Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECA
Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECA
Uploaded by
Rob WillestoneOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECA
Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECA
Uploaded by
Rob WillestoneCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECA
1 of 5
about:reader?url=http://www.weibull.com/hotwire/issue46/relbasics46.htm
weibull.com
ReliaSoft Publishing
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Failure Modes,
Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) are methodologies
designed to identify potential failure modes for a product or
process, to assess the risk associated with those failure modes, to
rank the issues in terms of importance and to identify and carry out
corrective actions to address the most serious concerns.
Although the purpose, terminology and other details can vary
according to type (e.g. Process FMEA, Design FMEA, etc.), the basic
methodology is similar for all. This article presents a brief general
overview of FMEA / FMECA analysis techniques and requirements.
FMEA / FMECA Overview
In general, FMEA / FMECA requires the identification of the
following basic information:
Item(s)
Function(s)
Failure(s)
Effect(s) of Failure
Cause(s) of Failure
8/1/2016 5:30 PM
Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECA
2 of 5
about:reader?url=http://www.weibull.com/hotwire/issue46/relbasics46.htm
Current Control(s)
Recommended Action(s)
Plus other relevant details
Most analyses of this type also include some method to assess the
risk associated with the issues identified during the analysis and to
prioritize corrective actions. Two common methods include:
Risk Priority Numbers (RPNs)
Criticality Analysis (FMEA with Criticality Analysis = FMECA)
Published Standards and Guidelines
There are a number of published guidelines and standards for the
requirements and recommended reporting format of FMEAs and
FMECAs. Some of the main published standards for this type of
analysis include SAE J1739, AIAG FMEA-4 and MIL-STD-1629A. In
addition, many industries and companies have developed their own
procedures to meet the specific requirements of their
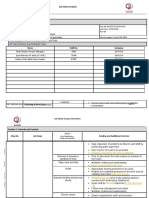
products/processes. Figure 1 shows a sample Process FMEA in the
Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) FMEA-4 format.
Basic Analysis Procedure for FMEA or FMECA
The basic steps for performing an FMEA/FMECA analysis include:
Assemble the team.
8/1/2016 5:30 PM
Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECA
3 of 5
about:reader?url=http://www.weibull.com/hotwire/issue46/relbasics46.htm
Establish the ground rules.
Gather and review relevant information.
Identify the item(s) or process(es) to be analyzed.
Identify the function(s), failure(s), effect(s), cause(s) and
control(s) for each item or process to be analyzed.
Evaluate the risk associated with the issues identified by the
analysis.
Prioritize and assign corrective actions.
Perform corrective actions and re-evaluate risk.
Distribute, review and update the analysis, as appropriate.
Risk Evaluation Methods
A typical FMEA incorporates some method to evaluate the risk
associated with the potential problems identified through the
analysis. The two most common methods, Risk Priority Numbers
and Criticality Analysis, are described next.
Risk Priority Numbers
To use the Risk Priority Number (RPN) method to assess risk, the
analysis team must:
Rate the severity of each effect of failure.
Rate the likelihood of occurrence for each cause of failure.
Rate the likelihood of prior detection for each cause of failure
(i.e. the likelihood of detecting the problem before it reaches the
8/1/2016 5:30 PM
Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECA
4 of 5
about:reader?url=http://www.weibull.com/hotwire/issue46/relbasics46.htm
end user or customer).
Calculate the RPN by obtaining the product of the three ratings:
RPN = Severity x Occurrence x Detection
The RPN can then be used to compare issues within the analysis
and to prioritize problems for corrective action.
Criticality Analysis
The MIL-STD-1629A document describes two types of criticality
analysis: quantitative and qualitative. To use the quantitative
criticality analysis method, the analysis team must:
Define the reliability/unreliability for each item, at a given
operating time.
Identify the portion of the items unreliability that can be
attributed to each potential failure mode.
Rate the probability of loss (or severity) that will result from each
failure mode that may occur.
Calculate the criticality for each potential failure mode by
obtaining the product of the three factors:
Mode Criticality = Item Unreliability x Mode Ratio of
Unreliability x Probability of Loss
Calculate the criticality for each item by obtaining the sum of the
criticalities for each failure mode that has been identified for the
item.
Item Criticality = SUM of Mode Criticalities
To use the qualitative criticality analysis method to evaluate risk
8/1/2016 5:30 PM
Basic Concepts of FMEA and FMECA
5 of 5
about:reader?url=http://www.weibull.com/hotwire/issue46/relbasics46.htm
and prioritize corrective actions, the analysis team must:
Rate the severity of the potential effects of failure.
Rate the likelihood of occurrence for each potential failure mode.
Compare failure modes via a Criticality Matrix, which identifies
severity on the horizontal axis and occurrence on the vertical axis.
Applications and Benefits
The FMEA / FMECA analysis procedure is a tool that has been
adapted in many different ways for many different purposes. It can
contribute to improved designs for products and processes,
resulting in higher reliability, better quality, increased safety,
enhanced customer satisfaction and reduced costs. The tool can
also be used to establish and optimize maintenance plans for
repairable systems and/or contribute to control plans and other
quality assurance procedures. It provides a knowledge base of
failure mode and corrective action information that can be used as a
resource in future troubleshooting efforts and as a training tool for
new engineers. In addition, an FMEA or FMECA is often required
to comply with safety and quality requirements, such as ISO 9001,
QS 9000, ISO/TS 16949, Six Sigma, FDA Good Manufacturing
Practices (GMPs), Process Safety Management Act (PSM), etc.
ReliaSoft's Xfmea software facilitates analysis, data management
and reporting for failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) and
failure modes, effects and criticality analysis (FMECA). The
software supports all major standards (AIAG FMEA-3, J1739,
ARP5580, MIL-STD-1629A, etc.) and provides extensive
customization capabilities for analysis and reporting, allowing you
to configure the software to meet your organization's specific
analysis and reporting procedures for all types of FMEA / FMECA.
8/1/2016 5:30 PM
You might also like
- The Gaming Playbook - GWIDocument39 pagesThe Gaming Playbook - GWILuis CintronNo ratings yet
- Smart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before UseDocument9 pagesSmart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before Useeliaszarmi100% (3)
- Zero Breakdown ConceptsDocument24 pagesZero Breakdown ConceptsAhmad Z. Sultan50% (4)
- QTP Automation and Coding StandardsDocument46 pagesQTP Automation and Coding Standardsnairunni60No ratings yet
- Software Maintenance: Management of Maintenance Maintenance Process Maintenance ModelsDocument24 pagesSoftware Maintenance: Management of Maintenance Maintenance Process Maintenance ModelsSumod SundarNo ratings yet
- BS 534 PDFDocument26 pagesBS 534 PDFRob Willestone50% (2)
- 2012 CQT BokDocument12 pages2012 CQT BokRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- AWS+Essentials+Student+Guide+Print+Out+V1 8Document56 pagesAWS+Essentials+Student+Guide+Print+Out+V1 8princechennai50% (2)
- QNet PresentationDocument36 pagesQNet PresentationMohamed Elsheemy100% (1)
- FMEADocument20 pagesFMEARonillo PormonNo ratings yet
- Application of Reliability Centred Maintenance To Dynamic PlantDocument13 pagesApplication of Reliability Centred Maintenance To Dynamic Plantgvc1No ratings yet
- 10% Rule of Preventive Maintenance: Ricky SmithDocument5 pages10% Rule of Preventive Maintenance: Ricky Smithfkarimz862467No ratings yet
- Positive Isolaton: Prepared By: Bikash Keshari KhilarDocument16 pagesPositive Isolaton: Prepared By: Bikash Keshari KhilarBikash KhilarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 - Reliability Centered Maintenance-2012Document31 pagesLecture 14 - Reliability Centered Maintenance-2012Falak Khan100% (1)
- RCM Analysis For SteamDocument13 pagesRCM Analysis For SteamDamianNo ratings yet
- HAZOP TrainingDocument21 pagesHAZOP TrainingEdmund MaletzkyNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Effects and Criticality Analysis PDFDocument2 pagesFailure Mode Effects and Criticality Analysis PDFMacNo ratings yet
- SafetyMgt Handouts Topic9Document7 pagesSafetyMgt Handouts Topic9ALyzha Mae LacuestaNo ratings yet
- Ageing Plant App5Document16 pagesAgeing Plant App5Mas Arman TewoNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA)Document23 pagesFailure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA)Parandhaman GRNo ratings yet
- Safety in MaintenanceDocument5 pagesSafety in MaintenanceKavindra MishraNo ratings yet
- Reliability Ab PDFDocument4 pagesReliability Ab PDFLuis Alberto SanchezNo ratings yet
- Study of Failure Modes of Rolling Bearings: A ReviewDocument7 pagesStudy of Failure Modes of Rolling Bearings: A ReviewIJMERNo ratings yet
- Technical Report Concerning RCM. by Elisony Edward Mweladzi. Dar Es Salaam Tanzania +255 754321825Document14 pagesTechnical Report Concerning RCM. by Elisony Edward Mweladzi. Dar Es Salaam Tanzania +255 754321825Elisony EdwardNo ratings yet
- 2-1 RCMDocument25 pages2-1 RCMDwi Mulyanti DwimulyantishopNo ratings yet
- For The Health of Your BusinessDocument14 pagesFor The Health of Your BusinessMauricio Santana0% (1)
- 07 - Mechanical IntegrityDocument2 pages07 - Mechanical IntegritysarifinNo ratings yet
- Air CompressorDocument4 pagesAir CompressorLajapathi RaiNo ratings yet
- Equipment Criticality AnalysisDocument20 pagesEquipment Criticality AnalysisArmandoNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Maintenance Presentation ReviewDocument17 pagesOil and Gas Maintenance Presentation ReviewcakjurisNo ratings yet
- MIQA ProgramDocument17 pagesMIQA Programcoolguy12345No ratings yet
- Machine Guarding: NotesDocument6 pagesMachine Guarding: NotesMBAHNo ratings yet
- Fmeca ProcedureDocument11 pagesFmeca Procedurewarigiyatno100% (1)
- PM Implementation Checklist and PM OverviewDocument36 pagesPM Implementation Checklist and PM OverviewPuneet GobindaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) - Identification of Failure Modes PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 8 Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) - Identification of Failure Modes PDFshahrukh AhsanNo ratings yet
- ABC Based Equipment CriticalityDocument7 pagesABC Based Equipment Criticalityyopy_yogieNo ratings yet
- The Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout) : Before You BeginDocument3 pagesThe Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout) : Before You BeginKanupriyaNo ratings yet
- Basics For FMEA and FMECADocument35 pagesBasics For FMEA and FMECAchameera82No ratings yet
- Engineering ControlsDocument6 pagesEngineering ControlsFakhri YudhaNo ratings yet
- Fault Tree AnalysisDocument18 pagesFault Tree AnalysisRadhi100% (1)
- Machinery Safeguards: Barriers and Enclosure Guards Controls and Operating SafelyDocument32 pagesMachinery Safeguards: Barriers and Enclosure Guards Controls and Operating SafelyMikhaylovMikkelsenNo ratings yet
- Practical Root Cause Analysis Using Cause Mapping: January 2014Document6 pagesPractical Root Cause Analysis Using Cause Mapping: January 2014Luis MedinaNo ratings yet
- FMECA of PUMP Pumping Water From Coalescer To Second Stage Recycler and DegasserDocument12 pagesFMECA of PUMP Pumping Water From Coalescer To Second Stage Recycler and DegasserM Ahmad TauqeerNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis of Centrifugal PumpDocument2 pagesFailure Mode and Effect Analysis of Centrifugal PumpHAFIZMUHAMMAD SAJID100% (1)
- Performance Indicators Forpower PlantDocument20 pagesPerformance Indicators Forpower PlantSiva KulanjiNo ratings yet
- Proceeding 2Document102 pagesProceeding 2userscribd2011No ratings yet
- MCN 401 Ise Module 4-1Document97 pagesMCN 401 Ise Module 4-1taapseveniaavaniNo ratings yet
- Computerised Maintenance Management SystemsDocument12 pagesComputerised Maintenance Management SystemsNeng AmnadNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Well Operation and Maintenance: Sverrir ThorhallssonDocument23 pagesGeothermal Well Operation and Maintenance: Sverrir ThorhallssonLaras PutiNo ratings yet
- Have You Been SET-UP? A Brief Discussion On Job Hazard Analysis (Jha)Document30 pagesHave You Been SET-UP? A Brief Discussion On Job Hazard Analysis (Jha)Ian KoNo ratings yet
- Intro To Reliability Fundamentals IEEE Rev2Document230 pagesIntro To Reliability Fundamentals IEEE Rev2L Braga100% (2)
- Managers Guide To PSM - January 2006Document10 pagesManagers Guide To PSM - January 2006rw992049No ratings yet
- Six Steps To Condition Based Maintenance - GoodDocument3 pagesSix Steps To Condition Based Maintenance - GoodSelvaraj BalasundramNo ratings yet
- GU-612 2012 Incident Notification and Investigation GuidelineDocument168 pagesGU-612 2012 Incident Notification and Investigation GuidelinenickchoNo ratings yet
- Down Time Handbook PDFDocument13 pagesDown Time Handbook PDFZegera Mgendi100% (1)
- Iso22000 2005Document48 pagesIso22000 2005STELLA MARISNo ratings yet
- Iso 2201Document11 pagesIso 2201kirandevi1981No ratings yet
- Fundamental of AIMSDocument5 pagesFundamental of AIMSTissa1969No ratings yet
- Motor Maintenance and Testing TG 5-29-13Document8 pagesMotor Maintenance and Testing TG 5-29-13LuHanson100% (1)
- Is All Safety-Critical Equipment Critical To SafetyDocument6 pagesIs All Safety-Critical Equipment Critical To SafetyLi QiNo ratings yet
- AP Factories RulesDocument76 pagesAP Factories RulesLoganathan DharmarNo ratings yet
- Why Are We So Bad at Maintenance ManagementDocument16 pagesWhy Are We So Bad at Maintenance ManagementMasoud AmirzadehfardNo ratings yet
- RCMDocument515 pagesRCMAntonio Perez100% (1)
- Riddor GuidelinesDocument3 pagesRiddor Guidelinesjoenediath9345No ratings yet
- Article - 9 Types of MaintenanceDocument14 pagesArticle - 9 Types of Maintenanceookyilwin3795No ratings yet
- DOE RCFA Guideline Document PDFDocument69 pagesDOE RCFA Guideline Document PDFrosyidnurdinfauziNo ratings yet
- React (Web Framework) - WikipediaDocument15 pagesReact (Web Framework) - WikipediaRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- Cqe Sample ExamDocument1 pageCqe Sample ExamRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- Pie Field Indicator Product Data Sheet EnglishDocument1 pagePie Field Indicator Product Data Sheet EnglishDarwin Zuni RosadoNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Flux Indicators Product Data Sheet EnglishDocument1 pageMagnetic Flux Indicators Product Data Sheet EnglishRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- Cqe Sample ExamDocument1 pageCqe Sample ExamRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- How To Apply Risk-Based Thinking To Quality ProcessesDocument58 pagesHow To Apply Risk-Based Thinking To Quality Processesnorlie100% (5)
- Sales and Marketing Risks To Consider Yes No N/A Comments / Action RequiredDocument2 pagesSales and Marketing Risks To Consider Yes No N/A Comments / Action RequiredRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- Welcome: at TheDocument32 pagesWelcome: at TheRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- Ts 16949 Proc Forms MatrixDocument1 pageTs 16949 Proc Forms MatrixRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- KPI Assessment FormDocument2 pagesKPI Assessment FormRob Willestone100% (1)
- QEHS ManualDocument100 pagesQEHS ManualRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- Asnt Level II RT InterpretationDocument43 pagesAsnt Level II RT InterpretationRob Willestone100% (13)
- Best Practice Quality Policy StatementsDocument3 pagesBest Practice Quality Policy StatementsRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- Management Vs Non Management GuidelinesDocument1 pageManagement Vs Non Management GuidelinesRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- E2 - Equipment Operators Daily ChecklistDocument1 pageE2 - Equipment Operators Daily ChecklistRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- Audit ChecklistDocument21 pagesAudit ChecklistRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- 9.14.1. Determined by Equation For Mass Per Unit Length According To API 5LDocument2 pages9.14.1. Determined by Equation For Mass Per Unit Length According To API 5LRob WillestoneNo ratings yet
- Mysql Replication UpdateDocument38 pagesMysql Replication Updatetanviet12No ratings yet
- Apple Iphone 13 Pro Max Teardown Report - UnitedLexDocument19 pagesApple Iphone 13 Pro Max Teardown Report - UnitedLexpatrick wangNo ratings yet
- Excel Solver - Step by Step Nonlinear Regression - BrownDocument11 pagesExcel Solver - Step by Step Nonlinear Regression - BrownfrendNo ratings yet
- ECLAT Algorithm For Frequent Item Sets Generation: January 2014Document4 pagesECLAT Algorithm For Frequent Item Sets Generation: January 2014SabaniNo ratings yet
- Uniclean SL For Labs BMT MedicalDocument15 pagesUniclean SL For Labs BMT MedicalSidorov IvanNo ratings yet
- LECTURER 2 Project Management ProcessDocument20 pagesLECTURER 2 Project Management ProcessKudakwashe Motsi100% (1)
- Visualizations in Spreadsheets and TableauDocument4 pagesVisualizations in Spreadsheets and Tableauhaseeb2597No ratings yet
- 2019 MAPEH Baler - Grade 6Document6 pages2019 MAPEH Baler - Grade 6Maria Rosario VelicariaNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Question BankDocument9 pagesData Structure Question BankBabu GiriNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Media Access Controller: Features of The Ethernet MACDocument61 pagesEthernet Media Access Controller: Features of The Ethernet MACRam MurthyNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint To Video SlidessDocument27 pagesPowerPoint To Video SlidessTanvi PatilNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Human Nutrition Science For Healthy Living 2nd Edition Stephenson Test Bank PDFDocument20 pagesDwnload Full Human Nutrition Science For Healthy Living 2nd Edition Stephenson Test Bank PDFfract.hiation.7wtul100% (14)
- GM RFX Training ModuleDocument32 pagesGM RFX Training ModuleWasi AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Jacques Godechot Las RevolucionesDocument2 pagesJacques Godechot Las RevolucionesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Component PlacingDocument6 pagesComponent PlacingPak TaniNo ratings yet
- Pos Energy SavingDocument2 pagesPos Energy Savingslide1931No ratings yet
- 3 SP3D DisenoDocument11 pages3 SP3D DisenoShanmugaraj RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Truck Loading System PDFDocument3 pagesTruck Loading System PDFSalah JallaliNo ratings yet
- (Servlet) Java Servlet Specification v2.2Document77 pages(Servlet) Java Servlet Specification v2.2Brian ChenNo ratings yet
- As 4043-1992 Software Configuration ManagementDocument8 pagesAs 4043-1992 Software Configuration ManagementSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Xeno BotsDocument4 pagesXeno BotsKartik RajpurohitNo ratings yet
- Gardtec 539 InstallationDocument64 pagesGardtec 539 InstallationrahulaborkarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vectors in C++ Word PDFDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Vectors in C++ Word PDFKarima BabaNo ratings yet
- Student's T TestDocument8 pagesStudent's T TestBernii MorrisNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Machine Learning Algorithm For Arrhythmia Classification Using Stacking Ensemble, Random Forest and J.48 AlgorithmDocument8 pagesHybrid Machine Learning Algorithm For Arrhythmia Classification Using Stacking Ensemble, Random Forest and J.48 AlgorithmInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet