Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PR2016 Weekly Guide 1448 SEM 1
PR2016 Weekly Guide 1448 SEM 1
Uploaded by
Leonardo Torres PaganOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PR2016 Weekly Guide 1448 SEM 1
PR2016 Weekly Guide 1448 SEM 1
Uploaded by
Leonardo Torres PaganCopyright:
Available Formats
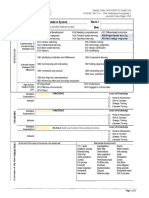
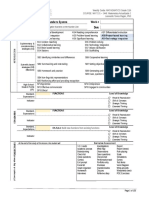
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INITIAL ACTIVITIES
Lesson SYLLABUS
Academic
Strategies (AS)
INTRODUCCION
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Week #
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INITIAL ACTIVITIES
Lesson
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INTEGERS
Lesson Integers
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
2
Tuesday, August 18, 2015
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.1.0
6.N.1.2 Reconoce que el valor absoluto de un nmero entero
es su distancia desde 0 en u na recta numrica; interpreta el
valor absoluto como la magnitud de u na cantidad positiva o
negativa en u na situacin de vida diaria
6.N.1.0
6.N.4.1 Reconoce problemas que contengan la suma de
nmeros enteros y los resuelve mediante la recta numrica,
patrones, modelos concretos y semi-concretos,
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
Read and write integers numbers;
Locate integers numbers using the
number line;
Compare integers numbers using the
number line and mentally;
Appreciate the clarity of mathematical
language
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INTEGERS
Lesson Properties of integers
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Thursday, August 20, 2015
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.A.8.3
6.A .8.3 Aplica la propiedad conmutativa, asociativa y
distributiva para crear y evaluar expresiones equivalentes,
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Recognize the properties of the
integers numbers;
Show desire for accuracy.
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INTEGERS
Lesson Order of operations
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
3
Tuesday, August 25, 2015
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.A.7.1
6.A .7.1 Aplica el orden de operaciones para evaluar
expresiones
6.N.3.0
6.N.3.3 Efecta con fluidez las operaciones y resuelve
problemas que involucran las operaciones bsicas con
nmeros enteros
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Use the order of operation to evaluate
expressions and formulas;
Develop ability to follow a sequence of
rules
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INTEGERS
Lesson STORM
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Thursday, August 27, 2015
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
6.N.3.0
6.N.3.4 Identifica y resuelve situaciones en las que se utilice
suma, resta, multiplicacin y divisin de nmeros enteros
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INTEGERS
Lesson Evaluation and formulas
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Tuesday, September 1,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.A.7.1
6.A .7.1 Aplica el orden de operaciones para evaluar
expresiones
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Use the order of operation to evaluate
expressions and formulas;
Develop ability to follow a sequence of
rules
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INTEGERS
Lesson Problem solving
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Thursday, September 3,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.4.1
6.N.3.4 Identifica y resuelve situaciones en las que se utilice
su m a, resta, multiplicacin y divisin de nmeros enteros
6.N.3.0
6.N.3.4 Identifica y resuelve situaciones en las que se utilice
sum a, resta, multiplicacin y divisin de nmeros enteros
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Solve problems using integers
numbers;
Develop an alert mind
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INTEGERS
Lesson TEST
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Tuesday, September 8,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.3.0
6.N.3.3 Efecta con fluidez las operaciones y resuelve
problemas que involucran las operaciones bsicas con
nmeros enteros
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Score correctly at least 70% of the
questions of the test;
Demonstrate respect for knowledge
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit INTEGERS
Lesson TEST DISCUSSION
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Thursday, September 10,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Identify his strengths and
weaknesses;
Show respect for thoroughness in
performing a task
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit FRACTIONS
Lesson Concept of fraction.
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Tuesday, September 15,
2015
INTRODUCCION
Equivalence
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
4.N.1.0
6.N.1.2 Reconoce que el valor absoluto de un numero entero
es su distancia desde 0 en u na recta numrica; interpreta el
valor absoluto como la magnitud de u na cantidad positiva o
negativa en u na situacin de vida diaria
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Define fractions visually;
Determine the equivalence relations
between fractions visually and
algebraically; Compare fractions;
Develop efficient mathematical
reasoning
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit FRACTIONS
Lesson Multiplication and division
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Thursday, September 17,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
5.N.3.0
7.N.2.3 Aplica las propiedades de las operaciones como o
estrategias para sumar, restar, multiplicar y dividir n m eros
racionales; estima y juzga la razonabilidad de los resultados al
resolver problemas
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Multiply fractions using the algorithm;
Divide fractions using the algorithm;
Develop and alert mind
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit FRACTIONS
Lesson Addition and subtraction
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Tuesday, September 22,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
5.N.3.2
7.N.2.3 Aplica las propiedades de las operaciones como o
estrategias para sumar, restar, multiplicar y dividir n m eros
racionales; estima y juzga la razonabilidad de los resultados al
resolver problemas
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
7.N.3.0
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
7.N.3.1 Comprende que la multiplicacin se extiende desde las Strategic Thinking
fracciones hasta los nmeros racionales al requerir que las
Extended Thinking
operaciones cumplan con las propiedades de las operaciones,
particularmente la propiedad distributiva, lo que lleva a
resultados como (/)(/) = /,y las reglas de multiplicacin de
n m eros con signos, Interpreta productos de nmeros
racionales en contextos de la vida diaria.
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Define homogeneous fractions;
Add and subtract fractions with like
denominators;
Appreciate the math rigor
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit FRACTIONS
Lesson Addition and subtraction
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Thursday, September 24,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
5.N.3.2
7.N.2.3 Aplica las propiedades de las operaciones como o
estrategias para sumar, restar, multiplicar y dividir nmeros
racionales; estima y juzga la razonabilidad de los resultados al
resolver problemas
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
7.N.3.0
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
7.N.3.1 Comprende que la multiplicacin se extiende desde las Strategic Thinking
fracciones hasta los nmeros racionales al requerir que las
Extended Thinking
operaciones cumplan con las propiedades de las operaciones,
particularmente la propiedad distributiva, lo que lleva a
resultados como (/)(/) = /,y las reglas de multiplicacin de
n m eros con signos, Interpreta productos de nmeros
racionales en contextos de la vida diaria.
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Define heterogeneous fractions;
Add and subtract fractions with unlike
denominators;
Develop sense of satisfaction with the
work done
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit FRACTIONS
Lesson Problem solving
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Tuesday, September 29,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
5.N.3.0
7.N.2.3 Aplica las propiedades de las operaciones como o
estrategias para sumar, restar, multiplicar y dividir nmeros
racionales; estima y juzga la razonabilidad de los resultados al
resolver problemas
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Solve problems that involve common
fractions;
Appreciate the beauty of math;
Develop the desire to seek the truth.
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit FRACTIONS
Lesson TEST AND ASSESSMENT
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
8
Thursday, October 1, 2015
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Score correctly at least 70% of the
questions of the test; Demonstrate
respect for knowledge
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit DECIMALS
Lesson Fractions and decimals
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
Tuesday, October 6, 2015
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.5.3
6.N.5.3 Demuestra las representaciones equivalentes de
fracciones y decimales; traduce con fluidez entre estas
representaciones (fraccin <)decimal <)porciento), segn
un contexto o situacin de problema,
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Establish the relationship between
decimals and common fractions;
Read and write decimals; Determine
the value of a digit;
Appreciate the clarity of mathematical
language .
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit DECIMALS
Lesson Addition and subtraction
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
9
Thursday, October 8, 2015
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
5.N.3.0
5.N.3.1 Utiliza cmputos escritos (algoritmos), estrategias de
estimaciones, cmputo mental, y los modelos concretos y
semiconcretos para resolver problemas de suma, resta,
multiplicacin y divisin con los nmeros cardinales de varios
dgitos y decimales hasta la centsima
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Add decimals, using the algorithm;
Subtract decimals, using the
algorithm;
Show desire for accuracy.
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit DECIMALS
Lesson Multiplication of decimals
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
10
Tuesday, October 13, 2015
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.3.0
5.N.3.1 Utiliza cmputos escritos (algoritmos), estrategias de
estimaciones, cmputo mental, y los modelos concretos y
semiconcretos para resolver problemas de suma, resta,
multiplicacin y divisin con los nmeros cardinales de varios
dgitos y decimales hasta la centsima
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Define multiplication of decimals;
Multiply decimals;
Appreciate the beauty of math
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit DECIMALS
Lesson Multiplication of decimals
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
10
Week #
Date
Thursday, October 15,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.3.0
5.N.3.1 Utiliza cmputos escritos (algoritmos), estrategias de
estimaciones, cmputo mental, y los modelos concretos y
semiconcretos para resolver problemas de suma, resta,
multiplicacin y divisin con los nmeros cardinales de varios
dgitos y decimales hasta la centsima
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
7.N.3.0
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
7.N.3.1 Comprende que la multiplicacin se extiende desde las Strategic Thinking
fracciones hasta los nmeros racionales al requerir que las
Extended Thinking
operaciones cumplan con las propiedades de las operaciones,
particularmente la propiedad distributiva, lo que lleva a
resultados como (/)(/) = /,y las reglas de multiplicacin de
n m eros con signos, Interpreta productos de nmeros
racionales en contextos de la vida diaria.
