishShNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect Te Nse The Present Perfect C Ontinuous Tense Present Perfect Simple vs. Present Perfect C Ontinuous Tense Practice ExercisesDocument15 pagesThe Present Perfect Te Nse The Present Perfect C Ontinuous Tense Present Perfect Simple vs. Present Perfect C Ontinuous Tense Practice ExercisesAdriana DiazNo ratings yet
- 12 English TensesDocument113 pages12 English Tensescharles izquierdoNo ratings yet
- Unit 29-ArticlesDocument15 pagesUnit 29-Articlesapi-252190418No ratings yet
- AdrianDocument138 pagesAdrianLili LiliNo ratings yet
- 1) Simple Past TenseDocument26 pages1) Simple Past TenseHima BinduNo ratings yet
- Present and Past HabitsDocument8 pagesPresent and Past HabitsDespina Trajkova GochevskiNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: 1. Simple Present TenseDocument7 pagesEnglish Tenses: 1. Simple Present TenseDhanes YuwonoNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument49 pagesTensesPepy_GumilarNo ratings yet
- Future PerfectDocument32 pagesFuture PerfectAnita RamosNo ratings yet
- Presentation On TensesDocument10 pagesPresentation On TensesKarthick Raj100% (2)
- Reduced Time ClausesDocument2 pagesReduced Time Clausesalmanzarjoel21No ratings yet
- GrammarDocument66 pagesGrammarinfo.kuijisNo ratings yet
- Grammar Focus: Difference Between "Enough" and "Too Much"Document15 pagesGrammar Focus: Difference Between "Enough" and "Too Much"Angel CaNo ratings yet
- Tenses English ClubDocument46 pagesTenses English ClubShah AkNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple Tense in EnglishDocument6 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Tense in EnglishAntoaneta StancuNo ratings yet
- Participle Clauses (English)Document3 pagesParticiple Clauses (English)schrodinguer1No ratings yet
- Upper Intermediate Unit 12aDocument2 pagesUpper Intermediate Unit 12aRichard HolguínNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous TenseDocument24 pagesPresent Continuous TenseMuhammad Zaky JundanaNo ratings yet
- MODALSDocument5 pagesMODALSCésar Muñoz NicolásNo ratings yet
- What Is The Passive Voice?Document14 pagesWhat Is The Passive Voice?Luis Felipe Aquino QuianeNo ratings yet
- Agus Rizkyawan 1 D4 Elektronika A 7110040022Document9 pagesAgus Rizkyawan 1 D4 Elektronika A 7110040022Agus RizkyawanNo ratings yet
- Basic Questions in EnglishDocument2 pagesBasic Questions in EnglishSherley AmelitaNo ratings yet
- What Did You Do Yesterday?Document10 pagesWhat Did You Do Yesterday?huikisNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous TenseDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous Tenseapi-3718916100% (4)
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish TensesIbrahim Elmogy50% (10)
- Subjunctive Mood Explanation and PracticeDocument3 pagesSubjunctive Mood Explanation and PracticeDiego EspinosaNo ratings yet
- T5 - Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument18 pagesT5 - Gerunds and InfinitivesnachotudelaNo ratings yet
- What Are Nouns?Document33 pagesWhat Are Nouns?unser1941No ratings yet
- Future Perfect Continuous TenseDocument5 pagesFuture Perfect Continuous TenseAditi ParmarNo ratings yet
- Basic Introduction To TensesDocument34 pagesBasic Introduction To TensesPriti PritiNo ratings yet
- Preposition of DirectionDocument17 pagesPreposition of DirectionAbid aliNo ratings yet
- 1definite and Indefinite Articles PDFDocument5 pages1definite and Indefinite Articles PDFgnomonicoNo ratings yet
- Subjunctive Mood LessonDocument14 pagesSubjunctive Mood LessonFrancis PeritoNo ratings yet
- Mrunal EnglishDocument9 pagesMrunal Englishnaklid100% (2)
- Intro Unit Related GrammarDocument8 pagesIntro Unit Related GrammarNavido AhmadiNo ratings yet
- Add - Ness To Form Nouns From AdjectivesDocument6 pagesAdd - Ness To Form Nouns From Adjectiveszahra saoudiNo ratings yet
- Grammar 2 Practice 1Document2 pagesGrammar 2 Practice 1api-252190418No ratings yet
- Adverb Shortcut RulesDocument2 pagesAdverb Shortcut Rulesnilvemangesh100% (1)
- Past Perfect: Had You Studied English Before You Moved To New York?Document6 pagesPast Perfect: Had You Studied English Before You Moved To New York?Stevan NestorovNo ratings yet
- Formula of VerbDocument3 pagesFormula of Verbrezaulaktel100% (2)
- Future TimeDocument18 pagesFuture Timeapi-252190418No ratings yet
- English Past Perfect and Present Perfect 1Document6 pagesEnglish Past Perfect and Present Perfect 1Osama Hayder100% (1)
- Prefixe - SuffixDocument5 pagesPrefixe - SuffixAmy LeafNo ratings yet
- 16 TensesDocument37 pages16 Tensess_zito3460No ratings yet
- Temas Ingles Por Niveles A1 Grammar TopicsDocument3 pagesTemas Ingles Por Niveles A1 Grammar TopicsPedro Rivero Romero100% (1)
- English TensesDocument13 pagesEnglish Tenseslog1alexNo ratings yet
- Grammar Rules SnapshotDocument11 pagesGrammar Rules SnapshotMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Practice ExercisesDocument5 pagesEnglish Grammar Practice ExercisesDiconyatryNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument34 pagesTENSESLalu FahrurroziNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives PDFDocument10 pagesComparatives and Superlatives PDFJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Modals of Advice TheoryDocument3 pagesModals of Advice TheoryFabian RojasNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Exam English 1 Grade 11 (Answer Key)Document4 pagesMid-Term Exam English 1 Grade 11 (Answer Key)jmosutton917100% (1)
- Week 11 SlidesDocument51 pagesWeek 11 SlidesR ZeiNo ratings yet
- TumDocument72 pagesTumserdarankNo ratings yet
- Cricket Rules PDFDocument11 pagesCricket Rules PDFapi-401963473No ratings yet
- Chinese Grammar PowerpptDocument20 pagesChinese Grammar PowerpptJohn CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Word Order in English PDFDocument2 pagesWord Order in English PDFYulia Cajas Suárez100% (1)
- Planificare Calendaristica. Upstream - Upper 2013Document5 pagesPlanificare Calendaristica. Upstream - Upper 2013mirela_ema74100% (1)
- Player Out-Of-BoundDocument5 pagesPlayer Out-Of-BoundNerissa ObliagaNo ratings yet
- Active or Passive - Past SimpleDocument3 pagesActive or Passive - Past SimpleMichael KillinNo ratings yet
- The Sentence TypesDocument6 pagesThe Sentence Typesapi-263480603No ratings yet
- Marking Rubric For Persuasive Texts (NAPLAN Criteria) : NameDocument2 pagesMarking Rubric For Persuasive Texts (NAPLAN Criteria) : NamegemNo ratings yet
- L'aggettivo BelloDocument30 pagesL'aggettivo BelloFrancesca SantoroNo ratings yet
- Análisis de Stock SUMELECDocument202 pagesAnálisis de Stock SUMELECBelenCrossNo ratings yet
- Three Groups of PrepositionsDocument5 pagesThree Groups of PrepositionsbilalturiNo ratings yet
- Pokemon Learning League Prepositions and Prepositional PhrasesDocument18 pagesPokemon Learning League Prepositions and Prepositional PhrasesTimothy Whitfield100% (1)
- Simulado de InglesDocument3 pagesSimulado de InglesJane Cristina da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Sentence Patterns EditedDocument33 pagesSentence Patterns EditedSyahrund MubarackNo ratings yet
- The Participles 2Document13 pagesThe Participles 2krostinichu100% (1)
- Forming and Using The Past Perfect TenseDocument4 pagesForming and Using The Past Perfect TenseIna ZainalNo ratings yet
- Planificare Click On 3Document6 pagesPlanificare Click On 3Ada ComanNo ratings yet
- Causative Form: Grammar in UseDocument9 pagesCausative Form: Grammar in UseSparkle MollyNo ratings yet
- "Fuck", As Most Words in The English Language, Is Derived FromDocument3 pages"Fuck", As Most Words in The English Language, Is Derived FromLauraRosanoNo ratings yet
- Boardwork AnswersDocument3 pagesBoardwork AnswersPearl OgayonNo ratings yet
- Time ClausesDocument5 pagesTime ClausesDana MindrilaNo ratings yet
- Capitalization and Punctuation RulesDocument6 pagesCapitalization and Punctuation RulesJoy Occeña100% (2)
- AppellantDocument7 pagesAppellantRickyNo ratings yet
- ProvimDocument4 pagesProvimPranvera ShehiNo ratings yet