Professional Documents
Culture Documents
History (
History (
Uploaded by
arif99pakCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MonkeysDocument4 pagesMonkeysapi-28090379569% (13)
- Wind Turbine Project ReportDocument19 pagesWind Turbine Project ReportMuaz Fabregas100% (2)
- Practical Self-Sufficiency PDFDocument280 pagesPractical Self-Sufficiency PDFFernando Cárdenas Wong95% (20)
- Concept Paper Windmill Power PlantDocument40 pagesConcept Paper Windmill Power PlantNoe S. Elizaga Jr.100% (1)
- PowerDocument2 pagesPowerraymond baliteNo ratings yet
- Government of Kerala: Income CertificateDocument1 pageGovernment of Kerala: Income CertificatethanseelnnNo ratings yet
- Trimble Precision IQ GFX 750 OptimizedDocument319 pagesTrimble Precision IQ GFX 750 OptimizedireneuszNo ratings yet
- Solar Updraft TowerDocument14 pagesSolar Updraft TowerAmeen OmerNo ratings yet
- Solar Updraft TowerDocument8 pagesSolar Updraft Towerbobo_sbNo ratings yet
- The Solar Updraft Tower Is A RenewableDocument6 pagesThe Solar Updraft Tower Is A RenewableIoana Valentina PopaNo ratings yet
- Musgrove Wind Engineering 30-3Document19 pagesMusgrove Wind Engineering 30-3Wei MaNo ratings yet
- Westinghouse Combustion Turbine Systems Division - WikipediaDocument186 pagesWestinghouse Combustion Turbine Systems Division - Wikipediadavidcairobalza100% (1)
- 2 Solar Millennium Fuchs 2011-04-04Document15 pages2 Solar Millennium Fuchs 2011-04-04Arun Sivasankar BharadwajNo ratings yet
- History: Dynamos and Engine Installed at Edison General Electric Company, New York 1895Document4 pagesHistory: Dynamos and Engine Installed at Edison General Electric Company, New York 1895mrjunoonNo ratings yet
- History of WindmillsDocument5 pagesHistory of WindmillsLaura García CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lectura 1 Semestre 2019 Pumping Hydrolectric Storage - Turbine HistoryDocument6 pagesLectura 1 Semestre 2019 Pumping Hydrolectric Storage - Turbine HistoryEduardo CardenasNo ratings yet
- Proyecto Wind La Ventosa MexicoDocument42 pagesProyecto Wind La Ventosa MexicoOscar MoralesNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectricity: MW Three Gorges Dam Peoples Republic of ChinaDocument4 pagesHydroelectricity: MW Three Gorges Dam Peoples Republic of ChinaKapil BajajNo ratings yet
- Pap Kraetzig 02Document16 pagesPap Kraetzig 02ersinNo ratings yet
- Combustion Technology For Generating Energy From Waste PDFDocument26 pagesCombustion Technology For Generating Energy From Waste PDFcaiosicNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Energy: T E C H N O L O G YDocument14 pagesOffshore Wind Energy: T E C H N O L O G YAbdullah KaymakcıNo ratings yet
- The Operation of Ravenswood Generating Station in QueensDocument3 pagesThe Operation of Ravenswood Generating Station in Queensyanam766No ratings yet
- UNIT-2 PHYSICS OF WIND POW-PART1 [Autosaved] (2)Document51 pagesUNIT-2 PHYSICS OF WIND POW-PART1 [Autosaved] (2)010 Monitha SaiNo ratings yet
- Supercapacitors turnitinDocument2 pagesSupercapacitors turnitinperiasamy_nanoNo ratings yet
- Development of MachinesDocument1 pageDevelopment of MachinesSathu satishNo ratings yet
- CFE - Los Azufres 2 Development ReportDocument4 pagesCFE - Los Azufres 2 Development ReportEko TjahjantokoNo ratings yet
- Solar Chimney Power Plants PDFDocument17 pagesSolar Chimney Power Plants PDFChristopher GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bharat Dynamic LTDDocument13 pagesBharat Dynamic LTDShimanthakumar PadashettyNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument16 pagesWind Energypaezbak100% (1)
- 9 Review Future On Power Electronics For Wind Turbine Systems REVIEW PAPER PDFDocument5 pages9 Review Future On Power Electronics For Wind Turbine Systems REVIEW PAPER PDFbatthharshNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind FarmsDocument6 pagesOffshore Wind Farmsapi-345217277No ratings yet