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Multiply decimals numbers
Academic prompts
Multiply decimals;
Brainstorming
Develop ability to follow a sequence of Check list
*Close questions
implications.
Comics
Appreciate the order of math
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit DECIMALS
Lesson PEAU
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
11
Tuesday, October 20, 2015
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
7.N.2.3 Aplica las propiedades de las operaciones como
estrategias para sumar, restar, multiplicar y dividir nmeros
racionales; estima y juzga la razonabilidad de los resultados al
resolver problemas
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit DECIMALS
Lesson PEAU
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
11
Week #
Date
Thursday, October 22,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit DECIMALS
Lesson Division of decimals (whole
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
12
Tuesday, October 27, 2015
INTRODUCCION
divisor)
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
4.N.3.0
5.N.3.1 Utiliza cmputos escritos (algoritmos), estrategias de
estimaciones, cmputo mental, y los modelos concretos y
semiconcretos para resolver problemas de suma, resta,
multiplicacin y divisin con los nmeros cardinales de varios
dgitos y decimales hasta la centsima
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Divde decimals with a whole divisor
Feel enthusiasm for math
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit DECIMALS
Lesson Division of decimals (decimal
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
12
Week #
Date
Thursday, October 29,
2015
INTRODUCCION
divisor)
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
5.N.3.0
5.N.3.1 Utiliza cmputos escritos (algoritmos), estrategias de
estimaciones, cmputo mental, y los modelos concretos y
semiconcretos para resolver problemas de suma, resta,
multiplicacin y divisin con los nmeros cardinales de varios
dgitos y decimales hasta la centsima
7.N.2.0
7.N.2.3 Aplica las propiedades de las operaciones como
estrategias para sumar, restar, multiplicar y dividir nmeros
racionales; estima y juzga la razonabilidad de los resultados al
resolver problemas
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
Divide decimals using the traditional
algorithm with a whole number
divisor;
Recognize the importance of math in
the real world
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit DECIMALS
Lesson TEST AND ASSESSMENT
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
13
Week #
Date
Tuesday, November 3,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
7.N.2.3 Aplica las propiedades de las operaciones como
estrategias para sumar, restar, multiplicar y dividir nmeros
racionales; estima y juzga la razonabilidad de los resultados al
resolver problemas
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Score correctly at least 70% of the
questions of the test; Demonstrate
respect for knowledge
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
13
INTRODUCCION
Lesson Ratios
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.5.0
7.N.4.1 Calcula las razones de cambio asociadas con razones
de fracciones, incluidas las razones de longitud, reas y otras
cantidades medidas en unidades iguales o diferentes
Indicator
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Define ratio;
Express two quantities as a ratio;
Simplify ratios;
Appreciate the clarity of mathematical
language
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Standard,
Expectations
Thursday, November 5,
2015
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
14
INTRODUCCION
Lesson Proportions
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
7.N.4.0
7.N.4.2 Decide si dos cantidades constituyen una relacin e
identifica la constante de proporcionalidad (razn de cambio)
en tablas, grficas, ecuaciones, diagramas y en descripciones
verbales de relaciones proporcionales
Indicator
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Define proportions;
Develop the habit of concentrating on
a given task.
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Tuesday, November 10,
2015
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
14
INTRODUCCION
Lesson Proportions
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
Thursday, November 12,
2015
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
7.N.4.0
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
7.N.4.4 Escribe y soluciona una proporcin con factores de
Strategic Thinking
conversin de escalas y medidas, porcentajes y probabilidades
Extended Thinking
de la vida diaria
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
7.N.4.3 Representa relaciones proporcionales mediante el uso Strategic Thinking
de ecuaciones
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Solve proportions numerically;
Solve real world problems that involve
proportions;
Appreciate the mathematical rigor.
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
15
INTRODUCCION
Lesson Percent
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
Tuesday, November 17,
2015
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.5.0
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
6.N.5.4 Interpreta el concepto de porciento como una razn o Strategic Thinking
proporcin de 100
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
7.N.4.4 Escribe y soluciona una proporcin con factores de
Strategic Thinking
conversin de escalas y medidas, porcentajes y probabilidades
Extended Thinking
de la vida diaria
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Read and write ratios as a percent;
Pursuit in a task with confidence
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
15
INTRODUCCION
Lesson HOLIDAY
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
Thursday, November 19,
2015
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
7.N.4.4 Escribe y soluciona una proporcin con factores de
Strategic Thinking
conversin de escalas y medidas, porcentajes y probabilidades
Extended Thinking
de la vida diaria
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
16
INTRODUCCION
Lesson Percent
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.5.0
6.N.5.4 Interpreta el concepto de porciento como una razn o
proporcin de 100
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Tuesday, November 24,
2015
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Define percent visually as a part of
one hundred (1/100);
Appreciate the order of math
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
16
INTRODUCCION
Lesson holiday
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
Thursday, November 26,
2015
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
7.N.4.4 Escribe y soluciona una proporcin con factores de
Strategic Thinking
conversin de escalas y medidas, porcentajes y probabilidades
Extended Thinking
de la vida diaria
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
17
INTRODUCCION
Lesson Percent
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.5.0
6.N.5.4 Interpreta el concepto de porciento como una razn o
proporcin de 100
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Tuesday, December 1,
2015
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Use proportions to solve percent
problems;
Appreciate the mathematical rigor.
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
17
INTRODUCCION
Lesson Percent
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
Thursday, December 3,
2015
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
6.N.5.0
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
6.N.5.4 Interpreta el concepto de porciento como una razn o Strategic Thinking
proporcin de 100
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
7.N.4.4 Escribe y soluciona una proporcin con factores de
Strategic Thinking
conversin de escalas y medidas, porcentajes y probabilidades
Extended Thinking
de la vida diaria
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Use proportions to solve percent
problems;
Appreciate the mathematical rigor.
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
18
INTRODUCCION
Lesson TEST AND ASSESSMENT
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Tuesday, December 8,
2015
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Score correctly at least 70% of the
questions of the test;
Demonstrate respect for knowledge
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
RATIO, PROPORTIONS &
PERCENTS
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
18
INTRODUCCION
Lesson TEST DISCUSSION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
Date
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Thursday, December 10,
2015
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Identify his strengths and
weaknesses;
Show respect for thoroughness in
performing a task
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit METRIC SYSTEM
Lesson Metric system
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
19
Thursday, December 10,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
4.M.9.0
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
4.M.9.4 Determina la unidad de medida apropiada para
Strategic Thinking
resolver problemas que involucran longitud, tiempo, capacidad
Extended Thinking
o peso
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Identify the correct measure unit;
Recognize the importance of order
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit METRIC SYSTEM
Lesson Conversion
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
19
Week #
Date
Tuesday, December 15,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
STANDARDS
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
4.M.11.0
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
4.M.11.1 Realiza conversiones de unidades de longitud
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
3.M.11.1 Selecciona las herramientas apropiadas de medida
Strategic Thinking
(regla, yarda, metro, taza, balanza entre otras) y unidades (del
Extended Thinking
sistema mtrico e ingls) y estima y mide la longitud, la
capacidad, el peso y la masa de objetos. Determina la unidad
de medida apropiada y/o el tamao en una situacin que
involucre atributos como: longitud, tiempo, capacidad, o peso/
masa
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Convert metric units within the
system;
Show respect for thoroughness in
performing a task
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit METRIC SYSTEM
Lesson
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Week #
Date
20
Thursday, December 17,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
5.M.7.2 Resuelve problemas al estimar medidas en unidades
mtricas e inglesas que involucran conversiones de diferentes
medidas estndar dentro de un mismo sistema de medicin
(cm - m; hrs. - min.). Convierte unidades de longitud y de peso
en un solo sistema
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
Convert metric units within the
system;
Show respect for thoroughness in
performing a task
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit METRIC SYSTEM
Lesson
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
20
Week #
Date
Tuesday, December 22,
INTRODUCCION
2015
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
21
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
21
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
22
Tuesday, January 19, 2016
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
22
Thursday, January 21,
INTRODUCCION
2016
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
23
Tuesday, January 26, 2016
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
23
Thursday, January 28,
INTRODUCCION
2016
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
24
Tuesday, February 2, 2016
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
24
Thursday, February 4,
INTRODUCCION
2016
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
25
Tuesday, February 9, 2016
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
25
Thursday, February 11,
INTRODUCCION
2016
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
26
Tuesday, February 16,
INTRODUCCION
2016
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
26
Thursday, February 18,
INTRODUCCION
2016
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
27
Tuesday, February 23,
INTRODUCCION
2016
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
27
Thursday, February 25,
INTRODUCCION
2016
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
28
Tuesday, March 1, 2016
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
28
Thursday, March 3, 2016
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
29
Tuesday, March 8, 2016
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
29
Thursday, March 10, 2016
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
30
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
Weekly Guide: MATHEMATICS Grade 12th
COURSE: MAT 131 1448: Matemtica Actualizada 1
Leonardo Torres Pagn, PhD
Unit
Week #
Lesson
Date
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
30
INTRODUCCION
Academic
Strategies (AS)
Suplementary &
complementary
strategies (SS)
Scientific based
strategies (SB)
(Marzano)
High School
Student Profile
(SP)
AS1 Conceptual development
AS2 Curricular integration
AS3 Cooperative learning
SS1 Context teaching
SS2 Collaborative learning
SS3 Brain based learning
SS4 Stations
AS4 Reading comprehension AS7 Differentiated instruction
AS5 Problem-based learning
AS8 Project-based learning
AS6 Significant learning
AS9 Technology integration
SS5 Problem solving
SS6 Technology integration
SS7 Values clarification
SS8 Scaffolding
SB1 Identifying similarities and differences
SB6 Cooperative learning
SB2 Summarizing and note taking
SB7 Setting objectives and providing feedback
SB3 Homework and practice
SB8 Generating and testing hypotheses
SB9 Cues, questions, and advance organizers
SB4 Non-linguistic representations
SB5 Reinforcing effort and providing recognition
SP1Apprentice
SP2 Effective communicator
SP3 Ethical
SP4 Entrepreneur
SP5 Engaged in communities
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Depth of Knowledge
Recall & Reproduction
Skills & Concepts
Strategic Thinking
Extended Thinking
Standard,
Expectations
STANDARDS
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
Indicator
Standard,
Expectations
(Concepts & Big ideas) OBJECTIVES
Indicator
At the end of the study of this lesson, the student without
difficulties (at least 70% of practice exercises done correctly) will
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Formative Assessment: A review of their work will help with assessing
students understanding of the concepts that were presented in todays lesson and
planning more effectively for future lessons.
3-2-1 cards
Academic prompts
Brainstorming
Check list
*Close questions
Comics
* Exit prompt
Focal list
Graph organizer
Homework
Interviews
Investigations
Mind map
Observations
Open questions
*Oral prompt
Performance task
Portfolio entry
Premises
Questionnaires
Quizzes
Reflexive diary
Report
Report (news)
Role playing
Scale
Simulations
Survey
*Test items
Venn Diagram
Whip-arounds
Windshield check
POE Exercises
CURRICULAR INTEGRATION
Transversal
themes
Morale
Strategies
Values
Technology
Standards
Accomodations
Peace education
Education & technology
Education for work
Civic & Ethics
Deliberation
Action research
Civism
Respect
Communication & Collaboration
Socratic dialogue
Values clarification
Reliability
Responsibility
Research & Information fluency
Digital citizenship
Technology operations & concepts
Discipline
Community
LLE
EE
Gifted &
Talented
504
ntiateDifere
Cultural identity
Environmental Education
Gender perspective
Dilemma
Role playing
Kindness
Justice
Creativity and innovations
Critical thinking, problem
solving & decision making
Content
Process
Word wall: Require students to use words from the Word Wall in their writing and to refer to the Word Wall to find
correct spellings. Leveled questions. Student journals. Math glossary. English worksheets. Read clearly and
slowly. Use motions, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate. Model appropriate nonverbal feedback for
students. Work in a group or with a partner asking and answering questions about a current event or book. Listen to
English movies. Replace an academic language word with a social language word to aid in understanding and building
new vocabulary. Allow student to choose topics and partners. Preferred seating. Complete a monitoring and selfevaluation chart. Pre-teach vocabulary using visuals. Pair words with pictures. Place math symbols on a sheet.
Encourage the use of math symbols. Use math cognates. Use color marker to highlight key words. Allow
students to nonverbally act out words to help them process vocabulary without having to speak. Promote structured and
appropriate discussion that requires students to utilize words from Word Wall in their verbal responses. Write simple
sentences to answer questions. Combine written language with corresponding visuals whenever possible. Provide a
text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on grammatical concepts. Student
Response Boards: Allow students to work in pairs if they need more support or accept pictures as correct answers
instead of written language.
Use topics that are of interest to the student. Praise student for asking and answering questions. Give the student a
choice of topics. Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating.
Complete a monitoring and self-evaluation chart. Pair words with pictures. Provide age appropriate materials. Provide
graphic organizers for theme, summarizing, mind maps. Combine written language with corresponding visuals
whenever possible. Provide a text that is challenging but engaging, focusing not only on vocabulary, but also on
grammatical concepts. Provide students with key words from the text and have them put a checkmark next to a word.
Allow student to check with a partner before answering or commenting. Use marking strategies. Provide powerpoint
slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately. Provide students with examples and non-examples
Continuous Progress Curriculum (Flexible Pacing)the content and pacing of curriculum and instruction are
matched to the student's abilities and needs. Advanced Placement (AP)students have the opportunity to complete
college level coursework and earn college credit through examination while still in high school. Ability Groupingthe
flexible regrouping of students based on individual instructional needs. Curriculum Compactingallows highly able
students to "compact" or eliminate material already mastered from the curriculum, thus allowing them to complete
subject material in a shorter time span. Subject Accelerationtaking a course earlier than is typical. Tiered
Assignmentsassignments within the same lesson plan which are structured at varied levels of complexity, depth and
abstractness to meet the need of students with diverse abilities. Learning Contractsgive students freedom to plan
their time and yet provide guidelines for completing work responsibly. Problem-Based Learningtype of problem
solving in which students are presented with an "ill-structured" problem that resembles a real-life situation. Students are
responsible for identifying additional data and resources that they need and for deciding how to present their findings
and demonstrate their learning. Enrichmentprovides students with experiences in regular classrooms that are
additional or supplemental to the established curriculum. Mentorshipsenrichment program that pairs an individual
student with someone who has advanced skills and experiences in a particular discipline. This mentor can serve as an
advisor, counselor, and role model to the student.
Accommodation: . Provide frequent and specific feedback to the student on performance. Preferred seating, Use
color marker to highlight key words. Provide powerpoint slides. Sort examples and non-examples appropriately.
Provide students with examples
Differentiation instructional strategiesthe modification of instruction based on a student's academic needs. 4-MAT,
anchor activities, compacting, complex instruction, cubing, expression options, graphic organizers, group
investigations, grouping activities, Independent projects, independent studies, interest centers, interest groups,
jigsaws, journal prompts, layered Curriculum, learning contracts, learning contracts, literature circles, Menus, ,
INITIAL ACTIVITIES: SYLLABUS
Unit: lessons
You might also like
- Science COT DLP 4th QuarterDocument5 pagesScience COT DLP 4th QuarterJewilyn Canilang Soquerata100% (8)
- Strategies For Teachers Working With Students With Orthopedic ImpairmentsDocument4 pagesStrategies For Teachers Working With Students With Orthopedic Impairmentsapi-268598032100% (2)
- The Nature of Mathematics Karl Smith LogicDocument41 pagesThe Nature of Mathematics Karl Smith LogicLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Action Research Proposal Tle GroupDocument6 pagesAction Research Proposal Tle GroupEarl Vestidas Capuras0% (1)
- (Addison-Wesley Data & Analytics Series) Laura Graesser - Wah Loon Keng - Foundations of Deep Reinforcement Learning - Theory and Practice in Python-Addison-Wesley Professional (2019) PDFDocument656 pages(Addison-Wesley Data & Analytics Series) Laura Graesser - Wah Loon Keng - Foundations of Deep Reinforcement Learning - Theory and Practice in Python-Addison-Wesley Professional (2019) PDFRolando YbanezNo ratings yet
- The Ancient China Project RubricDocument2 pagesThe Ancient China Project Rubricnwhite325No ratings yet
- PR2017 Guia SemanalDocument2 pagesPR2017 Guia SemanalLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit Rations, Proportions & Percents Week # Lesson DateDocument4 pagesUnit Rations, Proportions & Percents Week # Lesson DateLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument11 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Math 131 1448 PLAN DIARIO PLANTILLA TEMPLATEDocument8 pagesPR2016 Math 131 1448 PLAN DIARIO PLANTILLA TEMPLATELeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument9 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument13 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Planificacion Final July - 2015 - 16Document6 pagesPR2016 Planificacion Final July - 2015 - 16Leonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument8 