Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface)
FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface)
Uploaded by
Dinesh Kumar P0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesFDDI is a token ring technology that uses fiber optic cables to provide faster speeds of up to 100 Mbps over longer distances of up to 100 km compared to traditional token rings. It uses a dual counter-rotating ring topology with an outer ring for data transfer and an inner ring to take over if the outer ring fails. Stations can be dual attachment on both rings or single attachment on one ring. FDDI provides high reliability by using concentrators to connect stations to the rings and remove any faulty nodes. It uses a timed token rotation protocol to regulate asynchronous and synchronous traffic based on target and actual token rotation times.
Original Description:
FDDI
Original Title
FDDI
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFDDI is a token ring technology that uses fiber optic cables to provide faster speeds of up to 100 Mbps over longer distances of up to 100 km compared to traditional token rings. It uses a dual counter-rotating ring topology with an outer ring for data transfer and an inner ring to take over if the outer ring fails. Stations can be dual attachment on both rings or single attachment on one ring. FDDI provides high reliability by using concentrators to connect stations to the rings and remove any faulty nodes. It uses a timed token rotation protocol to regulate asynchronous and synchronous traffic based on target and actual token rotation times.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesFDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface)
FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface)
Uploaded by
Dinesh Kumar PFDDI is a token ring technology that uses fiber optic cables to provide faster speeds of up to 100 Mbps over longer distances of up to 100 km compared to traditional token rings. It uses a dual counter-rotating ring topology with an outer ring for data transfer and an inner ring to take over if the outer ring fails. Stations can be dual attachment on both rings or single attachment on one ring. FDDI provides high reliability by using concentrators to connect stations to the rings and remove any faulty nodes. It uses a timed token rotation protocol to regulate asynchronous and synchronous traffic based on target and actual token rotation times.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
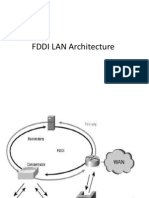
FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface):
Token rings are susceptible to failures
FDDI is a token ring technology with 100 Mbps
Uses fibre optical cables
Token ring:4 or 16 Mbps; FDDI upto 100 km
Token ring 50 to 250 stations; FDDI 500 stations
Operates in various transmission modes
Topology:
-
FDDI uses pair of rotating rings
Outer ring for data transfer
Inner ring replaces outer ring in case of failure
Replacement done by nearby station
Types of stations:
1. Dual attachment station (Class A)
2. Single attachment station (Class B)
FDDI Reliability:
-
Bypass switch or Concentrator (CON)
A station equipped with this will be removed if it was failed.
A CON is used to connect station to ring and remove faulty nodes
Uses creative topologies
Concentrator tree with loopback Upper and lower ends are connected
FDDI Components:
1
SMT (Station Management) Describe about management of stations
In FDDI packet is referred as frame
The Timed Token Rotation Protocol:
-
Timed token rotation protocol
Synchronous & Asynchronous services
Target Token Rotation Time(TTRT)
Token Rotation Time:
-
Time taken for a token to complete one cycle
Rules:
1. ASynchronous traffic: TRT<TTRT -> Allow data
2. Synchronous traffic: - Each station reserves bandwidth
Audio and Video transmission over FDDI:
-
Depends on TRT and TTRT ratio
1. If TRT<TTRT then data can be sent until condition violates
2. If TRT>TTRT then station can transmit only synchronous data
You might also like
- Comptia Net+ NotesDocument8 pagesComptia Net+ NotesZestypolo100% (2)
- Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) : Computer NetworksDocument16 pagesFiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) : Computer NetworksRam ChandruNo ratings yet
- Token Ring: Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceDocument23 pagesToken Ring: Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceGirija VaniNo ratings yet
- FDDI Unit3Document14 pagesFDDI Unit3fahad321activebsrNo ratings yet
- Local Area Networks: Guest Instructor Elaine WongDocument29 pagesLocal Area Networks: Guest Instructor Elaine WongSahil AbbasNo ratings yet
- TCOM513 Lecture2Document110 pagesTCOM513 Lecture2Pranveer Singh PariharNo ratings yet
- Token RingDocument23 pagesToken RingManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Networks: Token Ring and FDDI 1Document25 pagesNetworks: Token Ring and FDDI 1Febi Audi RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Network andDocument21 pagesNetwork andapi-3701823No ratings yet
- Presentation On Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) &Document16 pagesPresentation On Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) &Shaurya KapoorNo ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceDocument23 pagesFiber Distributed Data InterfaceKRISHAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- LAN (Local Area Network) : Ethernet (IEEE 802.3)Document6 pagesLAN (Local Area Network) : Ethernet (IEEE 802.3)Anand S PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed Data Interface: By: Aziz Ur RehmanDocument26 pagesFiber Distributed Data Interface: By: Aziz Ur Rehmanapi-19795318No ratings yet
- FDDIDocument12 pagesFDDI2224 Momynul IslamNo ratings yet
- Fddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)Document16 pagesFddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)jaigauthamNo ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceDocument27 pagesFiber Distributed Data InterfaceupamaharikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceDocument23 pagesFiber Distributed Data Interfacelakshay187No ratings yet
