Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: GERD" Redirects Here. For The Dam Under Construction in Ethiopia, See
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: GERD" Redirects Here. For The Dam Under Construction in Ethiopia, See
Uploaded by
mitaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Gastric Reflux Disease, Acid Reflux Disease, RefluxDocument4 pagesGastric Reflux Disease, Acid Reflux Disease, RefluxmitaNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: AdultsDocument15 pagesSigns and Symptoms: AdultsHelen McClintock100% (1)
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument18 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Diseasebrian3442No ratings yet
- Helicobacter Pylori: Gastrointestinal TractDocument13 pagesHelicobacter Pylori: Gastrointestinal TractMunzir Munzir KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Gerd by Iyas AlakielDocument23 pagesGerd by Iyas Alakielraph faithNo ratings yet
- S.J.M. Kraemer, HJ. Stein, H. Feussner, J.R. Siewert (Munich)Document1 pageS.J.M. Kraemer, HJ. Stein, H. Feussner, J.R. Siewert (Munich)Ilham ArabNo ratings yet
- A Peptic UlcerDocument7 pagesA Peptic Ulcerjenilyndchavez100% (1)
- Volvulus: Volvulus Is When A Loop ofDocument7 pagesVolvulus: Volvulus Is When A Loop ofranshNo ratings yet
- GerdDocument8 pagesGerdLoms KotopNo ratings yet
- This Is A New Doc Very New: Esophageal AchalasiaDocument14 pagesThis Is A New Doc Very New: Esophageal AchalasiahusseinNo ratings yet
- GERDDocument4 pagesGERDstudy mailNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument10 pagesIndexBabatunde EbenezerNo ratings yet
- Barrett's Esophagus: Possible ComplicationsDocument3 pagesBarrett's Esophagus: Possible ComplicationsindahkurNo ratings yet
- Esophageal DiseaseDocument2 pagesEsophageal Diseasenevelle4667No ratings yet
- Pathologies of GitDocument50 pagesPathologies of GitSajjad AliNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument7 pagesPeptic UlcerMarielle Adey Magcawas RNNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer 2Document38 pagesPeptic Ulcer 2tarekNo ratings yet
- This Is A New Doc Very NewDocument14 pagesThis Is A New Doc Very NewhusseinNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Diarrhea or Diarrhoea (From TheDocument10 pagesDiarrhea: Diarrhea or Diarrhoea (From ThesakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument11 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseMike GNo ratings yet
- Salmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia Enterocolitica and Shigella InfectionsDocument3 pagesSalmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia Enterocolitica and Shigella InfectionsKelvin BolusanNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument9 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfjoojoNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease - RepairedDocument40 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease - RepairedSowndharyaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea GuidelineDocument29 pagesDiarrhea GuidelineMonica GabrielNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument6 pagesCase ReportMae GandaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis: Classification and External ResourcesDocument7 pagesGastroenteritis: Classification and External ResourcesJo-mari Grace Ramos PabalateNo ratings yet
- Stomach Ulcers (Peptic Ulcers)Document25 pagesStomach Ulcers (Peptic Ulcers)Irtza MajeedNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With Diarrhea Dr. Mohamed Abu HmaidDocument61 pagesApproach To A Patient With Diarrhea Dr. Mohamed Abu Hmaidoss-20502745No ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer InfoDocument8 pagesPeptic Ulcer InfoSyazmin KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Oesophageal Reflux - SearchDocument1 pageOesophageal Reflux - SearchnarayananjeyabaluNo ratings yet
- Acid Peptic DiseaseDocument14 pagesAcid Peptic DiseasesalmanhabeebekNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease PharmacotherapyDocument22 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease PharmacotherapyrinirhynNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesGastroenteritis: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaoren89No ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument14 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseMohammad Yordan GandaraNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer HDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer HIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophagean Reflux DiseaseDocument13 pagesGastroesophagean Reflux Diseasedenisa malinaNo ratings yet
- Heller Myotomy: General SurgeryDocument3 pagesHeller Myotomy: General SurgeryRajko RaleNo ratings yet
- Non-Neoplastic Disorders of Esophagus: Dr. Naw May Emerald Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences UCSI UniversityDocument32 pagesNon-Neoplastic Disorders of Esophagus: Dr. Naw May Emerald Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences UCSI UniversitySindhu BabuNo ratings yet
- OesophagusDocument15 pagesOesophagusIBRAHEM JUMAHNo ratings yet
- Essay SuryaDocument5 pagesEssay SuryadewasayogaNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Food Bolus ObstructionDocument5 pagesEsophageal Food Bolus Obstructionnevelle4667No ratings yet
- Helicobacter Pylori: Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers: A Gastric Ulcer Would GiveDocument5 pagesHelicobacter Pylori: Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers: A Gastric Ulcer Would Giveleslie_08No ratings yet
- Ulcers, Peptic (Gastric, Duodenal)Document14 pagesUlcers, Peptic (Gastric, Duodenal)lagas_ralphNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea - WikipediaDocument25 pagesDiarrhea - WikipediaMd. Mahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Esophagitis BY MUSA AFRIDI 17-029Document5 pagesEsophagitis BY MUSA AFRIDI 17-029Essa AfridiNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: IntroductionDocument10 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease: IntroductionLie LhianzaNo ratings yet
- Barrett's EsophagusDocument10 pagesBarrett's EsophagusaryadroettninguNo ratings yet
- Presentation PathophysiologyDocument11 pagesPresentation PathophysiologyJade DeopidoNo ratings yet
- Stomach - GastritisDocument22 pagesStomach - GastritisaimanNo ratings yet
- Abdominal DistentionDocument6 pagesAbdominal DistentionDumapis RichardNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Surgery 2021Document80 pagesGastrointestinal Surgery 2021Esraa SalemNo ratings yet
- CA Pointers FinalsDocument5 pagesCA Pointers FinalsJennifer AmbrosioNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Diarrhea (from the Greek, διὰρροια meaning "a flowing through"Document4 pagesDiarrhea Diarrhea (from the Greek, διὰρροια meaning "a flowing through"Shock CoolNo ratings yet
- Gerd Info and LinksDocument14 pagesGerd Info and Linksapi-357798429No ratings yet
- ERGEDocument10 pagesERGEAvof's SamashNo ratings yet
- Liver D PDFDocument71 pagesLiver D PDFermichoNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: "Something Is Eating at Me"Document37 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: "Something Is Eating at Me"bobtaguba100% (1)
- Management of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersDocument7 pagesManagement of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal Disordersintotheunknown100% (2)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: GERD" Redirects Here. For The Dam Under Construction in Ethiopia, See
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: GERD" Redirects Here. For The Dam Under Construction in Ethiopia, See
Uploaded by
mitaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: GERD" Redirects Here. For The Dam Under Construction in Ethiopia, See
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: GERD" Redirects Here. For The Dam Under Construction in Ethiopia, See
Uploaded by
mitaCopyright:
Available Formats
GERD" redirects here. For the dam under construction in Ethiopia, see Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
gastric reflux disease, acid reflux disease, reflux
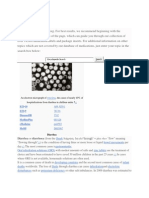
X-ray showing radiocontrast agent injected into the stomach entering
the esophagus due to severe reflux
Classification and external resources
Pronunciation
/gstrosfdil/ /riflks/[1][2][3]
Specialty
Gastroenterology
ICD-10
K21
ICD-9-CM
530.81
OMIM
109350
DiseasesDB
23596
MedlinePlus
000265
eMedicine
med/857 ped/1177radio/300
MeSH
D005764
[edit on Wikidata]
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also known as gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD)
and acid reflux, is a chronic condition of mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from
the stomach into the esophagus.[4] Occasional reflux causes heartburn, but chronic reflux leads to
reflux esophagitis, GERD, and sometimes Barrett's esophagus.
GERD is usually caused by changes in the junction between the stomach and the esophagus, including
abnormal relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter, which normally holds the top of the stomach closed,
impaired expulsion of gastric reflux from the esophagus, or a hiatal hernia. These changes may be permanent
or temporary.
Treatment is typically via lifestyle changes and medications such as proton pump inhibitors, H2 receptor
blockers or antacids with or without alginic acid.[5]Surgery may be an option in those who do not improve. In the
Western world between 10 and 20% of the population is affected. [5]
Contents
[hide]
1Signs and symptoms
1.1Adults
1.2Children
1.3Barrett's esophagus
2Causes
3Diagnosis
3.1Endoscopy
3.2Severity
3.3Differential diagnosis
4Treatment
4.1Lifestyle
4.2Medications
4.3Surgery
4.4Pregnancy
4.5Infants
4.6Overtreatment
5Epidemiology
6History
7Research
8References
9Further reading
10External links
Signs and symptoms
You might also like
- Gastric Reflux Disease, Acid Reflux Disease, RefluxDocument4 pagesGastric Reflux Disease, Acid Reflux Disease, RefluxmitaNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: AdultsDocument15 pagesSigns and Symptoms: AdultsHelen McClintock100% (1)
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument18 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Diseasebrian3442No ratings yet
- Helicobacter Pylori: Gastrointestinal TractDocument13 pagesHelicobacter Pylori: Gastrointestinal TractMunzir Munzir KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Gerd by Iyas AlakielDocument23 pagesGerd by Iyas Alakielraph faithNo ratings yet
- S.J.M. Kraemer, HJ. Stein, H. Feussner, J.R. Siewert (Munich)Document1 pageS.J.M. Kraemer, HJ. Stein, H. Feussner, J.R. Siewert (Munich)Ilham ArabNo ratings yet
- A Peptic UlcerDocument7 pagesA Peptic Ulcerjenilyndchavez100% (1)
- Volvulus: Volvulus Is When A Loop ofDocument7 pagesVolvulus: Volvulus Is When A Loop ofranshNo ratings yet
- GerdDocument8 pagesGerdLoms KotopNo ratings yet
- This Is A New Doc Very New: Esophageal AchalasiaDocument14 pagesThis Is A New Doc Very New: Esophageal AchalasiahusseinNo ratings yet
- GERDDocument4 pagesGERDstudy mailNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument10 pagesIndexBabatunde EbenezerNo ratings yet
- Barrett's Esophagus: Possible ComplicationsDocument3 pagesBarrett's Esophagus: Possible ComplicationsindahkurNo ratings yet
- Esophageal DiseaseDocument2 pagesEsophageal Diseasenevelle4667No ratings yet
- Pathologies of GitDocument50 pagesPathologies of GitSajjad AliNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument7 pagesPeptic UlcerMarielle Adey Magcawas RNNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer 2Document38 pagesPeptic Ulcer 2tarekNo ratings yet
- This Is A New Doc Very NewDocument14 pagesThis Is A New Doc Very NewhusseinNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Diarrhea or Diarrhoea (From TheDocument10 pagesDiarrhea: Diarrhea or Diarrhoea (From ThesakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument11 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseMike GNo ratings yet
- Salmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia Enterocolitica and Shigella InfectionsDocument3 pagesSalmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia Enterocolitica and Shigella InfectionsKelvin BolusanNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument9 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfjoojoNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease - RepairedDocument40 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease - RepairedSowndharyaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea GuidelineDocument29 pagesDiarrhea GuidelineMonica GabrielNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument6 pagesCase ReportMae GandaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis: Classification and External ResourcesDocument7 pagesGastroenteritis: Classification and External ResourcesJo-mari Grace Ramos PabalateNo ratings yet
- Stomach Ulcers (Peptic Ulcers)Document25 pagesStomach Ulcers (Peptic Ulcers)Irtza MajeedNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With Diarrhea Dr. Mohamed Abu HmaidDocument61 pagesApproach To A Patient With Diarrhea Dr. Mohamed Abu Hmaidoss-20502745No ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer InfoDocument8 pagesPeptic Ulcer InfoSyazmin KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Oesophageal Reflux - SearchDocument1 pageOesophageal Reflux - SearchnarayananjeyabaluNo ratings yet
- Acid Peptic DiseaseDocument14 pagesAcid Peptic DiseasesalmanhabeebekNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease PharmacotherapyDocument22 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease PharmacotherapyrinirhynNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesGastroenteritis: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaoren89No ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument14 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseMohammad Yordan GandaraNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer HDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer HIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophagean Reflux DiseaseDocument13 pagesGastroesophagean Reflux Diseasedenisa malinaNo ratings yet
- Heller Myotomy: General SurgeryDocument3 pagesHeller Myotomy: General SurgeryRajko RaleNo ratings yet
- Non-Neoplastic Disorders of Esophagus: Dr. Naw May Emerald Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences UCSI UniversityDocument32 pagesNon-Neoplastic Disorders of Esophagus: Dr. Naw May Emerald Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences UCSI UniversitySindhu BabuNo ratings yet
- OesophagusDocument15 pagesOesophagusIBRAHEM JUMAHNo ratings yet
- Essay SuryaDocument5 pagesEssay SuryadewasayogaNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Food Bolus ObstructionDocument5 pagesEsophageal Food Bolus Obstructionnevelle4667No ratings yet
- Helicobacter Pylori: Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers: A Gastric Ulcer Would GiveDocument5 pagesHelicobacter Pylori: Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers: A Gastric Ulcer Would Giveleslie_08No ratings yet
- Ulcers, Peptic (Gastric, Duodenal)Document14 pagesUlcers, Peptic (Gastric, Duodenal)lagas_ralphNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea - WikipediaDocument25 pagesDiarrhea - WikipediaMd. Mahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Esophagitis BY MUSA AFRIDI 17-029Document5 pagesEsophagitis BY MUSA AFRIDI 17-029Essa AfridiNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: IntroductionDocument10 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease: IntroductionLie LhianzaNo ratings yet
- Barrett's EsophagusDocument10 pagesBarrett's EsophagusaryadroettninguNo ratings yet
- Presentation PathophysiologyDocument11 pagesPresentation PathophysiologyJade DeopidoNo ratings yet
- Stomach - GastritisDocument22 pagesStomach - GastritisaimanNo ratings yet
- Abdominal DistentionDocument6 pagesAbdominal DistentionDumapis RichardNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Surgery 2021Document80 pagesGastrointestinal Surgery 2021Esraa SalemNo ratings yet
- CA Pointers FinalsDocument5 pagesCA Pointers FinalsJennifer AmbrosioNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Diarrhea (from the Greek, διὰρροια meaning "a flowing through"Document4 pagesDiarrhea Diarrhea (from the Greek, διὰρροια meaning "a flowing through"Shock CoolNo ratings yet
- Gerd Info and LinksDocument14 pagesGerd Info and Linksapi-357798429No ratings yet
- ERGEDocument10 pagesERGEAvof's SamashNo ratings yet
- Liver D PDFDocument71 pagesLiver D PDFermichoNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: "Something Is Eating at Me"Document37 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: "Something Is Eating at Me"bobtaguba100% (1)
- Management of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersDocument7 pagesManagement of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal Disordersintotheunknown100% (2)