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument11 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 - 6.3.13Document10 pagesPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 - 6.3.13Leonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument11 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 3Document16 pagesPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 3Leonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument12 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument9 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 1BDocument136 pagesPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 1BLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument17 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument9 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument9 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Adult Learner Autonomy ChecklistDocument7 pagesAdult Learner Autonomy ChecklistCharles Rei100% (1)
- Effective Schools Observation Grade 8 - Mackenzie SmithDocument4 pagesEffective Schools Observation Grade 8 - Mackenzie Smithapi-493639741No ratings yet
- Effective Schools Observation Grade 7 - Mackenzie SmithDocument4 pagesEffective Schools Observation Grade 7 - Mackenzie Smithapi-493639741No ratings yet
- PedagogyDocument32 pagesPedagogyMrs Rehan100% (2)
- Strategies Approaches ConditionsDocument6 pagesStrategies Approaches Conditionsapi-231047504No ratings yet
- How To Plan Teaching EffectivelyDocument28 pagesHow To Plan Teaching EffectivelyAinur Biy100% (1)
- Statistical Questions Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesStatistical Questions Lesson Planapi-534097479No ratings yet
- Ararat College HPLC ConferenceDocument32 pagesArarat College HPLC Conferenceapi-327445428No ratings yet
- 21 Century SUSD CharacteristicsDocument10 pages21 Century SUSD Characteristicscresta2014No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan and Observation: Alverno CollegeDocument6 pagesLesson Plan and Observation: Alverno Collegeapi-241165912No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan 2api-288764826No ratings yet
- 5d PresentationDocument32 pages5d Presentationapi-302412299No ratings yet
- InterviewDocument14 pagesInterviewCristel Anne Amoranto LlamadorNo ratings yet
- Effective Lesson PlanningDocument27 pagesEffective Lesson PlanningmawinNo ratings yet
- Cross Curricular LiteracyDocument241 pagesCross Curricular LiteracyJedda DeckerNo ratings yet
- Maculada, Jodi Marie Beed 3-cDocument7 pagesMaculada, Jodi Marie Beed 3-cMa Lourdes Abada MaculadaNo ratings yet
- Final Curriculum Evaluation DocumentDocument2 pagesFinal Curriculum Evaluation Documentapi-325889338No ratings yet
- Edma3200 Lesson5practicumDocument3 pagesEdma3200 Lesson5practicumapi-252533855No ratings yet
- Presentation LarouzDocument24 pagesPresentation LarouzMimoun ZeggaiNo ratings yet
- Team Rhyming Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesTeam Rhyming Lesson Planapi-318036319No ratings yet
- GCU ELM-305 Topic 7 Discussion Question ResponsesDocument3 pagesGCU ELM-305 Topic 7 Discussion Question ResponsesKristin HensleyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Curriculum ConnectionsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Curriculum Connectionsapi-397840564No ratings yet
- Differentiated Instruction in Secondary MathematicsDocument3 pagesDifferentiated Instruction in Secondary MathematicsEditha Cuenco100% (1)
- Lesson Plan ChecklistDocument2 pagesLesson Plan ChecklistAstroRia2No ratings yet
- Assignment #4: Mini Unit Plan: Lesson Overview & RationaleDocument29 pagesAssignment #4: Mini Unit Plan: Lesson Overview & Rationaleapi-296766699No ratings yet
- Universal Design For Learning Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesUniversal Design For Learning Lesson Planapi-397092685No ratings yet
- SPED 9 MIDTERM 1st Sem 2021 22.angeline P. OrdeÑizaDocument3 pagesSPED 9 MIDTERM 1st Sem 2021 22.angeline P. OrdeÑizarenato jr baylasNo ratings yet
- Effective Lesson PlanningDocument27 pagesEffective Lesson PlanningAlberto Laborte Jr.No ratings yet
- 2324VTC - Creating Stimulating Classroom - Staff - KennethDocument70 pages2324VTC - Creating Stimulating Classroom - Staff - KennetharetkusuNo ratings yet
- College of Education Lesson Plan GuidebookDocument13 pagesCollege of Education Lesson Plan Guidebookapi-242142698No ratings yet
- Observation 4/12/12Document4 pagesObservation 4/12/12MissDurstNo ratings yet
- Content Standard(s) Addressed by This Lesson:: STEPP Lesson Plan FormDocument6 pagesContent Standard(s) Addressed by This Lesson:: STEPP Lesson Plan Formapi-282071507No ratings yet
- Teaching a Child with Special Needs at Home and at School: Strategies and Tools That Really Work!From EverandTeaching a Child with Special Needs at Home and at School: Strategies and Tools That Really Work!No ratings yet
- FTC MATH 1010 Week 1 OverviewDocument93 pagesFTC MATH 1010 Week 1 OverviewLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Intro To Expressions & Equations: Prerequisite Skills NeededDocument21 pagesIntro To Expressions & Equations: Prerequisite Skills NeededLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument17 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument9 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument12 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 1BDocument136 pagesPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 1BLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument9 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument8 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 - 6.3.13Document10 pagesPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 - 6.3.13Leonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument13 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument11 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument11 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument9 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument11 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument9 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDocument10 pagesUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 3Document16 pagesPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 3Leonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 MAT 131 1477 Weekly Plan GenericDocument91 pagesPR2016 MAT 131 1477 Weekly Plan GenericLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: Week PlanDocument1 pageMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: Week PlanLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Unit Template UbD 131 - 1468 PRECALCULUSDocument5 pagesPR2016 Unit Template UbD 131 - 1468 PRECALCULUSLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 MAT 131 1468 Weekly Plan GenericDocument91 pagesPR2016 MAT 131 1468 Weekly Plan GenericLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Unit Guide: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 pagesUnit Guide: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayLeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- PR2016 Math 131 1448 PLAN DIARIO PLANTILLA TEMPLATEDocument8 pagesPR2016 Math 131 1448 PLAN DIARIO PLANTILLA TEMPLATELeonardo Torres PaganNo ratings yet
- Practical Research: Quezon Memorial AcademyDocument3 pagesPractical Research: Quezon Memorial AcademyCamille Joy Fernandez CadaNo ratings yet
- Principles of AssessmentDocument74 pagesPrinciples of AssessmentRiyan ElaineNo ratings yet
- 100 Common SAT Vocabulary Words For PracticeDocument1 page100 Common SAT Vocabulary Words For PracticeMarcus Skookumchuck VanniniNo ratings yet
- CEB Managing Troubled Projects v1Document30 pagesCEB Managing Troubled Projects v1shazz_28No ratings yet
- Diss 2ndquarter ConditioningDocument35 pagesDiss 2ndquarter Conditioningsaraumshainamae265No ratings yet
- Parallel Assessment in English 10 Quarter 2 Module 2Document1 pageParallel Assessment in English 10 Quarter 2 Module 2Hazel SolisNo ratings yet
- OUMH1303 English For Oral CommunicationDocument7 pagesOUMH1303 English For Oral CommunicationSk Bohor BaruNo ratings yet
- Resume: Name: XXXXXX XXXXXX XXXXXXXXXDocument2 pagesResume: Name: XXXXXX XXXXXX XXXXXXXXXAditya Sangita Kisan SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism - ReportDocument114 pagesPlagiarism - ReportashNo ratings yet
- Design Heuristic WorkshopDocument22 pagesDesign Heuristic WorkshopMaryel LaraNo ratings yet
- Applied Text AnalysisDocument13 pagesApplied Text AnalysisТаня БродаNo ratings yet
- Written Summary of Activity 1Document2 pagesWritten Summary of Activity 1Honey Bee S. PlatolonNo ratings yet
- Assumptions About The Nature of Social Science PDFDocument19 pagesAssumptions About The Nature of Social Science PDFHaroon BilalNo ratings yet
- Personal Entrepreneurial Competencies (Pecs) Self-Rating: QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesPersonal Entrepreneurial Competencies (Pecs) Self-Rating: Questionnairemary ann coperNo ratings yet
- Legal Research MethodsDocument259 pagesLegal Research Methodsritesh100% (1)
- Pr5 HomonymyDocument45 pagesPr5 HomonymyMoi WarheadNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Propaganda 2Document3 pagesThe Psychology of Propaganda 2Noorbina IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Language Strategies For Color: Joris BleysDocument30 pagesLanguage Strategies For Color: Joris BleysGiosuè BaggioNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of QualityDocument18 pagesBasic Concept of QualityPrabath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Achieving Inclusion For WebDocument16 pagesAchieving Inclusion For WebSteph GotlibNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesMay Anne AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - TTL 1 Educ 302Document46 pagesLesson 4 - TTL 1 Educ 302Mark Jerick RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 HRM and Organisational StrategiesDocument29 pagesChapter-3 HRM and Organisational StrategiesBablu Pavan100% (1)
- Part D Tim Hortons Due 10 6Document3 pagesPart D Tim Hortons Due 10 6Abhishek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Anton Makarenko - G.N. FilonovDocument9 pagesAnton Makarenko - G.N. FilonovsergevictorNo ratings yet