Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ion Comps Missing Words
Ion Comps Missing Words
Uploaded by
joh thonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ion Comps Missing Words
Ion Comps Missing Words
Uploaded by
joh thonCopyright:
Available Formats
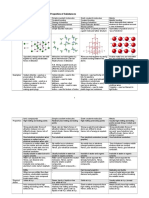
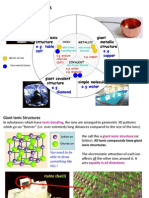
Ionic substances form giant ionic lattices containing oppositely charged ions.
They have high
melting and boiling points, and conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water.
Simple molecular substances consist of molecules in which the atoms are joined by strong covalent
bonds. Their molecules are held together by weak forces, so these substances have low melting and
boiling points. They do not conduct electricity.
Giant covalent structures contain many atoms joined together by covalent bonds to form a giant
lattice. They have high melting and boiling points. Graphite and diamond have different properties
because they have different structures. Graphite conducts heat and electricity well because it also
has free electrons.
Nanoparticles are 1-100 nm in size, typically the size of small molecules - far too small to see with
a microscope. They have remarkable properties that are different to the same substance in bulk
form.
Metals form giant structures containing free electrons, making them good conductors of heat and
electricity.
Ionic compounds
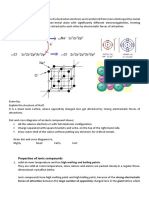
Ionic bonds form when a metal reacts with a non-metal. Metals form positive ions; non-metals form
negative ions. Ionic bonds are the electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Positively charged Na ions and negatively charged Cl ions
The oppositely charged ions are arranged in a regular way to form giant ionic lattices. Ionic
compounds often form crystals as a result. The illustration shows part of a sodium chloride (NaCl)
ionic lattice.
Properties of ionic compounds
High melting and boiling points - Ionic bonds are very strong - a lot of energy is needed to
break them. So ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
Conductive when liquid - Ions are charged particles, but ionic compounds can only conduct
electricity if their ions are free to move. Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity when
they are solid - only when dissolved in water or melted.
Properties of ionic compounds
Ionic
compound
Properties
High melting point: 800C
Sodium
Non-conductive in its solid state, but when dissolved in water or molten NaCl will
chloride, NaCl
conduct electricity.
Magnesium
oxide, MgO
Higher melting point than sodium chloride: around 2,800C. This is because its
Mg2+ and O2- ions have a greater number of charges, so they form stronger ionic
bonds than the Na+ and Cl- ions in sodium chloride.
Because magnesium oxide stays solid at such high temperatures, it remains nonconductive. It is used for high-temperature electrical insulation.
You might also like
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding: Properties of Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding: Properties of Ionic CompoundsChanupa YanethNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesIonic Bonding and StructureKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- Comparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Document3 pagesComparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Fatima Ahmed-VeriterNo ratings yet
- Ions and Ionic BondDocument21 pagesIons and Ionic Bondchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- The Crystal Structure and Properties of Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesThe Crystal Structure and Properties of Ionic CompoundskushanNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument39 pagesIonic and Covalent Bondingchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Document11 pagesCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964No ratings yet
- BondsDocument24 pagesBondsPavithran Kamaleswari Year 10No ratings yet
- Notes3 Unit1Document2 pagesNotes3 Unit1arun iyer BitcoinminerandmathematicianNo ratings yet
- L7 - Ionic Compounds PropertiesDocument19 pagesL7 - Ionic Compounds PropertiesKashifNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileDocument17 pagesCovalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileMahi QuaziNo ratings yet
- Describe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesDescribe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent Compoundsmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocument6 pagesChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and AtomsDocument12 pagesElements, Compounds and Atomsananya.arumugarajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Ionic BondingDocument1 pageChapter 6 - Ionic BondingKayla WNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Bonding Revision GuidesDocument1 pageBonding Revision Guidesapi-255623302No ratings yet
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocument16 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- Notes W4Document5 pagesNotes W4sy.valNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- CH 3, ChemDocument6 pagesCH 3, ChemAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.Document34 pagesIonic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.allenbrien077No ratings yet
- 06 ANSWERS SummaryDocument1 page06 ANSWERS SummaryJean AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Metallic Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument3 pagesMetallic Ionic and Covalent BondinglesarouNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Notes 5Document3 pagesCsec Chemistry Notes 5debestieNo ratings yet
- Bonding Summary NotesDocument17 pagesBonding Summary NotesaleenNo ratings yet
- Ionic Solids: Cations AnionsDocument2 pagesIonic Solids: Cations AnionsMyrna Getuaban SidonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Board NotesDocument19 pagesChemical Bonding Board NotesEmaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesChemistry Chemical Bondinghamarirasoi0803No ratings yet
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocument14 pagesLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNo ratings yet
- Module-Ii Chemical Bonding: General Chemistry CHEM-1001Document193 pagesModule-Ii Chemical Bonding: General Chemistry CHEM-1001Shivansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesChemistry - Chemical BondingMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument17 pagesBonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyKhemou DjvickzNo ratings yet
- When Atoms Meet: Chemical BondingDocument88 pagesWhen Atoms Meet: Chemical BondingWilsonNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistryMohammad Ammar GanatraNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocument10 pagesBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Properties of Ionic Compounds - KeyDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Properties of Ionic Compounds - Keyrandomlol7777No ratings yet
- Chemistry GSCE NotesDocument16 pagesChemistry GSCE NotesMariaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument40 pagesChemical BondingabuhurairabscNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document57 pagesCH 10Akef AfanehNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument87 pagesChemical BondingMichael Dela Torre Diaz Jr.No ratings yet
- Assignment - 2Document15 pagesAssignment - 2padhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelDocument34 pagesChemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelAhmed KhalilNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument23 pagesBondingFaiza AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Xture of SolidsDocument12 pagesXture of Solidsmuonekechibukeleonard52No ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliDocument11 pagesBonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliPro IdiotNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sodium Chloride Giant Ionic BondDocument12 pagesChemistry Sodium Chloride Giant Ionic BondtsteadmanNo ratings yet
- Structure & Bonding - IONIC BONDINGDocument23 pagesStructure & Bonding - IONIC BONDINGTrishana GreenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 2Document32 pagesChemical Bond 2Yak Raj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chemical StructureDocument6 pagesChemical StructuremonkeysaltaccNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument2 pagesChemistry-Ionic and Covalent Bondingifaitchwould2No ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond NotesDocument8 pagesGiant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond Notesnihan.8558No ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)