Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematics M-Term 3 Zadocf6Notes
Mathematics M-Term 3 Zadocf6Notes
Uploaded by
Zainariah AbdullahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics M-Term 3 Zadocf6Notes
Mathematics M-Term 3 Zadocf6Notes
Uploaded by
Zainariah AbdullahCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics M-Term 3
zadocf6notes
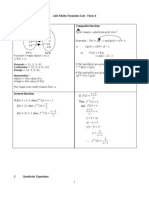
SUMMARY: DIFFERENTIATION OF FUNCTIONS
1. Types of Differentiation
First Principle:
f x x f x
dy
f x lim
x 0
dx
x
Derivatives of some common functions
Functions
(a) Constant:
(b) Power:
Derivatives
dy
0
dx
dy
nax n 1
dx
y=c
y = axn
n
n 1
d
f (c)
x Composite
n f x fns. f x
dx
(d) Logarithmic fns:
y = ln f(x)
(e) Exponential fns:
ye
dy f ' x
dx
f x
x
dy
f ' x e f
dx
d yn
dy
ny n 1
dx
dx
f x
(f) Implicit fns
2. Rules of Differentiation
a)
Constant Multiple Rule
b)
d
d
cf x c f x
dx
dx
Sum and Difference Rule
d
f x g x f x g x
dx
c)
Product Rule
d
f x g x f x g x g x f x
dx
d)
Quotient Rule
g x f x f x g x
d f x
2
dx g x
g x
Mathematics M-Term 3
zadocf6notes
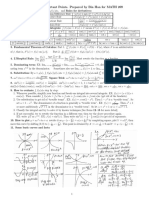
SUMMARY: APPLICATION OF DIFFERENTIATION
1. Gradient of a curve
dy
= Gradient of a curve, y=f(x) at a point P
dx
dy
= Gradient of the tangent to the curve at point P.
dx
2. Increasing and Decreasing functions
dy
0 , then f(x) is an increasing function.
dx
dy
0 , then f(x) is a decreasing function
If y = f(x) is differentiable in (x1, x2 ) and
dx
If y = f(x) is differentiable in (x1, x2 ) and
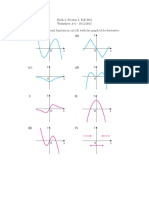
Increasing Function
Decreasing Function
3. Stationary Points
Points P, Q and R are the stationary points of the curve, y=f(x)
At stationary points,
(a) Maximum and Minimum Point
At maximum point P,
dy
d2y
0 ,
0
dx
dx 2
2
dy
f x 0
dx
Mathematics M-Term 3
zadocf6notes
At minimum point Q,
dy
d2y
0 ,
0
dx
dx 2
Or
At point of inflexion R,
d2y
0
dx 2
and
dy
d2y
has the same sign OR
changes sign at the x-coord. of R
dx
dx 2
4. Curve Sketching
Systematic Steps for Curve Sketching
1. Check the equation for any symmetry
2. Determine the points where the curve cuts the coordinates axes
3. Find the Stationary Points
4. Determine the region where the graph exist
5. Determine the behaviour of the curve as x
Note: Different functions require different steps.
Steps: Curve Sketching for Quadratic,Cubic,Quartic fns
Find the obvious points ( y-intercepts and x-intercepts)
Find the points where
dy
0 (stationary points)
dx
Steps: Curve Sketching for Algebraic Rational Functions
Find the obvious points ( y-intercepts and x-intercepts)
dy
0 (stationary points)
dx
Determine the vertical and horizontal asymptotes if any
Find the points where
For checking purposes
Determine whether there is symmetry about the y-axis
Determine the range of y if necessary
Mathematics M-Term 3
zadocf6notes
You might also like
- Differnetial Equation Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesDiffernetial Equation Cheat SheetDebayan Dasgupta100% (5)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDocument5 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralstasos_rex31390% (2)
- H2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimDocument27 pagesH2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimGale HawthorneNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics M-Term 3 Zadocf6NotesDocument4 pagesMathematics M-Term 3 Zadocf6NotesZainariah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Ma 2211Document11 pagesMa 2211Saravanan MJNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummaryZainariah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- m3f15 wrksht6Document4 pagesm3f15 wrksht6EnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0Document30 pagesChapter 0Mc VinothNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedFadzilah YayaNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC Stuff You Must KnowDocument7 pagesAP Calculus BC Stuff You Must KnowJulian PradeepNo ratings yet
- Rumus Matematika Sma InterDocument19 pagesRumus Matematika Sma InterAde JayusNo ratings yet
- Kuliah1 2015Document36 pagesKuliah1 2015wiraNo ratings yet
- Apps of Differentiation SummaryDocument4 pagesApps of Differentiation SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Math ReveiwDocument3 pagesMath ReveiwApache_mooNo ratings yet
- Ma1505 CheatDocument4 pagesMa1505 CheatSouseiseki ChromeNo ratings yet
- 05 2016 - 2017 H2 Maths Differentiation and Its Applications Notes (Final)Document32 pages05 2016 - 2017 H2 Maths Differentiation and Its Applications Notes (Final)ihohsrogsNo ratings yet
- Maths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XDocument16 pagesMaths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XAt TanwiNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: PS+QR QsDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet: PS+QR QsTsehayMegersaNo ratings yet
- 2 Functions of One Variable ExercisesDocument7 pages2 Functions of One Variable Exercisesoceanflow.lrNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Differential and Integral CalculusDocument6 pagesBasic Concepts of Differential and Integral CalculusManoj KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Tcu12 CRC SinglegDocument2 pagesTcu12 CRC SinglegTyler BienhoffNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Formulae ListDocument8 pagesAdd Maths Formulae ListWong Hui SeanNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 3 Derivative of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Dr. Ghada AbdelhadyDocument32 pagesLecture # 3 Derivative of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Dr. Ghada AbdelhadyEsraa AhmadNo ratings yet
- Functions of Several Variables2Document5 pagesFunctions of Several Variables2ngothaiquynhNo ratings yet
- 2.3 and 2.4 Differentiation FormulasDocument12 pages2.3 and 2.4 Differentiation FormulasMaylalaine AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- 209 Formula SheetDocument4 pages209 Formula SheetAlan ChoyNo ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaleeshiNo ratings yet
- Notes Day 18-22Document12 pagesNotes Day 18-22api-272815616No ratings yet
- Integration PDFDocument8 pagesIntegration PDFAre Peace El MananaNo ratings yet
- Math 1920 ReviewDocument7 pagesMath 1920 Reviewxihu813No ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument13 pagesIntegral Calculusgech95465195No ratings yet
- Stuff Must Know Cold NewDocument3 pagesStuff Must Know Cold NewZach FergerNo ratings yet
- Math 285 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesMath 285 Formula SheetjosiahgerberNo ratings yet
- Calculus Review and Formulas: 1 FunctionsDocument11 pagesCalculus Review and Formulas: 1 FunctionsRaymond BalladNo ratings yet
- Topics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014Document5 pagesTopics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014YonYonNo ratings yet
- Calculus Reference (SparkCharts)Document2 pagesCalculus Reference (SparkCharts)www_webb100% (1)
- K 04240010220123020 Homework 02Document3 pagesK 04240010220123020 Homework 02alex_58357No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus Study Guide: AL TEX Version: 1 DisclaimerDocument18 pagesMultivariable Calculus Study Guide: AL TEX Version: 1 DisclaimerOBNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Document19 pagesAdditional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Syazleen Nabilah AkmalNo ratings yet
- Class XII Mathematics Continuity and Differentiability Chapter Notes Key DefinitionsDocument5 pagesClass XII Mathematics Continuity and Differentiability Chapter Notes Key DefinitionsAbhi XavierNo ratings yet
- Theory Definite Integrals PDFDocument35 pagesTheory Definite Integrals PDFvaranasilkoNo ratings yet
- 02 Finite DifferencesDocument27 pages02 Finite DifferencesCham AmirruddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Differentiation Rules: X X y V C V B Ae yDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Differentiation Rules: X X y V C V B Ae yAoSd' TikmanNo ratings yet
- Exame TestDocument2 pagesExame TestSer BlancNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Fourier SeriesDocument11 pagesWeek 8 Fourier SeriesLuqman NHNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Revision Sheet For Class 11 and Class 12 PhysicsDocument0 pagesMathematics Revision Sheet For Class 11 and Class 12 PhysicsSunil PandeyNo ratings yet
- Calculus1eng w5Document66 pagesCalculus1eng w5nedimuzel06No ratings yet
- Roots Newton-Raphson MethodDocument8 pagesRoots Newton-Raphson MethodAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course - Differentiation - 1 - VMathDocument56 pagesBridge Course - Differentiation - 1 - VMathTusharkanti SahuNo ratings yet
- Continuity and Differentiability (Phase 1) - TatvaDocument50 pagesContinuity and Differentiability (Phase 1) - TatvaShiwanshi RaiNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Notes Chapters 1-3Document7 pagesDifferential Equations Notes Chapters 1-3bwahahahaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Economics W 04Document18 pagesMathematical Economics W 04AsiiyahNo ratings yet
- Applications of DerivativesDocument10 pagesApplications of DerivativesRana JahanzaibNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesMathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDarrenPurtillWrightNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)