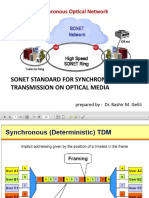
- Synchronous Optical Network: Sonet Standard For Synchronous Data Transmission On Optical MediaDocument19 pagesSynchronous Optical Network: Sonet Standard For Synchronous Data Transmission On Optical Mediamohammed draeyNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Caramat, Exequiel Kirby EDocument20 pagesPrepared By: Caramat, Exequiel Kirby EPopoyNo ratings yet
- Traditional vs. Synchronized: Juniper Business Use OnlyDocument8 pagesTraditional vs. Synchronized: Juniper Business Use Onlyanusree_bhattacharjeNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Overview: Standards and Opera - OnDocument7 pagesEthernet Overview: Standards and Opera - OnMalinga DabareraNo ratings yet
- Networking WithDocument13 pagesNetworking With09m008_159913639No ratings yet
- Optical NWDocument39 pagesOptical NWAbhijeet NandanwankarNo ratings yet
- Q. What Does FDDI Stand For?Document77 pagesQ. What Does FDDI Stand For?GauravNo ratings yet
- Token RingDocument26 pagesToken Ringapi-281601506No ratings yet
- Station Management ProtocolDocument9 pagesStation Management ProtocolAnish VeettiyankalNo ratings yet
- IEEE 803.2 / 802.2: Network TopologyDocument7 pagesIEEE 803.2 / 802.2: Network TopologySudhir MaherwalNo ratings yet
- Clase 2. Servicios WAN - Parte 1 PDFDocument71 pagesClase 2. Servicios WAN - Parte 1 PDFCarmita PinduisacaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Communication and Networks (ECE4005)Document64 pagesFiber Optic Communication and Networks (ECE4005)sai KarthikNo ratings yet
- ALC SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideDocument46 pagesALC SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideMaster22No ratings yet
- FDDIDocument1 pageFDDIdolon10No ratings yet
- Syed Shujat Ali 1421-311065 M Masoud Ahmad 1421-211016 Numan Ahmad Naseer 1421-211Document21 pagesSyed Shujat Ali 1421-311065 M Masoud Ahmad 1421-211016 Numan Ahmad Naseer 1421-211Roberto CotzaNo ratings yet
- What Is NGN-WPS OfficeDocument17 pagesWhat Is NGN-WPS OfficeYawar ArslanNo ratings yet
- Dvanced Omputer Etworks: LinklayerDocument73 pagesDvanced Omputer Etworks: LinklayerAmna HudaNo ratings yet
- GPONDocument33 pagesGPONRajiv Ranjan100% (2)
- William Stallings Data and Computer Communications: LAN SystemsDocument38 pagesWilliam Stallings Data and Computer Communications: LAN SystemsLê Đắc Nhường (Dac-Nhuong Le)No ratings yet
- Networking Concepts: Fore Academy Security EssentialsDocument10 pagesNetworking Concepts: Fore Academy Security EssentialsAisyatul FadlilahNo ratings yet
- Transmissions Back OfficeDocument9 pagesTransmissions Back OfficeEdwin NgaruiyaNo ratings yet
- First Generation Optical NetworkDocument68 pagesFirst Generation Optical NetworkPonmalar Sivaraj50% (2)
- Fddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)Document15 pagesFddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)ashok_it87No ratings yet
- What Is Fddi?: Counter-Rotating Fiber Optic Rings)Document21 pagesWhat Is Fddi?: Counter-Rotating Fiber Optic Rings)jibeshmNo ratings yet
- CCNA1 M6 Ethernet FundamentalsDocument17 pagesCCNA1 M6 Ethernet FundamentalstheonewhoNo ratings yet
- LANDocument38 pagesLANDenise NelsonNo ratings yet
- Abb C37.94Document4 pagesAbb C37.94JMColsNo ratings yet
- UMTS and IMT-2000Document168 pagesUMTS and IMT-2000Kumara Raja JettiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Link Layer and LansDocument20 pages2 - Link Layer and Lansep21b004No ratings yet
- Welcome To The FDDI Tutorial!Document63 pagesWelcome To The FDDI Tutorial!api-19772839No ratings yet
- Optical NetworksDocument46 pagesOptical NetworksChakravarthi ChittajalluNo ratings yet
- Mac 2Document58 pagesMac 2thisisabhay01No ratings yet
- Subject Code: CS2060: High Speed NetworksDocument9 pagesSubject Code: CS2060: High Speed NetworksmanoprabhaNo ratings yet
- Other Technologies & Network Architecture: Session 7Document23 pagesOther Technologies & Network Architecture: Session 7Aravind BhomboreNo ratings yet
- MacDocument58 pagesMacAnnisa HaditaNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Optical Networks Sonet/Sdh:: Multiplexing SimplificationDocument21 pagesUnit-V Optical Networks Sonet/Sdh:: Multiplexing SimplificationPiriyangaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument19 pagesComputer Networkingemad11518No ratings yet
- Optical Transport Network (OTN)Document20 pagesOptical Transport Network (OTN)Harish KumawatNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- Int 3 MTDocument1 pageInt 3 MTDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering SyllabusDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering SyllabusDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Important Questions in AIDocument2 pagesImportant Questions in AIDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- DSL & CategoriesDocument7 pagesDSL & CategoriesDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- C PgmsDocument8 pagesC PgmsDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Slip & PPP ProtocolDocument9 pagesSlip & PPP ProtocolDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Experiment Details - AlgorithmDocument2 pagesExperiment Details - AlgorithmDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- First Order Logic: More Expressive Than Propositional LogicDocument2 pagesFirst Order Logic: More Expressive Than Propositional LogicDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Pointers in CDocument7 pagesPointers in CDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Basic DfwmacDocument6 pagesBasic DfwmacDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Cellular Wireless NetworksDocument5 pagesCellular Wireless NetworksDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- DNS - Domain Name Server - UDP - Networks & DBMS Lab - C ProgramDocument3 pagesDNS - Domain Name Server - UDP - Networks & DBMS Lab - C ProgramDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Cdma: Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Systems UseDocument5 pagesCdma: Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Systems UseDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet