Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology 2.3 Worksheet
Biology 2.3 Worksheet
Uploaded by
Amisha Vastani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
290 views2 pagesThis document discusses proteins, enzymes, and digestion. It defines proteins and enzymes, noting that enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to speed up biochemical reactions in living things. Enzymes have an active site that binds to substrates and are made up of amino acids. The document examines how enzymes work, how their activity is affected by temperature, and what it means for an enzyme to be denatured. It also explores the specific digestive enzymes amylase, protease, lipase and where they act in the gut to break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats for absorption and use by the body.
Original Description:
GCSE Double Award Biology Worksheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses proteins, enzymes, and digestion. It defines proteins and enzymes, noting that enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to speed up biochemical reactions in living things. Enzymes have an active site that binds to substrates and are made up of amino acids. The document examines how enzymes work, how their activity is affected by temperature, and what it means for an enzyme to be denatured. It also explores the specific digestive enzymes amylase, protease, lipase and where they act in the gut to break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats for absorption and use by the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
290 views2 pagesBiology 2.3 Worksheet
Biology 2.3 Worksheet
Uploaded by
Amisha VastaniThis document discusses proteins, enzymes, and digestion. It defines proteins and enzymes, noting that enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to speed up biochemical reactions in living things. Enzymes have an active site that binds to substrates and are made up of amino acids. The document examines how enzymes work, how their activity is affected by temperature, and what it means for an enzyme to be denatured. It also explores the specific digestive enzymes amylase, protease, lipase and where they act in the gut to break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats for absorption and use by the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Proteins, Catalysts and Enzymes & Digestion
1. What is an amino acid?
2. What is a protein?
3. How are proteins used in the body?
4. Define an enzyme
5. Define a catalyst
6. What is the active site?
7. What are enzymes made of?
8. How do enzymes speed up reactions in your body?
9. Why does milk left in the sun go off quickly?
10.What does it mean if an enzyme is denatured?
11.Draw an enzyme- controlled temperature- rate of reaction graph dont forget to label
it!
12.Fill in the gaps:
1
The chemical that take place in living . happen at relatively low
..
The rate of these -controlled reactions with an increase in temperature.
However, this is only true up to temperatures of about .
After this the structure of the enzyme I affected and the .. of the
is changed. The enzyme has been .
13.How do your digestive enzymes differ from most of your other enzymes?
14.What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down starch in your gut?
15.Which enzymes break down protein in your gut?
16.Which enzymes break down fat in your gut?
17.Make a table that describes amylase, protease and lipase. For each enzyme show
where it is made, which reaction it catalyses and where it works in the gut.
18.Why is digestion of your food so important? Explain your answer in terms of the
molecules involved.
You might also like
- Nutrition Label Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesNutrition Label Worksheet PDFCha Marie100% (2)
- PrescriptionChart - Used in OSCEsDocument4 pagesPrescriptionChart - Used in OSCEsAmisha Vastani100% (1)
- Autotroph Vs Heterotroph WorksheetDocument3 pagesAutotroph Vs Heterotroph WorksheetEdison Alfonso Sturgess100% (1)
- Tissues Review PacketDocument6 pagesTissues Review PacketR NovNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Label WorksheetDocument4 pagesNutrition Label Worksheetapi-28884873825% (4)
- Cell Biology Worksheet Blank4Document10 pagesCell Biology Worksheet Blank4Loveena SteadmanNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetDocument3 pagesBiology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetAbhay MonNo ratings yet
- Water Quality WorksheetDocument4 pagesWater Quality WorksheetMheyMartinezNo ratings yet
- CH 11.4 MeiosisDocument9 pagesCH 11.4 MeiosisKelsey Koehler0% (1)
- Human Digestive System Sls WorksheetDocument2 pagesHuman Digestive System Sls WorksheetMatthew NgNo ratings yet
- SQUIREdownloadabletemplateDocument4 pagesSQUIREdownloadabletemplateAmisha Vastani100% (1)
- Biology Worksheet Answer Key Class9 PDFDocument2 pagesBiology Worksheet Answer Key Class9 PDFSrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Classification Notes WorksheetDocument5 pagesClassification Notes WorksheetsenjicsNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Living EnvironmentDocument21 pagesA Guide To Living Environmentapi-294580305No ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology WorksheetDocument4 pagesHuman and Social Biology WorksheetRussell Randy100% (1)
- Cell Structure WorksheetDocument6 pagesCell Structure Worksheetafaflotfi_155696459No ratings yet
- Symmetry in BiologyDocument5 pagesSymmetry in Biologytr4lNo ratings yet
- First Periodic Test Science I Sy 2010-2011-1Document7 pagesFirst Periodic Test Science I Sy 2010-2011-1Myra Jamindang Tamayo33% (3)
- Class XII Biology Worksheet Genetics and EvolutionDocument10 pagesClass XII Biology Worksheet Genetics and EvolutionMohamad Qulam Zaki100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Response in PlantDocument34 pagesChapter 5 Response in Plantintan syaheeraNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument4 pagesClassification of Living ThingsmceldowneaNo ratings yet
- Flower Parts & Pollination Worksheet: NameDocument1 pageFlower Parts & Pollination Worksheet: NameRaquel Tellez MamarilNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Dominance and CodominanceDocument13 pagesIncomplete Dominance and CodominanceSuccess MentorNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7 InvertebratesDocument8 pagesWorksheet 7 InvertebratesAbdulla Saleem100% (1)
- Cell Unit Pre-AssessmentDocument19 pagesCell Unit Pre-Assessmentapi-282053052No ratings yet
- Chapter 11: The MoleDocument40 pagesChapter 11: The Molefluffyelissa_1032007100% (1)
- Classification, Dichotomous Key Potato Chip SortDocument2 pagesClassification, Dichotomous Key Potato Chip Sortchabries100% (1)
- Plant Response To StimuliDocument38 pagesPlant Response To Stimulideepak_rc731757No ratings yet
- Worksheet in BloodDocument12 pagesWorksheet in BloodBryan Mae H. DegorioNo ratings yet
- Study of Different Field: Studentsdisha - inDocument5 pagesStudy of Different Field: Studentsdisha - inRohit GanjooNo ratings yet
- h20 WorksheetDocument36 pagesh20 Worksheetsimianchan50% (2)
- Body PartsDocument1 pageBody PartsMauro Cortese CaqueoNo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology WorksheetDocument1 pageHuman and Social Biology WorksheetShakay WrightNo ratings yet
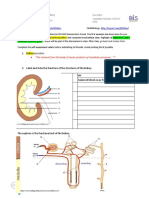
- Essential Biology Kidney WorksheetDocument9 pagesEssential Biology Kidney WorksheetKarishmaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Integumentary WorksheetDocument2 pagesWeek 6 Integumentary WorksheetAthia ZamanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument10 pagesClassification of Living ThingsAngela100% (2)
- Carnivores Vs Herbivores WorksheetDocument4 pagesCarnivores Vs Herbivores Worksheetsandapeharda9717No ratings yet
- AP Biology Worksheet Pedigrees 2Document2 pagesAP Biology Worksheet Pedigrees 2Victoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Muscular System WorksheetDocument4 pagesMuscular System WorksheetCyrus Flores,No ratings yet
- Human Body System RubricDocument3 pagesHuman Body System Rubricapi-304340733No ratings yet
- Biology Grade 12 Unit 4 Summary The Processes of EvolutionDocument15 pagesBiology Grade 12 Unit 4 Summary The Processes of EvolutionAll in One TubeNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer WorksheetDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer WorksheetjcsdyobiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Allele WorksheetDocument2 pagesMultiple Allele WorksheetTim SooNo ratings yet
- Matching WorksheetDocument2 pagesMatching WorksheetcanisaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument36 pagesBiologyoluchi igweNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetDanielGuimarãesCosta100% (1)
- 0609 Animal AdaptationsDocument20 pages0609 Animal AdaptationsIvan XLCNo ratings yet
- WorksheetsDocument26 pagesWorksheetsw3wzzzNo ratings yet
- Biology Weekly Worksheet g7s2pb Transport in HumansDocument5 pagesBiology Weekly Worksheet g7s2pb Transport in HumansD'ferti AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument20 pagesSeparating MixturesBon Wa PaschalNo ratings yet
- Starter: - in The Back of Your Books - Think of A Job A Person Might Do - What Do They Need To Do Their Job Properly?Document22 pagesStarter: - in The Back of Your Books - Think of A Job A Person Might Do - What Do They Need To Do Their Job Properly?Kelvin RequenaNo ratings yet
- Bc35worksheet4 Lipidanab 1 6Document5 pagesBc35worksheet4 Lipidanab 1 6YnuehSolomonNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument31 pagesCharacteristics of Living ThingsOscar DamianiNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument4 pagesWorksheetapi-278551567No ratings yet
- Social Practice of The Language 6Document9 pagesSocial Practice of The Language 6Brenda LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis ExperimentDocument3 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis ExperimentstjustinsNo ratings yet
- Reproduction QuestionsDocument29 pagesReproduction Questionspkrajenpillaygmailcom0% (1)
- Physical Education Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesPhysical Education Lesson Planapi-202718495No ratings yet
- Writing WorksheetDocument20 pagesWriting Worksheetbigbencollege2930No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument35 pagesRespirationnabeeha malhiNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet Nutrition in AnimalsDocument1 pageScience Worksheet Nutrition in AnimalsSabsNo ratings yet
- UKMi-Gentamicin InfoDocument4 pagesUKMi-Gentamicin InfoAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - AddictionDocument6 pagesTopic 6 - AddictionAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
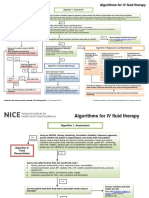
- IV Fluid Composition TableDocument1 pageIV Fluid Composition TableAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Adult Pocket Opioid PrescribingDocument19 pagesAdult Pocket Opioid PrescribingAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Poster SetDocument5 pagesIV Fluid Poster SetAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobials - SPDocument27 pagesAntimicrobials - SPAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Springer - Compact Agreement Journals PDFDocument32 pagesSpringer - Compact Agreement Journals PDFAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Springer - Compact Agreement Journals PDFDocument32 pagesSpringer - Compact Agreement Journals PDFAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Organism in The Environment PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesOrganism in The Environment PhotosynthesisAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Normal Pregnancy, Caesarean Section and Breech PresentationDocument8 pagesNormal Pregnancy, Caesarean Section and Breech PresentationAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Organs Animal and Plant CellsDocument5 pagesCells, Tissues and Organs Animal and Plant CellsAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet