Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yearly Plan 2015 Science Form 2: SMK Menjalara Bandar Menjalara 52100 Kepong, Kuala Lumpur
Yearly Plan 2015 Science Form 2: SMK Menjalara Bandar Menjalara 52100 Kepong, Kuala Lumpur
Uploaded by
Cheng Kai WahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yearly Plan 2015 Science Form 2: SMK Menjalara Bandar Menjalara 52100 Kepong, Kuala Lumpur
Yearly Plan 2015 Science Form 2: SMK Menjalara Bandar Menjalara 52100 Kepong, Kuala Lumpur
Uploaded by
Cheng Kai WahCopyright:
Available Formats
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
SMK MENJALARA
BANDAR MENJALARA
52100 KEPONG, KUALA LUMPUR
YEARLY PLAN 2015
SCIENCE
FORM 2
PROVIDED BY
NORLIZA IBRAHIM
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
THEME: MANAGEMENT AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 1 - THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES
Week
1
Date
12/1/15 16/1/15
19/1/15 23/1/15
26/1/15 30/1/15
2/2/15 6/2/15
9/2/15 13/2/15
16/2/15 - 20/2/15
Learning Objectives
1.1
Understanding the sensory
organs and their functions.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to:
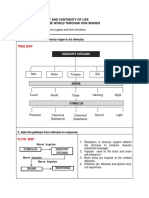
(a) identify and relate a sensory organ to its stimulus,
(b) state the pathway from stimulus to response.
1.2
Understanding the sense of
touch.
A student is able to:
(a) identify the structure of the human skin involved in stimuli
detection,
(b) state the function of different receptors pressure, heat, pain,
(c) draw conclusion on the sensitivity of the skin at different parts of
the body towards stimuli.
1.3
Understanding the sense of
smell.
A student is able to:
(a) identify the structure of the nose,
(b) identify the position of the sensory cells in the detection of smell.
1.4
Understanding the sense of
taste.
A student is able to:
(a) identify the different areas of the tongue that respond to different
taste,
(b) relate the sense of taste with the sense of smell.
1.5
Understanding the sense of
hearing.
A student is able to:
(a) identify the structure of the human ear,
(b) explain the function of the different parts of the ear,
(c) describe how we hear.
1.6
Understanding the sense of
sight.
A student is able to:
(a) identify the structure of the human eye,
(b) explain the functions of different parts of the eye,
(c) describe how we see.
1.7
Understanding light and sight.
A student is able to:
(a) describe the properties of light i.e. reflection and refraction,
(b) state the various defects of vision,
(c) explain ways to correct vision defects,
(d) state and give examples of the limitations of sight,
(e) connect stereoscopic and monocular visions with the survival of
animals,
(f) identify the appropriate device to overcome the limitations of
sight.
CUTI TAHUN BARU CINA
Assessment Evidences
Band 4
Remarks
I-Think (Flow Map)
HOTS
I-Think (Flow Map)
HOTS
Band 2
I-Think (Flow Map)
Band 2
I-Think (Flow Map)
Band 2
Band 4
HOTS
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
23/2/15 27/2/15
2/3/15 6/3/15
1.8
Understanding sound and
hearing.
A student is able to:
(a) describe the properties of sound,
(b) explain the reflection and absorption of sound,
(c) explain the defects of hearing,
(d) explain ways of rectifying the defects in hearing,
(e) state the limitations of hearing,
(f) state the device used to overcome the limitations of hearing,
(g) explain stereophonic hearing.
1.9
Understanding the stimuli and
responses in plants.
A student is able to:
(a) state the stimuli that cause response in plants,
(b) identify the parts of plants sensitive to specific stimulus,
(c) relate the response in plants to their survival.
9/3/15 13/3/15
UJIAN 1
16/3/15 20/3/15
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 1
Band 4
HOTS
Band 5
HOTS
THEME: MANAGEMENT AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 2 - NUTRITION
Week
10
11
Date
23/3/15 27/3/15
30/3/15 3/4/15
Learning Objectives
2.1
Analysing the classes of food.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to:
(a) explain through examples the classes of food,
(b) state the function of each class of food,
(c) test for starch, glucose, protein and fats.
2.2
Evaluating the importance of
a balanced diet.
A student is able to:
(a) state what a balanced diet is,
(b) state the factors that must be considered when planning a
balanced diet,
(c) explain how the factors affect a balanced diet,
(d) state the quantity of energy in each gram of carbohydrate, protein
and fats,
(e) estimate the calories of food taken in a meal,
(f) plan a balanced diet.
2.3
Understanding the digestive
system in man.
A student is able to:
(a) explain what digestion is,
(b) identify the parts of the digestive system,
(c) describe the flow of food particles in the alimentary canal,
(d) state the functions of the organs in the digestive system,
(e) describe the process of digestion in the alimentary canal,
Assessment Evidences
Band 2
Band 4
Remarks
I-Think (Tree Map)
HOTS
I-Think (Bubble Map)
Band 3
I-Think (Circle Map)
I-Think (Flow Map)
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
(f) list the end products of digestion of carbohydrate, protein and
fats.
12
6/4/15 10/4/15
2.4
Understanding the process of
absorption of digested food.
A student is able to:
(a) explain the process of absorption of the products of digestion,
(b) make inference about the absorption of glucose through a Visking
tube.
2.5
Understanding the
reabsorption of water and
defecation.
A student is able to:
(a) state how water is reabsorbed in the large intestine,
(b) explain defecation,
(c) relate the problem of defecation with eating habits.
2.6
Put into practice
the habits of healthy eating.
A student is able to:
(a) justify the importance of eating nutritious food,
(b) put into practice the habits of healthy eating,
(c) justify the generous distribution of food to the
underprivileged/needy,
(d) relate the dining culture of different people to sensitivities and
religious beliefs.
Band 5
HOTS
Band 3
Band 6
HOTS
THEME: MAN AND THE VARIETY OF LIVING THINGS
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 3 - BIODIVERSITY
Week
13
Date
13/4/15 17/4/15
Learning Objectives
3.1
Understanding variety of
living organisms and their
classification.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to:
(a) explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat,
(b) classify various animals based on common characteristics,
(c) classify various plants based on common characteristics,
(d) explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Assessment Evidences
Band 3
Remarks
I-Think (Tree Map)
I-Think (Bubble Map)
THEME: MAN AND THE VARIETY OF LIVING THINGS
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 4 - INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Week
14
Date
20/4/15 24/4/15
Learning Objectives
4.1
Analysing the
interdependence among living
organisms.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to:
(a) state what species, population and community are,
(b) state what habitat and ecosystem are,
(c) identify various habitats in one ecosystem,
(d) explain through examples the interdependence among living
Assessment Evidences
Band 2
Remarks
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
organisms and the environment to create a balanced ecosystem
15
16
17
18
27/4/15 1/5/15
4/5/15 8/5/15
11/5/15 15/5/15
18/5/15 22/5/15
4.2
Evaluating the interaction
between living organisms.
A student is able to:
(a) list the types of interactions between living organisms,
(b) explain with examples the interactions between living organisms,
(c) justify the importance of interaction between living organisms
and the environment,
(d) explain through examples the advantages and disadvantages of
biological control in regulating the number of pest in certain
areas.
4.3
Synthesizing food web.
A student is able to:
(a) explain what producers, consumers and decomposers are,
(b) combine a few food chains to construct a food web,
(c) identify the producer, consumer and decomposer in a food web,
(d) construct a pyramid number from a food chain,
(e) relate the food web and the pyramid number to energy flow,
(f) predict the consequences if a certain component of living
organisms in the ecosystem is missing.
4.4
Analysing photosynthesis.
A student is able to:
(a) state what photosynthesis is,
(b) state the factors required for photosynthesis,
(c) state the products of photosynthesis,
(d) control the variables that are required for photosynthesis,
(e) explain the role of photosynthesis in maintaining a balanced
ecosystem.
4.5
Evaluating the importance of
conservation and preservation
of living organisms.
A student is able to:
(a) explain what conservation and preservation are,
(b) explain the steps taken to preserve and conserve living
organisms,
(c) justify the importance of conservation and preservation
of living organisms,
(d) support activities organised by various parties to preserve and
conserve the living organisms.
4.6
Evaluating the role of man in
maintaining the balance in
nature.
A student is able to:
(a) explain the effects of human activities on the balance in nature,
(b) describe how man solves problems related to environment,
(c) justify that human need a stable, productive and balanced
ecosystem.
PENTAKSIRAN PERTENGAHAN TAHUN PBS
Band 3
Band 6
I-Think (Tree Map)
HOTS
Band 2
Band 3
I-Think (Flow Map)
HOTS
Band 4
Band 5
Band 6
HOTS
Band 2
HOTS
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
19
25/5/15 29/5/15
1/6/15 5/6/15
CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN
8/6/15 12/6/15
THEME: MATTER IN NATURE
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 5 - WATER AND SOLUTION
Week
20
21
22
Date
15/6/15 19/6/15
22/6/15 26/6/15
29/6/15 3/7/15
Learning Objectives
5.1
Analysing the physical
characteristics of water.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to:
(a) state the meaning of the freezing point of water,
(b) state the meaning of the boiling point of water,
(c) describe the physical characteristics of water,
(d) explain through examples the effects of impurities on the
physical characteristics of water.
5.2
Analysing the composition of
water.
A student is able to:
(a) determine the composition of water,
(b) test the presence of hydrogen and oxygen.
5.3
Analysing the
process of
evaporation of
water.
A student is able to:
(a) explain what evaporation is,
(b) explain through examples the factors that affect the rate of
evaporation of water with reference to the Kinetic Theory,
(c) compare and contrast between evaporation and boiling,
(d) describe the application of the evaporation of water in daily life.
5.4
Analysing solution and
solubility.
A student is able to:
(a) explain what solute, solvent and solution are,
(b) contrast and compare between dilute solution, concentrated
and saturated solution,
(c) explain what suspension is,
(d) explain what solubility is,
(e) explain the factors affecting the solubility of solutes in water,
(f) explain the importance of water as a universal solvent in life,
(e) give examples on the uses of organic solvents in our everyday
life.
5.5
Analysing acid and alkali.
A student is able to:
(a) identify the properties of acid,
Assessment Evidences
Remarks
Band 1
Band 4
I-Think (Bubble Map)
HOTS
Band 4
HOTS
Band 5
I-Think (Double Bubble
Map)
HOTS
Band 2
Band 4
Band 5
I-Think (Bubble Map)
HOTS
Band 4
I-Think (Circle Map)
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
(b) identify the properties of alkali,
(c) state that acid and alkali only show their properties in the
presence of water,
(c) explain through examples the definition of acid and alkali,
HOTS
(d) identify the substances which are acidic or alkaline in everyday
life,
(e) state the uses of acid and alkali in daily life,
(f) explain the meaning of neutralisation,
(g) write an equation in words to describe the neutralisation
process,
(h) explain through examples the uses of neutralisation in daily life.
23
24
6/7/15 10/7/15
5.6
Analysing the methods of
water purification.
A student is able to:
(a) list the natural sources of water,
(b) state the reasons for water purification,
(c) describe the various types of water purification,
(d) compare the strengths and weaknesses of the various types of
water purification.
5.7
Analysing the water supply
system.
A student is able to:
(a) describe how the water supply system works,
(b) explain ways to save water.
5.8
Understanding the
preservation of water quality.
A student is able to:
(a) give examples of water pollutants,
(b) explain the effect of water pollution on living things,
(c) explain ways to control water pollution,
(d) explain ways to preserve water and its quality.
13/7/15 17/7/15
Band 3
I-Think (Bubble Map)
I-Think (Tree Map)
Band 3
I-Think (Flow Map)
Band 6
HOTS
CUTI HARI RAYA PUASA
THEME: MATTER IN NATURE
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 6 - AIR PRESSURE
Week
25
Date
20/7/15 24/7/15
Learning Objectives
6.1
Understanding air pressure.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to :
(a) explain the existence of air pressure with reference to the
Kinetic Theory,
(b) explain the factors affecting air pressure.
6.2
Applying the principle of air
A student is able to:
(a) explain with examples things that use the principle of air
Assessment Evidences
Remarks
Band 4
I-Think (Bubble Map)
HOTS
Band 4
HOTS
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
pressure in daily life.
pressure,
(b) generate ideas to solve problems using the principle of air
pressure,
(c) relate the safety measures taken when using gas under high
pressure.
THEME: FORCE AND MOTION
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 7 - DYNAMICS
Week
26
27
Date
27/7/15 31/7/15
3/8/15 7/8/15
Learning Objectives
7.1
Understanding force.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to:
(a) state that a force is a push or a pull,
(b) explain the effects of forces,
(c) explain the various types of forces.
7.2
Understanding the
measurement of force.
A student is able to:
(a) state the unit of force,
(b) explain how a spring balance works,
(c) measure the magnitude of force.
7.3
Application of frictional
force.
A student is able to:
(a) explain with example the existence of frictional force,
(b) state the direction and the magnitude of frictional force,
(c) carry out an experiment to show how different types of surfaces
affect frictional force,
(d) explain the advantages and disadvantages of friction,
(e) explain ways to increase friction,
(f) explain ways to reduce friction,
(g) explain with examples the application of friction in daily life.
7.4
Application of work.
A student is able to:
(a) explain with examples how work is done,
(b) state the unit of work,
(c) calculate the work done.
7.5
Application of power.
A student is able to:
(a) state the meaning of power,
(b) state the unit of power,
(c) calculate power on the work done.
7.6
Analysing the importance of
force in life.
A student is able to:
(a) describe how life will be if force does not exist.
Assessment Evidences
Band 4
Remarks
I-Think (Bubble Map)
HOTS
Band 1
Band 5
I-Think (Bubble Map)
HOTS
Band 4
HOTS
Band 4
HOTS
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
THEME: FORCE AND MOTION
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 8 - SUPPPORT AND MOVEMENT
Week
28
Date
10/8/15 14/8/15
Learning Objectives
8.1
Understanding the support
systems in animals.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to:
(a) explain the support system in vertebrates and the various support
systems in invertebrates,
(b) compare and contrast the support system between land and
aquatic vertebrates,
(c) compare and contrast the support system between land and
aquatic invertebrates.
8.2
Understanding the support
systems in plants.
A student is able to:
(a) explain the various support systems in woody and non woody
plants,
(b) classify plants based on their support systems.
8.3
Appreciating the support
system in living things.
A student is able to:
(a) justify the importance of the support system to living things.
Assessment Evidences
Remarks
Band 3
I-Think (Tree Map)
I-Think (Double Bubble
Map)
Band 4
I-Think (Tree Map)
HOTS
THEME: TECHNOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 9 - STABILITY
Week
29
Date
17/8/15 21/8/15
Learning Objectives
9.1
Understanding that the centre
of gravity affects stability.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to:
(a) determine the point of equilibrium in regular and irregular shapes,
(b) relate the point of equilibrium as the centre of gravity of objects,
(c) relate the centre of gravity to the stability of objects,
(d) determine the factors affecting the stability of object.
9.2
Appreciating the importance
of stability.
A student is able to:
(a) suggest ways to improve the stability of objects around them,
(b) explain with examples the application of stability in life.
Assessment Evidences
Remarks
Band 4
Band 5
I-Think (Bubble Map)
HOTS
Band 6
HOTS
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
THEME: TECHNOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY
LEARNING AREA: CHAPTER 10 - SIMPLE MACHINE
Week
30
Date
24/8/15 28/8/15
31
31/8/15 4/9/15
32
7/9/15 11/9/15
33
14/9/15 18/9/15
Learning Objectives
10.1
Analysing levers.
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to:
(a) list things around them that use the principle of the lever,
(b) state what a lever can do,
(c) identify load, force and fulcrum in the lever,
(d) classify levers,
(e) explain what is meant by the moment of a force,
(b) solve problems related to levers.
10.2
Appreciating the innovative
efforts in the design of
machine to simplify work
.
A student is able to:
(a) design or improvise a device that use the principle of a lever.
Assessment Evidences
Remarks
Band 1
Band 2
Band 3
Band 4
I-Think (Circle Map)
I-Think (Tree Map)
HOTS
Band 6
HOTS
ULANGKAJI / MELENGKAPKAN PENTAKSIRAN SEKOLAH (PS)
21/9/15 25/9/15
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 2
34
28/9/15 2/10/15
ULANGKAJI / MELENGKAPKAN PENTAKSIRAN SEKOLAH (PS)
35
5/10/15 9/10/15
PENTAKSIRAN AKHIR TAHUN PBS
36
12/10/15 16/10/15
37
19/10/15 23/10/15
38
26/10/15 30/10/15
PERBINCANGAN DAN PEMBETULAN PENTAKSIRAN AKHIR TAHUN PBS /
MELENGKAPKAN PENTAKSIRAN SEKOLAH (PS)
:: Science Yearly Plan Form 2 ::
39
2/11/15 6/11/15
40
9/11/15 13/11/15
41
16/11/15 19/11/15
21/11/15 31/12/15
CUTI BERGILIR SPM / AKTIVITI BERSAMA PELAJAR
CUTI AKHIR TAHUN
You might also like
- RF 265 266 Ab Samsung Refri PDFDocument107 pagesRF 265 266 Ab Samsung Refri PDFaderlochNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Sustainability Multidisciplinary Ubd UnitDocument11 pages4th Grade Sustainability Multidisciplinary Ubd Unitapi-267230750No ratings yet
- Environmental Science Curriculum GuideDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Science Curriculum GuideAshMere MontesinesNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Biological SciencesDocument10 pagesSyllabus Biological SciencesAris PetNo ratings yet
- S5 LT-II-h-8Document6 pagesS5 LT-II-h-8Kristine Joy PitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Understanding Our EnvironmentDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Understanding Our EnvironmentJosieA_YNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1Document8 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1ssukgantiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science CAPE SyllabusDocument61 pagesEnvironmental Science CAPE Syllabustevin_prawl75% (16)
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1adleenshazNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Mahfuzah AzmiNo ratings yet
- RPT Science FRM 1Document9 pagesRPT Science FRM 1Maslen DadeeNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1300664No ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1 2015Document6 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1 2015Muhd Mustaffa Kamal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan For Science Form 1Document27 pagesYearly Plan For Science Form 1Nor FaizahNo ratings yet
- RPT Sains Ting. 1Document10 pagesRPT Sains Ting. 1Norzaliatun RamliNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan 2017 SC F2Document11 pagesYearly Lesson Plan 2017 SC F2Aisya OmeiraNo ratings yet
- RPT SC F2 2015Document21 pagesRPT SC F2 2015kriizNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Year 1Document45 pagesIntegrated Science Year 1Andre Swaggerific PickettNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science F1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science F1Lydia HuangNo ratings yet
- Barren County High School Course Syllabus: AP Environmental Science SyllabusDocument8 pagesBarren County High School Course Syllabus: AP Environmental Science Syllabusshadab0123No ratings yet
- Sci - LP1-9 Environmental Principles, QE ReviewDocument9 pagesSci - LP1-9 Environmental Principles, QE ReviewluigimanzanaresNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Choo Li MingNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Noralizah IsmadiNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Nur Hayati YusofNo ratings yet
- Biology Life+on+Earth+Program+ 2007Document14 pagesBiology Life+on+Earth+Program+ 2007Elijah MercadoNo ratings yet
- PEE - Level of Organization in EcologyDocument27 pagesPEE - Level of Organization in EcologyNathaniel NapayNo ratings yet
- DLL Science Grade9 Quarter1 Week2 (Palawan Division)Document5 pagesDLL Science Grade9 Quarter1 Week2 (Palawan Division)Cherry TamboongNo ratings yet
- Unit - Chesapeake Bay Jody FagnanoDocument26 pagesUnit - Chesapeake Bay Jody Fagnanoapi-307317734No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For COT First QuarterDocument4 pagesLesson Plan For COT First QuarterJunnel Maravilla100% (1)
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Badlishah Annual Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 (2016)Document30 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Badlishah Annual Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 (2016)wienna1987No ratings yet
- Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities NotesDocument15 pagesWeek Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities NoteswahyuniLoveSudirNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Biology Form 4 2015Document48 pagesYearly Plan Biology Form 4 2015FidaNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 2Document14 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Sains Ting 2Norhidayah Binti PazilNo ratings yet
- Bio@Lp 2012Document46 pagesBio@Lp 2012Mariah ThezNo ratings yet
- AP Envi Syllabus.Document15 pagesAP Envi Syllabus.Sherlyn TalleNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledGwendolyn CalatravaNo ratings yet
- Class 6th HOLIDAY HOMEWORK (2022-23)Document8 pagesClass 6th HOLIDAY HOMEWORK (2022-23)ShauryaNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1-12 Daily LessonDocument2 pagesGRADES 1-12 Daily LessonSj Miasco-MejongNo ratings yet
- Living and Working in Space: Habitat: Teacher's GuideDocument8 pagesLiving and Working in Space: Habitat: Teacher's GuideDemetrius CioncaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6: Divine Word College of LegazpiDocument33 pagesGrade 6: Divine Word College of LegazpiJanelle Grecia NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Plan Sains t2Document39 pagesPlan Sains t2Arif ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: History of Life On EarthDocument43 pagesLesson Plan: History of Life On EarthVanezaKateYeclaRetinioNo ratings yet
- Science - Grade 5 - Text: Course DescriptionDocument6 pagesScience - Grade 5 - Text: Course DescriptionZanfalawy BashaNo ratings yet
- Sci - LP2-1 Biology, Branches and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesSci - LP2-1 Biology, Branches and ApplicationsluigimanzanaresNo ratings yet
- Siaton Campus: Socsci Ed6Document14 pagesSiaton Campus: Socsci Ed6canon140102No ratings yet
- Sci - LP2-5 Reproduction, EcologyDocument10 pagesSci - LP2-5 Reproduction, EcologyluigimanzanaresNo ratings yet
- G8 Q4 Bio ReviewedDocument5 pagesG8 Q4 Bio ReviewedSha RonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Health 9Document2 pagesLesson Plan Health 9Erlyn DalNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems & Interactions: Grade 7Document26 pagesEcosystems & Interactions: Grade 7api-296438662No ratings yet
- RPT Sains Ting. 3 2016Document20 pagesRPT Sains Ting. 3 2016NorSafarien RahimNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Grade 8 ScienceDocument42 pagesUnit Plan Grade 8 Scienceapi-242221534100% (1)
- Curriculum ScienceDocument2 pagesCurriculum ScienceAlewasi WalaaNo ratings yet
- Ubdstage 3 Climatefinalsept 7Document6 pagesUbdstage 3 Climatefinalsept 7api-291164571No ratings yet
- Yearly Planning Science1 EditedDocument24 pagesYearly Planning Science1 Editedalena67No ratings yet
- Beaconhouse School System Academic Year 2021-22: Scheme of Work For Class 6Document9 pagesBeaconhouse School System Academic Year 2021-22: Scheme of Work For Class 6Saima Usman/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Unit Plan Interactions and EcosystemsDocument20 pagesScience 7 Unit Plan Interactions and Ecosystemsapi-266874931No ratings yet
- GR 7 SummernaturallyDocument1 pageGR 7 SummernaturallyDushyant SinghNo ratings yet
- SC 102 Course Outline 1st Sem 2018Document3 pagesSC 102 Course Outline 1st Sem 2018Jocelle Ann RicablancaNo ratings yet
- Future Earth: Advancing Civic Understanding of the AnthropoceneFrom EverandFuture Earth: Advancing Civic Understanding of the AnthropoceneNo ratings yet
- Ocbc Financial Wellness Index ReportDocument37 pagesOcbc Financial Wellness Index ReportCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Annex 1 - General InformationDocument4 pagesAnnex 1 - General InformationCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Attendance - Week 1 - 21102021: Student AnswersDocument4 pagesAttendance - Week 1 - 21102021: Student AnswersCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- FEM3004 Chapter 3 Sampling DistributionDocument20 pagesFEM3004 Chapter 3 Sampling DistributionCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- MASCO 3eDocument242 pagesMASCO 3eCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Attitudes & Knowledge Regarding Municipal Waste Among Students. Case Study: Bucharest Academy of Economic StudiesDocument14 pagesEvaluation of Attitudes & Knowledge Regarding Municipal Waste Among Students. Case Study: Bucharest Academy of Economic StudiesCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Ac EcDocument20 pagesAc EcCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Resources, Conservation and Recycling: The Effects of Behavior and Attitudes On Drop-Off Recycling ActivitiesDocument8 pagesResources, Conservation and Recycling: The Effects of Behavior and Attitudes On Drop-Off Recycling ActivitiesCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Alternative Solid Waste Management For Putrajaya Malaysia Towards Low-Carbon SocietyDocument2 pagesAlternative Solid Waste Management For Putrajaya Malaysia Towards Low-Carbon SocietyCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Household Hazardous Waste Management in MalaysiaDocument8 pagesHousehold Hazardous Waste Management in MalaysiaCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 7 Analyzing The Moderating VariableDocument27 pages11 Chapter 7 Analyzing The Moderating VariableCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Clustering The Consumers According To Their Environmental Concern: A Study in The Turkish MarketDocument6 pagesClustering The Consumers According To Their Environmental Concern: A Study in The Turkish MarketCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Why Are Consumers Going Green - The Role of Environmental Concerns in Private Green-Is Adoption - Kranz Picot 2011Document13 pagesWhy Are Consumers Going Green - The Role of Environmental Concerns in Private Green-Is Adoption - Kranz Picot 2011Cheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Bicycle Policy in DenmarkDocument38 pagesBicycle Policy in DenmarkCheng Kai Wah100% (1)
- Trudel 2016Document69 pagesTrudel 2016Cheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- f2 Chapter 1-1.1Document2 pagesf2 Chapter 1-1.1Cheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- Design of Partially Combined Sewerage SystemDocument18 pagesDesign of Partially Combined Sewerage SystemBurhan Zaheer100% (1)
- DLL - Epp 6 - Q4 - W1Document6 pagesDLL - Epp 6 - Q4 - W1Akho Nhi100% (1)
- Dee Deng's PresentationDocument31 pagesDee Deng's PresentationИгорь МореходовNo ratings yet
- Safety, Efficacy, and Mechanisms of Action of Cannabinoids in Neurological Disorders.Document9 pagesSafety, Efficacy, and Mechanisms of Action of Cannabinoids in Neurological Disorders.Sindy Licette PiñeroNo ratings yet
- IS-15683-Product-Manual FireextinguisherDocument15 pagesIS-15683-Product-Manual FireextinguisherGyanendra Narayan NayakNo ratings yet
- Setting Outlook RulesDocument2 pagesSetting Outlook Ruleswijaya_dny0% (1)
- AADE 05 NTCE 52 - PatilDocument8 pagesAADE 05 NTCE 52 - PatilAhmad Reza FarokhiNo ratings yet
- Polyflex 201 EnglishDocument2 pagesPolyflex 201 EnglishcesarNo ratings yet
- Managing Windows Server: With Windows Admin CenterDocument31 pagesManaging Windows Server: With Windows Admin CenterKocsis Csaba ÖrkényNo ratings yet
- FDN-218144 Introduction To The Social and Medical Models of DisabilityDocument4 pagesFDN-218144 Introduction To The Social and Medical Models of DisabilityAarya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Personal Branding Workbook - Ext - 2nd EdDocument23 pagesPersonal Branding Workbook - Ext - 2nd EdMiguelito JeromeNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Integral TheoryDocument24 pagesAn Overview of Integral TheoryRytis JuozapavičiusNo ratings yet
- Jessica: Allman Bros. Intro (Acoustic) (Reverb)Document8 pagesJessica: Allman Bros. Intro (Acoustic) (Reverb)Josue Daniel ResendizNo ratings yet
- TRD Vs ASMEDocument1 pageTRD Vs ASMEsirang07100% (1)
- Current Transducer Test FormDocument8 pagesCurrent Transducer Test FormArun Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- Steyr S MaticDocument6 pagesSteyr S Maticclcasal0% (1)
- SLES. ESP - Intervention of Learning Resources K 12 2020Document33 pagesSLES. ESP - Intervention of Learning Resources K 12 2020Catherinei BorilloNo ratings yet
- Regents Cells and Human BodyDocument8 pagesRegents Cells and Human Bodyapi-303120399No ratings yet
- Lexi BDocument62 pagesLexi BPetruss RonyyNo ratings yet
- Napul ResumeDocument2 pagesNapul ResumeNp LbNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives Interactive PracticeDocument5 pagesComparatives and Superlatives Interactive Practiceyenifer sanchezNo ratings yet
- 5 Day Bro Split Workout Routine Spreadsheet - LiftVault - Com - 4Document30 pages5 Day Bro Split Workout Routine Spreadsheet - LiftVault - Com - 4deepak799sgNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae of Supramaniyan KumarDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae of Supramaniyan KumarSupramaniyan kumarNo ratings yet
- Instrukcja Obsługi TC-6 Felicia - AngielskiDocument24 pagesInstrukcja Obsługi TC-6 Felicia - Angielskiadrianadik100% (2)
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their Properties PDFDocument13 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their Properties PDFpieNo ratings yet
- LMP 400-401 430-431 Series: Maximum Working Pressure Up To 6 Mpa (60 Bar) - Flow Rate Up To 740 L/MinDocument12 pagesLMP 400-401 430-431 Series: Maximum Working Pressure Up To 6 Mpa (60 Bar) - Flow Rate Up To 740 L/MinChris BanksNo ratings yet
- Stage 7 SampleDocument48 pagesStage 7 SampleYug ChotaiNo ratings yet
- Read The Following Text and Answer The QuestionsDocument10 pagesRead The Following Text and Answer The QuestionsNixon RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Case Digests in PropertyDocument95 pagesCase Digests in PropertyRemelyn SeldaNo ratings yet