- Solar Power: An Introduction To The History, Technologies, Policy Applications and Future of Solar PowerDocument51 pagesSolar Power: An Introduction To The History, Technologies, Policy Applications and Future of Solar PowerdewsfefcvnbcvNo ratings yet
- Status of Geothermal Industry in AustraliaDocument8 pagesStatus of Geothermal Industry in AustraliaRyan Hofmann100% (1)
- Wind - Energy - 5A - PPT PresentationDocument51 pagesWind - Energy - 5A - PPT PresentationGian BanaresNo ratings yet
- A Short History of The CANDU Nuclear Power System: Gord L. BrooksDocument34 pagesA Short History of The CANDU Nuclear Power System: Gord L. BrooksAnonymous 1hOgJqwZuzNo ratings yet
- Full Charge Ahead: Power StorageDocument5 pagesFull Charge Ahead: Power Storagekdizzle28No ratings yet
- Vishnu 1Document5 pagesVishnu 1KIRAN KENNo ratings yet
- GT HistoryDocument12 pagesGT HistoryBrosGeeNo ratings yet
- HydropowerDocument38 pagesHydropowerBrijesh Chauhan100% (3)
- Smart Grid AssignmentDocument16 pagesSmart Grid Assignmentabstudio0049No ratings yet
- Power Engineering, Also Called Power Systems Engineering, Is A Subfield ofDocument8 pagesPower Engineering, Also Called Power Systems Engineering, Is A Subfield ofsharathVEMNo ratings yet
- Green Power GenerationDocument90 pagesGreen Power GenerationFarhan SaadatNo ratings yet
- Floating Wind Turbine - WikipediaDocument21 pagesFloating Wind Turbine - WikipediavineeshNo ratings yet
- CDM CeaDocument14 pagesCDM Ceaanjes1No ratings yet
- Wind TurbinesDocument18 pagesWind Turbinesapi-271021803No ratings yet
- Who and When LiesDocument1 pageWho and When LiesMarc Nelson Pequit Jr.No ratings yet
- Power StationDocument10 pagesPower Stationletter_ashish4444No ratings yet
- Flying Cloud Fact SheetDocument2 pagesFlying Cloud Fact Sheetscuderia_f147No ratings yet
- Wind TurbineDocument24 pagesWind TurbinerjiyfrauefaboovyohNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument16 pagesWind EnergyJoeNo ratings yet
- This Article Needs Additional Citations For VerificationDocument12 pagesThis Article Needs Additional Citations For VerificationKiranParvathaneniNo ratings yet
- CEL - Geotermia 2010 - 127 - 0927Document4 pagesCEL - Geotermia 2010 - 127 - 0927Ricardo PosadaNo ratings yet
- Micropower Electrostatic Generator MegDocument3 pagesMicropower Electrostatic Generator MegMahaManthra100% (1)
- English Culture: Essay (Article) About Uk Inventions in The Mexican ContextDocument21 pagesEnglish Culture: Essay (Article) About Uk Inventions in The Mexican Contextjuan moralesNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectricity Is The Term Referring ToDocument13 pagesHydroelectricity Is The Term Referring ToOkdi Dwi SektiawanNo ratings yet
- History: Electric Power Three-Phase AC Power AC and DC Power Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pagesHistory: Electric Power Three-Phase AC Power AC and DC Power Electrical EngineeringJarod Herrera PNo ratings yet
- ARTICLEDocument1 pageARTICLEFortuna EBizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 III - Hydropower EnergyDocument20 pagesChapter 6 III - Hydropower EnergyAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- Power Sytem StudyDocument7 pagesPower Sytem StudyAnupam0103No ratings yet
- Edificio Solar Lisbon Portugal enDocument34 pagesEdificio Solar Lisbon Portugal engabrielneryNo ratings yet
- Electricity in UKDocument4 pagesElectricity in UKhugogallagherNo ratings yet
- Gasoline Turbine Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesGasoline Turbine Review of LiteratureNesdale BuenaflorNo ratings yet
- Central-Station Electric Lighting: With Notes on the Methods Used for the Distribution of ElectricityFrom EverandCentral-Station Electric Lighting: With Notes on the Methods Used for the Distribution of ElectricityNo ratings yet
- Electricity for the farm Light, heat and power by inexpensive methods from the water wheel or farm engineFrom EverandElectricity for the farm Light, heat and power by inexpensive methods from the water wheel or farm engineRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Baffle PlatesDocument1 pageBaffle Platesarif99pakNo ratings yet
- The Most Popular Products and SpecificationsDocument1 pageThe Most Popular Products and Specificationsarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Asme U1Document1 pageAsme U1arif99pakNo ratings yet
- Checker PlateDocument1 pageChecker Platearif99pakNo ratings yet
- Concrete Stave SilosDocument3 pagesConcrete Stave Silosarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Storage TanksDocument2 pagesStorage Tanksarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Fire Tube BoilerDocument2 pagesFire Tube Boilerarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Boiler TubeDocument2 pagesBoiler Tubearif99pakNo ratings yet
- Draft Reference LetterDocument1 pageDraft Reference Letterarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Why Use A Spreader Bar?Document1 pageWhy Use A Spreader Bar?arif99pakNo ratings yet
- Stairs: Winchester Mystery House M. C. EscherDocument1 pageStairs: Winchester Mystery House M. C. Escherarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Storage Tanks: Basically There Are Eight Types of Tanks Used To Store LiquidsDocument1 pageStorage Tanks: Basically There Are Eight Types of Tanks Used To Store Liquidsarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Over Time SheetDocument4 pagesOver Time Sheetarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Pressure VesselsDocument1 pagePressure Vesselsarif99pakNo ratings yet
- EZ Pilot Pro RTF Instruction Manual-V2.1Document27 pagesEZ Pilot Pro RTF Instruction Manual-V2.1abuk5566No ratings yet
- Roadmap For Bible StudyDocument1 pageRoadmap For Bible Study4gen_3No ratings yet
- Investor Presentation (Company Update)Document42 pagesInvestor Presentation (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Nolasco Labor I CompilationDocument115 pagesNolasco Labor I CompilationNico QuebalNo ratings yet
- Tony Robbins NotesDocument3 pagesTony Robbins Notesrationalgaze0% (2)
- Sonali Bank Presentation SlideDocument16 pagesSonali Bank Presentation SlideCyndi WrightNo ratings yet
- PCS GSM PicoCell Booster Updated R5 PDFDocument3 pagesPCS GSM PicoCell Booster Updated R5 PDFpandavision76No ratings yet
- Haloo Cupcake VMDocument17 pagesHaloo Cupcake VMboema.ifNo ratings yet
- Prep 1st Term 2021 PDFDocument8 pagesPrep 1st Term 2021 PDFWajid Jamil100% (4)
- S.S.C Public Examination: Model Paper-1 General Science Paper - 1Document4 pagesS.S.C Public Examination: Model Paper-1 General Science Paper - 1Dhatri Subasri Navya KNo ratings yet
- CV Rinaldi Setiawan Welder 2Document14 pagesCV Rinaldi Setiawan Welder 2myudi20182No ratings yet
- Prasanna Resume Aug - 23Document1 pagePrasanna Resume Aug - 23vishal.singhNo ratings yet
- SAmple Format (Police Report)Document3 pagesSAmple Format (Police Report)Johnpatrick DejesusNo ratings yet
- Let Reviewer 2017Document40 pagesLet Reviewer 2017Claudene GellaNo ratings yet
- Comenzi LinuxDocument6 pagesComenzi LinuxDOMA TANIELNo ratings yet
- Chap-6 Financial AnalysisDocument15 pagesChap-6 Financial Analysis✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬No ratings yet
- More Than 15,000 Rape Kits Still Sit Untested in North CarolinaDocument52 pagesMore Than 15,000 Rape Kits Still Sit Untested in North CarolinaDevetta BlountNo ratings yet
- Essentials of VastuDocument34 pagesEssentials of VastuSampathKumarGodavarthi100% (1)
- Listening Activities 030223Document2 pagesListening Activities 030223Gethwy LoLNo ratings yet
- 1Document11 pages1SonnyNo ratings yet
- Guia Ingles Iv Segunda Unidad Enero 2022Document16 pagesGuia Ingles Iv Segunda Unidad Enero 2022wallpapersNo ratings yet
- Adverb of Affirmation and Negation Worksheet 3Document6 pagesAdverb of Affirmation and Negation Worksheet 3MARIZ BALBANo ratings yet
- Jadawal Semester I Muda Praja Angk. Xxxii 2021-2022Document12 pagesJadawal Semester I Muda Praja Angk. Xxxii 2021-2022Mirino SampariNo ratings yet
- Diferencijal 966Document2 pagesDiferencijal 966Husika HusikaaNo ratings yet
- 30 IELTS Writing Band 8.0Document31 pages30 IELTS Writing Band 8.0Elize WillyNo ratings yet
- RubikDocument40 pagesRubikHardik ShahNo ratings yet
History (
History (
Uploaded by
arif99pakOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
History (
History (
Uploaded by
arif99pakCopyright:
Available Formats
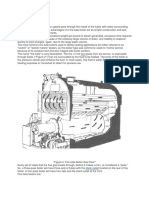
History[edit]
Transmission[edit]
It has been suggested that this section be split into an article
titled History of pneumatic power. (Discuss) (November 2015)
City-wide compressed air energy systems have been built since 1870.[15] Cities such as Paris,
France; Birmingham, England; Dresden, Rixdorf and Offenbach, Germany and Buenos Aires,
Argentina installed such systems. Victor Popp constructed the first systems to power clocks by
sending a pulse of air every minute to change their pointer arms. They quickly evolved to deliver
power to homes and industry.[16] As of 1896, the Paris system had 2.2 MW of generation distributed
at 550 kPa in 50 km of air pipes for motors in light and heavy industry. Usage was measured by
meters.[15] The systems were the main source of house-delivered energy in those days and also
powered the machines of dentists, seamstresses, printing facilities and bakeries.
Storage[edit]
1978 The first utility-scale compressed air energy storage project was the 290 megawatt
Huntorf plant in Germany using a salt dome.
1991 A 110 megawatt plant with a capacity of 26 hours was built in McIntosh, Alabama (1991).
The Alabama facility's $65 million cost works out to $590 per kW of generation capacity and
about $23 per kW-hr of storage capacity, using a 19 million cubic foot solution mined salt cavern
to store air at up to 1100 psi. Although the compression phase is approximately 82% efficient,
the expansion phase requires combustion of natural gas at one third the rate of a gas turbine
producing the same amount of electricity.[17][18][19]
November 2009 The US Department of Energy awards $24.9 million in matching funds for
phase one of a 300 MW, $356 million Pacific Gas and Electric CAES installation utilizing a saline
porous rock formation being developed near Bakersfield in Kern County, California. Goals of the
project are to build and validate an advanced design.[20]
December, 2010 The US Department of Energy provides $29.4 million in funding to conduct
preliminary work on a 150 MW salt-based CAES project being developed by Iberdrola USA in
Watkins Glen, New York. The goal is to incorporate smart grid technology to balance
renewable intermittent energy sources.[20][21]
December, 2012 General Compression completes construction of a 2 MW near-isothermal
CAES project in Gaines, TX; the world's third CAES project. The project uses no fuel.[22]
2013 (projected) The first adiabatic CAES project, a 200 megawatt facility called ADELE, is
planned for construction in Germany. This project has been DELAYED for undisclosed reasons
until at least 2016.[23]
2016 (projected) Apex has planned a CAES plant for Anderson County, Texas to go online in
2016.[24] This project has been DELAYED and will not go into operation until July 2017[25]
2017 (projected) - Storelectric Ltd is planning to build a 40 MW 100% renewable energy pilot
plant in Cheshire, UK, with 800 MWh storage capacity. "This would be 20 times larger than any
100% renewable energy CAES built so far, representing a step-change in the storage industry."
according to their website.[26]
You might also like
- MonkeysDocument4 pagesMonkeysapi-28090379569% (13)
- Wind Turbine Project ReportDocument19 pagesWind Turbine Project ReportMuaz Fabregas100% (2)
- Practical Self-Sufficiency PDFDocument280 pagesPractical Self-Sufficiency PDFFernando Cárdenas Wong95% (20)
- Concept Paper Windmill Power PlantDocument40 pagesConcept Paper Windmill Power PlantNoe S. Elizaga Jr.100% (1)
- PowerDocument2 pagesPowerraymond baliteNo ratings yet
- Government of Kerala: Income CertificateDocument1 pageGovernment of Kerala: Income CertificatethanseelnnNo ratings yet
- Trimble Precision IQ GFX 750 OptimizedDocument319 pagesTrimble Precision IQ GFX 750 OptimizedireneuszNo ratings yet
- Solar Updraft TowerDocument14 pagesSolar Updraft TowerAmeen OmerNo ratings yet
- Solar Updraft TowerDocument8 pagesSolar Updraft Towerbobo_sbNo ratings yet
- The Solar Updraft Tower Is A RenewableDocument6 pagesThe Solar Updraft Tower Is A RenewableIoana Valentina PopaNo ratings yet
- Musgrove Wind Engineering 30-3Document19 pagesMusgrove Wind Engineering 30-3Wei MaNo ratings yet
- Westinghouse Combustion Turbine Systems Division - WikipediaDocument186 pagesWestinghouse Combustion Turbine Systems Division - Wikipediadavidcairobalza100% (1)
- 2 Solar Millennium Fuchs 2011-04-04Document15 pages2 Solar Millennium Fuchs 2011-04-04Arun Sivasankar BharadwajNo ratings yet
- History: Dynamos and Engine Installed at Edison General Electric Company, New York 1895Document4 pagesHistory: Dynamos and Engine Installed at Edison General Electric Company, New York 1895mrjunoonNo ratings yet
- History of WindmillsDocument5 pagesHistory of WindmillsLaura García CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lectura 1 Semestre 2019 Pumping Hydrolectric Storage - Turbine HistoryDocument6 pagesLectura 1 Semestre 2019 Pumping Hydrolectric Storage - Turbine HistoryEduardo CardenasNo ratings yet
- Proyecto Wind La Ventosa MexicoDocument42 pagesProyecto Wind La Ventosa MexicoOscar MoralesNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectricity: MW Three Gorges Dam Peoples Republic of ChinaDocument4 pagesHydroelectricity: MW Three Gorges Dam Peoples Republic of ChinaKapil BajajNo ratings yet
- Pap Kraetzig 02Document16 pagesPap Kraetzig 02ersinNo ratings yet
- Combustion Technology For Generating Energy From Waste PDFDocument26 pagesCombustion Technology For Generating Energy From Waste PDFcaiosicNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Energy: T E C H N O L O G YDocument14 pagesOffshore Wind Energy: T E C H N O L O G YAbdullah KaymakcıNo ratings yet
- The Operation of Ravenswood Generating Station in QueensDocument3 pagesThe Operation of Ravenswood Generating Station in Queensyanam766No ratings yet
- UNIT-2 PHYSICS OF WIND POW-PART1 [Autosaved] (2)Document51 pagesUNIT-2 PHYSICS OF WIND POW-PART1 [Autosaved] (2)010 Monitha SaiNo ratings yet
- Supercapacitors turnitinDocument2 pagesSupercapacitors turnitinperiasamy_nanoNo ratings yet
- Development of MachinesDocument1 pageDevelopment of MachinesSathu satishNo ratings yet
- CFE - Los Azufres 2 Development ReportDocument4 pagesCFE - Los Azufres 2 Development ReportEko TjahjantokoNo ratings yet
- Solar Chimney Power Plants PDFDocument17 pagesSolar Chimney Power Plants PDFChristopher GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bharat Dynamic LTDDocument13 pagesBharat Dynamic LTDShimanthakumar PadashettyNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument16 pagesWind Energypaezbak100% (1)
- 9 Review Future On Power Electronics For Wind Turbine Systems REVIEW PAPER PDFDocument5 pages9 Review Future On Power Electronics For Wind Turbine Systems REVIEW PAPER PDFbatthharshNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind FarmsDocument6 pagesOffshore Wind Farmsapi-345217277No ratings yet
- Solar Power: An Introduction To The History, Technologies, Policy Applications and Future of Solar PowerDocument51 pagesSolar Power: An Introduction To The History, Technologies, Policy Applications and Future of Solar PowerdewsfefcvnbcvNo ratings yet
- Status of Geothermal Industry in AustraliaDocument8 pagesStatus of Geothermal Industry in AustraliaRyan Hofmann100% (1)
- Wind - Energy - 5A - PPT PresentationDocument51 pagesWind - Energy - 5A - PPT PresentationGian BanaresNo ratings yet
- A Short History of The CANDU Nuclear Power System: Gord L. BrooksDocument34 pagesA Short History of The CANDU Nuclear Power System: Gord L. BrooksAnonymous 1hOgJqwZuzNo ratings yet
- Full Charge Ahead: Power StorageDocument5 pagesFull Charge Ahead: Power Storagekdizzle28No ratings yet
- Vishnu 1Document5 pagesVishnu 1KIRAN KENNo ratings yet
- GT HistoryDocument12 pagesGT HistoryBrosGeeNo ratings yet
- HydropowerDocument38 pagesHydropowerBrijesh Chauhan100% (3)
- Smart Grid AssignmentDocument16 pagesSmart Grid Assignmentabstudio0049No ratings yet
- Power Engineering, Also Called Power Systems Engineering, Is A Subfield ofDocument8 pagesPower Engineering, Also Called Power Systems Engineering, Is A Subfield ofsharathVEMNo ratings yet
- Green Power GenerationDocument90 pagesGreen Power GenerationFarhan SaadatNo ratings yet
- Floating Wind Turbine - WikipediaDocument21 pagesFloating Wind Turbine - WikipediavineeshNo ratings yet
- CDM CeaDocument14 pagesCDM Ceaanjes1No ratings yet
- Wind TurbinesDocument18 pagesWind Turbinesapi-271021803No ratings yet
- Who and When LiesDocument1 pageWho and When LiesMarc Nelson Pequit Jr.No ratings yet
- Power StationDocument10 pagesPower Stationletter_ashish4444No ratings yet
- Flying Cloud Fact SheetDocument2 pagesFlying Cloud Fact Sheetscuderia_f147No ratings yet
- Wind TurbineDocument24 pagesWind TurbinerjiyfrauefaboovyohNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument16 pagesWind EnergyJoeNo ratings yet
- This Article Needs Additional Citations For VerificationDocument12 pagesThis Article Needs Additional Citations For VerificationKiranParvathaneniNo ratings yet
- CEL - Geotermia 2010 - 127 - 0927Document4 pagesCEL - Geotermia 2010 - 127 - 0927Ricardo PosadaNo ratings yet
- Micropower Electrostatic Generator MegDocument3 pagesMicropower Electrostatic Generator MegMahaManthra100% (1)
- English Culture: Essay (Article) About Uk Inventions in The Mexican ContextDocument21 pagesEnglish Culture: Essay (Article) About Uk Inventions in The Mexican Contextjuan moralesNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectricity Is The Term Referring ToDocument13 pagesHydroelectricity Is The Term Referring ToOkdi Dwi SektiawanNo ratings yet
- History: Electric Power Three-Phase AC Power AC and DC Power Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pagesHistory: Electric Power Three-Phase AC Power AC and DC Power Electrical EngineeringJarod Herrera PNo ratings yet
- ARTICLEDocument1 pageARTICLEFortuna EBizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 III - Hydropower EnergyDocument20 pagesChapter 6 III - Hydropower EnergyAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- Power Sytem StudyDocument7 pagesPower Sytem StudyAnupam0103No ratings yet
- Edificio Solar Lisbon Portugal enDocument34 pagesEdificio Solar Lisbon Portugal engabrielneryNo ratings yet
- Electricity in UKDocument4 pagesElectricity in UKhugogallagherNo ratings yet
- Gasoline Turbine Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesGasoline Turbine Review of LiteratureNesdale BuenaflorNo ratings yet
- Central-Station Electric Lighting: With Notes on the Methods Used for the Distribution of ElectricityFrom EverandCentral-Station Electric Lighting: With Notes on the Methods Used for the Distribution of ElectricityNo ratings yet
- Electricity for the farm Light, heat and power by inexpensive methods from the water wheel or farm engineFrom EverandElectricity for the farm Light, heat and power by inexpensive methods from the water wheel or farm engineRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Baffle PlatesDocument1 pageBaffle Platesarif99pakNo ratings yet
- The Most Popular Products and SpecificationsDocument1 pageThe Most Popular Products and Specificationsarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Asme U1Document1 pageAsme U1arif99pakNo ratings yet
- Checker PlateDocument1 pageChecker Platearif99pakNo ratings yet
- Concrete Stave SilosDocument3 pagesConcrete Stave Silosarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Storage TanksDocument2 pagesStorage Tanksarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Fire Tube BoilerDocument2 pagesFire Tube Boilerarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Boiler TubeDocument2 pagesBoiler Tubearif99pakNo ratings yet
- Draft Reference LetterDocument1 pageDraft Reference Letterarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Why Use A Spreader Bar?Document1 pageWhy Use A Spreader Bar?arif99pakNo ratings yet
- Stairs: Winchester Mystery House M. C. EscherDocument1 pageStairs: Winchester Mystery House M. C. Escherarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Storage Tanks: Basically There Are Eight Types of Tanks Used To Store LiquidsDocument1 pageStorage Tanks: Basically There Are Eight Types of Tanks Used To Store Liquidsarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Over Time SheetDocument4 pagesOver Time Sheetarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Pressure VesselsDocument1 pagePressure Vesselsarif99pakNo ratings yet
- EZ Pilot Pro RTF Instruction Manual-V2.1Document27 pagesEZ Pilot Pro RTF Instruction Manual-V2.1abuk5566No ratings yet
- Roadmap For Bible StudyDocument1 pageRoadmap For Bible Study4gen_3No ratings yet
- Investor Presentation (Company Update)Document42 pagesInvestor Presentation (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Nolasco Labor I CompilationDocument115 pagesNolasco Labor I CompilationNico QuebalNo ratings yet
- Tony Robbins NotesDocument3 pagesTony Robbins Notesrationalgaze0% (2)
- Sonali Bank Presentation SlideDocument16 pagesSonali Bank Presentation SlideCyndi WrightNo ratings yet
- PCS GSM PicoCell Booster Updated R5 PDFDocument3 pagesPCS GSM PicoCell Booster Updated R5 PDFpandavision76No ratings yet
- Haloo Cupcake VMDocument17 pagesHaloo Cupcake VMboema.ifNo ratings yet
- Prep 1st Term 2021 PDFDocument8 pagesPrep 1st Term 2021 PDFWajid Jamil100% (4)
- S.S.C Public Examination: Model Paper-1 General Science Paper - 1Document4 pagesS.S.C Public Examination: Model Paper-1 General Science Paper - 1Dhatri Subasri Navya KNo ratings yet
- CV Rinaldi Setiawan Welder 2Document14 pagesCV Rinaldi Setiawan Welder 2myudi20182No ratings yet
- Prasanna Resume Aug - 23Document1 pagePrasanna Resume Aug - 23vishal.singhNo ratings yet
- SAmple Format (Police Report)Document3 pagesSAmple Format (Police Report)Johnpatrick DejesusNo ratings yet
- Let Reviewer 2017Document40 pagesLet Reviewer 2017Claudene GellaNo ratings yet
- Comenzi LinuxDocument6 pagesComenzi LinuxDOMA TANIELNo ratings yet
- Chap-6 Financial AnalysisDocument15 pagesChap-6 Financial Analysis✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬No ratings yet
- More Than 15,000 Rape Kits Still Sit Untested in North CarolinaDocument52 pagesMore Than 15,000 Rape Kits Still Sit Untested in North CarolinaDevetta BlountNo ratings yet
- Essentials of VastuDocument34 pagesEssentials of VastuSampathKumarGodavarthi100% (1)
- Listening Activities 030223Document2 pagesListening Activities 030223Gethwy LoLNo ratings yet
- 1Document11 pages1SonnyNo ratings yet
- Guia Ingles Iv Segunda Unidad Enero 2022Document16 pagesGuia Ingles Iv Segunda Unidad Enero 2022wallpapersNo ratings yet
- Adverb of Affirmation and Negation Worksheet 3Document6 pagesAdverb of Affirmation and Negation Worksheet 3MARIZ BALBANo ratings yet
- Jadawal Semester I Muda Praja Angk. Xxxii 2021-2022Document12 pagesJadawal Semester I Muda Praja Angk. Xxxii 2021-2022Mirino SampariNo ratings yet
- Diferencijal 966Document2 pagesDiferencijal 966Husika HusikaaNo ratings yet
- 30 IELTS Writing Band 8.0Document31 pages30 IELTS Writing Band 8.0Elize WillyNo ratings yet
- RubikDocument40 pagesRubikHardik ShahNo ratings yet






















![UNIT-2 PHYSICS OF WIND POW-PART1 [Autosaved] (2)](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/749074245/149x198/5fe25996d5/1720523149?v=1)